Inductive benefit simulation algorithm of VMS travel time
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
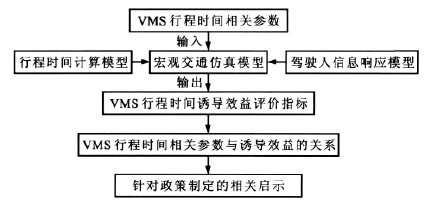
摘要: 基于宏观交通仿真模型, 提出了可变情报板(VMS)行程时间诱导效益仿真算法, 分析了驾驶人的信息关注率和信息理解偏差系数对VMS行程时间诱导效益的影响。以行程时间计算模型和驾驶人信息响应模型与METANET仿真模型为理论基础, 以路网总耗时改善率为诱导效益目标, 在3种不同规模的路网上进行仿真试验。仿真结果表明: VMS行程时间对于改善路网运行效率通常具有正面的诱导效益; 信息关注率越高, 信息理解偏差系数越小, 诱导效益越显著; 当信息关注率为80%以上时, 小型、中型、大型3种路网的诱导效益分别达到28.89%、15.87%、10.53%以上。可见, 仿真算法有效。Abstract: Based on macroscopic traffic simulation model, the inductive benefit simulation method of variable message sign(VMS) travel time was proposed, and the influences of information concern ratio and information comprehension deviation coefficients for drivers on the inductive benefit of VMS travel time were analyzed. The travel time calculation model, driver information response model and METANET simulation model were taken as theory foundations, the improving ratio of total road network consuming time was taken as inductive benefit objective, and simulation tests on three road networks with different sizes were carried out. Simulation result shows that VMS travel time normally has positive inductive benefit on improving the running efficiency of road network. The higher the information concern ratio is, the smaller the information comprehension deviation coefficient is, and the more significant the inductive benefit is. While information concern ratio is over 80G, the inductive benefits of small, medium and large road networks are above 28. 89%, 15. 87% and 10. 53% respectively. So the simulation algorithm is effective.
-
表 1 路网尺寸
Table 1. Road network sizes

-
[1] RICHARDS A, MCDONALD M. Questionnaire surveys to evaluate user response to variable message signs in an urban network[J]. Intelligent Transport Systems, 2007, 1 (3): 177-185. doi: 10.1049/iet-its:20060046 [2] ERKE A, SAGBERG F, HAGMAN R. Effects of route guidance variable message signs (VMS) on driver behaviour[J]. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2007, 10 (6): 447-457. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2007.03.003 [3] 干宏程. VMS诱导信息影响下的路径选择行为分析[J]. 系统工程, 2008, 26 (3): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4098.2008.03.003GAN Hong-cheng. Exploring drivers'route choice response to real-time guidance information of variable message signs[J]. Systems Engineering, 2008, 26 (3): 11-16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4098.2008.03.003 [4] 干宏程, 孙立军, 陈建阳. 提供交通信息条件下的途中改道行为研究[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 34 (11): 1484-1488. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.11.013GAN Hong-cheng, SUN Li-jun, CHEN Jian-yang. Study on traveler behavior under influence of advanced traveler information system[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2006, 34 (11): 1484-1488. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.11.013 [5] 魏赟, 范炳全, 韩印, 等. 交通诱导信息对路网中车辆行为的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2009, 9 (6): 114-120, 126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2009.06.022WEI Yun, FAN Bing-quan, HAN Yin, et al. Impact of traffic guidance information on vehicle behavior in network[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2009, 9 (6): 114-120, 126. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2009.06.022 [6] 吴文祥, 黄海军. 平行路径网络中信息对交通行为的影响研究[J]. 管理科学学报, 2003, 6 (2): 12-16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9807.2003.02.002WU Wen-xiang, HUANG Hai-jun. Study on behavior impacts caused by travel information systems in parallel route[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China, 2003, 6 (2): 12-16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9807.2003.02.002 [7] 安实, 李静, 崔建勋. 面向多智能体的出行前信息下通勤者出行行为研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2009, 22 (3): 95-100. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.03.017AN Shi, LI Jing, CUI Jian-xun. Research on commuter's travel behavior faced to multi-agent under pre-trip information[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2009, 22 (3): 95-100. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.03.017 [8] 石小法, 王炜, 李文权. 交通信息对交通网络的影响研究[J]. 系统工程学报, 2001, 16 (3): 167-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2001.03.002SHI Xiao-fa, WANG Wei, LI Wen-quan. Information effects in transportation network[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2001, 16 (3): 167-171. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5781.2001.03.002 [9] MAMMAR S, MESSMER A, JENSEN P, et al. Automatic control of variable message signs in AALBORG[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 1996, 4 (3): 131-150. doi: 10.1016/S0968-090X(96)00005-8 [10] 孟超, 邵春福, 李玮, 等. VMS对驾驶人路径选择行为影响的仿真研究[J]. 城市交通, 2009, 7 (1): 76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5328.2009.01.020MENG Chao, SHAO Chun-fu, LI Wei, et al. Impact simulation of VMSs on driver's route selection behaviors[J]. Urban Transport of China, 2009, 7 (1): 76-81. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5328.2009.01.020 [11] 杨晓光, 伍速锋, 云美萍. 日常出行中的交通信息有效性仿真研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2007, 43 (4): 12-15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.04.005YANG Xiao-guang, WU Su-feng, YUN Mei-ping. Validity analysis of traffic information on day-to-day travel by simulating[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2007, 43 (4): 12-15. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.04.005 [12] 杨珍珍, 干宏程. 面向大型社会活动的快速路网控制策略仿真评价方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2010, 27 (12): 4473-4475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201012024.htmYANG Zhen-zhen, GAN Hong-cheng. Large social event oriented freeway network control strategy simulation evaluation approach[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2010, 27 (12): 4473-4475. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201012024.htm [13] 尚华艳, 黄海军, 高自由. 基于元胞传输模型的可变信息标准选址问题研究[J]. 物理学报, 2007, 56 (8): 4342-4347. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2007.08.006SHANG Hua-yan, HUANG Hai-jun, GAO Zi-you. Locating the variable message signs by cell transmission model[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2007, 56 (8): 4342-4347. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2007.08.006 [14] GAN Hong-cheng, SUN Li-jun, CHEN Jian-yang, et al. Advanced traveler information system for metropolitan expressways in Shanghai, China[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2006 (1944): 35-40. [15] GAN Hong-cheng. Graphical route information panel for the urban freeway network in Shanghai, China[J]. Intelligent Transport Systems, 2010, 4 (3): 212-220. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2010.0017 [16] KOTSIALOS A, PAPAGEORGIOU M, MANGEAS M, et al. Coordinated and integrated control of motorway networks via non-linear optimal control[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2002, 10 (1): 65-84. doi: 10.1016/S0968-090X(01)00005-5 -





 下载:
下载: