Influence factors on post-construction settlement of high backfills adjacent to abutment
-
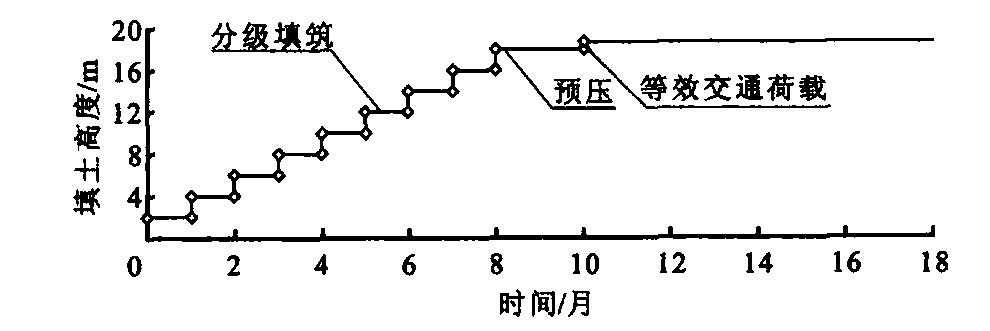
摘要: 为了揭示桥台后高填方路堤工后沉降的影响因素, 应用ABAQUS有限元程序建立了沿桥台纵向的平面应变计算模型, 对回填材料进行了相关参数的沉降敏感性分析。高等级公路沉降实测结果与数值计算结果的对比分析表明, 模型的计算结果能反映实际工况下路堤沉降的变化规律, 可合理预测高填土路堤实际变形特征, 弹性模量、渗透系数、容重、施工间歇期是影响近桥台处路堤工后沉降的主要因素, 建议回填设计中应通过综合提高回填材料力学性能与改善施工方法的手段来达到减轻桥台后跳车的目的。Abstract: In order to analyse the post-construction settlement rules of high backfills adjacent to(abutment, ) a plane-strain numerical model was presented by ABAQUS/standard finite element code, the influence degrees of backfills parameters on settlement were studied.The simplified method is verified to be reasonable and feasible by making the comparison between the numerical analysis and field measure results because its computation result can indicate the rules and properties of backfills real settlement, some parameters, such as elastic modulus, permeability coefficient, unit weight and preloading time, are the major influence factors on the post-construction settlement of backfills.Perhaps the "bridge bump" is reduced while the mechanical characteristics of backfills and construction method are improved in design.
-
表 1 Clay Plasticity模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of Clay Plasticity model
材料类型 γd/(kN·m-3) c′/kPa φ′/(°) κ υ λ M α0 β K e1 k/(m·d-1) 粉质粘土 17.8 22.4 31.6 0.04 0.31 0.07 1.27 0.00 1.00 1.00 1.02 2.31×10-4 表 2 Drucker-Prager模型参数
Table 2. Parameters of Drucker-Prager model
材料类型 γd/(kN·m-3) c′/kPa φ′/(°) E υ β′ K ψ k/(m·d-1) 圆砾 19.8 0.0 41.3 50000 0.21 34.7 1.00 34.7 1.0 粘性土 18.3 29.3 36.5 28000 0.24 28.7 1.00 28.7 3.63×10-4 表 3 Drucker-Prager模型硬化参数
Table 3. Tabular parameters of Drucker-Prager hardening curves
粘性土 圆砾 σ1-σ3 εp σ1-σ3 εp 170.1 0.000 204.9 0.000 649.9 0.035 352.9 0.039 740.3 0.050 919.7 0.045 801.4 0.073 1 059.8 0.073 848.0 0.091 1 124.5 0.092 表 4 线弹性模型参数
Table 4. Parameters of elastic model
材料类型 γd/(kN·m-3) c′/kPa φ′/(°) E/kPa υ k/(m·d-1) 沥青混凝土 21.4 — — 2.86×106 0.16 1.00×10-7 水泥混凝土 24.3 — — 3.54×107 0.15 2.00×10-8 -
[1] Zhang Xing-qiang, Yan Shu-wang, Zhao Cheng-gang. Analysis of soil deformation due to bridge abutment under automobile loading[J]. Highway, 2002, 47(5): 31-35. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202205008.htm [2] Chen Shao-ping. Subgrade settlement fitting between small bridge abutment and bridge culvert in soft soil areas[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences(Earcth Science Edition), 2001, 26(4): 365-367. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJNS202105005.htm [3] Liu Dai-quan, Liu Xiao-ming, Long Zheng-cong. Mechanical analysis of bump at bridge-head and discussion of rigid-flexibility transition design parameters of abutment back[J]. Highway, 2002, 47(6): 81-84. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202004009.htm [4] Gregory J M. Tensile reinforcement effects on bridge approach settlement[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1993, 112(4): 749-761. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC202001006.htm [5] Weng Xing-zhong, Du Jian, Hong Jian-jun, et al. A settlement stabilization analysis of airfield pavement great area high filling [J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University(Natural Science Edition), 2001, 2(5): 7-10. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJNS202105005.htm [6] 钱家欢. 土力学[M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 1990. [7] Kim J S, Barker R M. Effect of live load surcharge on retaining walls and abutments[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(10): 803-813. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGU201903009.htm [8] Kutara K, Miki H, Mashita Y, et al. Settlement and countermeasures of the road with low embankment on soft ground [J]. Technical Reports of Civil Engineering, 1980, 22(8): 12-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC2020S1003.htm [9] Yin Zong-ze, Zhu Hong, Wu Yu. Finite element analysis of foundation settlement of Shanghai-Nanjing expressway embankment[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 1998, 18(2): 22-26. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ202005012.htm -





 下载:
下载: