Finite element analysis of infinitely long beam resting on continuous viscoelastic foundation subjected to moving loads
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
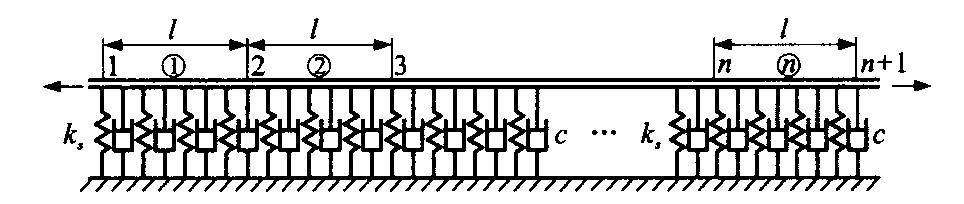
摘要: 把无限长梁、连续粘弹性基础和移动荷载视为一个系统, 并将该系统进行有限单元离散, 梁单元的弯曲形函数采用Hermitian三次方插值函数, 利用弹性系统动力学总势能不变值原理, 得到单元的刚度矩阵、质量矩阵、阻尼矩阵和节点荷载列阵, 建立该系统的振动方程组; 再用Wilsonθ法求解该振动方程组, 得到梁中点的位移时程曲线。举例分析了基础的粘弹性特性和梁的抗弯刚度对梁动力响应的影响。计算结果表明: 增大基础的弹性系数、阻尼系数和梁的抗弯刚度都有利于减小梁的动力响应。Abstract: The beam, foundation and moving loads were considered as a system, and the system was separated into a number of finite elements.Hermitian cubic interpolation function were utilized as the bending shape functions of the two-node beam element.The element stiffness matrix, mass matrix, damping matrix, and vector of element nodal forces could be obtained by the principle of total potential energy with stationary value in elastic system dynamics. The vibration equations of the system were established. The equations were solved by Wilson θ-method, and the displacement time histories of the beam at mid-point were found. Several numerical examples were presented, and the influences of the viscoelastic characteristic of foundation and the bending stiffness of beam on dynamic responses of beam were analyzed.Calculation results show that the increase either of spring stiffness, or of damping coefficient of foundation or of the bending stiffness of beam each leads to the decrease of dynamic responses of beam.
-
表 1 长梁中点在移动荷载作用下的最大竖向位移
Table 1. Maximum displacement of long beam at mid-point subjected to moving loads
梁及基础参数 单个荷载P=112800 N作用下长梁中点最大竖向位移/m 三个荷载P1与P2、P2与P3之间距离为1.8 m, P1=P2=P3=112800N作用下长梁中点最大竖向位移/m 50型钢轨I=2.037×10-5 m4 ks=8×107 N/m2 c=0 1.1215×10-3 1.2279×10-3 c=1.3×105 Ns/m2 1.0223×10-3 1.0074×10-3 ks=1.6×108 N/m2 c=0 6.8052×10-4 7.3234×10-4 c=1.3×105 Ns/m2 6.0310×10-4 5.7984×10-4 60型钢轨I=3.217×10-5 m4 ks=8×107N/m2 c=0 1.1625×10-3 1.2019×10-3 c=1.3×105 Ns/m2 9.1647×10-4 9.2879×10-4 ks=1.6×108 N/m2 c=0 6.2875×10-4 6.4796×10-4 c=1.3×105 Ns/m2 5.4165×10-4 5.2476×10-4 75型钢轨I=4.49×10-5 m4 ks=8×107 N/m2 c=0 1.1151×10-3 1.038 3×10-3 c=1.3×105 Ns/m2 8.4569×10-4 8.927 7×10-4 ks=1.6×108 N/m2 c=0 6.6603×10-4 5.9460×10-4 c=1.3×105 Ns/m2 5.0035×10-4 4.911 8×10-4 -
[1] YoshidaD M, WeaverW. Finite element analysis of beams and plates with moving loads[J]. Publication of InternationalAssociation forBridge and Structural Engineering, 1971, 31 (1): 179—195. [2] FilhoF V. F inite element analysis of structures under movingloads[J]. Shock andVibrationDigest, 1978, 10 (8): 27-35. [3] OlssonM. Finite element, modal co-ordinate analysis of stru-ctures subjected to m oving loads[J]. Journal ofSound andVibration, 1985, 99 (1): 1—12. [4] ThambiratnamD, ZhugeY. Dynamic analysis of beams on anelastic foundation subjected to moving loads[J]. Journal ofSound andVibration, 1996, 198 (2): 149—169. [5] WU Jong-shyong, DAIChang-wang. Dynamic responses of multispan nonuniform beam due to moving loads[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1987, 113 (3): 458—474. [6] CloughR W, PenzienJ. Dynamics ofStructures[M]. McGraw-HillInc., NewYork, 1975. [7] MeirovitchL. AnalyticalMethods inVibrations[M]. Macmil-lanCompany, London, U. K., 1967. [8] PilkeyW D, ChangP Y. ModernFormulas forStatics andDynamics[M]. McGraw-HillBookCo., NewYork, 1978. [9] CaiC W, CheungY K, ChanH C. Dynamic response of infinitecontinuous beam s subjected to a moving force— an exactmethod[J]. Journal ofSound andVibration, 1988, 123 (3): 461—472. [10] DeanG Duffy. The response of an infinite railroad track to amoving, vibrating mass[J]. Journal ofAppliedMechanics, 1990, 57 (1): 66—73. [11] 郝瀛. 铁道工程[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2000. [12] 曾庆元. 弹性系统总势能不变值原理[J]. 华中理工大学学报, 2000, 28 (1): 1—3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG200001000.htmZENG Qing-yuan. The principle of total potential energy withstationary value in elastic system dynam ics[J]. Journal ofHuazhongU niversity ofScience andTechnology, 2000, 28 (1): 1-3. (inChinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG200001000.htm [13] 曾庆元, 郭向荣. 列车桥梁时变系统振动分析理论与应用[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1999. [14] 曾庆元, 杨平. 形成矩阵的"对号入座"法则与桁梁空间分析的桁段有限元法[J]. 铁道学报, 1986, 8 (2): 48—59. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1986.02.006ZENG Qing-yuan, YANG Ping. The"set-in-right-position"rule for forming structural matrices and the finite truss-element method for space analysis of truss bridges[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1986, 8 (2): 48-59. (inChinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1986.02.006 [15] ZENG Qing-yuan, L OU Ping, XIANG Jun. The principle of total potential energy with stationary value in elastic systemdynamics and its application to the analysis of vibration and dynamic stability[J]. Journal of Huazhong University ofScience andTechnology (UrbanScience), 2002, 19 (1): 7—14. [16] ZENG Qing-yuan, L OU Ping, XIANG Jun. The principle oftotal potential energy with stationary value in elastic systemdynamics and its vibration analysis[A ]. Proceedings of International Conference on Engineering and Technological Sciences 2000, Session5[C]. Beijing: SciencePress, 2000.183—193. [17] LOU Ping, ZENG Qing-yuan. On three approaches to formula-tion of the equations of motion of a dynamic system[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering (Madras), 2002, 29 (2): 119—123. [18] 李德建. 列车—轨道时变系统空间振动分析[D]. 长沙: 长沙铁道学院, 1996. [19] 郭文华. 中小跨度铁路桥梁横向刚度分析[D]. 长沙: 长沙铁道学院, 1999. -





 下载:
下载: