Properties of acoustics and vibration of skeleton dense quiet pavement
-
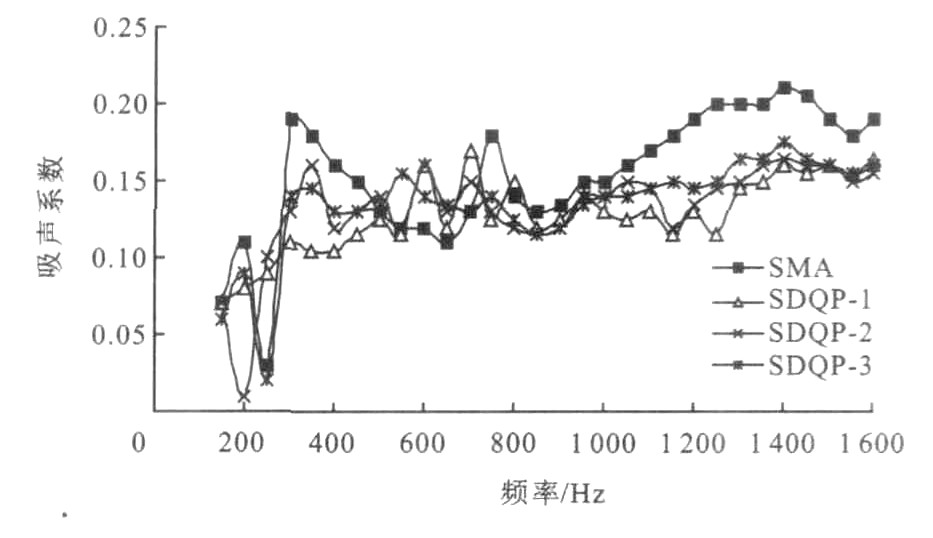
摘要: 为探讨骨架密实型低噪声路面的降噪机理, 分别采用驻波管装置测试了SDQP路面的吸声系数, 重复加载法测试了SDQP混合料的复合模量, 轮胎/路面振动测试装置研究了轮胎在不同路面上的垂直振动衰减特性。结果表明SDQP路面与SMA路面的吸声系数没有明显的差异, 在整个频段上吸声系数很小; SDQP混合料的动态模量随着橡胶颗粒掺量的增加呈下降趋势, 而阻尼逐渐提高; 轮胎在SDQP路面的衰减系数最大, 且随着橡胶颗粒掺量的增加而增大, 说明SDQP路面具有较好的阻尼减振降噪能力, 吸声降噪性能并不占优。Abstract: In order to study the noise reduction mechanism of skeleton dense quiet pavement(SDQP), the absorption coefficient, complex moduli of SDQP mixture and the properties of vertical vibration attenuation of tire aimed at different pavements were tested by respectively using standing-wave meter, repetitive loading method and tire/pavement vibration test system.Test result shows that the absorption coefficient of SDQP is close to that of SMA, the values of the absorption coefficients are very small in all frequency bands, and the dynamic moduli of SDQP decreases with the increase of rubber granules content, while the damping of SDQP increases; the attenuation coefficient of tire placed on SDQP is the maximum, and increases with the increase of rubber granules content, which indicates that SDQP has good noise reduction ability of damping and vibration attenuation, and the primary mechanism of noise reduction is not sound absorption.
-
表 1 矿料性能指标
Table 1. Property indices of mineral materials
矿料 技术指标 测试值 要求值 粗集料 表观相对密度 2.721 不小于2.500 毛体积相对密度 2.676 — 压碎值/% 11.2 不大于26.0 洛杉矶磨耗率/% 10.8 不大于28.0 针片装颗粒含量/% 10 不大于15 吸水率/% 0.7 不大于2.0 细集料 表观相对密度 2.7 不小于2.5 矿粉 表观相对密度 2.715 — 表 2 SBS改性沥青性能
Table 2. Properties of SBS modified asphalt
相对密度(25℃) 针入度(25℃)/0.1mm 针入度指数 软化点/℃ 弹性恢复(25℃)/% 延度(5℃)/cm 1.019 62.0 -0.2389 83 80 36 表 3 不同路面的内部阻尼和弹性劲度
Table 3. Dampings and stiffnesses of different pavements
材料类型 动态模量/MPa 相位角/(°) 内部阻尼/MPa 弹性劲度/MPa 备注 SMA 956.6 10.54 174.98 940.46 无橡胶颗粒 SDQP-1 946.3 12.30 201.59 924.58 橡胶掺量为1% SDQP-2 892.8 14.07 217.05 866.02 橡胶掺量为2% SDQP-3 887.0 19.21 291.85 837.61 橡胶掺量为3% 表 4 衰减系数
Table 4. Attenuation coefficients
材料类型 SMA SDQP-1 SDQP-2 SDQP-3 衰减系数 1.2474 1.3020 1.3274 1.3567 -
[1] Nelson P M. Designing porous road surfaces to reduce traffic noise[R]. Crowthorne: Transportation Research Laboratory, 1994. [2] 曹卫东, 周海生, 吕伟民. 废橡胶颗粒改性沥青混合料的设计与性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2005, 8(5): 562-566. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2005.05.016Cao Wei-dong, Zhou Hai-sheng, Lu Wei-min. Research onthe design and properties of crumb rubber modified asphalt mix[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2005, 8(5): 562-566. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2005.05.016 [3] 曹卫东, 葛剑敏, 周海生, 等. 骨架密实型低噪声路面的试验研究及应用[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 34(8): 1 026-1 030. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.08.007Cao Wei-dong, Ge Jian-min, Zhou Hai-sheng, et al. Experimental research and application of skeleton dense-graded noise reduction pavement[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2006, 34(8): 1 026-1 030. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.08.007 [4] JTG F40-2004, 公路沥青路面施工技术规范[S]. [5] JTJ 052-2000, 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程[S]. [6] 洪宗辉. 环境噪声控制工程[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. [7] 吕伟民. 沥青混合料设计原理与方法[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2001. [8] 王旭东, 沙爱民, 许志鸿. 沥青路面材料动力特性与动态参数[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2002. [9] 盛美萍, 王敏庆, 孙进才. 噪声与振动控制技术基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. [10] 韩森, 董雨明, 陈海峰, 等. 露石水泥混凝土路面降噪特性[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2005, 5(2): 32-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC200502007.htmHan Sen, Dong Yu-ming, Chen Hai-feng, et al. Noise reduction performance of exposed-aggregate cement concrete pavement[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2005, 5(2): 32-34. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC200502007.htm -





 下载:
下载: