Analysis and evaluation of reliability for stochastic and dynamic transport network
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
摘要: 为分析随机动态交通网络中出行者的旅行选择与停车行为, 利用网络均衡原理和不动点理论, 建立了供需相互作用下的不动点模型, 提出了计划可靠度和停车可靠度指标, 并对随机动态交通路网的可靠性进行了评价。发现停车设施的位置和步行距离对出行者的计划可靠度和停车可靠度水平影响较大, 停车费相当时, 出行者将优先选择距离目的地近的停车设施; 在早晨上班高峰期, 距离目的地较远的停车设施的停车可靠度较高。分析结果表明: 提出的可靠度指标能有效地衡量一天中不同时段道路网络和停车设施的服务水平。Abstract: In order to analyze the travel and parking behaviors of commuter in stochastic and dynamic transport network, a fixed point model was set up by using network equilibrium rule and fixed point theory, and a schedule reliability and a parking reliability were put forward to measure the stability of the network. It is found that the location of parking facility and walking distance have significant influence on the levels of both the schedule reliability and parking reliability of commuter, specifically, commuters often park their cars at the nearer locations from their workplaces among multiple parking locations with the same parking charges; during traffic peak period in the morning, the parking reliability of farther location is higher than that of nearer location. Analysis result shows that the indices can effectively measure the service levels of road network and parking facilities in everyday different periods.
-
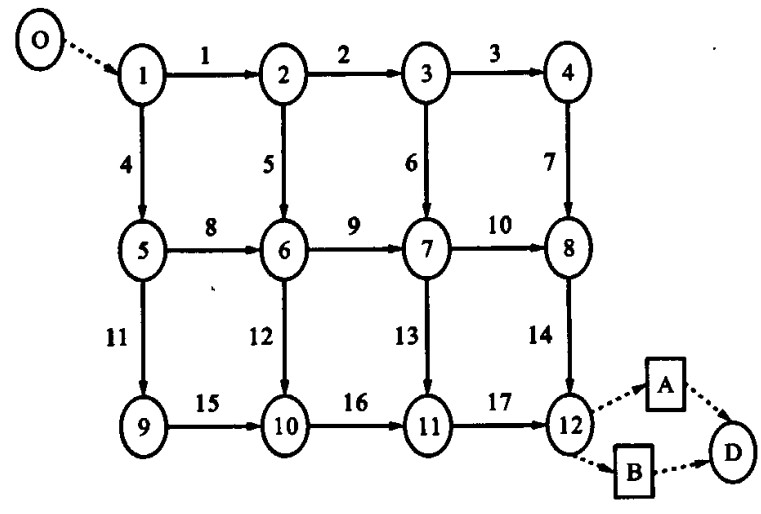
表 1 输入参数
Table 1. Input parameters

-
[1] Bell M G H, Iida Y. Transportation Network Analysis[M]. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 1997. [2] Chen A, Yang Hai, Lo H K, et al. A capacity related reliability for transportation networks[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 1999, 33(2): 183-200. doi: 10.1002/atr.5670330207 [3] Chen A, Yang Hai, Lo H K, et al. Capacity reliability of a road network: an assessment methodology and numerical results[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2002, 36(3): 225-252. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(00)00048-5 [4] Clark S, Watling D. Modeling network travel time reliability under stochastic demand[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2005, 39(2): 119-140. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2003.10.006 [5] Du Zheng-ping, Nicholson A. Degradable transportation systems: sensitivity and reliability analysis[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 1997, 31(3): 225-237. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(96)00023-9 [6] Lam W H K, Tam M L. Reliability assessment on searching time for parking in urban areas[C]//Iida Y, Bell M G H. The Network Reliability of Transport. Oxford: Elsevier, 2003: 61-78. [7] Lam W H K, Li Zhi-chun, Huang Hai-jun, et al. Modeling time-dependent travel choice problems in road networks with multiple user classes and multiple parking facilities[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2006, 40(5): 368-395. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2005.05.003 [8] Taylor M A P. Travel time variability— the case of two public modes[J]. Transportation Science, 1982, 16(4): 507-521. doi: 10.1287/trsc.16.4.507 [9] Huang Hai-jun, Li Zhi-chun. A multiclass, multicriteria logit-based traffic equilibrium assignment model under ATIS [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 176(3): 1 464-1 477. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2005.09.035 [10] 钟慧玲, 徐建闽, 屠宇. 基于专用短程通信的停车引导和信息系统[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 24(2): 66-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8879.2004.02.016Zhong Hui-ling, Xu Jian-min, Tu Yu. Parking guidance and information system based on dedicated short range communication[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2004, 24(2): 66-69. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8879.2004.02.016 [11] Huang Hai-jun, Li Zhi-chun, Lam W H K, et al. A time-dependent activity and travel choice model with multiple parking options[C]//Mahmassani H S. Transportation and Traffic Theory. Oxford: Elsevier, 2005: 717-739. [12] 李志纯, 黄海军. 弹性需求下的组合出行模型与求解算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2005, 18(3): 94-98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2005.03.019Li Zhi-chun, Huang Hai-jun. Model and solution algorithm with combined travel under elastic demand[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2005, 18(3): 94-98. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2005.03.019 [13] 李志纯, 谷强, 史峰. 弹性需求下拥挤道路收费的模型与算法研究[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2001, 1(3): 81-85. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.03.020Li Zhi-chun, Gu Qiang, Shi Feng. Toll model and algorithm of road jammed with traffic based on elastic demand[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2001, 1(3): 81-85. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2001.03.020 -





 下载:
下载: