Multi-user and multi-mode assignment model of mixed stochastic traffic balance
-
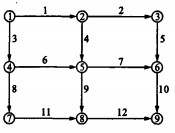
摘要: 为了实现交通网络混合交通流随机平衡分配, 分析了广义费用下多用户多方式的路径选择机理与网络平衡条件及信息条件下多用户多方式对路径选择的影响特征, 运用数学规划理论, 建立了基于信息条件的随机混合交通平衡分配模型, 并证明了模型解的等价性与唯一性。计算结果表明: 在信息市场占有率为30%, 经过6次迭代, 模型的解能够很快收敛, 显示了信息条件占有率对交通方式选择和流量分配的影响程度, 因此, 模型可行。Abstract: In order to realize the stochastic-balanceable assignment of mixed traffic flow in traffic network, the theory of routing selection and the conditions of network equilibrium were analyzed based on multi-user and multi-mode on the conditions of generalized cost and traffic information, a stochastic-balanceable assignment model of mixed traffic flow was put forward by using mathematical programming theory on the condition of traffic information, and the equivalence and uniqueness of the solution for the model were demonstrated. Computation result shows that the solution of the model quickly converges when the possessive ratio of traffic information market is 30%, and the iteration times are only 6, which indicates the effect degrees of traffic information on traffic mode choice and traffic flow assignment, so the model is feasible.
-
Key words:
- traffic network /
- information conditions /
- multi-user and multi-mode /
- traffic assignment
-
表 1 公共交通方式行程时间函数
Table 1. Travel time functions of public traffic mode

表 2 私家车方式行程时间函数
Table 2. Travel time functions of private car mode

表 3 路段上公交方式平衡流量
Table 3. Balance flows of bus mode on links

表 4 路段上私家车方式平衡流量
Table 4. Balance flows of private car mode on links

-
[1] 四兵锋, 高自友. 城市交通超级网络均衡配流模型及算法[J]. 公路交通科技, 1998, 15(S1): 67-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK8S1.019.htmSi Bing-feng, Gao Zi-you. The equilibrium assignment model and algorithm for urban traffic hyper-networks[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 1998, 15(S1): 67-71. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK8S1.019.htm [2] 李志纯, 谷强, 史峰. 弹性需求下拥挤道路收费的模型与算法研究[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2001, 1(3): 81-85. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.03.020Li Zhi-chun, Gu Qiang, Shi Feng. Toll model and algorithm of road jammed with traffic based on elastic demand[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2001, 1(3): 81-85. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.03.020 [3] 罗文昌. 混合交通随机用户平衡分配模型及算法[J]. 宁波大学学报: 理工版, 2005, 18(4): 451-457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5132.2005.04.009Luo Wen-chang. Stochastic user equilibrium model and algorithm based on mixed traffic[J]. Journal of Ningbo University: Natural Science and Engineering Edition, 2005, 18(4): 451-457. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5132.2005.04.009 [4] 况爱武, 王正武. ATIS影响下的混合随机用户均衡交通分配模型研究[J]. 重庆交通学院学报, 2006, 25(6): 109-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0696.2006.06.028Kuang Ai-wu, Wang Zheng-wu. Research on the mixed stochastic user equilibrium traffic assignment model under influence of ATIS[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2006, 25(6): 109-112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0696.2006.06.028 [5] 杜进有, 罗霞. 城市交通组合随机用户平衡模型[J]. 系统工程理论方法应用, 2006, 15(6): 456-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTGL200605013.htmDu Jin-you, Luo Xia. Study on a combined stochastic user equilibrium model for urban traffic[J]. Systems EngineeringTheory Methodology Application, 2006, 15(6): 456-458. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTGL200605013.htm [6] 四兵锋, 孙壮志, 赵小梅. 基于随机用户平衡的混合交通网络流量分离模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(1): 93-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200601019.htmSi Bing-feng, Sun Zhuang-zhi, Zhao Xiao-mei. Mixed traffic network flow-split model based on stochastic user equilibrium[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2006, 19(1): 93-98. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200601019.htm [7] 袁鹏程, 韩印, 范炳全. 网络流量随机条件下的随机交通网络平衡分析[J]. 城市交通, 2007, 5(3): 53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5328.2007.03.012Yuan Peng-cheng, Han Yin, Fan Bing-quan. Stochastic transportation networks equilibrium analysis based on stochastic traffic flows[J]. Urban Transport of China, 2007, 5(3): 53-57. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5328.2007.03.012 [8] Lo H K, Luo X W, Siu B W Y. Degradable transport network: travel time budget of travelers with heterogeneous risk aversion[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2006, 40(9): 792-806. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2005.10.003 [9] 史峰, 李志纯. 拥挤道路使用收费的理论构架[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2002, 2(2): 78-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2002.02.019Shi Feng, Li Zhi-chun. Theoretic framework and development on research of congested road-use pricing[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2002, 2(2): 78-82. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2002.02.019 [10] 黄海军. 城市交通网络平衡分析理论与实践[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1994. -





 下载:
下载: