Modeling and simulation of railway vehicle wheel considering thermo-mechanical coupling
-
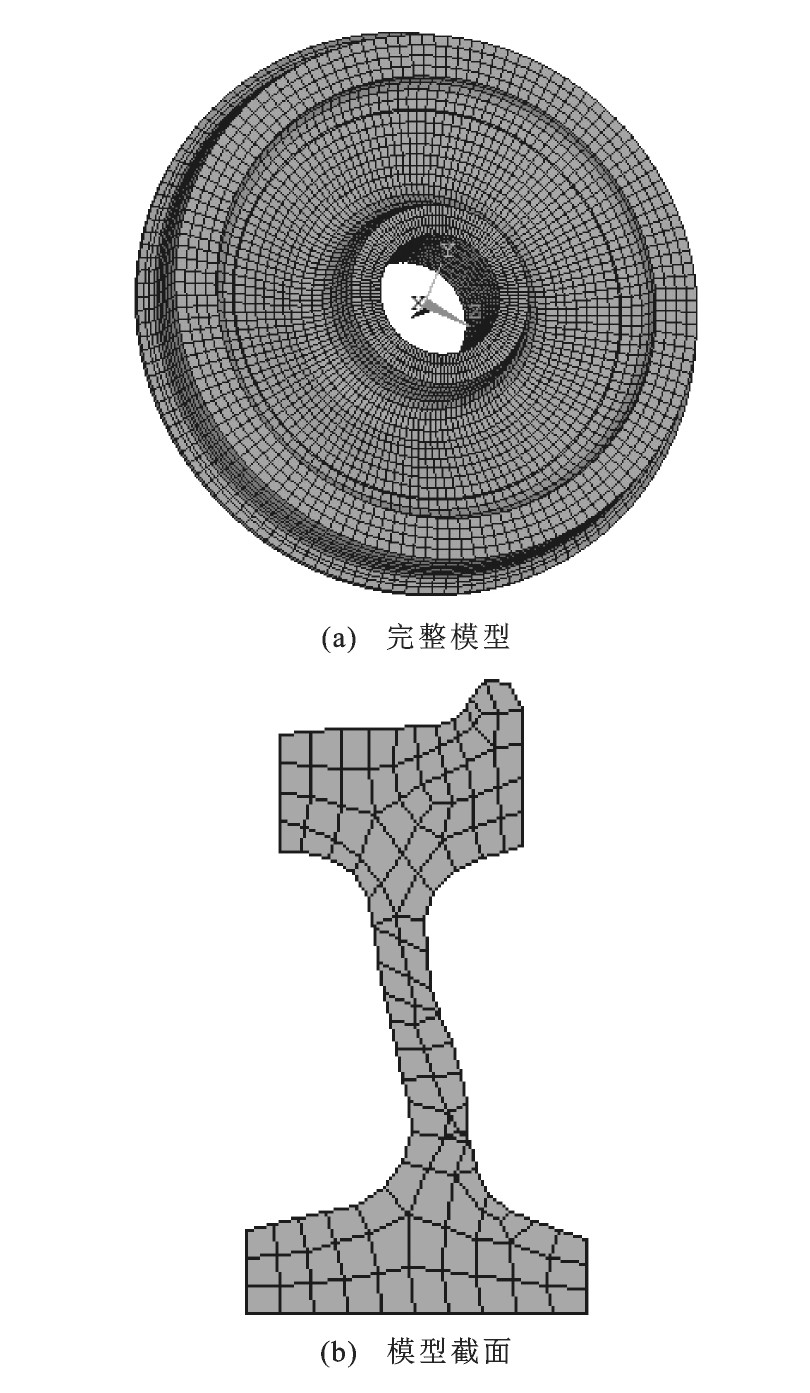
摘要: 以城市轨道车辆车轮为研究对象, 建立了S型辐板轨道车辆车轮模型, 利用有限元方法研究了不同磨耗情况下车轮结构应力和热应力的变化特点, 分析了结构场和温度场的耦合作用对车轮应力特性的影响, 获得了热力耦合作用下的车轮结构应力和热应力的耦合规律。仿真结果表明: 随着车轮踏面的磨耗, 其结构应力、热应力与耦合应力均呈非线性变化, 在车轮直径为800~840mm的磨损区间, 耦合应力较稳定, 当磨损到直径小于800mm之后, 其耦合应力增长较快, 特别是磨耗到770mm时, 耦合应力骤升, 磨耗到限时耦合应力达到179.5 MPa; 车轮的耦合应力是复杂的三维空间力系的叠加, 在耦合应力分布上, 车轮辐板处耦合应力最大点位置发生漂移现象, 制动结束时的车轮辐板处耦合应力最大, 大于结构应力最大值与热应力最大值, 因此, 耦合应力在车轮应力中占主导作用, 在车轮的结构设计时, 建议考虑结构应力和热应力的耦合作用, 把耦合应力作为车轮疲劳强度的评价指标。Abstract: Urban railway vehicle wheel was taken as research object, and an S-plate wheel model was established.The features of structural stress and thermal stress of wheel under different abrasions were investigated respectively by using FEM, the effects of thermo-mechanical coupling in the structure field and the thermal field on the stress characteristic of wheel were analysed, and the coupling rules of structural stress and thermal stress were obtained by considering thermomechanical coupling.Simulation result shows that the structural stress, the thermal stress and the coupling stress are all nonlinear with the development of tread abrasion of wheel.The coupling stress is stable when the wheel diameter ranges from 840 mm to 800 mm.When the diameter is less than 800 mm, the coupling stress grows faster, especially, when the diameter is 770 mm, the coupling stress rises rapidly.The coupling stress reaches 179.5 MPa under the abrasion-limit working condition.The coupling stress of wheel is produced by the superposition of complex three dimensional force system.For the coupling stress distribution, the phenomenonof drift exists at the position of the maximum coupling stress of wheel plate.The coupling stress of wheel plate becomes maximum at the brake end time, and is greater than both the maximum structural stress and the maximum thermal stress.Therefore, the coupling stress plays a leading role in the wheel stresses.For the structure design of wheel, it is recommended to consider the coupling role between the structural stress and the thermal stress, and to think the coupling stress as the evaluation index of wheel fatigue strength.
-
Key words:
- railway vehicle /
- wheel /
- thermo-mechanical coupling /
- structure field /
- thermal field /
- abrasion
-
表 1 车轮参数
Table 1. Parameters of wheel

表 2 车轮材料属性
Table 2. Material properties of wheel

表 3 工况4的受力
Table 3. Forces of working condition 4
kN 
-
[1] 文永蓬, 尚慧琳, 董其炜, 等. 城市轨道车辆车轮轮缘磨耗分析[J]. 科技导报, 2013, 31(26): 40-43. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2013.26.005WEN Yong-peng, SHANG Hui-lin, DONG Qi-wei, et al. Wear of wheel flange of urban rail vehicle[J]. Science and Technology Review, 2013, 31(26): 40-43. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2013.26.005 [2] PENG D, JONES R, CONSTABLE T, et al. The tool for assessing the damage tolerance of railway wheel under service conditions[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2012, 57(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2011.12.002 [3] ZWIERCZYK P T, VÁRADI K. Thermal stress analysis of a railway wheel in sliding-rolling motion[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2014, 136(3): 69-74. [4] 蓝春红, 吴萌岭, 王勇, 等. 重载货车踏面制动时车轮温度场与应力场研究[J]. 铁道车辆, 2011, 49(7): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2011.07.001LAN Chun-hong, WU Meng-ling, WANG Yong, et al. Research on the temperature field and stress field of wheels at time of tread braking of heavy haul freight cars[J]. Rolling Stock, 2011, 49(7): 1-5. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2011.07.001 [5] LINGAMANAIK S N, CHEN B K. Thermo-mechanical modelling of residual stresses induced by martensitic phase transformation and cooling during quenching of railway wheels[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2011, 211(9): 1547-1552. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.04.007 [6] LINGAMANAIK S N, CHEN B K. Prediction of residual stresses in low carbon bainitic-martensitic railway wheels using heat transfer coefficients derived from quenching experiments[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2013, 77(3): 153-160. [7] NEJAD R M. Using three-dimensional finite element analysis for simulation of residual stresses in railway wheels[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2014, 45: 449-455. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.07.018 [8] NEJAD R M, FARHANGDOOST K, SHARIATI M. Numerical study on fatigue crack growth in railway wheels under the influence of residual stresses[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2015, 52: 75-89. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.03.002 [9] NEJAD R M, SHARIATI M, FARHANGDOOST K. Effect of wear on rolling contact fatigue crack growth in rails[J]. Tribology International, 2016, 94: 118-125. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2015.08.035 [10] VINEESH K P, VAKKALAGADDA M R K, TRIPATHI A K, et al. Non-uniformity in braking in coaching and freight stock in Indian Railways and associated causes[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 59: 493-508. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.11.023 [11] VAKKALAGADDA M R K, VINEESH K P, MISHRA A, et al. Locomotive wheel failure from gauge widening/condemning: effect of wheel profile, brake block type, and braking conditions[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 59: 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.11.013 [12] HAIDARI A, TEHRANI P H. Thermal load effects on fatigue life of a cracked railway wheel[J]. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures, 2015, 12(6): 1144-1157. doi: 10.1590/1679-78251658 [13] 梁红琴, 赵永翔, 杨冰, 等. 高速动车组拖车车轮疲劳强度的分析评定[J]. 机车电传动, 2013(2): 18-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCDC201302006.htmLIANG Hong-qin, ZHAO Yong-xiang, YANG Bing, et al. Fatigue strength analysis and check of high-speed EMUs trailer wheel[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2013(2): 18-20. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCDC201302006.htm [14] 米彩盈, 李芾. 高速动力车车轮强度分析的工程方法[J]. 铁道机车与动车, 2005(9): 11-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LRJX200509005.htmMI Cai-ying, LI Fu. Project method of strength analysis about wheels of high-speed power car[J]. Railway Locomotive and Motor Car, 2005(9): 11-13. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LRJX200509005.htm [15] 何莹, 刘志明, 胡宝义. 动车组车轮强度标准与分析方法[J]. 北京交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 33(1): 15-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFJT200901006.htmHE Ying, LIU Zhi-ming, HU Bao-yi. EMU's wheel strength standards and analytical methods[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 33(1): 15-19. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFJT200901006.htm [16] 肖楠. 铁路重载货车车轮辐板热机疲劳强度评价方法[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2011.XIAO Nan. Method of thermo-mechanical fatigue strength assessment on railway heavy-haul freight car wheel plate[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011. (in Chinese). [17] 郑红霞, 刘玉军, 张全忠, 等. 典型制动条件下货车车轮温度场和热应力场的有限元仿真[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2009, 28(4): 500-504. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-8728.2009.04.018ZHENG Hong-xia, LIU Yu-jun, ZHANG Quan-zhong, et al. Finite element simulation of the temperature field and thermal stress field of a freight wheel under typical braking conditions[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2009, 28(4): 500-504. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-8728.2009.04.018 [18] 肖楠, 谢基龙, 周素霞. 地铁车轮踏面制动疲劳强度评价方法及应用[J]. 工程力学, 2010, 27(9): 234-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201009040.htmXIAO Nan, XIE Ji-long, ZHOU Su-xia. Method to assess fatigue strength of tread breaking of metro vehicle wheel and its application[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2010, 27(9): 234-239. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201009040.htm [19] 朱小娟, 高伟民, 王生华. 上海地铁车辆统型车轮强度及热力学计算分析[J]. 电力机车与城轨车辆, 2008, 31(4): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DJJI200804002.htmZHU Xiao-juan, GAO Wei-min, WANG Sheng-hua. Calculation and analysis on stress and thermal capability of the unified type wheel for Shanghai metro vehicles[J]. Electric Locomotive and Mass Transit Vehicles, 2008, 31(4): 1-3. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DJJI200804002.htm [20] 文永蓬, 周伟浩, 徐小峻, 等. 考虑热力耦合的轨道车轮辐板参数优化研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2016, 13(9): 8-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD201610023.htmWEN Yong-peng, ZHOU Wei-hao, XU Xiao-jun, et al. Study on parameter optimization for the rail wheel considering thermal-mechanical coupling[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2016, 13(9): 8-16. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD201610023.htm [21] CAPRICCIOLI A, FROSI P. Multipurpose ANSYS FEprocedure for welding processes simulation[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2009, 84(2-6): 546-553. [22] 张萍, 温泽峰, 吴磊, 等. 不同热流加载方式下车轮踏面制动温度和应力场模拟分析[J]. 润滑与密封, 2013, 38(5): 69-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RHMF201305020.htmZHANG Ping, WEN Ze-feng, WU Lei, et al. Temperature and stress field analysis of wheel tread braking process using different heat flux loading modes[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2013, 38(5): 69-74. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RHMF201305020.htm [23] 应之丁, 李小宁, 林建平, 等. 列车车轮踏面制动温度循环试验与温度场仿真分析[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2010, 31(3): 70-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201003014.htmYING Zhi-ding, LI Xiao-ning, LIN Jian-ping, et al. The temperatuer cycle test of wheel tread braking for freight trains and the simulation analysis of the temperature field[J]. China Railway Science, 2010, 31(3): 70-75. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201003014.htm [24] 陈倩, 李芾, 王军平, 等. 40t轴重货车制动热负荷分析[J]. 铁道机车车辆, 2012, 32(4): 32-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJC201204009.htmCHEN Qian, LI Fu, WANG Jun-ping, et al. Thermal load analysis of wheels for 40taxle-load freight car under braking conditions[J]. Railway Locomotive and Car, 2012, 32(4): 32-36. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJC201204009.htm [25] 候耐. 重载货车车轮踏面制动热负荷研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2011.HOU Nai. Heatload analysis of heavy-haul freight car wheel for tread breaking[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011. (in Chinese). [26] 李金良, 肖楠, 谢基龙. 重载货车车轮踏面制动辐板热应力分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(12): 133-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201212023.htmLI Jin-liang, XIAO Nan, XIE Ji-long. Thermal stress analysis of the heavy-haul freight car's wheel web plate under the wheel tread braking[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(12): 133-138. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201212023.htm -





 下载:
下载: