Supply-demand coordination development of urban road traffic system
-
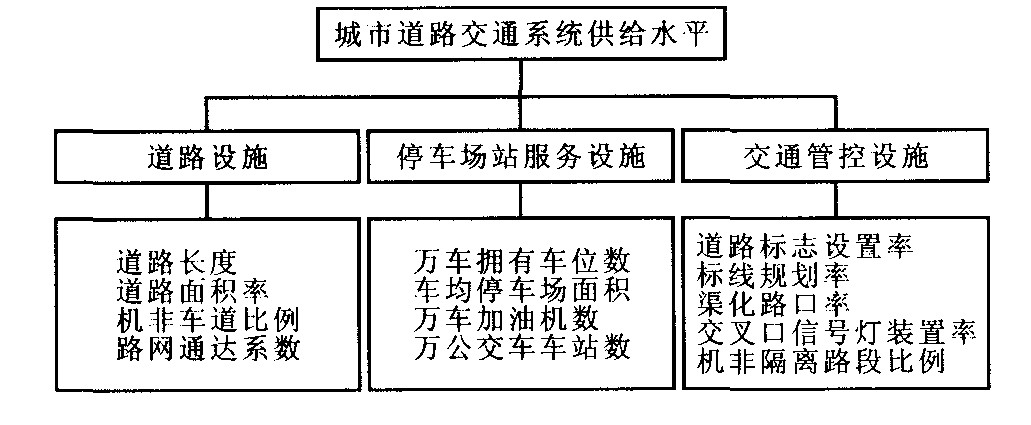
摘要: 在分析城市道路交通供、需系统构成的基础上, 采用范围法、目标法构建了两系统发展水平评价指标体系, 引入供需系统协调发展度的概念, 给出了判定系统协调发展水平及趋势的定量化评价方法。供需评价结果与实际情况相符, 表明该方法可行。Abstract: Based on the supply-demand theory, this paper constructed the evaluation indices of supply-demand system of urban road traffic, proposed a concept of coordination development level of supply-demand system and a quantitative evaluation method of determining the coordination development level. An example show that this method can reflect the real circumstance, which shows the method is feasible.
-
Key words:
- traffic management /
- urban road traffic /
- coordination development /
- traffic supply /
- traffic demand
-
表 1 类别判定
Table 1. Systematic sorts
GD (t) 协调类型 协调类 0.90~1.00 优质协调发展类 0.80~0.89 良好协调发展类 0.70~0.79 中级协调发展类 0.60~0.69 初级协调发展类 过渡类 0.50~0.59 勉强协调发展类 0.40~0.49 濒临失调衰退类 失调类 0.30~0.39 轻度失调衰退类 0.20~0.29 中度失调衰退类 0.10~0.19 严重失调衰退类 0~0.09 极度失调衰退类 表 2 类型判定
Table 2. Systematic styles
F1 (t, x) 与F2 (t, y) 的关系 协调关系判别 F1 (t, x) > F2 (t, y) 供给充足型 F1 (t, x) =F2 (t, y) 供需同步型 F1 (t, x) < F2 (t, y) 供给不足型 表 3 趋势判定
Table 3. Systematic trends
协调发展趋势函数 协调发展趋势 β (t) > 1 增长型 β (t) =1 平稳型 β (t) < 1 衰退型 表 4 评价结果
Table 4. Systematic evaluation result
时间 交通供给系统发展水平 交通需求系统发展水平 供需系统协调度G (t) 供需系统协调发展度GD (t) 协调发展趋势指数β (t) 1996 0.631 0.662 0.995 4 0.802 1 1997 0.653 0.681 0.996 5 0.815 2 1.016 3 1998 0.675 0.702 0.996 9 0.828 4 1.016 2 1999 0.692 0.718 0.997 3 0.838 4 1.012 1 2000 0.727 0.753 0.997 5 0.859 1 1.024 7 2001 0.754 0.773 0.998 8 0.873 2 1.016 4 -
[1] 张生瑞, 严宝杰. 交通运输系统协调发展的理论分析[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 22(2): 51-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200202017.htmZHANG Sheng-rui, YAN Bao-jie. Analysis of the transportation system coordination[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2002, 22(2): 51-53. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200202017.htm [2] 魏连雨, 杨春风. 城市交通基础设施规模及协调发展[J]. 西安公路交通大学学报, 2001, 21(2): 66-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200102021.htmWEI Lian-yu, YANG Chun-feng. The urban traffic infrastructure scale and its harmonious development[J]. Journal of Xi'anHighway University, 2001, 21(2): 66-69. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200102021.htm [3] 刘求实, 沈红. 区域可持续发展指标体系与评价方法研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 1997, 7(4): 60-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ199704013.htmLIU Qiu-shi, SHEN Hong. Research of indices system and evaluation method of regional continuous development[J]. China Population Resources and Environment, 1997, 7(4): 60-64. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ199704013.htm [4] 杨士弘, 廖重斌, 郑宗清. 城市生态环境学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995. [5] 申金山, 宋健民, 关可. 城市基础设施与社会环境发展的定量评价方法与应用[J]. 城市环境与城市生态, 2000, 13(5): 10-12.SHEN Jin-shan, SONG Jian-min, GUAN Ke. Quantitative evaluation method and its application for infrastructure and social economy coordinated development[J]. Urban Environment and Urban Ecology, 2000, 13(5): 10-12. (in Chinese) [6] 王成纲. 论我国城市交通需求管理[J]. 长沙交通学院学报, 2001, 17(4): 67-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSJX200104015.htmWANG Cheng-gang. On the managementof the demand for city communicationsin China[J]. Journal ofChangsha Communications University, 2001, 17(4): 67-71. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSJX200104015.htm -





 下载:
下载: