Bi-level programming model of traffic microcirculation optimization for historic district
-
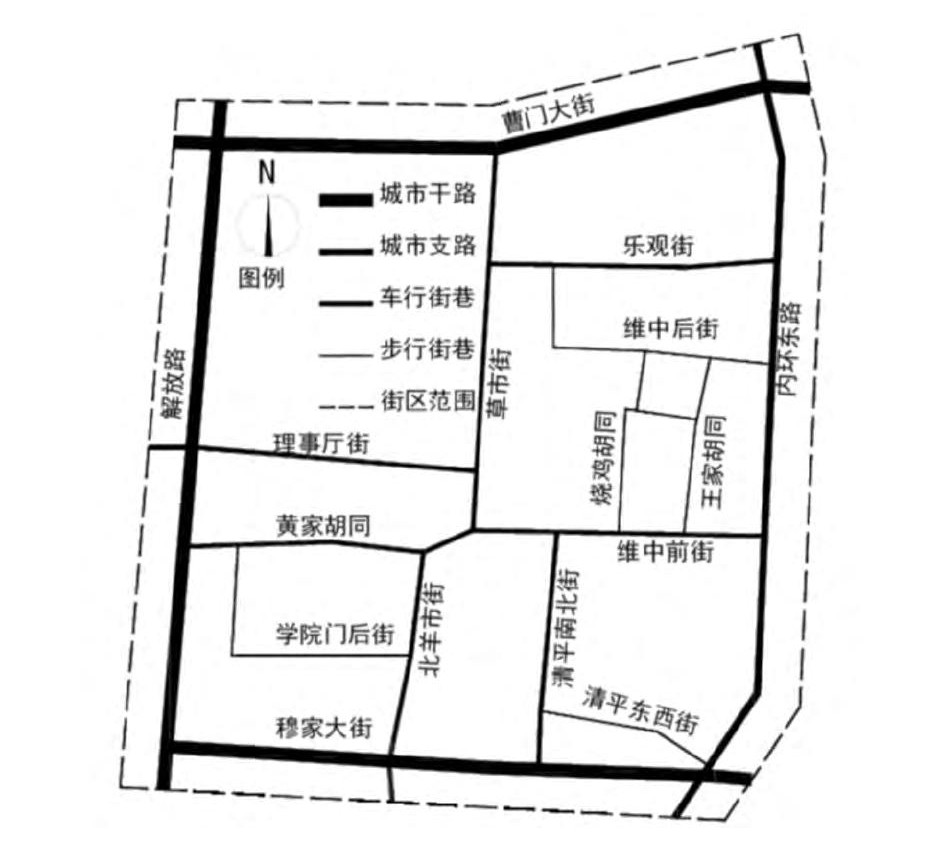
摘要: 为满足历史街区日益增加的交通需求, 利用街区内密布的街巷网络组织交通微循环, 建立了历史街区交通微循环优化的双层规划模型, 以提高干路畅通性与路网平均行程车速、缩短绕行时间和控制环境污染为优化目标, 以街区内街巷的通畅和历史遗存保护为约束条件, 构建上层模型, 采用用户均衡交通分配与借助TransCAD求解下层模型, 并选取开封市草市街历史街区进行实例分析。计算结果表明: 优化计算使干路平均饱和度可由0.69最多降至0.36;路网平均行程车速可由26.33 km·h-1最多提升至28.87 km·h-1; 街区内街巷平均饱和度可由0.07最多提升至0.37;绕行时间及环境污染得到控制。可见, 该模型的应用缓解了干路网络的交通压力, 提高了街区可达性及总体运行效率, 具有良好的交通效益和环境效益。Abstract: In order to fulfill the increasing traffic demand of historic district, rich streets and alleys in the district were used to organize traffic microcirculation, and a bi-level programming model of traffic microcirculation optimization for historic district was built.The up-level model was built targeting on increasing the transit efficiency of trunk roads, increasing the average travel speed of road network, deceasing bypass time and controlling environmental pollution in the constraint conditions district unblocking and historical relics protection of streets and alleys.User equilibrium traffic assignment was used to solve the down-level model by using TransCAD.The historic district of Caoshi Street in Kaifeng was taken as an example to carry out case analysis.Calculation result shows that optimization calculation makes the average saturation of trunk road decease from 0.69 to 0.36 at most, the average travel speed of road network increase from 26.33 km·h-1 to 28.87 km·h-1 at most, the average saturation of streets and alleys in the district increase from 0.07 to 0.37 at most, and bypass time and environmental pollution are controlled.Obviously, the model application relieves the traffic pressure of trunk road network and improves district accessibility and overall operating efficiency, which has good traffic benefit and environmental benefit.
-
表 1 历史街区各路段现状
Table 1. Status of road segments in historic district

表 2 不同交通组织方案下各路段高峰交通量
Table 2. Peak traffic volumes of road segments in different traffic organization plans

表 3 不同交通组织方案下各路段高峰饱和度
Table 3. Peak saturations of road segments in different traffic organization plans

表 4 上层模型计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of up-level model

-
[1] 戴湘毅, 王晓文, 王晶. 历史街区定义探析[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2007, 19(5): 36-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDL200705009.htmDAI Xiang-yi, WANG Xiao-wen, WANG Jing. An analysis of the definition of historic distric[J]. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 2007, 19(5): 36-39. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDL200705009.htm [2] 邓一凌, 过秀成, 严亚丹, 等. 历史城区微循环路网分层规划方法研究[J]. 城市规划学刊, 2012(3): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3363.2012.03.010DENG Yi-ling, GUO Xiu-cheng, YAN Ya-dan, et al. Double-layered planning to facilitate micro-circulation of traffic in historic areas[J]. Urban Planning Forum, 2012(3): 70-75. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3363.2012.03.010 [3] 李新建. 从交通期望线论我国历史城市保护中的新区发展空间结构问题[J]. 城市规划学刊, 2013(4): 49-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXGH201304010.htmLI Xin-jian. Spatial structure of new district for Chinese historic cities: based on origin-destination traffic study[J]. Urban Planning Forum, 2013(4): 49-53. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXGH201304010.htm [4] 孔哲, 窦雪萍, 罗丽梅, 等. 大城市历史城区绿色交通发展对策[J]. 规划师, 2011, 27(增): 141-144, 148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHSI2011S1030.htmKONG Zhe, DOU Xue-ping, LUO Li-mei, et al. Strengths of green traffic in old town of large city[J]. Planners, 2011, 27(S): 141-144, 148. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHSI2011S1030.htm [5] 罗侃. 区域交通微循环路网规划研究[J]. 价值工程, 2011, 30(30): 52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2011.30.033LUO Kan. Planning research on regional transportation microcirculation road network[J]. Value Engineering, 2011, 30(30): 52. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2011.30.033 [6] 史峰, 黄恩厚, 陈群, 等. 城市微循环交通网络中单行交通组织优化[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2009, 9(4): 30-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT200904007.htmSHI Feng, HUANG En-hou, CHEN Qun, et al. Optimization of one-way traffic organization for urban micro-circulation transportation network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2009, 9(4): 30-35. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT200904007.htm [7] 宋雪鸿. 城市交通微循环问题的解决策略及其应用研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2008.SONG Xue-hong. Research on the solution strategy and application of urban traffic microcirculation[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2008. (in Chinese). [8] 王浩苏, 罗霞. 基于多目标的城市交通微循环系统优化模型研究[J]. 成都大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 33(1): 79-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDDD201401023.htmWANG Hao-su, LUO Xia. Research on optimization model of urban traffic microcirculation system based on multiobjective[J]. Journal of Chengdu University: Natural Science Edition, 2014, 33(1): 79-82. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDDD201401023.htm [9] 陆建, 王炜. 城市道路网规划指标体系[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2004, 4(4): 62-67. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2004.04.016LU Jian, WANG Wei. Planning indices system of urban road network[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2004, 4(4): 62-67. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2004.04.016 [10] 张海明. 城市居住片区交通微循环系统研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2011.ZHANG Hai-ming. The research of urban traffic microcirculation system in residential district[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2011. (in Chinese). [11] 孙晶. 城市道路单向交通方案设计若干问题研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012.SUN Jing. Research on a number of issues about design of one-way roadway[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2012. (in Chinese). [12] EBBEN M, VAN DER ZEE D J, VAN DER HEIJDEN M. Dynamic one-way traffic control in automated transportation systems[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2004, 38(5): 441-458. [13] 王秋平, 王思颖, 任歆雨, 等. 基于城市交通网络的历史街区单向交通组织优化[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 46(3): 342-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAJZ201403007.htmWANG Qiu-ping, WANG Si-ying, REN Xin-yu, et al. Oneway traffic organization optimization of the historic district based on urban traffic network[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2014, 46(3): 342-347. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAJZ201403007.htm [14] 丁猛. 历史街区交通微循环系统研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2015.DING Meng. Studies on traffic microcirculation system of historic district[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2015. (in Chinese). [15] YANG Hai, BELL M G H. Transport bilevel programming problems: recent methodological advances[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2001, 35(1): 1-4. [16] CHIOU S W. Bilevel programming for the continuous transport network design problem[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2005, 39(4): 361-383. [17] OUYANG Yan-feng, GEROLIMINIS N, NIE Yu. Optimization of urban transportation service networks[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2015, 81: 331-332. [18] GAO Zi-you, WU Jian-jun, SUN Hui-jun. Solution algorithm for the bi-level discrete network design problem[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2005, 39(6): 479-495. [19] SHI Feng, HUANG En-hou, CHEN Qun, et al. Bi-level programming model for reconstruction of urban branch road network[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2009, 16(1): 172-176. [20] TONG Lu, ZHOU Xue-song, MILLER H J. Transportation network design for maximizing space-time accessibility[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2015, 81: 555-576. [21] LA GENNUSA M, FERRANTE P, LO CASTO B, et al. An integrated environmental indicator for urban transportation systems: description and application[J]. Energies, 2015, 8(10): 11076-11094. [22] VIJAYARAGHAVAN T A S, ANANTHARAMAIAH K M. Fleet assignment strategies in urban transportation using express and partial services[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 1995, 29(2): 157-171. [23] TASIC I, PORTER R J. Modeling spatial relationships between multimodal transportation infrastructure and traffic safety outcomes in urban environments[J]. Safety Science, 2016, 82: 325-337. [24] LI Tie-zhu, LIN Jin-shan, WU Meng-ting, et al. Concept and spatial analysis method of urban environmental traffic capacity[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2009, 135(11): 873-879. [25] MURPHY E. Urban spatial location advantage: the dual of the transportation problem and its implications for land-use and transport planning[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2012, 46(1): 91-101. -





 下载:
下载: