Effects of spallation on rail thermo-elasto-plasticity in wheel-rail sliding contact
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
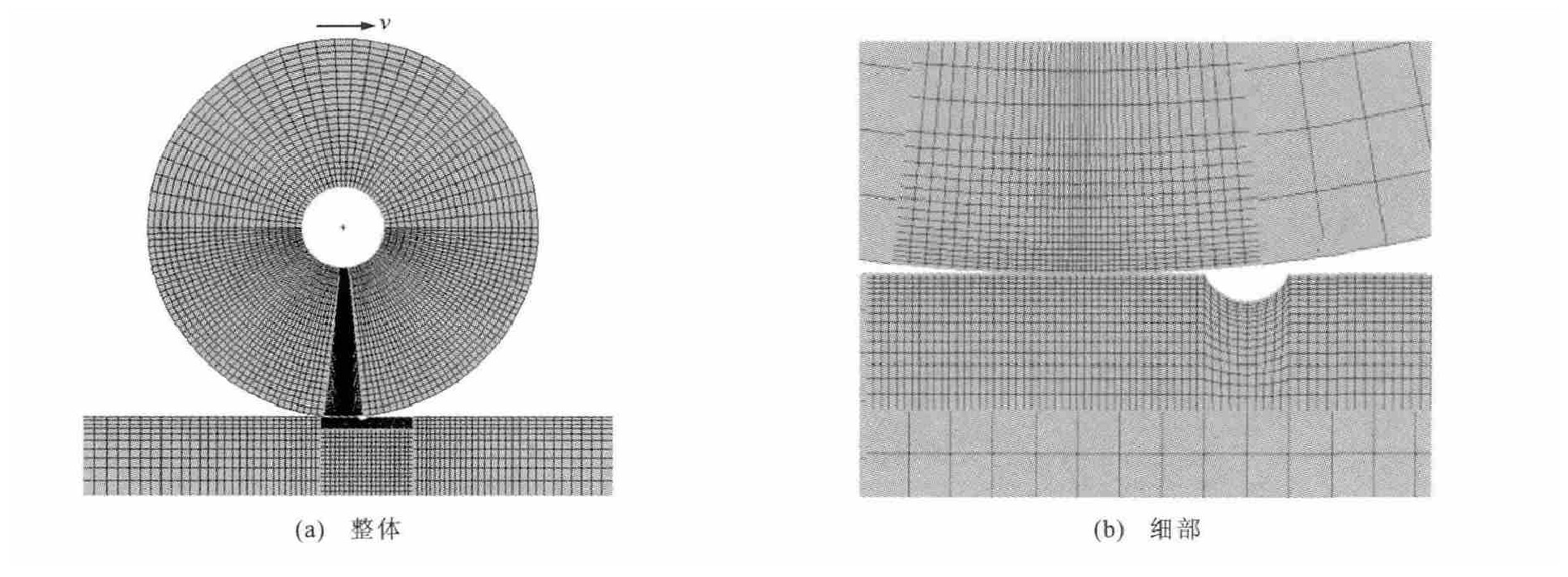
摘要: 利用有限元软件ANSYS建立了钢轨轨面剥离掉块伤损条件下的轮轨滑动接触有限元模型, 考虑了轮轨材料的非线性影响, 计算了车轮经过剥离掉块凹坑时的轮轨接触冲击行为, 并采用瞬态分析方法研究了不同剥离掉块伤损长度、深度、摩擦因数与轮轨间相对滑动速度对钢轨剥离掉块伤损区域热弹塑性的影响。分析结果表明: 在剥离掉块伤损区域长度为2 cm、深度为4 mm时, 钢轨等效塑性应变最大, 且伤损区域后侧的值为前侧的3~4倍; 在剥离掉块伤损区域长度为2 cm、深度为6 mm时, 塑性变形最大, 且伤损区域后侧的值约为前侧的2倍; 轮轨接触应力随摩擦因数的增大而减小, 钢轨的摩擦温升、等效塑性应变、塑性变形、等效应力与纵向剪切应力均随随摩擦因数的增大而增大, 当摩擦因数大于0.3时, 等效应力和纵向剪切应力的增长速率变缓; 当相对滑动速度等于3 m·s-1或大于等于6 m·s-1时, 钢轨的受力、变形和温升最不利。Abstract: A finite element model with rail spallations in wheel-rail sliding contact was established by using the finite element software ANSYS, the material nonlinearity was considered, the impact behaviors of wheel-rail contact were calculated when the wheels passed through the rail spallations, and the influences of length and depth of rail spalling area, friction coefficient and sliding speed on the thermo-elasto-plasticity of rail spalling area were analyzed by transient analysis.Analysis result shows when the length of spalling area is 2 cm and the depth is 4 mm, the equivalent plastic strain of rail reaches to the maximum, and the value in the rear of spalling area is 3-4 times as large as the value in the front.When the length of spalling area is 2 cm and the depth is 6 mm, the plastic deformation reaches to the maximum, and the value in the rear is about twice as large as the value in the front.The contact stress reduces with the increase of friction coefficient, while the frictional rising temperature, equivalent plastic strain, plastic deformation, equivalent stress and longitudinal shear stress of rail increase.When the friction coefficient is bigger than 0.3, the growth of equivalent stress and longitudinal shear stress becomes slower as the increase of fraction coefficient.When the sliding speed is equal to 3 m·s-1, or is not less than 6 m·s-1, the stress, deformation and temperature of rail are in most unfavorable conditions.
-
表 1 材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters

-
[1] 王志平. 重载快速大运量区段P60钢轨鱼鳞伤和剥离掉块的研究[J]. 华东交通大学学报, 2005, 22(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0523.2005.04.001WANG Zhi-ping. Research of the 60 kg/m rail corner fine cracks and shelling defects on heavy-haul and fast speed railway[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2005, 22(4): 1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0523.2005.04.001 [2] DOIH, MIYAMOTO T, NISHIYAMA Y, et al. A new experimental device to investigate creep forces between wheel and rail[J]. Wear, 2011, 274(1/2): 40-46. [3] SICHANI M S, ENBLOM R, BERG M. A novel method to model wheel-rail normal contact in vehicle dynamics simulation[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2014, 52(12): 1752-1764. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2014.961932 [4] BIAN Jian, GU Yuan-tong, MURRAY M H. A dynamic wheel-rail impact analysis of railway track under wheel flat by finite element analysis[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2013, 51(6): 784-797. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2013.774031 [5] ZHU Yi, OLOFSSON U, SÖDERBERG A. Adhesion modeling in the wheel-rail contact under dry and lubricated conditions using measured 3D surfaces[J]. Tribology International, 2013, 61: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2012.11.022 [6] WEI Lai, ZENG Jing, WU Ping-bo, et al. Indirect method for wheel-rail force measurement and derailment evaluation[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2014, 52(12): 1622-1641. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2014.953180 [7] KUMINEK T, ANIOEK K. Methodology and verification of calculations for contact stresses in a wheel-rail system[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2014, 52(1): 111-124. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2013.863361 [8] ALONSO A, GUIRAL A, BAEZA L, et al. Wheel-rail contact: experimental study of the creep forces-creepage relationships[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2014, 52(S1): 469-487. [9] 吴磊, 温泽峰, 金学松. 轮轨摩擦耦合热弹性有限元分析模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2007, 7(6): 21-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2007.06.005WU Lei, WEN Ze-feng, JIN Xue-song. Elastic finite element analysis model of coupling friction heat for wheel/rail[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2007, 7(6): 21-27. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2007.06.005 [10] IGNESTIA M, MALVEZZI M, MARINI L, et al. Development of a wear model for the prediction of wheel and rail profile evolution in railway systems[J]. Wear, 2012, 284-285: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.01.020 [11] ROVIRA A, RODA A, MARSHALL M B, et al. Experimental and numerical modelling of wheel-rail contact and wear[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(5/6): 911-924. [12] GORYACHEVA I G, SOSHENKOV S N, TORSKAYA E V. Modelling of wear and fatigue defect formation in wheel-rail contact[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2013, 51(6): 767-783. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2011.602419 [13] SUNDH J, OLOFSSON U. Relating contact temperature and wear transitions in a wheel-rail contact[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(1/2): 78-85. [14] SEO J, KWON S, LEE D. Effects of surface defects on rolling contact fatigue of rail[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 10: 1274-1278. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.04.212 [15] 孙效杰, 周文祥. 踏面磨耗及其对轮轨接触几何关系的影响[J]. 铁道车辆, 2010, 48(7): 1-4, 14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2010.07.001SUN Xiao-jie, ZHOU Wen-xiang. Tread wear and its effect on wheel-rail contact geometry[J]. Railway Vehicles, 2010, 48(7): 1-4, 14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2010.07.001 [16] 李伟, 曾全军, 朱士友, 等. 地铁钢轨波磨对车辆和轨道动态行为的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2015, 15(1): 34-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2015.01.005LI Wei, ZENG Quan-jun, ZHU Shi-you, et al. Effect of metro rail corrugation on dynamic behaviors of vehicle and track[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2015, 15(1): 34-42. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2015.01.005 [17] 白雁, 袁昊. 城市轨道交通钢轨伤损的评价分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2006, 16(3): 124-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.03.024BAI Yan, YUAN Hao. Evaluation analysis on rail damage of urban rail transit[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2006, 16(3): 124-128. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.03.024 [18] 周清跃, 张建峰, 郭战伟, 等. 重载铁路钢轨的伤损及预防对策研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2010, 31(1): 27-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201001007.htmZHOU Qing-yue, ZHANG Jian-feng, GUO Zhan-wei, et al. Research on the rail damages and the preventive countermeasures in heavy haul railways[J]. China Railway Science, 2010, 31(1): 27-31. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201001007.htm [19] 任安超, 周桂峰, 吉玉, 等. 50 kg·m-1钢轨踏面掉块缺陷分析[J]. 钢铁, 2009, 44(1): 91-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GANT200901024.htmREN An-chao, ZHOU Gui-feng, JI Yu, et al. Analysis on swap block on tread of 50 kg·m-1 rail[J]. Iron and Steel, 2009, 44(1): 91-94. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GANT200901024.htm [20] 周剑华, 任安超, 吉玉, 等. U71Mn钢轨踏面剥离掉块缺陷分析[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2013, 34(2): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.02.01ZHOU Jian-hua, REN An-chao, JI Yu, et al. Analysis of the reasons for the spalling defects on U71Mn rail treads[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34(2): 1-6. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.02.01 [21] 陈朝阳, 张银花, 刘丰收, 等. 朔黄铁路曲线下股热处理钢轨剥离伤损成因分析[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2008, 29(4): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200804005.htmCHEN Zhao-yang, ZHANG Yin-hua, LIU Feng-shou, et al. Analysis on the formation cause of spalling and damage of the heat-treated low rail on Shuohuang Railway curve[J]. China Railway Science, 2008, 29(4): 28-34. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200804005.htm [22] 吴雄先, 邓建辉, 王飞龙. 钢轨踏面掉块原因分析[J]. 理化检验: 物理分册, 2009, 45(1): 39-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJW200901019.htmWU Xiong-xian, DENG Jian-hui, WANG Fei-long. Reason analysis of peeling on rail tread[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part A: Physical Testing, 2009, 45(1): 39-41. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJW200901019.htm [23] CHEN Y C, LEE S Y. Elastic-plastic wheel-rail thermal contact on corrugated rails during wheel braking[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2009, 131(1): 1-9. -





 下载:
下载: