Spacing calculation and selection on opposite vehicle access of large public building
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
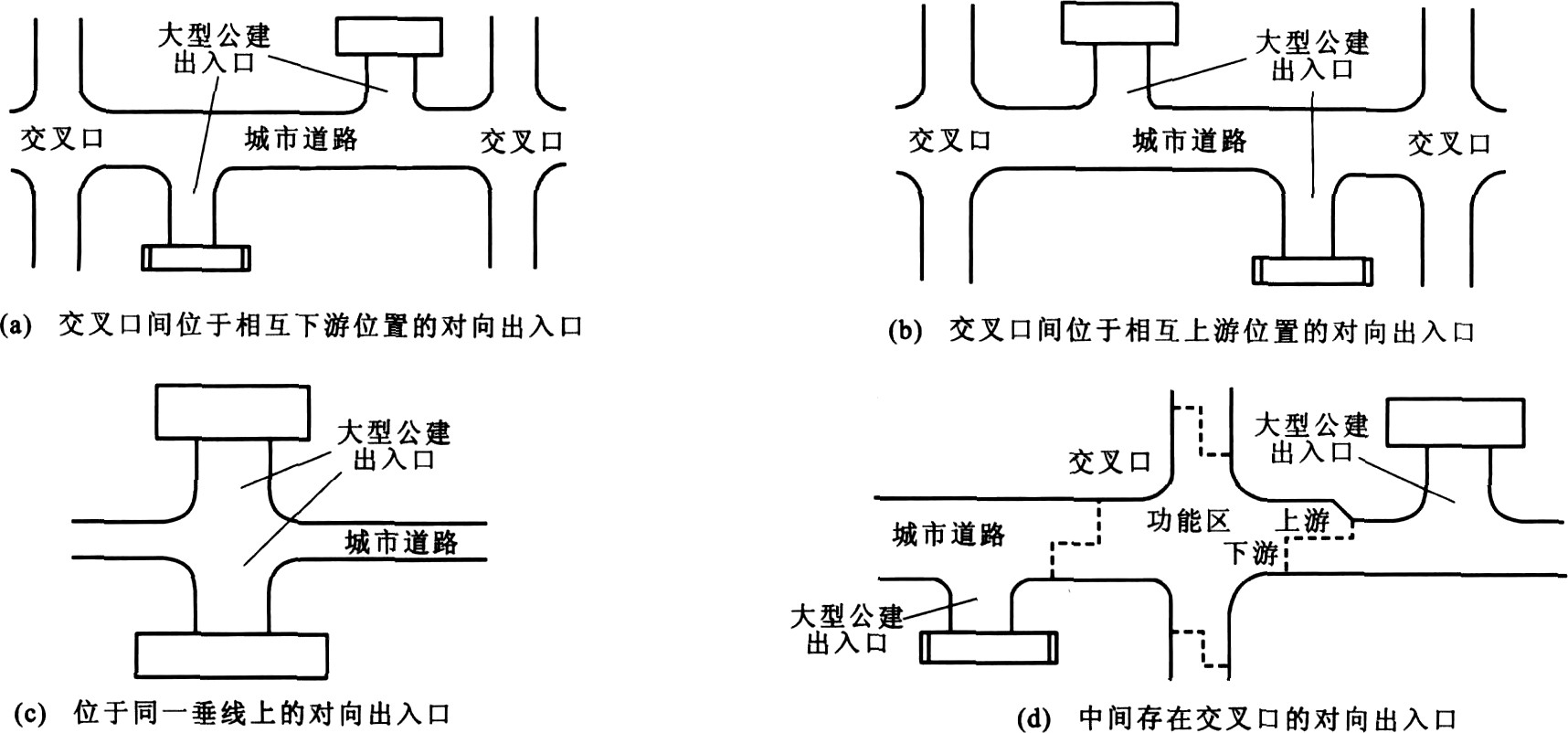
摘要: 为降低交通事故率, 参考出入口管理策略, 分析大型公建对向机动车出入口特征, 以消除间距不足引发的冲突点为优化目标, 根据微观交通流理论, 建立对向出入口最小间距模型, 给出避开交叉口功能区的最大间距, 构成间距范围。结合交通仿真与熵权法, 利用基于交通冲突技术的逼近理想解排序法, 对间距候选方案进行安全评价, 得出最优间距, 并以某大型公建区域为例进行计算及优选。计算结果表明: 该区域对向出入口间距范围为83.98~278.76 m, 最优间距为120.73 m, 对应最优解贴近度为0.5182, 间距值位于间距范围内时, 存在最大贴近度。Abstract: To reduce crash rate, the access management(AM)strategy was considered, and opposite vehicle access features of large public buildings were analyzed.A minimum opposite access spacing model was established based on microscopic traffic flow theory, and its optimization objective was to eliminate conflicts due to inadequate spacing.The maximum spacing was deduced to keep access from the functional area of intersections, and a spacing range was formed, traffic simulation and entropy weight method were utilized, and the technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution(TOPSIS)based on traffic conflict techniques was proposed to evaluate the spacing schemes and search the optimal spacing from several spacing values.A large public building area was taken as an example for spacing calculation and selection.Calculation result indicates that the range of opposite access spacing is 83.98~278.76 m, its optimum spacing is 120.73 m, and the closeness degree of optimal solution is 0.518 2.When spacing value is in the range, there is a miximum value of closeness degree.
-
Key words:
- traffic planning /
- access spacing /
- access management /
- traffic conflict technique /
- TOPSIS /
- large public building
-
表 1 对向出入口最小间距
Table 1. Minimum spacings of opposite-side access
W/m V/(km·h-1) ain/(m·s-2) aout/(m·s-2) Ldx/m 6.0 20 0.6 0.8 36.46 7.0 30 1.2 1.4 43.44 7.5 40 1.8 2.0 54.06 8.0 50 2.4 2.6 65.41 8.0 60 3.0 3.2 77.82 -
[1] Committee on Access Management. Access management manual[R]. Washington DC: TRB, 2003. [2] Center for Transportation Research and Education. Access management handbook[R]. Ames: Iowa State University, 2000. [3] GLUCK J, LEVINSON H S, STOVER V. Impacts of access management techniques (NCHRP Report 420)[R]. Washington DC: National Academy Press, 1999. [4] ZHANG Ning, QI ANZhen-dong, ZHUO Xi, et al. Analysis of traffic featuresin vehicle access roads tolarge public build-ings in the urban area[C]//University of Pretoria. Proceedings of the26th Southern African Transport Conference. Pretoria: Document Transformation Technologies CC, 2007: 785-793. [5] 陈峻, 王炜, 黄艳君. 城市客运场站交通影响分析及设计[J]. 中国公路学报, 2004, 17(2): 78-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200402017.htmCHEN Jun, WANG Wei, HUANG Yan-jun. Traffic impact analysis and design for urban passenger stations[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2004, 17(2): 78-81. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200402017.htm [6] 刘庆涛. 大型客运枢纽对城市交通的影响分析[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2008.LIU Qing-tao. Urban traffic impact analysis of large passenger transport hinge[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2008. (in Chinese) [7] 任其亮, 彭其渊. 大型建筑周围路网交通影响度的敏感性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2006, 41(5): 663-668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2006.05.024REN Qi-liang, PENG Qi-yuan. Sensitivity analysis of traffic impact of large buildings on traffic of road network[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2006, 41(5): 663-668. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2006.05.024 [8] GB 50220—95, 城市道路交通规划设计规范[S].GB 50220—95, code for transport planning on urban road[S]. (in Chinese) [9] 张宁, 陈恺, 黄卫. 公路出入口管理策略研究综述[J]. 公路, 2006(6): 28-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL200606005.htmZHANG Ning, CHEN Kai, HUANG Wei. Summary of researches on access management of highway[J]. Highway, 2006(6): 28-33. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL200606005.htm [10] 张宁, 陈恺, 高朝晖, 等. 基于微观仿真的远引掉头选址规划方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2008, 8(1): 78-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2008.01.016ZHANG Ning, CHEN Kai, GAO Zhao-hui, et al. Site planning method of u-turn followed by right-turn based on microsimulation[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2008, 8(1): 78-82. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2008.01.016 [11] 卓曦. 大型公共建筑机动车出入口布局及交通组织研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2006.ZHUO Xi. Research on layout and traffic organization of vehicle access of large public buildings[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2006. (in Chinese) [12] 郑海鳌, 陈智民, 尤建新. 基于仿真技术的连锁零售企业配送中心布局决策模型[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2009, 29(5): 17-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL200905005.htmZHENG Hai-ao, CHEN Zhi-min, YOU Jian-xin. Decision-making model of distribution centers location based on simulation-tool for chain retail enterprises[J]. Systems Engineering—Theory and Practice, 2009, 29(5): 17-26. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL200905005.htm [13] 张宁, 陈恺, 何铁军, 等. 远引掉头方式下中央分隔带开口间距[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 29(1): 78-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200901018.htmZHANG Ning, CHEN Kai, HE Tie-jun, et al. Median opening space under the condition of indirect left turn[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 29(1): 78-82. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200901018.htm [14] 杨玉中, 吴立云, 丛建春. 基于熵权的煤矿运输安全性模糊综合评价[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2009, 41(4): 257-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200904060.htmYANG Yu-zhong, WU Li-yun, CONG Jian-chun. Fuzzy synthetic evaluation on safety of coalmine transportation systems based on entropy weight[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009, 41(4): 257-259. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200904060.htm -





 下载:
下载: