Improved algorithm for lightweight identification of 3D GPR images of hidden road defects
-
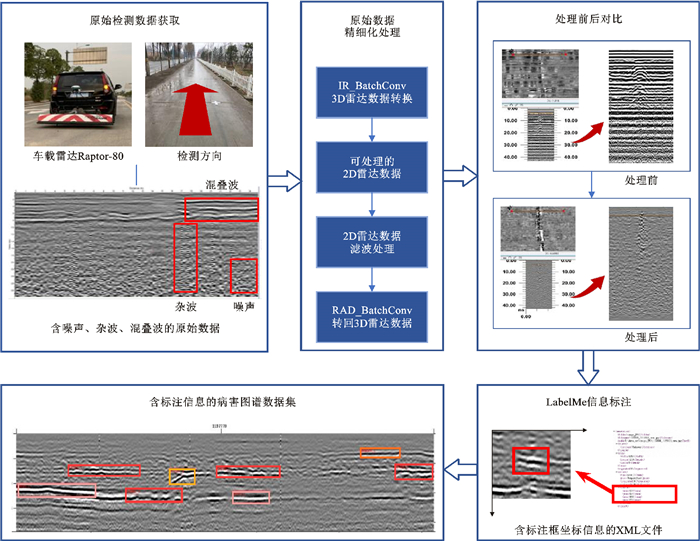
摘要: 针对目前三维探地雷达检测技术中对于道路隐性病害实时检测真实数据规模较小、人工解译困难、传统算法检测精度和效率不足的问题,提出了一种基于YOLOv8的轻量化改进算法YOLOv8-CES;根据采集到的道路隐性病害三维探地雷达图谱,对病害进行信息标注分类以建立数据集;基于无参SimAM注意力机制对小目标检测做出改进,提出了一种Cut_SimAM注意力机制,添加于主干网络中以提高对目标区域的关注度和小目标检测能力;基于C2f结构,在颈部网络引入C2f_EFAttention特征提取模块,优化特征融合过程,降低了参数量提高检测效率;使用Slide Loss滑动加权损失函数结合D-IoU边界框损失函数,加快模型收敛,提高了对困难样本的检测精度;采用多类别平均精度、参数量、计算量、检测帧率等指标,通过消融试验验证了各个模块对模型性能的影响,通过对比试验评价了改进算法相较于其他算法的检测精度和检测效率。试验结果表明:在采集到的雷达病害图谱数据集中,YOLOv8-CES的多类别平均精度达到了61.5%,相较于基线模型提高了3.6%,且参数量从3.0×106降低至2.5×106,每秒浮点运算次数从8.1 GFLOPs减少至7.1 GFLOPs,每秒检测帧数提高16.7%;改进后的模型对于道路隐性病害的识别与分类精度更高,且模型对于计算资源的需求量更低。YOLOv8-CES算法的高精度和轻量化设计使其更有利于嵌入三维探地雷达检测设备并实现实时检测,表明其在道路检测方面具有潜在应用价值。Abstract: To address the problems of small real data scale, difficulty in manual interpretation, and insufficient accuracy and efficiency of traditional algorithms in real-time detection of hidden road defects using three-dimensional ground penetrating radar (3D GPR), a lightweight improved algorithm based on the YOLOv8 algorithm YOLOv8-CES was proposed. Based on the collected 3D GPR images of hidden road defects, defect information was annotated and classified to establish a dataset. A Cut_SimAM attention mechanism was proposed based on the parameter-free SimAM attention mechanism to improve small target detection, and it was added to the backbone network to enhance focus on target regions and improve small object detection ability. Based on the C2f structure, a C2f_EFAttention feature extraction module was introduced into the neck network to optimize the feature fusion process, reduce the number of parameters, and improve detection efficiency. The Slide Loss sliding weighted loss function was used in combination with the D-IoU bounding box loss function to accelerate model convergence and improve detection accuracy for difficult samples. Ablation experiments were conducted to verify the effect of each module on model performance, using mean average precision (mAP), number of parameters, floating point operations per second (FLOPs), and frames per second (FPS) as indicators. The detection accuracy and efficiency of the improved algorithm compared with other algorithms were evaluated through comparative experiments. Test results show that in the collected 3D GPR image dataset of defects, the mAP of YOLOv8-CES reaches 61.5%, increasing by 3.6% compared with the baseline model. The number of parameters reduces from 3.0×106 to 2.5×106, and FLOPs reduces from 8.1 GFLOPs to 7.1 GFLOPs; FPS increases by 16.7%. The improved model achieves higher accuracy and lower computational demand in the recognition and classification of hidden road defects. The high accuracy and lightweight design of the YOLOv8-CES algorithm make it more suitable for embedding in 3D GPR detection devices and achieving real-time detection, indicating its potential application value in road detection.
-
Key words:
- road engineering /
- defect detection /
- YOLOv8 /
- deep learning /
- ground penetrating radar /
- attention mechanism
-
表 1 Raptor-80车载式雷达技术参数
Table 1. Technical parameters of Raptor-80 vehicle-mounted radar
技术指标 天线中心频率/MHz 通道数 采样间距/cm 时窗/ns 驻留时间/μs 检测速度/(km·h-1) 技术参数 800 24 2.5~5.0 25~75 3 30 表 2 病害数据集分类
Table 2. Classification of defects dataset
病害类型 层间不良 层间含水 层间松散 结构松散 标注名称 poor_l water_l loose_l loose_s 病害数量/处 3 092 2 742 3 035 231 病害特征 水平方向有加强同相轴 呈“白-黑-白”条状分布 深度方向有加强同相轴 局部同相轴断裂起伏 特征图 



取芯验证 



表 3 试验环境配置
Table 3. Experimental environment configuration
环境配置 参数 操作系统 Windows 11 CPU Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-14900KF GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4080 内存/GB 64 显存/GB 16 深度学习框架 PyTorch 2.3.1 编程语言 Python 3.8 CUDA 11.8 表 4 消融试验设计
Table 4. Ablation experiment design
模型 SimAM Cut_SimAM EFAttention Slide Loss YOLOv8n YOLOv8-Sim √ YOLOv8-C √ YOLOv8-E √ YOLOv8-S √ YOLOv8-CE √ √ YOLOv8-CES √ √ √ 表 5 不同注意力机制对比试验
Table 5. Comparison of different attention mechanisms
% 注意力机制 召回率 精确率 mAP poor_l water_l loose_l loose_s YOLOv8n 59.6 52.0 56.8 61.2 65.8 49.7 50.3 EMA 52.6 53.1 54.2 60.6 66.3 42.3 48.3 CBAM 53.4 53.6 56.1 62.1 63.2 48.8 50.2 SENet 54.4 56.4 56.7 61.5 64.0 49.2 52.1 SimAM 54.7 58.8 57.9 60.9 65.2 50.1 55.5 Cut_SimAM 56.8 53.8 58.1 61.2 65.3 53.6 52.2 注:表中加粗数字为最优值,下同。 表 6 YOLOv8-C与YOLOv8-CE测试集对比
Table 6. Comparison between YOLOv8-C and YOLOv8-CE test sets
模型 召回率/% 精确率/% mAP/% 参数量/106 检测帧率/FPS 计算量/GFLOPs YOLOv8-C 56.2 58.0 60.0 3.0 180.6 8.1 YOLOv8-CE 57.2 55.7 58.5 2.5 214.3 7.1 表 7 不同边界框损失函数训练结果对比
Table 7. Comparison of training results for different bounding box loss functions
模型 召回率/% 精确率/% mAP/% poor_l/% water_l/% loose_l/% loose_s/% YOLOv8-CE 54.8 57.6 56.0 62.7 67.2 52.3 41.9 C-IoU 56.9 58.3 59.4 61.0 65.9 51.8 58.9 D-IoU 58.3 57.6 59.7 64.1 67.1 53.5 54.2 W-IoU 58.3 52.8 56.2 62.4 67.7 52.4 42.2 NWD 56.8 54.5 58.6 60.7 65.0 51.8 56.9 注:YOLOv8-CE表示未使用Slide Loss损失函数,C-IoU、D-IoU、W-IoU、NWD表示搭载了Slide Loss的YOLOv8-CE模型所用的边界框损失函数。 表 8 测试集消融试验
Table 8. Ablation experiment on test sets
模型 召回率/% 精确率/% mAP/% 参数量/106 检测帧率/FPS 计算量/GFLOPs YOLOv8n 53.8 60.2 57.9 3.0 195.8 8.1 YOLOv8-Sim 56.8 61.1 59.2 3.0 180.1 8.1 YOLOv8-C 56.2 58.0 60.0 3.0 180.6 8.1 YOLOv8-E 56.2 58.7 57.4 2.5 225.9 7.1 YOLOv8-S 59.8 51.0 57.5 3.0 237.0 8.1 YOLOv8-CE 57.2 55.7 58.5 2.5 214.3 7.1 YOLOv8-CES 61.4 59.8 61.5 2.5 228.5 7.1 表 9 不同算法对比
Table 9. Comparison of different algorithms
模型 召回率/% 精确率/% mAP/% 参数量/106 检测帧率/FPS 计算量/GFLOPs Faster R-CNN 60.8 58.8 53.7 41.4 13.2 134.5 SSD 58.2 57.1 56.3 26.5 51.7 60.6 YOLOv5 56.0 57.2 54.3 12.8 139.0 17.3 YOLOv7 56.5 54.3 55.1 17.3 156.8 18.8 YOLOv8m 60.4 50.6 56.2 25.9 130.5 10.3 YOLOv8s 57.1 54.7 58.2 11.1 177.6 8.2 YOLOv8n 53.8 60.2 57.9 3.0 195.8 8.1 YOLOv8-CES 61.4 59.8 61.5 2.5 228.5 7.1 -
[1] 交通运输部. 2024年交通运输行业发展统计公报[N]. 中国交通报, 2025-06-12(002).Ministry of Transport of China. Statistical bulletin on the development of transportation industry in 2024[N]. China Communications News, 2025-06-12(002). [2] 侯斐斐, 施荣华, 雷文太, 等. 面向探地雷达B-scan图像的目标检测算法综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 191-200.HOU Fei-fei, SHI Rong-hua, LEI Wen-tai, et al. A review of target detection algorithm for GPR B-scan processing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 191-200. [3] 李世念, 王秀荣, 林恬, 等. 基于GprMax的道路空洞三维探地雷达正演数值模拟[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(3): 132-138.LI Shi-nian, WANG Xiu-rong, LIN Tian, et al. Numerical simulation of 3D ground penetrating radar based on GprMax for the road cavity[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(3): 132-138. [4] 朱洪洲, 阳绪缘. 沥青路面内部缺陷无损检测技术研究综述[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(25): 10588-10604.ZHU Hong-zhou, YANG Xu-yuan. Review of non-destructive testing techniques for internal defects in asphalt pavements[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(25): 10588-10604. [5] LEI W T, HOU F F, XI J C, et al. Automatic hyperbola detection and fitting in GPR B-scan image[J]. Automation in Construction, 2019, 106: 102839. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2019.102839 [6] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//IEEE. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2014: 580-587. [7] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//IEEE. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1440-1448. [8] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [9] HE K M, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). New York: IEEE, 2017: 2980-2988. [10] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2016: 779-788. [11] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//LEIBE B, MATA J, SEBE N, et al. Computer Vision-ECCV 2016. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [12] DU Y C, PAN N, XU Z H, et al. Pavement distress detection and classification based on YOLO network[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2021, 22(13): 1659-1672. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2020.1714047 [13] UKHWAH E N, YUNIARNO E M, SUPRAPTO Y K. Asphalt pavement pothole detection using deep learning method based on YOLO Neural Network[C]//IEEE. 2019 International Seminar on Intelligent Technology and Its Applications. New York: IEEE, 2019: 35-40. [14] LIU Z, WU W X, GU X Y, et al. Application of combining YOLO models and 3D GPR images in road detection and maintenance[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(6): 1081. doi: 10.3390/rs13061081 [15] 王惠琴, 杨发东, 何永强, 等. 面向探地雷达常见地下目标的GDS-YOLOv8n检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(6): 1170-1183.WANG Hui-qin, YANG Fa-dong, HE Yong-qiang, et al. Detection of common underground targets in ground penetrating radar Images using the GDS-YOLOv8n model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(6): 1170-1183. [16] 刘震, 顾兴宇, 李骏, 等. 探地雷达数值模拟与道路裂缝图像检测的深度学习增强方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(6): 2455-2471.LIU Zhen, GU Xing-yu, LI Jun, et al. Deep learning-enhanced numerical simulation of ground penetrating radar and image detection of road cracks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(6): 2455-2471. [17] HOU F F, LIU X, FAN X Y, et al. DL-aided underground cavity morphology recognition based on 3D GPR data[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10(15): 2806. doi: 10.3390/math10152806 [18] QIN H, ZHANG D H, TANG Y, et al. Automatic recognition of tunnel lining elements from GPR images using deep convolutional networks with data augmentation[J]. Automation in Construction, 2021, 130: 103830. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103830 [19] 熊洪强. 基于生成对抗网络的探地雷达目标检测方法及应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2024.XIONG Hong-qiang. Research on object detection method and applications of ground penetrating radar based on generative adversarial networks[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2024. [20] 张军, 姜文涛, 张云, 等. 基于极限梯度提升和探地雷达时频特征的水泥路面脱空识别[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(1): 104-114, 121.ZHANG Jun, JIANG Wen-tao, ZHANG Yun, et al. Cement pavement void identification based on XGBoost and GPR time frequency features[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2024, 52(1): 104-114, 121. [21] YANG L X, ZHANG R Y, LI L D, et al. SimAM: a simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks[C]//PMLR. 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Vancouver: PMLR, 2021: 11863-11874. [22] TANG Y, PERTSAU D, ZHAO D, et al. LANet: lightweight attention network for medical image segmentation[C]//MAMMADOVA G, ALIEV T, AIDA-ZADE K, et al. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Berlin: Springer, 2024: 2226. [23] YU Z P, HUANG H B, CHEN W J, et al. YOLO-FaceV2: a scale and occlusion aware face detector[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2024, 155: 110714. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110714 [24] 葛道辉, 李洪升, 张亮, 等. 轻量级神经网络架构综述[J]. 软件学报, 2020, 31(9): 2627-2653.GE Dao-hui, LI Hong-sheng, ZHANG Liang, et al. Survey of lightweight neural network[J]. Journal of Software, 2020, 31(9): 2627-2653. [25] 徐小华, 周长兵, 胡忠旭, 等. 轻量级深度神经网络模型适配边缘智能研究综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2024, 51(7): 257-271.XU Xiao-hua, ZHOU Zhang-bing, HU Zhong-xu, et al. Lightweight deep neural network models for edge intelligence: a survey[J]. Computer Science, 2024, 51(7): 257-271. [26] LIU Z, WANG S Q, GU X Y, et al. Non-destructive testing and intelligent evaluation of road structural conditions using GPR and FWD[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2025, 12(3): 462-476. doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2023.09.006 [27] 管进超, 丁玲, 杨旭, 等. 多维图像融合驱动的复杂场景路表破损识别[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2024, 24(3): 154-170. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.03.010GUAN Jin-chao, DING Ling, YANG Xu, et al. Pavement surface distress detection in complex scenarios driven by multi-dimensional image fusion[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2024, 24(3): 154-170. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.03.010 [28] 蒋仕新, 邹小雪, 杨建喜, 等. 复杂背景下基于改进YOLO v8s的混凝土桥梁裂缝检测方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2024, 24(6): 135-147. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.06.009JIANG Shi-xin, ZOU Xiao-xue, YANG Jian-xi, et al. Concrete bridge crack detection method based on improved YOLO v8s in complex backgrounds[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2024, 24(6): 135-147. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.06.009 [29] 李颖, 费怡瑄, 安毅生, 等. 智能交通场景下的地图匹配技术综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2024, 24(5): 301-332. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.05.020LI Ying, FEI Yi-xuan, AN Yi-sheng, et al. Review on map matching technologies in intelligent transportation scenarios[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2024, 24(5): 301-332. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.05.020 [30] YU B, WANG Y C, CHEN Q H, et al. A review of road 3D modeling based on light detection and ranging point clouds[J]. Journal of Road Engineering, 2024, 4(4): 386-398. doi: 10.1016/j.jreng.2024.04.009 [31] YANG X, ZHANG J Q, LIU W B, et al. Automation in road distress detection, diagnosis and treatment[J]. Journal of Road Engineering, 2024, 4(1): 1-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jreng.2024.01.005 -





 下载:
下载: