Characteristic of wind-sand flow field of box-type movable sand barrier
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
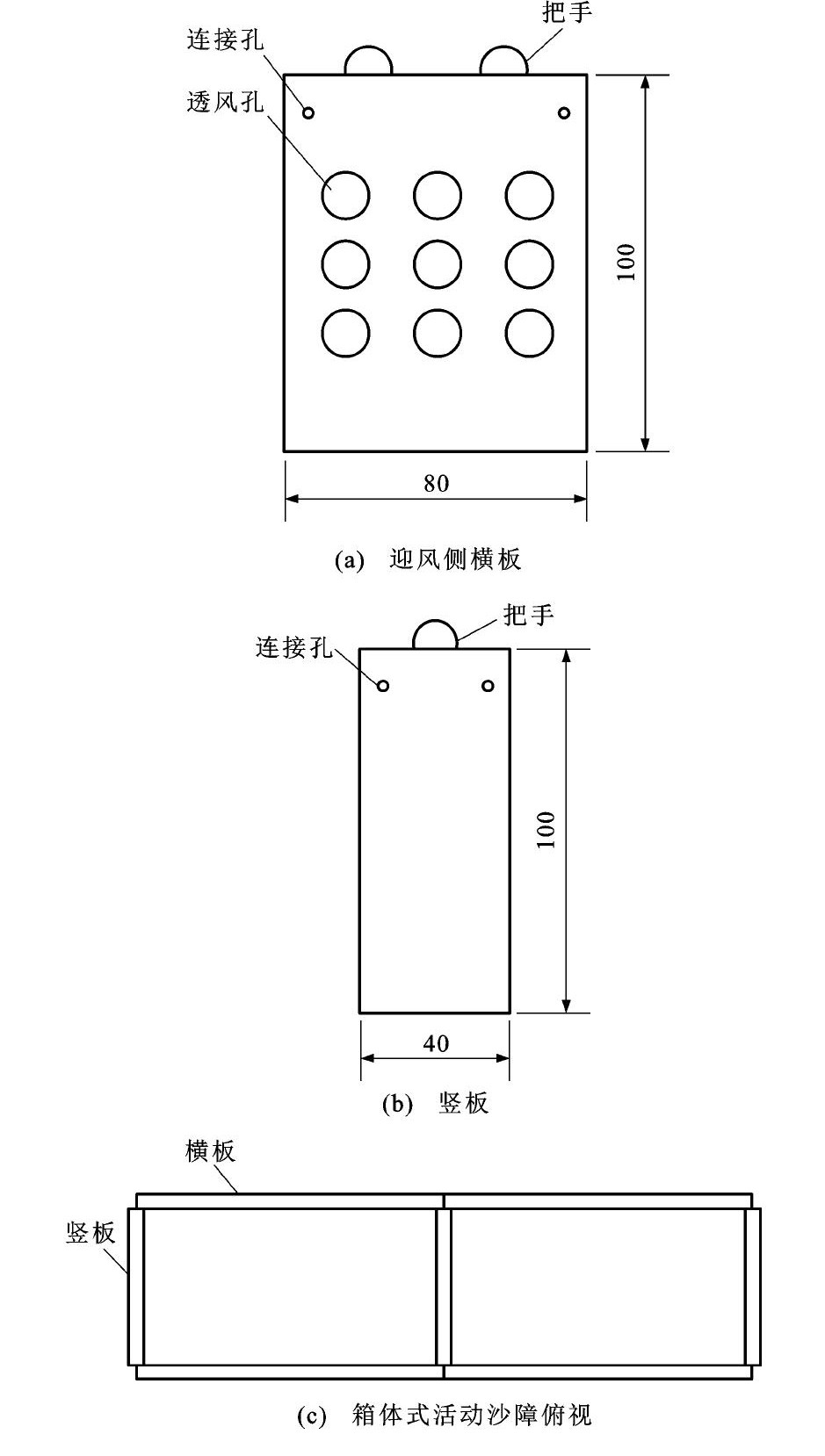
摘要: 研究在野外调查的基础上, 采用计算流体力学三维数值建模方法并结合室内风洞试验, 分析了箱体式活动沙障在孔隙率与风速变化作用下的控沙特点及其周围风沙流场的演化过程。分析结果表明: 在沙障的控制下, 顺着风向在沙障前后依次出现减速区、减速上扬区、加速区与障后涡流区, 在沙障腔体内形成明显的腔内减速区与涡流区, 过境风沙流在沙障的减速区、障后涡流区与腔体内发生沉落, 可见箱体式活动沙障发挥了控沙作用; 随着风速增大, 障前减速上扬区高度增大, 但沙障迎风侧孔隙率的变化对减速上扬区高度没有影响; 当沙障迎风侧横板孔隙率小于5%时, 对来流的消减效果显著, 积沙在沙障前卸载, 不能充分发挥沙障背风侧涡流区的控沙作用; 当孔隙率大于25%时, 沙障能够充分发挥控沙作用, 在沙障的迎风侧、背风侧与腔体内都有积沙卸载; 当孔隙率继续增大至30%时, 沙障控沙效果没有明显提高; 选定孔隙率为30%条件下, 随着风速的增大, 沙障后积沙增加, 沙障腔体内积沙减少, 而沙障迎风侧积沙出现先增加后减少的变化趋势。Abstract: On the basis of field investigation, the sand-controlled characteristics of box-type movable sand barrier and the evolution process of wind-sand flow field around the barrier were analyzed by using computational fluid dynamics three-dimensional numerical modeling method and indoor wind tunnel test under the effect of changeable porosity and wind velocity.Analysis result indicates that under the control of sand barrier, there are deceleration zone, deceleration uptrend zone, acceleration zone, and vortex zone successively before and after sand barrier along the direction of wind.Deceleration zone and vortex zone form obviously in the cavities of sand barrier, the transient wind-sand flow sinks down in deceleration zone, vortex zone behind and the cavities of sand barrier, so the box-type movable sand barrier plays an important role in sandcontrol.As the increase of wind velocity, the height of deceleration uptrend zone increases, but the porosity change of windward side of sand barrier does not cause any effect to the height of deceleration uptrend zone.When the porosity of windward side of sand barrier is less than 5%, the flow weakens observably, and the sand deposites in the front of sand barrier, which can not make full use of the sand-control function of vortex zone behind sand barrier.When the porosity is more than 25%, the sand barrier can play full sand-controlled role, sand deposites in thewindward side, leeward side and cavities of sand barrier.When the porosity continues to increase to 30%, the sand-controlled effect does not improve obviously.Under the condition that the porosity is 30%, when the wind velocity continues to increase, the sand accumulation increases behind the sand barrier and decreases in the cavities of sand barrier, however, the tendency of decrease after the first increase occurs in the windward side of sand barrier.
-
表 1 减速上扬区高度
Table 1. Heights of deceleration uptrend zone

-
[1] CHENG Jian-jun, XUE Chun-xiao. The sand-damage-prevention engineering system for the railway in the desert region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 125 (2): 30-37. [2] 李凯崇, 刘贺业, 蒋富强, 等. 斜插板挡沙墙风沙防治现场试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2013, 34 (2): 46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.02.09LI Kai-chong, LIU He-ye, JIANG Fu-qiang, et al. Field test study on the prevention and treatment of wind drift sand by retaining wall with inclined plank[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34 (2): 46-51. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2013.02.09 [3] 景文宏, 程建军, 蒋富强. 轨枕式挡墙挡风沙功效的数值模拟及试验研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2016, 13 (1): 46-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.01.008JING Wen-hong, CHENG Jian-jun, JIANG Fu-qiang. Numerical simulation and experimental research on effect of sleeper typed retaining wall for wind and sand retaining[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2016, 13 (1): 46-54. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.01.008 [4] 辛国伟, 程建军, 杨印海. 铁路沿线挂板式沙障开孔特征与风沙流场的影响研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2016, 38 (10): 99-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.10.014XIN Guo-wei, CHENG Jian-jun, YANG Yin-hai. Study on effect of characteristics of hanging-type concrete sand barrier opening and wind-sand field along railway[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38 (10): 99-107. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.10.014 [5] ZAKERI J A, ABBASI R. Field investigation of variation of loading pattern of concrete sleeper due to ballast sandy contamination in sandy desert areas[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2012, 26 (12): 3885-3892. doi: 10.1007/s12206-012-0886-5 [6] ZAKERI J A. Investigation on railway track maintenance in sandy-dry areas[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering: Maintenance, Management, Life-Cycle Design and Performance, 2012, 8 (2): 135-140. [7] CHENG Jian-jun, XIN Guo-wei, ZHI Ling-yan, et al. Unloading characteristics of sand-drift in wind-shallow areas along railway and the effect of sand removal by force of wind[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x [8] CHENG Jian-jun, LEI Jia-qiang, LI Sheng-yu, et al. Disturbance of the inclined inserting-type sand fence to wind-sand flow fields and its sand control characteristics[J]. Aeolian Research, 2016, 21: 139-150. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2016.04.008 [9] CHENG Jian-jun, JIANG Fu-qiang, XUE Chun-xiao, et al. Characteristics of the disastrous wind-sand environment along railways in the gobi area of Xinjiang, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 102 (1): 344-354. [10] 辛国伟, 程建军, 王连, 等. 铁路沿线地表条件与风沙流场的互馈规律研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2016, 60 (9): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDBS201609005.htmXIN Guo-wei, CHENG Jian-jun, WANG Lian, et al. Research on the law of mutual feedback between ground surface condition and wind-sand field along the railway[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2016, 60 (9): 22-27. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDBS201609005.htm [11] 李凯崇, 薛春晓, 刘贺业, 等. 不同类型挡沙墙风沙防护机理的风洞实验研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2015, 32 (1): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2015.01.004LI Kai-chong, XUE Chun-xiao, LIU He-ye, et al. Wind tunnel test on sand-preventing mechanism of different kinds of sand-barriers[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2015, 32 (1): 17-21. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2015.01.004 [12] 钟卫, 刘涌江, 杨涛. 3种沙障防风固沙效益比较的风洞实验研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2008, 22 (6): 7-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2008.06.002ZHONG Wei, LIU Yong-jiang, YANG Tao. Wind tunnel test study on effect contrast of wind-breaking and sand-fixing of three sand-barriers[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 22 (6): 7-12. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2008.06.002 [13] 薄天利, 郑晓静. 防沙栅栏风洞实验的数值模拟[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 41 (5): 97-101. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0455-2059.2005.05.022BO Tian-li, ZHENG Xiao-jing. Numerical simulation on sand fence in wind tunnel experiment[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University: Natural Sciences, 2005, 41 (5): 97-101. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0455-2059.2005.05.022 [14] LI Bai-liang, SHERMAN D J. Aerodynamics and morphodynamics of sand fences: a review[J]. Aeolian Research, 2015, 17: 33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2014.11.005 [15] BRADLEY E F, MULHEARN P J. Development of velocity and shear stress distribution in the wake of a porous shelter fence[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1983, 15 (1-3): 145-156. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(83)90185-X [16] DONG Zhi-bao, LUO Wan-yin, QIAN Guang-qiang, et al. A wind tunnel simulation of the mean velocity fields behind upright porous fences[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2007, 146 (1): 82-93. [17] 程建军, 庞巧东. 戈壁强风区挡风构筑物限制下列车气动力学特性分析[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2013, 57 (1): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDBS201301002.htmCHENG Jian-jun, PANG Qiao-dong. Analysis on train aerodynamics characteristics under different types of windbreak structures at strong wind zone in gobi[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2013, 57 (1): 1-5. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDBS201301002.htm [18] 王康龙. 风沙流的双流体模型参数及输沙量分布特征研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2014.WANG Kang-long. Investigation of parameters in two-phase model for windblown sand movement and characteristic of mass flux distribution[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2014. (in Chinese). [19] 庞巧东, 刘建军, 程建军, 等. 戈壁铁路挡风墙背风侧涡流长度及积沙的研究[J]. 石河子大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 29 (5): 629-632. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7383.2011.05.021PANG Qiao-dong, LIU Jian-jun, CHENG Jian-jun, et al. The length of the vortex and aeolian sand of wind break walls in the gobi along railways[J]. Journal of Shihezi University: Natural Science, 2011, 29 (5): 629-632. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7383.2011.05.021 [20] 高永平, 钱伟平. 浅析兰新铁路防风工程[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2009, 23 (增): 48-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK2009S1014.htmGAO Yong-ping, QIAN Wei-ping. Analysis on windproof engineering of Lanzhou-Xinjiang Railway[J]. Resources Environment and Engineering, 2009, 23 (S): 48-51. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK2009S1014.htm [21] CHENG Jian-jun, LEI Jia-qiang, LI Sheng-yu, et al. Effect of hanging-type sand fence on characteristics of wind-sand flow fields[J]. Wind and Structures, 2016, 22 (5): 555-571. doi: 10.12989/was.2016.22.5.555 [22] 程建军, 蒋富强, 薛春晓, 等. 强风区铁路风沙防治工程最大输沙量与携沙风荷载计算方法[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2012, 33 (1): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201201001.htmCHENG Jian-jun, JIANG Fu-qiang, XUE Chun-xiao, et al. Computational method for maximum sediment discharge and sand-carrying wind load in the prevention and treatment of wind drift sand for railway in strong wind area[J]. China Railway Science, 2012, 33 (1): 1-5. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201201001.htm [23] 程建军, 蒋富强, 杨印海, 等. 戈壁铁路沿线风沙灾害特征与挡风沙措施及功效研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2010, 31 (5): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201005003.htmCHENG Jian-jun, JIANG Fu-qiang, YANG Yin-hai, et al. Study on the hazard characteristics of the drifting sand along the railway in gobi area and the efficacy of the control engineering measures[J]. China Railway Science, 2010, 31 (5): 15-20. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201005003.htm [24] 辛国伟, 程建军, 景文宏, 等. 来流廓线对风沙流场和风沙堆积影响的数值模拟——以挡沙墙为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33 (3): 672-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201603031.htmXIN Guo-wei, CHENG Jian-jun, JING Wen-hong, et al. Numerical simulation of the influence of incoming flow profile on sand flow field and aeolian sand deposition: a case study around sand retaining wall[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33 (3): 672-679. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201603031.htm [25] 薛春晓, 蒋富强, 程建军, 等. 兰新铁路百里风区挡沙墙防沙效益研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2011, 33 (4): 859-862. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201104025.htmXUE Chun-xiao, JIANG Fu-qiang, CHENG Jian-jun, et al. Research on sand preventing benefit of sand retaining wall in a strong wind sector along Lanzhou-Xinjiang Railway[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2011, 33 (4): 859-862. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201104025.htm -





 下载:
下载: