Multi-objective optimization model and ant colony optimization of liner ship scheduling
-
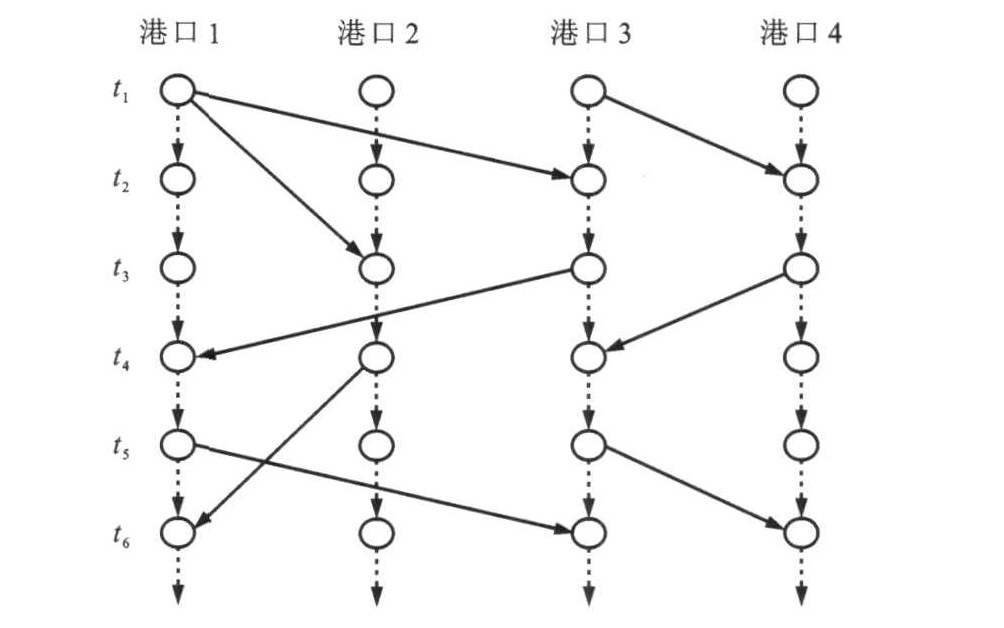
摘要: 针对班轮船舶调度问题, 在将班轮合理配置到各往返航班上和不存在时间冲突的基础上, 以最小班轮变动成本、最小航线运载量缺口和最小班轮航次总绝对偏差为目标函数, 构造了基于港口时段与往返航班的时空网络, 建立了班轮调度的0-1整数规划数学模型。基于某船务公司实际运载数据, 利用蚁群算法求解模型, 并用邻域搜索技术提高求解效率。计算结果表明: 在运载量满足运营要求的前提下, 班轮运营的日均总变动成本从198 086.3元降低到170 472.2元, 下降了约13.9%;班轮航次数总绝对偏差从4.4次降低到2.4次, 下降了约45.5%, 班轮利用率更加均衡; 运载量缺口仍旧为0。可见, 模型可行, 算法有效。Abstract: Aiming at liner ship scheduling problem, on the basis of rational allocation for liner ships to different round trips and non-existing time conflict, the minimum variation cost on liner ship, the minimum carrying amount notch on route and the absolute minimum deviation of total liner voyages were taken as objective functions, a time-space network was constructed based on port periods and round liners, and a 0-1 integer programming mathematical model was established. The historical data of a certain liner shipping company were analyzed, ant colony optimization was used to solve the model, and a neighborhood search technique was integrated to raise the efficiency. Calculation result shows that while the carrying amount can meet the running requirement, the daily liner variation cost of liner running decreases from 198 086.3 yuan to 170 472.2 yuan, and decreases by about 13.9%. The absolute deviation of total liner voyages decreases from 4.4 times to 2.2 times, and decreases by about 45. 5%, and liner utilization ratio is more equilibrium. Obviously, the proposed model is feasible, and the algorithm is effective.
-
表 1 原有班轮调度方案
Table 1. Original liner scheduling scheme
航线编号 往返航班编号 班轮编号 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 3 1 4 1 1 5 1 1 6 1 2 7 1 2 8 4 2 9 2 2 10 2 2 11 2 2 12 2 3 13 3 3 14 3 3 15 4 3 16 4 3 17 3 3 18 4 3 19 4 4 20 5 4 21 5 4 22 5 表 2 优化后班轮调度方案
Table 2. Optimized liner scheduling scheme
航线编号 往返航班编号 班轮编号 1 1 4 1 2 1 1 3 1 1 4 1 1 5 4 1 6 1 2 7 2 2 8 3 2 9 3 2 10 2 2 11 3 2 12 3 3 13 5 3 14 5 3 15 2 3 16 5 3 17 5 3 18 2 3 19 2 4 20 4 4 21 4 4 22 4 表 3 调度方案对比
Table 3. Comparison of scheduling schemes
班轮编号 原有方案航班次数 优化后方案航班次数 1 6 4 2 4 5 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 3 4 -
[1] CHRISTIANSEN M, FAGERHOLT K, RONEN D. Ship routing and scheduling: status and perspectives[J]. Transportation Science, 2004, 38(1): 1-18. doi: 10.1287/trsc.1030.0036 [2] DANIEL A. Routing andscheduling with time windows: models and algorithms for tramp sea cargos and rail carblocks[D]. Atlanta: Georgia Institute of Technology, 2006. [3] 杨秋平, 谢新连, 赵家保. 船队规划研究现状与动态[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2010, 10(4): 85-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2010.04.014YANG Qiu-ping, XIE Xin-lian, ZHAO Jia-bao. Research status and prospect of fleet planning[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2010, 10(4): 85-90. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2010.04.014 [4] TING S C, TZENG G H. Ship scheduling and cost analy sis for route planningin liner shipping[J]. Maritime Economics and Logistics, 2003, 5(4): 378-392. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.mel.9100087 [5] AGARWAL R, ERGUN Ö. Ship scheduling and network design for cargo routing in liner shipping[J]. Transportation Science, 2008, 42(2): 175-196. doi: 10.1287/trsc.1070.0205 [6] YAN Shang-yao, CHEN C Y, LINS C. Ship scheduling and container shipment planning for liners in short-term operations[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2009, 14(4): 417-435. doi: 10.1007/s00773-009-0059-0 [7] DORIGO M, DICARO G, GAMBARDELLA L M. Ant algorithms for discrete optimization[J]. Artificial Life, 1999, 5(2): 137-172. doi: 10.1162/106454699568728 [8] CHIRA C, PINTEA C M, DUMITRESCU D. An agentbased approach to combinatorial opti mization[J]. International Journal of Computers, Communications and Control, 2008, 3(S): 212-217. [9] DORIGO M, BLUM C. Ant colony optimization theory: a survey[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2005, 344(2/3): 243-278. [10] 崔小燕, 李旭宏, 毛海军, 等. 受限单分配枢纽选址问题的并行蚁群算法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2011, 11(3): 74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2011.03.013CUI Xiao-yan, LI Xu-hong, MAO Hai-jun, et al. Parallel ant colony optimization of location problemfor limited single allocation hub[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2011, 11(3): 74-81. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2011.03.013 [11] KOLISCH R, DREXL A. Local search for nonpreem ptive multi-mode resource-constrained project scheduling[J]. IIE Transactions, 1997, 29(11): 987-999. [12] ANGUS D, WOODWARD C. Multiple objective ant colony optimization[J]. Swarm Intelligence, 2009, 3(1): 69-85. [13] 冀俊忠, 黄振, 刘椿年, 等. 基于多粒度的旅行商问题描述及其蚁群优化算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2010, 47(3): 434-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201003009.htmJI Jun-zhong, HUANG Zhen, LIU Chun-nian, et al. An ant colony algorithm based on multiple grain representation for the traveling salesman problems[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2010, 47(3): 434-444. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201003009.htm [14] 李琳, 刘士新, 唐加福. 改进的蚁群算法求解带时间窗的车辆路径问题[J]. 控制与决策, 2010, 25(9): 1379-1383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201009021.htmLI Lin, LIU Shi-xin, TANG Jia-fu. I mproved ant colony algorithm for solving vehicle routing problem with time windows[J]. Control and Decision, 2010, 25(9): 1379-1383. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201009021.htm [15] 李志威, 张旭梅. 基于动态扫描和蚂蚁算法的物流配送网络优化研究[J]. 管理工程学报, 2006, 20(4): 9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6062.2006.04.002LI Zhi-wei, ZHANG Xu-mei. Study on the optimization of logistics distribution network based on dynamic sweep and ant algorithm[J]. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, 2006, 20(4): 9-12. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6062.2006.04.002 -





 下载:
下载: