Finite element analysis of slab track subjected to moving load
-
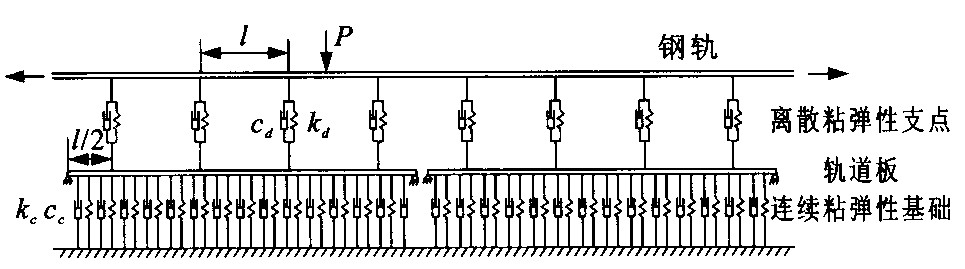
摘要: 用有限元法分析了板式轨道在移动荷载作用下的动力响应。视板式轨道为如下模型: 钢轨为离散粘弹性支点支承的长梁; 轨道板为连续粘弹性基础支承的短梁。视板式轨道及移动荷载为一个系统, 运用弹性系统动力学总势能不变值原理及形成矩阵的"对号入座"法则建立该系统的振动方程组。研究了移动荷载的速度、钢轨的类型和钢轨支点的弹性系数对钢轨及轨道板动力响应的影响。算例结果表明: 在其他参数相同的情况下, 增大钢轨支点的弹性系数, 钢轨的动力响应减小; 使用较重型的钢轨有利于减小钢轨和轨道板的动力响应; 随着移动荷载速度的提高, 钢轨和轨道板的动力响应增大。Abstract: A finite element method was applied to analyze the dynamic response of slab track subjected to a moving load. The slab track was treated as a model, in which rail was regarded as a long beam supported by discrete viscoelastic supports, and slab as a short beam supported by continuously viscoelastic foundation. The slab track and moving load were considered as a system. Vibration equations of the system could be formulated by using the principle of total potential energy with stationary value in elastic system dynamics and the "set-in-right-position"rule for formulating matrixes. The effects of the speed of the moving load, the rail type, and the spring stiffness of rail support on the response of rail and slab were studied. From the presented numerical examples, when the other parameters being the same, with the increasing of spring stiffness of rail support, the dynamic response of rail decreases; with the increasing of rail type, the dynamic response of rail and slab decreases; with the increasing of moving load speed, the dynamic response of rail and slab increases.
-
Key words:
- railway engineering /
- slab track /
- finite element method /
- moving load /
- dynamic response /
- structural analysis
-
表 1 钢轨和轨道板的最大竖向位移
Table 1. Maximum vertical defection of rail and slab
/10-4m 荷载移动速度/m·s-1 50型钢轨板式轨道的钢轨最大竖向位移 50型钢轨板式轨道的轨道板最大竖向位移 60型钢轨板式轨道的钢轨最大竖向位移 60型钢轨板式轨道的轨道板最大竖向位移 75型钢轨板式轨道的钢轨最大竖向位移 75型钢轨板式轨道的轨道板最大竖向位移 静止荷载 11.8936 5.1256 10.4434 4.6284 9.4778 4.2787 v=15 11.9139 5.1922 10.4584 4.6858 9.4894 4.3288 v=30 11.9371 5.2264 10.4745 4.7122 9.5020 4.3506 v=50 11.9978 5.3124 10.5204 4.7786 9.5393 4.4054 v=70 12.1191 5.4425 10.6027 4.8795 9.6031 4.4890 v=85 12.2269 5.5712 10.6888 4.9740 9.6747 4.5686 v=100 12.3764 5.7478 10.8014 5.1122 9.7668 4.6786 表 2 钢轨和轨道板的最大竖向位移
Table 2. Maximum vertical defection of rail and slab
/10-4m 钢轨支点的弹性系数kd/N·m-1 50型钢轨板式轨道的钢轨最大竖向位移 50型钢轨板式轨道的轨道板最大竖向位移 60型钢轨板式轨道的钢轨最大竖向位移 60型钢轨板式轨道的轨道板最大竖向位移 75型钢轨板式轨道的钢轨最大竖向位移 75型钢轨板式轨道的轨道板最大竖向位移 3.0×107 16.9232 5.1113 14.9475 4.6123 13.6525 4.2700 6.0×107 11.9978 5.3124 10.5204 4.7786 9.5393 4.4054 1.2×108 9.1386 5.3261 7.9632 4.7704 7.1677 4.3717 -
[1] Tsunehiko SAITO. Stress analysis of concrete track slabs on an elastic foundation by the finite element method[J]. Quarterly Reports of Railway Technical Research Institute, 1974, 15(4): 186-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKF202115008.htm [2] Tong P, Rossettos J N. Finite-Element Method: Basic Technique and Implementation[M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 1977. [3] LOU Ping, ZENG Qing-yuan. Finite element analysis of infinite long beam resting on continuous viscoelastic foundation subjected to moving loads[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2003, 3(2): 1-6. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB202009005.htm [4] ZENG Qing-yuan. The principle of total potential energy with stationary value in elastic system dynamics[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2000, 28(1): 1-3. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BGYS202105006.htm [5] 曾庆元, 郭向荣. 列车桥梁时变系统振动分析理论与应用[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1999. [6] ZENG Qing-yuan, LOU Ping, XIANG Jun. The principle of total potential energy with stationary value in elastic system dynamics and itsapplication to the analysisof vibration and dynamic stability [J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Urban Science), 2002, 19(1): 7-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DOUB202106002.htm [7] ZENG Qing-yuan, YANG Ping. The" Set-in-right-position" rule for forming structural matricesand the finite truss-element method for space analysis of truss bridges[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1986, 8(2): 48-59. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGJS201601011.htm [8] LOU Ping, ZENG Qing-yuan. On three approaches to formulation of the equations of motion of a dynamic system[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2002, 29(2): 119-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LAWS201504002.htm -





 下载:
下载: