Optimization model of energy-efficient driving for train in urban rail transit based on particle swarm algorithm
-
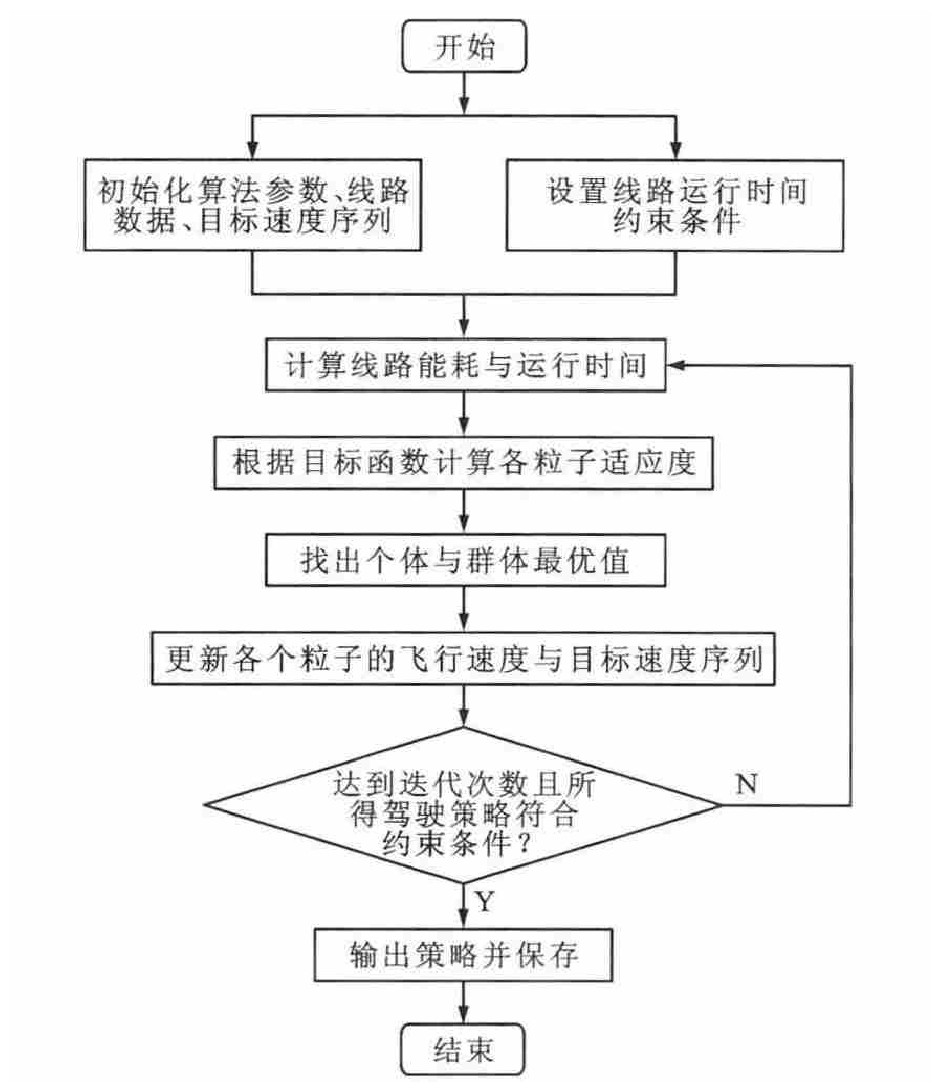
摘要: 为了降低城市轨道交通中列车在站间运行的能耗, 研究了列车的站间节能驾驶策略, 在考虑线路限速和坡度的情况下, 建立了时间约束下的列车节能优化模型, 采用粒子群算法优化目标速度序列得出了列车节能驾驶策略。节能驾驶优化方法通过2个阶段来实现, 第1阶段在站间运行时间不变的情况下, 采用粒子群算法优化了列车在站间的节能驾驶策略, 得到了运行时间和能耗的关系, 第2阶段在多站间总运行时间不变的前提下, 将运行时间进行重新分配, 得到了列车在全线运行的节能驾驶策略。以北京地铁亦庄线实际线路数据和车辆参数为基础, 对优化方法进行仿真验证。仿真结果表明: 经过第1阶段的优化, 列车在万源街-荣京东街的单站间运行能耗降低了6.15%, 经过第2阶段的优化, 列车在多站间总运行能耗降低了14.77%。可见, 优化模型可以有效降低列车的运行能耗, 为列车时刻表的编制提供依据。Abstract: In order to reduce the interstation operation energy consumption of train in urban rail transit, the interstation energy-efficient driving strategy of train was studied.On the basis of considering speed limit and gradient, a energy-efficient optimization model with the constraint of trip time was established, the optimal energy-efficient driving strategy was proposed by using particle swarm optimization(PSO)to optimize the target speed sequence.The optimization method of energy-efficient driving was realized through two phases.In the first phase, under the condition of constant interstation trip time, the interstation energy-efficient driving strategy of train was optimized with PSO, and the relationship between trip time and energy consumption was obtained.In the second phase, under the condition of the constant total trip time of whole interstations, the trip time was redistributed, and the energy-efficient driving strategy of train for the whole line was obtained.Based on the real track data and vehicle parameters of Yizhuang Lineof Beijing Subway, the optimization method was simulated and verified.Simulation result shows that after optimization, the interstation operation energy consumption of train reduces by 6.15%in the first phase in Wanyuan Street-Rongjingdong Street, and the total operation energy consumption of whole interstations reduces by 14.77% in the second phase.So the model can effectively reduce the operation energy consumption of train, and provides a basis for the generation of train timetable.
-
表 1 亦庄线计划运行时间
Table 1. Scheduled operation times of Yizhuang Line

表 2 站间驾驶策略优化结果
Table 2. Optimization results of interstation driving strategy

表 3 站间最小运行时间
Table 3. Minimum operation times of interstations

-
[1] ICHIKAWA K. Application of optimization theory for bounded state variable problems to the operation of train[J]. Bulletin of JSME, 1968, 11(47): 857-865. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.11.857 [2] KHMELNITSKY E. On an optimal control problem of train operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(7): 1257-1266. doi: 10.1109/9.867018 [3] GOLOVITCHER I M. Energy efficient control of rail vehicles[C]//IEEE. 2001IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. New York: IEEE, 2001: 658-663. [4] LIU Rong-fang, GOLOVITCHER I M. Energy-efficient operation of rail vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2003, 37(10): 917-932. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2003.07.001 [5] HOWLETT P G, PUDNEY P J, VU X. Local energy minimization in optimal train control[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2692-2698. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.028 [6] MIYATAKE M, KO H. Optimization of train speed profile for minimum energy consumption[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2010, 5(3): 263-269. doi: 10.1002/tee.20528 [7] LU Shao-feng, HILLMANSEN S, HO T K, et al. Singletrain trajectory optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2): 743-750. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2234118 [8] CHUANG H J, CHEN C S, LIN C H, et al. Design of optimal coasting speed for saving social cost in mass rapid transit systems[C]//IEEE. Third International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies. New York: IEEE, 2008: 2833-2839. [9] 付印平. 列车追踪运行与节能优化建模及模拟研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2009.FU Yin-ping. Researeh on modeling and simulations of train tracking operation and saving energy optimization[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2009. (in Chinese). [10] KE B R, CHEN M C, LIN C L. Block-layout design using MAX-MIN ant system for saving energy on mass rapid transit systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009, 10(2): 226-235. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2009.2018324 [11] KE B R, LIN C L, LAI C W. Optimization of train-speed trajectory and control for mass rapid transit systems[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2011, 19(7): 675-687. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2011.03.003 [12] KE B R, LIN C L, YANG C C. Optimisation of train energyefficient operation for mass rapid transit systems[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2012, 6(1): 58-66. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2010.0144 [13] 于雪松. 城市轨道交通列车节能优化及能耗评估[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2012.YU Xue-song. Energy-efficient optimization and energy consumption evaluation of uran rail transit train[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2012. (in Chinese). [14] 吴洋, 王月明, 曾理. 晚点情况下地铁列车间隔的实时调整方法[J]. 电力机车与城轨车辆, 2003, 26(5): 21-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1187.2003.05.007WU Yang, WANG Yue-ming, ZENG Li. Method of realtime adjustment of metro trains headway after a delay[J]. Electric Locomotives and Mass Transit Vehicles, 2003, 26(5): 21-23. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1187.2003.05.007 [15] 吴洋. 晚点情况下地铁列车实时运行调整及速度控制模式研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2004.WU Yang. Research of train operation adjustment for delay and train speed controlling model[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2004. (in Chinese). [16] 吴洋, 罗霞. 一种晚点地铁列车实时调整策略及其动态速控模式[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2005, 26(6): 113-118. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2005.06.023WU Yang, LUO Xia. Tactic for real-time operation adjustment and corresponding dynamic velocity control mode for delayed metro trains[J]. China Railway Science, 2005, 26(6): 113-118. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2005.06.023 [17] NASRI A, MOGHADAM M F, MOKHTARI H. Timetable optimization for maximum usage of regenerative energy of braking in electrical railway systems[C]//IEEE. 2010International Symposium on Power Electronics Electrical Drives Automation and Motion. New York: IEEE, 2010: 1218-1221. [18] 颜邦杰, 张辰秋, 林志铭, 等. 捷运列车排点与节能[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2011, 29(1): 139-144. doi: 10.3963/j.ISSN1674-4861.2011.01.033YAN Bang-jie, ZHANG Chen-qiu, LIN Zhi-ming, et al. MRT timetable and energy conservation[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2011, 29(1): 139-144. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.ISSN1674-4861.2011.01.033 [19] WONG K K, HO T K. Dwell-time and run-time control for DC mass rapid transit railways[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2007, 1(6): 956-966. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa:20060132 [20] LI Xiang, WANG De-chun, LI Ke-ping, et al. A green train scheduling model and fuzzy multi-objective optimization algorithm[J]. Applied Mathematical Modellings, 2013, 37(4): 2063-2073. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2012.04.046 [21] SU Shuai, LI Xiang, TANG Tao, et al. A subway train timetable optimization approach based on energy-efficient operation strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2): 883-893. -





 下载:
下载: