Bi-level programming model of timing optimization for multiple bus priority intersection
-
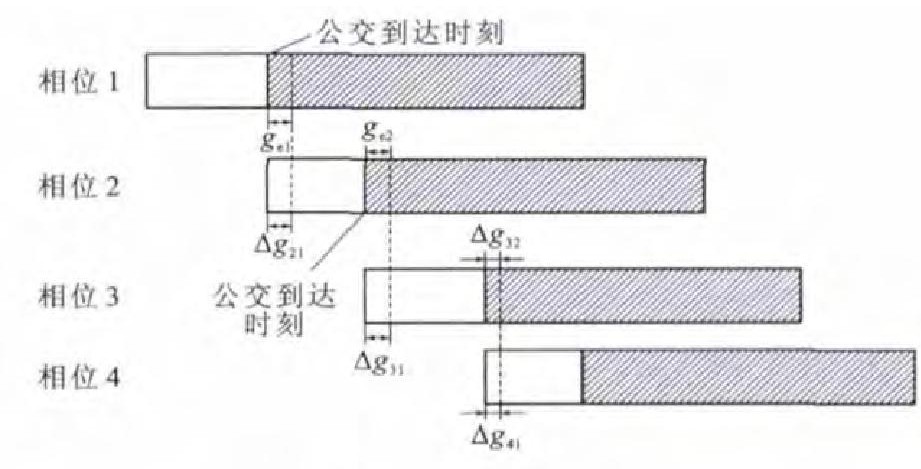
摘要: 公交优先感应信号控制会对非优先相位车辆产生不利影响, 为了均衡非优先相位的损失, 降低交叉口及下游公交站台的乘客延误, 建立了多路公交优先交叉口配时优化的双层规划模型。上层模型描述了基于交叉口延误以及下游公交站台乘客排队延误的优先策略时长优化, 下层模型在计算交叉口停驶-加速延误的基础上描述了各相位绿时损失的均衡过程, 以优先策略时长为决策变量, 将优先策略的影响引入到下层模型。利用Gauss-Seidel迭代法设计了求解算法, 并进行了实例分析。分析结果表明: 配时优化后, 周期内交叉口和下游站台乘客的总延误减少了23 576.12s, 同时交叉口车辆停驶-加速延误减少了62.87s, 双层规划模型在公交优先的前提下保障了交叉口的整体效益。Abstract: Induction signal control based on bus priority had negative effects on vehicles in nonpriority phases. In order to equilibrate the loss of non-priority phases, as well as to reduce the passenger delay at the intersection and the downstream stations, a bi-level programming model of signal timing optimization for multiple bus priority intersection was proposed. In the upper model, priority strategies were optimized based on the intersection delay and the passenger queuing delay at downstream stations. In the lower model, the equilibrium process of green loss was described based on the calculation of acceleration-deceleration delay at the intersection. With priority strategies as decision-making variables, the influence of priority strategies was introduced to the lower model. The solution algorithm was designed by using the Gauss-Seidel iterative method. An application example was analyzed. Analysis result indicates that after signal timing optimization, total passenger delays at the intersection and downstream stations in the period reduces by 23 576.12 s. Besides, the vehicle acceleration-deceleration delay at the intersection reduces by 62.87s. Bi-level programming model ensures the overall efficiency at the intersection under consideration of bus priority.
-
表 1 交叉口交通流数据与控制参数
Table 1. Traffic flow data and control parameters of intersection

表 2 优化模型计算结果
Table 2. Calculation result of optimal model

-
[1] WU Jian-ping, HOUNSELL N. Bus priority using presignals[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 1998, 32 (8): 563-583. doi: 10.1016/S0965-8564(98)00008-1 [2] 马万经, 杨晓光. 单点公交优先感应控制策略效益分析与仿真验证[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2008, 20 (12): 3309-3313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200812062.htmMA Wan-jing, YANG Xiao-guang. Efficiency analysis of transit signal priority strategies on isolated intersection[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2008, 20 (12): 3309-3313. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200812062.htm [3] WAHLSTEDT J. Impacts of bus priority in coordinated traffic signals[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2011, 16: 578-587. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.04.478 [4] LIU Hong-chao, ZHANG Jie, CHENG Ding-xin. Analytical approach to evaluating transit signal priority[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2008, 8 (2): 48-57. doi: 10.1016/S1570-6672(08)60017-3 [5] ZHOU Guang-wei, GAN A, SHEN L D. Optimization of adaptive transit signal priority using parallel genetic algorithm[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2007, 12 (2): 131-140. doi: 10.1016/S1007-0214(07)70020-2 [6] 李劲夫. 公交优先交叉口信号控制参数的多目标优化方法[J]. 长沙大学学报, 2012, 26 (2): 64-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDX201202025.htmLI Jin-fu. Multi-objective optimization method of intersection signal control parameter based on bus priority[J]. Journal of Changsha University, 2012, 26 (2): 64-68. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDX201202025.htm [7] 李淑庆, 李哲, 朱文英. 一体化公交网络均衡配流模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2013, 13 (1): 62-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2013.01.010LI Shu-qing, LI Zhe, ZHU Wen-ying. Equilibrium assignment model of integrated transit network[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2013, 13 (1): 62-69. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2013.01.010 [8] KIM S, PARK M, CHON K S. Bus signal priority strategies for multi-directional bus routes[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2012, 16 (5): 855-861. doi: 10.1007/s12205-012-1507-7 [9] 柏海舰, 董瑞娟, 张敏, 等. 基于同步多样性的公交时刻优化方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2013, 13 (3): 79-85. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201303011BAI Hai-jian, DONG Rui-juan, ZHANG Min, et al. Optimization method of bus time based on synchronization diversity[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2013, 13 (3): 79-85. (in Chinese). http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201303011 [10] MA Wan-jing, LIU Yue, YANG Xiao-guang. A dynamic programming approach for optimal signal priority control upon multiple high-frequency bus requests[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems: Technology, Planning, and Operations, 2013, 17 (4): 282-293. doi: 10.1080/15472450.2012.729380 [11] MA Wan-jing, LIU Yue, YANG Xiao-guang. A dynamic programming model for bus signal priority with multiple requests[C]∥TRB. Transportation Research Board 90th Annual Meeting. Washington DC: TRB, 2011: 2851-2866. [12] 孙煦, 陆化普. 公交优先下交叉口配时优化的双层模型与遗传算法[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2012, 38 (6): 859-864. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201206011.htmSUN Xu, LU Hua-pu. Bi-level optimization model of intersection timing about bus priority condition based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2012, 38 (6): 859-864. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201206011.htm [13] HE Qing, HEAD K L, DING Jun. Heuristic algorithm for priority traffic signal control[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2011 (2259): 1-7. [14] 张卫华, 石琴, 刘强. 公交优先信号交叉口延误计算与配时优化方法[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 城市科学版, 2004, 21 (4): 30-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCJ200404009.htmZHANG Wei-hua, SHI Qin, LIU Qiang. Study of vehicle delay calculation and optimal signal-planning method for intersections with induced signal based on bus priority[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Urban Science Edition, 2004, 21 (4): 30-33. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCJ200404009.htm [15] YANG Hai, ZHANG Xiao-ning, MENG Qiang. Stackelberg games and multiple equilibrium behaviors on networks[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2007, 41 (8): 841-861. [16] ALLEVI E, GNUDI A, KONNOV I V, et al. Gauss-Seidel method for multi-valued inclusions with Z mappings[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 2012, 53 (1): 97-105. -





 下载:
下载: