Permanent deformation prediction model of sandy soil under repeated load
-
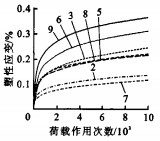
摘要: 为预估路基的永久变形, 在万能材料试验机上对砂土进行了重复加载动三轴试验, 得到了砂土永久变形的发展曲线, 建立了塑性应变和荷载作用次数之间的关系式, 使用最小二乘法拟合出该式中的系数与含水量和回弹模量之间的回归公式, 并对回归公式进行了可靠性分析。当荷载作用次数为10000次时, 现有路基土永久变形模型预估结果与试验结果相对误差最小为52%, 最大高达376%;而系数与含水量和回弹模量之间的回归公式相关系数最小值为0.31, 平均值为0.41, 大于临界值0.28, 试验曲线与理论曲线相关系数大于0.99。分析结果表明: 建立的砂土永久变形预估公式可靠性较高, 而现有预估模型不适用于砂土。Abstract: In order to predict the permanent deformation of subgrade, a dynamic triaxial test of sandy soil under repeated load was made by using universal testing machine(UTM), the development curves of the deformation were got, the relationship formula between plastic strain and load acting time was found, the regression formulas among the coefficients of the relationship formula, water content and resilient modulus were fitted by using least square method, and their reliability was analyzed. Analysis result shows that when load acting time reaches 10 000, the minimum and maximum relative errors between permanent deformation prediction result and measured result are 52% and 376% respectively; the minimum and average correlative coefficients of the regression formulas are 0.31 and 0.41 respectively, which are greater than the critical value of 0.28, and the correlative coefficient between theoretical curve and measured one is more than 0.99. So the reliability of the proposed prediction formulas of permanent deformation for sandy soil is higher, but existing prediction model is not suitable for sandy soil.
-
Key words:
- subgrade engineering /
- sandy soil /
- permanent deformation /
- repeated load test /
- prediction model
-
表 1 土的基本性质
Table 1. Basic properties of soil
指标 最大干密度DMD/(g·cm-3) 最佳含水量/% 相对密度 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数 测定值 2.00 11.1 2.658 20.64 16.09 10.55 表 2 永久变形曲线拟合结果
Table 2. Fitting result of permanent deformation curve
工况 回弹应变εr 回弹模量/MPa R2 lg(ε0/εr) lg(ρ) lg(β) 91-105-48 0.001 25 38.40 0.998 7 0.702 430 536 5.439 378 -0.882 56 91-105-69 0.001 85 37.30 0.999 6 0.664 794 386 4.583 399 -0.769 70 91-110-48 0.001 55 30.97 0.998 0 0.690 481 894 4.612 529 -0.816 25 91-110-69 0.001 75 39.43 0.998 5 0.902 779 666 5.240 023 -0.851 34 91-120-48 0.001 60 30.00 0.998 7 0.426 307 892 3.258 652 -0.642 92 91-120-69 0.001 95 35.38 0.999 5 0.561 834 989 3.236 714 -0.635 37 96-105-28 0.000 60 46.67 0.999 5 0.758 407 192 6.594 742 -0.807 80 96-105-48 0.001 05 45.71 0.999 7 0.492 028 301 4.116 664 -0.722 60 96-105-69 0.001 40 49.29 0.998 9 0.566 521 666 3.750 246 -0.719 47 96-110-28 0.000 65 43.08 0.999 8 0.629 566 412 2.521 400 -0.509 38 96-110-48 0.001 20 40.00 0.999 7 0.573 065 095 2.815 113 -0.600 05 96-110-69 0.001 85 37.30 0.999 5 0.540 363 300 3.387 230 -0.684 79 96-120-28 0.001 00 28.00 0.998 6 0.597 695 186 2.760 121 -0.619 28 96-120-48 0.001 75 27.43 0.998 4 0.520 389 945 2.690 905 -0.593 07 96-120-69 0.002 15 32.09 0.999 3 0.508 921 011 3.037 904 -0.643 40 -
[1] 李明国, 牛晓霞, 申爱琴. 山区高速公路沥青路面的抗车辙能力[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 26(6): 19-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8879.2006.06.005Li Ming-guo, Niu Xiao-xia, Shen Ai-qin. Anti-rut ability of asphalt pavement on mountain freeway[J]. Journal of Chang an University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 26(6): 19-22. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8879.2006.06.005 [2] Dorman G M. The extension to practice of a fundamental procedure for the design of flexible pavements[C]//University of Michigan. Proceedings International Conference on the Structural Design of Asphalt Pavements. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 1962: 511-522. [3] 邱延峻, 孙振堂. 柔性路面路基土的永久变形[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2000, 35(2): 116-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2000.02.002Qiu Yan-jun, Sun Zhen-tang. Permanent deformation of sub-grade soils in flexible pavements[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2000, 35(2): 116-120. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2000.02.002 [4] Qiu Yan-jun, Dennis N D, Elliott R P. Deformation characteristics of subgrade soils under repeated loading[J]. Geotechnical Engineering, 1999, 30: 85-97. [5] Monismith C L, Ogawa N, Freeme C R. Permanent deformation characteristics of subgrade soils due to repeated loading[J]. TRR, 1975, 537: 1-17. [6] Barksdale R D. Compressive stress pulse times in flexible pavements for use in dynamic testing[J]. HRR, 1971, 345: 32-44. [7] Kenis W J. FHWA predictive design procedure, VESYSuser s manual: an interim design method for flexible pavement using the VESYS structural subsystem[R]. Washing-ton DC: Transportation Federal Highway Administration Office, 1978. [8] Bonaquist R, Witczak M W. Plasticity modeling applied to the pavement deformation response of granular materials in flexible pavement systems[J]. TRR, 1996, 1540: 7-14. [9] Muhanna AS, Rahman MS, Lambe P C. Resilient modulus and permanent strain of subgrade soils[J]. TRR, 1998, 1619: 85-93. [10] Werkmeister S, Dawson AR, Wellner F. Permanent deformation behavior of granular materials and the shakedown concept[J]. TRR, 2001, 1757: 75-81. [11] Werkmeister S, Dawson AR, Wellner F. Pavement design model for unbound granular materials[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2004, 130(5): 665-674. [12] Tseng K, Lytton R. Prediction of permanent deformation in flexible pavement materials[J]. Implication of Aggregates in the Design, Construction, and Performance of Flexible Pavements, 1989, 1016: 154-172. [13] Transportation Research Board of the National Academies. Guide for mechanistic-empirical design of new and rehabilitated structures[R]. Washington DC: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 2004. [14] Ayres MJ. Development of a rational probabilistic approach for flexible pavement analysis[D]. College Park: University of Maryland, 1997. [15] 杜顺成, 戴经梁. 沥青混合料永久变形评价指标[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(5): 18-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200605004.htmDu Shun-cheng, Dai Jing-liang. Permanent deformation evaluation index of asphalt mixture[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2006, 19(5): 18-22. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200605004.htm [16] 王鹏, 曾凡奇, 黄晓明. 沥青高温性能指标的灰色关联度分析[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2006, 6(3): 32-36. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200603008Wang Peng, Zen Fan-qi, Huang Xiao-ming. Grey relation degree analysis of high-temperature performance indexes of asphalt[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2006, 6(3): 32-36. (in Chinese) http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200603008 -





 下载:
下载: