Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of traffic accident for highway vehicle queue tail
-
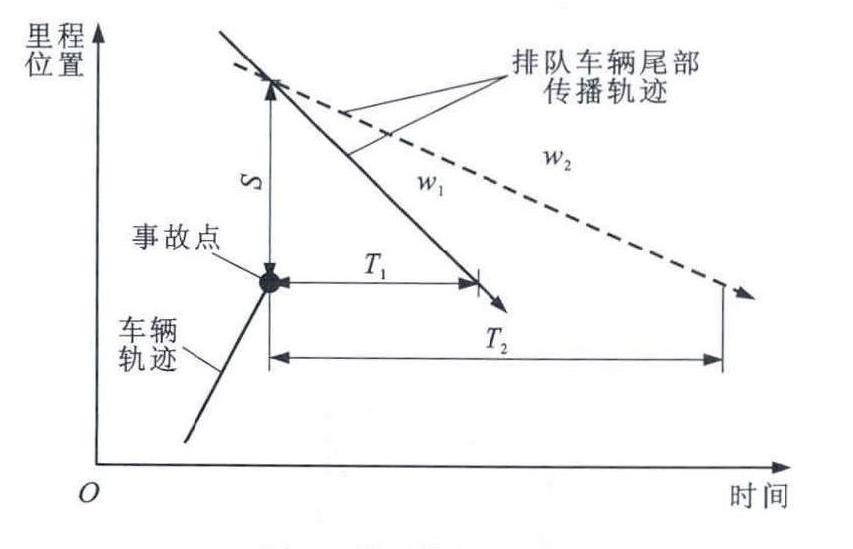
摘要: 根据高速公路常发拥堵路段的交通流数据, 采用累计占有率法绘制交通流占有率波动曲线, 用来判断拥堵路段内车辆排队尾部轨迹, 分析了占有率、里程位置、时间间隔的关系, 确定了累计占有率曲线的拐点。分析了排队传播、消散过程中交通事故频数与时间、空间距离的关系, 对分布特征进行了统计分析。分析结果表明: 车辆在时间和空间上接近排队车辆尾部时, 发生交通事故的频数明显增加, 时间距离与空间距离以排队尾部为中心呈现正态分布, 不同行驶方向路段内正态分布曲线不存在显著差异, 但拥堵传播与消散过程的正态分布曲线存在显著差异。建立的事故发生概率的联合正态分布模型, 可用于预测排队车辆尾部附近的交通事故风险, 为实施动态交通控制以提高快速道路交通安全提供理论依据。Abstract: Based on the traffic flow data of recurrent congestion section on highway, the cumulative occupancy method was used to draw the fluctuating curve of traffic flow occupancy, which was used to judge the trajectory of vehicle queue tail at congestion section.The relations among occupancy, mileage position and time interval were analyzed.The inflection point of cumulative occupancy curve was determined.For the queue propagating and dissipating processes, the relations between traffic accident frequencies and temporal and sptial distances were analyzed, and the distribution features were statistically studied.Analysis result shows that when vehicle temporally and spatially approaches the queue tail, the occurrence frequency of traffic accident obviously increases, and the temporal distance and spatial distance follow the normal distribution centered on the queue tail.Normal distribution curves in different driving directions have no significant differences, but have significant differences between congestion propagation and dissipation processes.The developed joint normal distribution model of traffic accident occurring probability can be used to predict the traffic accident risks in the vicinity of queue tail, and to provide the theoretical foundation for applying dynamic traffic control for improving highway safety.
-
Key words:
- traffic safety /
- highway /
- traffic accident /
- queue tail /
- spatial and temporal distribution
-
表 1 K-S单样本检验结果
Table 1. One-sample K-S test results

表 2 K-S双样本检验结果
Table 2. Two-sample K-S test results

-
[1] ABDEL-ATY M, UDDIN N, PANDE A, et al. Predicting freeway crashes from loop detector data by matched case-control logistic regression[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2004(1897): 88-95. [2] ABDEL-ATY M, UDDIN N, PANDE A. Split models for predicting multivehicle crashes during high-speed and lowspeed operating conditions on freeways[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2005(1908): 51-58. [3] PANDE A, ABDEL-ATY M. Comprehensive analysis of the relationship between real-time traffic surveillance data and rear-end crashes on freeways[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2006(1953): 31-40. [4] HOSSAIN M, MUROMACHI Y. Understanding crash mechanisms and selecting interventions to mitigate real-time hazards on urban expressways[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2011(2213): 53-62. [5] XU Cheng-cheng, WANG Wei, LIU Pan. A genetic programming model for real-time crash prediction on freeways[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2). 574-586. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2226240 [6] ZHENG Z D, AHN S, MONSERE C M. Impact of traffic oscillations on freeway crash occurrences[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2010, 42(2): 626-636. [7] CHUNGK, JANG K, OUM S, et al. Investigation of attributesof kinematic waves preceding traffic collisions[C]//TRB. The90th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board. Washington DC. TRB, 2011.28-39. [8] YEO H, JANG K, SKABARDONIS A. Impact of trafficstates on freeway collision frequency[C]//TRB. The 89thAnnual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board. Washington DC: TRB, 2010: 13-27. [9] XU Cheng-cheng, LIU Pan, WANG Wei, et al. Evaluationof the impacts of traffic states on crash risks on freeways[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2012, 47(1): 162-171. [10] LI Zhi-bin, AHN S, CHUNG K, et al. Surrogate safetymeasure for evaluating rear-end collision risk related to kine-matic waves near freeway recurrent bottlenecks[J]. AccidentAnalysis and Prevention, 2014, 64(4): 52-61. [11] LI Zhi-bin, WANG Wei, CHEN Ruo-yun, et al. Evaluationof the impacts of speed variation on freeway traffic collisionsin various traffic states[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2013, 14(8〉. 861-866. [12] CASSIDYM J, BERTINI R L. Some traffic features of free-way bottlenecks[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Meth-odological, 1999, 33(1): 25-42. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(98)00023-X [13] CHUNG K, RUDJANAKANOKNAD J, CASSIDY M J. Relation between traffic density and capacity drop at three freeway bottlenecks[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2007, 41(1): 82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2006.02.011 [14] SMIRNOVN V. Tables for estimating the goodness of fit of empirical distributions[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1948, 19(2): 279-281. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177730256 [15] JUSTEL A, PENA D, ZAMAR R. A multivariate Kolmogorov-Smirnov test of goodness of fit[J]. Statistics and Probability Letters, 1997, 35(3): 251-259. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7152(97)00020-5 [16] CARLSON R C, PAPAMICHAIL I, PAPAGEORGIOU M, et al. Optimal mainstream traffic flow control of large-scale motorway networks[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2010, 18(2): 193-212. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2009.05.014 [17] WANG Yi-bin, PAPAGEORGIOU M, SARROS G, et al. Feedback route guidance applied to a large-scale express ring road[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2006(1965): 79-88. [18] LI Zhi-bin, LIU Pan, WANG Wei, et al. Development of a control strategy of variable speed limits to reduce rear-end collision risks near freeway recurrent bottlenecks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(2): 866-877. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2293199 [19] WU Yi-hu, YU Dan, YU Wei, et al. Double-layer ramp-metering model for incident congestion on expressway[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering: English Edition, 2014, 1(2): 129-137. doi: 10.1016/S2095-7564(15)30097-0 -





 下载:
下载: