Evolution of day-to-day route choice behavior considering risk aversion and perception updating
-
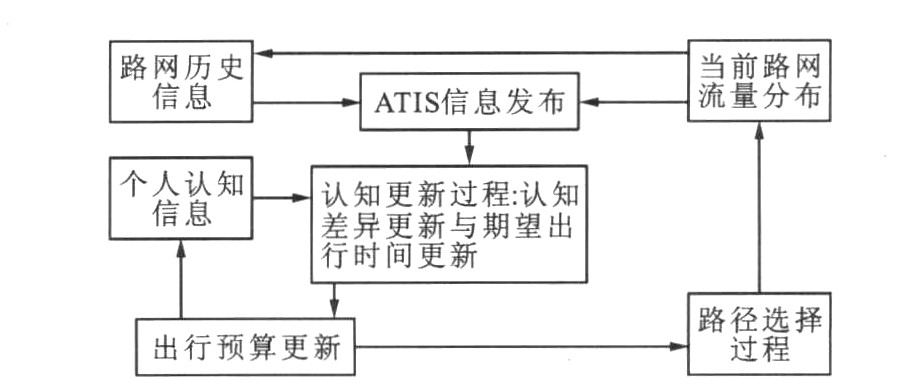
摘要: 为了刻画出行者的日常择路行为, 利用动力学系统方法和不动点理论, 建立了一个集成风险规避和认知更新的演化模型, 分析了演化过程的稳定性, 并在一个简单网络上进行了验证。发现在模拟开始的前15 d内, 出行时间预算、路径期望出行时间、实际出行时间以及路径流量都出现了较大的波动, 但经过大约30 d的摸索以后, 开始趋向于随机用户均衡状态。分析结果表明: 模型所设计的择路演化过程类似于经典的相继平均算法的计算过程, 可以确保收敛到稳定状态, 并与初始状态参数的取值无关。Abstract: In order to depict travelers' day-to-day route choice behaviors, an integrated model considering risk aversion and perception updating was proposed by using dynamics system approach and fixed point theory, its evolution stability was discussed and validated in a simple network.It is pointed that travel time budget, expected route travel time, actual route travel time and route flow appear a large of turbulence in 15 d at the beginning of simulation, but the traffic pattern evolves to stochastic user equilibrium state after nearly thirty days' travel.Analysis result indicates that the route choice evolution adopted in the model is highly similar to the computational steps of the classical method of successive average(MSA), so the evolution stability can be assured, and the final flow pattern is independent of initial values of all state variables.
-
表 1 参数取值
Table 1. Parameter values
路段 ta0/min Ca/veh 路段 ta0/min Ca/veh 1-2 20 360 5-6 12 180 2-3 12 360 4-7 15 240 1-4 15 240 5-8 10 150 2-5 12 180 6-9 30 360 3-6 12 360 7-8 15 240 4-5 10 150 8-9 15 240 表 2 基于Logit随机用户均衡流量
Table 2. Stochastic user equilibrium flow based on Logit
λ 0.01 0.05 0.10 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 3.00 5.00 f1-4-7-8-9/veh 86.39 94.12 99.99 113.00 115.80 116.70 117.20 117.60 117.90 -
[1] 黄海军. 城市交通网络平衡分析——理论与实践[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1994. [2] DAGANZO C F, SHEFFI Y. On stochastic models of traffic as-signment[J]. Transportation Science, 1977, 11(3): 253-274. doi: 10.1287/trsc.11.3.253 [3] 黎茂盛, 王炜, 史峰. 降级路网的认知及交通流平衡分析模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(6): 87-91. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2006.06.017LI Mao-sheng, WANG Wei, SHI Feng. Cognition of degraded road network and equilibrium analysis model on trafficflow[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2006, 19(6): 87-91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2006.06.017 [4] LO H K, LUO X W, SI UB WY. Degradable transport network: travel time budget of travelers with heterogeneous riskaversion[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2006, 40(9): 792-806. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2005.10.003 [5] 李志纯, 朱道立. 随机动态交通网络可靠度分析与评价[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2008, 8(1): 106-112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2008.01.021LI Zhi-chun, ZHU Dao-li. Analysis and evaluation of reliability for stochastic and dynamic transport network[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2008, 8(1): 106-112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2008.01.021 [6] LO H K, TUNG Y K. Network with degradable links: capacity analysis and design[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2003, 37(4): 345-363. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(02)00017-6 [7] 许良, 高自友. 基于路段能力可靠性的城市交通网络设计[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(2): 86-90. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2006.02.015XU Liang, GAO Zi-you. Urban transport network design based on link capacity reliability[J]. China Journal of High-way and Transport, 2006, 19(2): 86-90. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2006.02.015 [8] 吴文祥, 黄海军. 平行路径网络中信息对交通行为的影响研究[J]. 管理科学学报, 2003, 6(2): 12-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCYJ200302002.htmWU Wen-xiang, HUANG Hai-jun. Study on behavior impacts caused by travel information systems in parallel route network[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China, 2003, 6(2): 12-16. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCYJ200302002.htm [9] HUANG Hai-jun, LI U Tian-liang, GUO Xiao-lei, et al. Efficiency loss of a stochastic user equilibrium in a traffic network with ATIS market penetration[C]//MAO Bao-hua. Traffic and Transportation Studies Proceedings of ICTTS 2006. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 709-719. [10] 任伟, 高自友, 任华玲. ATIS市场占有率问题研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2006, 6(1): 37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2006.01.013REN Wei, GAO Zi-you, REN Hua-ling. Research on ATIS market penetration problem[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2006, 6(1): 37-41. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2006.01.013 [11] CANTARELLA G E, CASCETTA E. Dynamic processesand equilibriumin transportation networks: towards a unifying theory[J]. Transportation Science, 1995, 29(4): 305-329. doi: 10.1287/trsc.29.4.305 [12] WATLI NG D P. Stability of the stochastic equilibrium as-signment problem: a dynamical systems approach[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 1999, 33(4): 281-312. [13] WATLI NG D P, HAZELTON ML. The dynamics and equilibria of day-to-day assignment models[J]. Networks and Spatial Economics, 2003, 3(3): 349-370. [14] HUANG Hai-jun, LI U Tian-liang, YANG Hai. Modeling the evolutions of day-to-day route choice and year-to-year ATIS adoption with mixed stochastic user equilibrium[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2008, 42(2): 111-127. [15] 刘天亮, 黄海军. 日常择路行为的多智能体模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2007, 56(11): 6321-6325. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB200711029.htmLI U Tian-liang, HUANG Hai-jun. Multi-agent simulationon day-to-day route choice behavior[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2007, 56(11): 6321-6325. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB200711029.htm [16] J HA M, MADANATS, PEETAS. Perception updating and day-to-day travel choice dynamics in traffic networks with information provision[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 1998, 6(3): 189-212. -





 下载:
下载: