Constant air gap control simulation of linear induction motor of metro vehicle
-
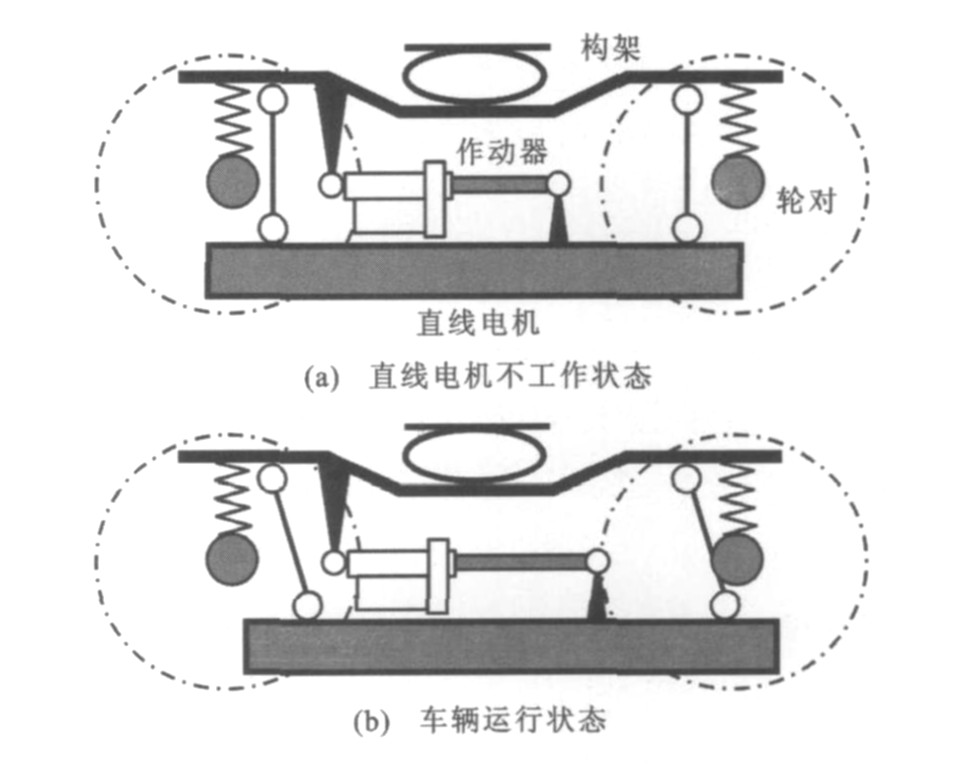
摘要: 为了研究直线电机悬挂方式对车辆动力学性能的影响, 以及通过主动悬挂以减小直线电机气隙变化和轮轨冲击力, 建立了基于多体动力学的地铁车辆仿真模型。采用经典电磁场理论建立了直线电机电磁力仿真模型, 以及机电作动器驱动的直线电机恒隙控制系统模型。采用数值仿真研究了直线电机恒隙控制方法及其对车辆动力学性能的影响。仿真结果表明: 直线电机采用架悬结构并选择大挠度的一系垂向弹簧时, 气隙变化主要是由载荷变化引起的, 变化频率很低, 易实现恒隙控制。恒隙控制可以保证车辆在不同荷载工况下满足气隙要求, 降低轮轨垂向作用力10 kN左右, 减小车体垂向平稳性指标0.1左右。车辆动力学性能较传统直线电机车辆得到改善, 并能提供平稳的牵引力。Abstract: In order to research the influence of suspension types of linear induction motor(LIM)on the dynamics performance of vehicle system, and further decrease the air gap fluctuation of LIM and reduce wheel-rail impact by using active suspension, the multi-body dynamics model of metro vehicle was set up.The electromagnetic force model of LIM was built by using classical electromagnetic theory.The model of constant air gap control system with electromechanical actuator was established.The constant air gap control strategy and its influence on the vehicle's dynamics were studied by numerical simulation.Simulation result shows that the air gap change is mainly caused by the change of load when large-deflection primary suspension and LIM frame suspension are adopted, its frequency is very low, so the constant air gap control of LIM is easy to carry out.The control can guarantee that the vehicle meets the requirement of air gap under different load conditions, vertical wheel-rail interaction force reduces by about 10 kN, and the comfort index decreases by about 0.1.Moreover, the dynamics performance of the vehicle will be improved campared with traditional LIM vehicle, and its traction force is smoother.
-
Key words:
- metro vehicle /
- linear induction motor /
- constant air gap control /
- dynamics simulation
-
表 1 LIM主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of LIM
参数 数值 参数 数值 初级电压/V 1 100 极距/mm 192 频率/Hz 45 初级宽度/mm 250 初级电流/A 300 每极每相槽数 2 额定推力/kN 16 每相串联匝数 180 同步速度/(m·s-1) 17 次级铝板厚度/mm 6 相数 3 次级铁轭厚度/mm 28 极数 6 额定气隙/mm 10 表 2 气隙变化值比较
Table 2. Comparison of air gap change values
刚度方案 车速/(km·h-1) 气隙变化值/mm 工况1 工况2 工况3 工况4 减小 增大 减小 增大 减小 增大 减小 增大 1 40 -4.24 0.27 -3.37 0.97 -3.21 1.41 -6.38 1.18 60 -3.67 1.05 -3.40 1.19 -3.45 2.31 -4.94 2.16 80 -3.43 1.76 -3.39 1.50 -3.64 2.54 -4.75 2.38 100 -3.36 2.59 -3.35 1.72 -4.06 2.97 -4.37 3.27 2 40 -3.09 0.62 -2.84 1.28 -2.98 1.59 -4.76 1.53 60 -2.87 1.60 -2.86 1.40 -3.26 2.15 -4.16 2.36 80 -2.63 2.22 -2.89 1.62 -3.37 2.44 -3.44 2.70 100 -2.60 2.88 -2.89 1.83 -3.69 2.76 -3.54 3.35 3 40 -2.39 1.14 -2.59 1.42 -2.82 1.70 -3.84 2.02 60 -2.33 1.94 -2.61 1.53 -3.11 2.08 -3.56 2.50 80 -2.11 2.51 -2.60 1.64 -3.26 2.37 -2.96 2.91 100 -2.11 3.06 -2.58 1.67 -3.44 2.62 -3.03 3.40 4 40 -1.92 1.47 -2.45 1.52 -2.70 1.76 -3.24 2.32 60 -1.95 2.17 -2.46 1.60 -2.99 2.04 -3.11 2.64 80 -1.77 2.71 -2.44 1.67 -3.06 2.33 -2.65 3.05 100 -1.79 3.20 -2.47 1.74 -3.26 2.53 -2.68 3.45 5 40 -1.58 1.69 -2.37 1.58 -2.60 1.79 -2.81 2.52 60 -1.67 2.33 -2.37 1.64 -2.89 2.03 -2.77 2.76 80 -1.54 2.86 -2.35 1.65 -2.98 2.30 -2.40 3.16 100 -1.55 3.32 -2.39 1.77 -3.13 2.48 -2.41 3.50 表 3 车体平稳性指标比较
Table 3. Comparison of riding indexes of carbody
刚度方案 车速/(km·h-1) 工况1 工况2 工况3 工况4 横向 垂向 横向 垂向 横向 垂向 横向 垂向 1 40 1.52 1.59 1.65 1.67 1.56 1.60 1.52 1.61 60 1.94 1.89 1.96 1.97 1.97 1.91 1.94 1.89 80 2.27 2.09 2.27 2.21 2.30 2.13 2.27 2.09 100 2.57 2.29 2.57 2.38 2.63 2.33 2.57 2.29 2 40 1.53 1.58 1.66 1.66 1.57 1.60 1.53 1.59 60 1.94 1.90 1.96 1.96 1.97 1.91 1.94 1.89 80 2.26 2.11 2.27 2.20 2.30 2.14 2.26 2.10 100 2.56 2.31 2.54 2.41 2.62 2.34 2.56 2.30 3 40 1.55 1.57 1.66 1.66 1.60 1.61 1.55 1.58 60 1.93 1.90 1.96 1.95 1.97 1.91 1.93 1.89 80 2.26 2.11 2.27 2.19 2.29 2.14 2.26 2.11 100 2.56 2.31 2.53 2.42 2.62 2.35 2.56 2.31 4 40 1.56 1.57 1.67 1.65 1.60 1.60 1.56 1.57 60 1.93 1.91 1.96 1.95 1.96 1.90 1.93 1.89 80 2.25 2.11 2.23 2.17 2.29 2.14 2.25 2.11 100 2.55 2.32 2.52 2.41 2.61 2.35 2.56 2.32 5 40 1.56 1.57 1.67 1.65 1.61 1.60 1.56 1.58 60 1.93 1.91 1.96 1.95 1.96 1.90 1.93 1.89 80 2.25 2.11 2.21 2.18 2.29 2.14 2.25 2.11 100 2.55 2.32 2.54 2.41 2.61 2.35 2.55 2.32 -
[1] 姚保庆. 直线牵引电机的控制及电磁性能的研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2007.YAO Bao-qing. Study on control and electromagnetic performance of linear traction motor[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2007. (in Chinese) [2] 郭焕. 直线感应电机的直接推力控制与仿真[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007.GUO Huan. Direct thrust control and simulation of linear induction motor[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007. (in Chinese) [3] 刘彬彬, 曾京, 罗仁, 等. 直线感应电机车辆建模与动力学仿真[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2009, 9(5): 37-43, 61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC200905006.htmLIU Bin-bin, ZENG Jing, LUO Ren, et al. Modeling and dynamics simulation of vehicle with linear induction motor[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2009, 9(5): 37-43, 61. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC200905006.htm [4] 林俊. 采用独立车轮的直线电机轨道车辆动力学性能研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2006.LIN Jun. Research on the dynamics for LIM vehicle with independent wheel[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2006. (in Chinese) [5] 魏庆朝, 邓亚士, 冯雅薇. 电机悬挂方式对LIM地铁系统动力特性的影响研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2007(11): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC200711012.htmWEI Qing-chao, DENG Ya-shi, FENG Ya-wei. Study of suspension mode influences on LIM metro system dynamic characters[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2007(11): 59-64. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC200711012.htm [6] KIM D K, KWON B I I. A novel equivalent circuit model of linear induction motor based on finite element analysis andits coupling with external circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(10): 3407-3409. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.879078 [7] 李中秀. 中低速磁悬浮列车间隙传感器的研制[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2006.LI Zhong-xiu. Research of eddy current sensor of middle-low speed maglev train[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2006. (in Chinese) [8] 龙许友, 魏庆朝, 冯雅薇, 等. 轨道不平顺激励下直线电机车辆/轨道动力响应[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2008, 8(2): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC200802005.htmLONG Xu-you, WEI Qing-chao, FENG Ya-wei, et al. Dynamic response of linear metro vehicle/track exited by track irregularity[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2008, 8(2): 9-13. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC200802005.htm [9] FAIZ J, JAFARI H. Accurate modeling of single-sided linear induction motor considers end effect and equivalent thickness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2000, 36(5): 3785-3790. doi: 10.1109/20.908365 [10] MIRSALIM M, DOROUDI A, MOGHANI J S. Obtaining the operating characteristics of linear induction motors: a new approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2002, 38(2): 1365-1370. -





 下载:
下载: