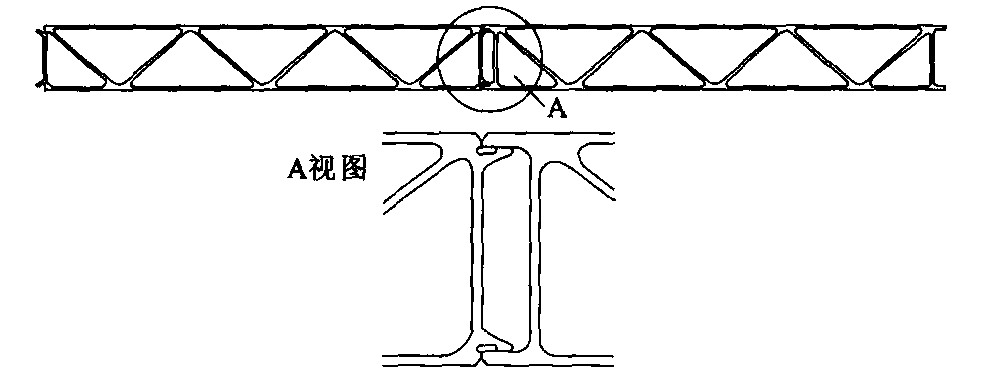
Chinese domestic components of high-speed maglev train body
-
摘要: 分析了由德国进口的上海磁浮列车车体结构静力学性能, 结合中国铝合金挤压型材的生产工艺水平, 提出了大型整体铝合金挤压型材拼装的磁浮列车车体设计方案。根据磁浮列车空气动力性能研究结果, 参照轮轨系统列车车体结构设计规范, 分析了作用于高速磁浮列车车体结构上的八种载荷组合工况。对两种车体结构静力分析结果的比较表明车体应力与振动频率均满足规范要求, 车体实现国产化是可行的。Abstract: Structure static analysis of Shanghai maglev train body imported from Germany was carried. Combined with the manufacture technology level of aluminum alloy profiled extrusion material, maglev train body made up of the large-type integral aluminum alloy extrusion material was put forward. Based on the research result of its aerodynamic performances, the eight loads series acted on high-speed maglev train body were made sure refers to the design rules of wheel-rail system car body configuration. Static analysis results of two car bodies show that carbody stress and frequencies satisfy design demands, it is feasible that maglev train body can be made in China.
-
表 1 八种载荷组合工况下车体的应力
Table 1. Carbody stress under eight loads series
/MPa 工况 国产化车体 上海磁浮列车车体 最大应力值 发生部位底架边梁 最大应力值 发生部位底架边梁 1 67.70 第6个支撑处 76.3 第3个支撑处 2 88.27 第6个支撑处 99.2 第3个支撑处 3 88.10 第6个支撑处 94.8 第4个支撑处 4 88.62 第6个支撑处 95.6 第4个支撑处 5 175.80 第1个支撑处 192.3 第1个支撑处 6 93.79 第6个支撑处 100.2 第6个支撑处 7 180.80 第1个支撑处 190.5 第1个支撑处 8 93.93 第6个支撑处 99.7 第6个支撑处 表 2 车体前6阶自振频率
Table 2. Former six self-vibrancy frequencies of carbody
/Hz 阶次 国产化车体 上海磁浮列车车体 频率 振型 频率 振型 1 11.796 侧墙一阶横向弯曲 6.6 侧墙一阶横向弯曲 2 12.582 车体点头 7.0 车体点头 3 15.488 车顶一阶扭转 9.6 车体一阶垂向 4 18.760 车体一阶垂向弯曲 10.0 车体局部 5 19.921 车体局部 10.4 车体抬头 6 20.130 车顶一阶扭转 13.3 车顶二阶扭转 -
[1] 李强北. 国外磁浮列车述评(上)[J]. 国外铁道车辆, 1996, 33(4): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWTD604.000.htmLI Qiang-bei. Foreign maglev train review[J]. Foreign Rolling Stock, 1996, 33(4): 1-8. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWTD604.000.htm [2] 李强北. 国外磁浮列车述评(下)[J]. 国外铁道车辆, 1996, 33(5): 7-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWTD605.001.htmLI Qiang-bei. Foreign maglev train review[J]. Foreign Rolling Stock, 1996, 33(5): 7-13. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWTD605.001.htm [3] 中南大学. 上海磁浮列车研究报告[R]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2003. [4] 刘华清. 德国磁悬浮列车Transrapid[M]. 成都: 电子科技大学出版社, 1995. [5] Hiroshi Y 山梨磁悬浮试验线车辆MLX01的动力学性能[J]. 国外铁道车辆2000, 37 (5): 27-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWTD200005009.htmHiroshi Y. Dynamic performance of MLX01 car on Yamanashi magnetic test line[J]. Foreign Rolling Stock, 2000, 37(5): 27-32. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWTD200005009.htm [6] Dukkipati RV. Lateral stability analysis of a railway truck on roller rig[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2001, 36(2): 189-204. doi: 10.1016/S0094-114X(00)00017-3 [7] 沈志云. 高速磁浮列车对轨道的动力作用及其与轮轨高速铁路的比较[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2001, 1(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.04.001SHEN Zhi-yun. Dynamic interaction of high speed maglev train on girders and its comparison with the case in ordinary high speed railways[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2001, 1(4): 1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.04.001 [8] 曾佑文, 王少华, 张昆仑. EMS磁浮列车-轨道垂向耦合动力学研究[J]. 铁道学报, 1999, 21(2): 21-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB902.004.htmZENG You-wen, WANG Shao-hua, ZHANG Kun-lun. A study of vertical coupling dynamics of EMS maglev train and guideway systems[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1999, 21(2): 21-25. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB902.004.htm [9] 范钦海. 高速常导磁浮车辆对轨道平顺性要求的探讨[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2002, 23(1): 73-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200201013.htmFAN Qin-hai. Discussion on the demand of high-speed EMS vehicle on guideway irregularity[J]. China Railway Science, 2002, 23(1): 73-76. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200201013.htm -





 下载:
下载: