Fatigue damage characteristics of rib-to-deck weld root on orthotropic steel bridge deck
-
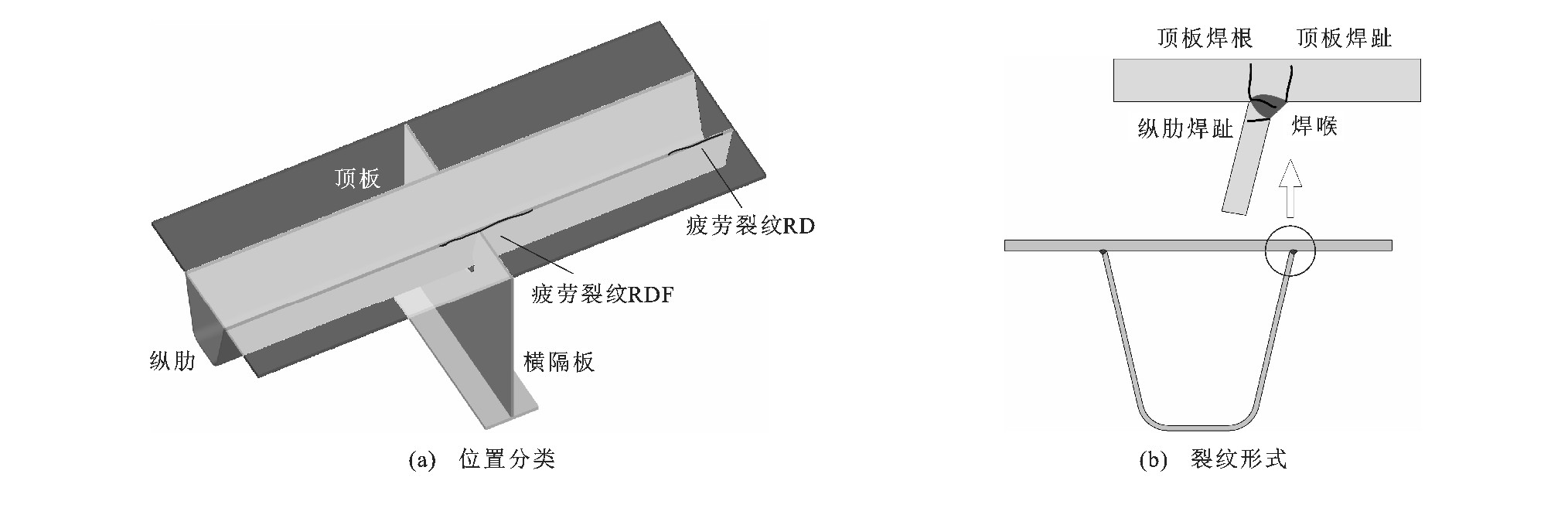
摘要: 针对闭口肋正交异性钢桥面板顶板焊根处疲劳裂纹处于纵肋内部, 不易发现与危害大等问题, 根据所处位置的不同, 将顶板焊根疲劳细节分为横隔板节间内(RD细节) 和跨横隔板截面(RDF细节) 2种类型, 采用有限元方法分析了2种细节的应力影响面, 考虑了轮迹横向概率分布、多轴轮载作用以及铺装与桥面板相互作用等影响, 研究了2种细节的疲劳损伤特征。分析结果表明: 当轮载作用于目标细节正上方时为最不利状态, 纵桥向轮载中心移至目标细节前后0.6m范围内应力较大, 横桥向2种细节的轮载影响均在1.0m范围内; 考虑轮迹横向分布影响, 简化计算时, RD、RDF细节的等效应力幅横向折减系数可以分别取0.92、0.96;在双、三联轴作用下, RD细节的损伤度分别是单轴荷载的2.10、3.21倍, 若近似采用单轴叠加, 所得损伤度可能偏于不安全, 建议寿命评估时考虑车辆类型影响; 计入铺装与桥面板相互作用后, 细节处应力幅明显降低, 顶板厚度为12mm的铺装模型焊根处应力幅几乎与16mm厚的钢桥面板相当, 且降低程度随铺装弹性模量的增大而增大; 对于45°扩散角简化铺装扩散模型, 当顶板厚度不小于16mm时, 其应力幅小于同时考虑铺装扩散作用与铺装刚度贡献的实体模型, 且差值随顶板厚度的增加而增大, 简化时需要考虑其适用范围, 否则会偏于不安全; 当顶板厚度为18mm且考虑铺装作用时, 2种细节疲劳寿命满足设计使用寿命要求, RDF细节疲劳寿命约为RD细节的67%, 较为不利。Abstract: For the problems that the root-deck fatigue cracks of orthotropic steel decks with closed ribs located inside ribs were invisible and greatly harmful, the deck root welding fatigue details were divided into RD details (rib-to-deck details) and RDF details (rib-to-deck details crossing floor beams) according to the connected locations of longitudinal ribs and deck, and the finite element method was applied to study the stress influence surfaces of two fatigue details.The transverse frequency distribution of wheelmark, multiaxial loads and pavement-deck interactionwere considered, and the damage characteristics of two fatigue details were analyzed.Analysis result shows that the target details are in the most unfavorable condition when the wheel is right above each of them.In the longitudinal direction, the stress is relatively higher when the distances of wheel load and target details are no more than 0.6 m.In the transverse direction, the wheel load influence ranges of two details are within 1.0 m.When the transverse distribution of wheelmark is considered, the transverse reduction coefficients of equivalent stress ranges of two details in simplified computation are 0.92 and 0.96, respectively.Under the dual-axle and tri-axle loads, the damages of RD details are 2.10 times and 3.21 times of the damage under single-axle load, respectively.It is unsafe to compute the damage by approximately adding the damage of each axis load, so it is suggested to consider vehicle type while assessing the fatigue life.The stress range of each detail obviously reduces when the pavement-deck interaction is considered, and the change will increase with the increase of elastic modulus of pavement.The stress range of deck with 12 mm thickness considering pavement is almost equal to the range of bare deck with 16 mm thickness at the welding root.For the simplified diffusion model of pavement with 45°dispersion angle, when the thickness of deck is no less than 16 mm, the stress range is simultaneously less than the range of soild model considering the contributions of diffusion and stiffness of pavement, and the difference increases with the increase of thickness of deck, so it is slightly risky to simplify the dispersion effect of pavement without considering its scope of application.When the thickness of deck is 18 mm and the contribution of pavement is considered, the fatigue lifes of two details can meet the design requirement of service life, and RDF details are about 67% of RD details in fatigue life.
-
Key words:
- bridge engineering /
- orthotropic steel bridge deck /
- deck /
- rib /
- root of weld joint /
- stress influence surface /
- fatigue life
-
表 1 应力影响面特征值
Table 1. Characteristic values of stress influence surfaces

表 2 轮迹横向分布对应力幅的影响
Table 2. Transverse distribution effect of wheelmarks on stress ranges

表 3 多轴轮载作用下等效应力幅
Table 3. Equivalent stress ranges under multiaxial wheel loads

表 4 桥面铺装参数
Table 4. Parameters of bridge deck pavement

表 5 虎门二桥疲劳荷载谱
Table 5. Fatigue load spectrums of Second Humen Bridge

表 6 疲劳寿命评估结果
Table 6. Evaluation result of fatigue life

-
[1] MADDOX S J. The fatigue behavior of trapezoidal stiffener to deck plate welds in orthotropic bridge decks[R]. Wokingham: Transport Research Laboratory, 1974. [2] YA S, YAMADA K, ISHIKAWA T. Fatigue durability of trough rib to deck plate welded detail of some orthotropic steel decks[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2010, 56A: 77-90. [3] XIAO Zhi-gang, YAMADA K, YA S, et al. Stress analyses and fatigue evaluation of rib-to-deck joints in steel orthotropic decks[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2008, 30 (8): 1387-1397. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.10.008 [4] 曾志斌. 正交异性钢桥面板典型疲劳裂纹分类及其原因分析[J]. 钢结构, 2011, 26 (2): 9-15, 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2011.02.003ZENG Zhi-bin. Classification and reasons of typical fatigue cracks in orthotropic steel deck[J]. Steel Construction, 2011, 26 (2): 9-15, 26. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2011.02.003 [5] MORI T, SHIGIHARA S, NAKAMURA H. Fatigue tests on welded connections between deck plate and trough rib in steel plate deck in consideration of weld penetration[J]. Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshuu A, 2006, 62 (3): 570-581. doi: 10.2208/jsceja.62.570 [6] TSAKOPOULOS P A, FISHER J W. Full-scale fatigue tests of steel orthotropic decks for the Williamsburg Bridge[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2003, 8 (5): 323-333. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2003)8:5(323) [7] SIM H B, UANG C M, SIKORSKY C. Effects of fabrication procedures on fatigue resistance of welded joints in steel orthotropic decks[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2009, 14 (5): 366-373. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2009)14:5(366) [8] 张允士, 李法雄, 熊锋, 等. 正交异性钢桥面板疲劳裂纹成因分析及控制[J]. 公路交通科技, 2013, 30 (8): 75-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2013.08.013ZHANG Yun-shi, LI Fa-xiong, XIONG Feng, et al. Cause analysis and control measures of fatigue cracks in orthotropic steel deck[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2013, 30 (8): 75-80. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2013.08.013 [9] AASHTO, AASHTO LRFD bridge design specifications (2005)[S]. [10] TSAKOPOULOS P A, FISHER J W. Full-scale fatigue tests of steel orthotropic deck panel for the Bronx-Whitestone Bridge rehabilitation[J]. Bridge Structures, 2005, 1 (1): 55-66. doi: 10.1080/15732480412331294704 [11] FISHER J W, BARSOM J M. Evaluation of cracking in the rib-to-deck welds of the Bronx-Whitestone Bridge[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21 (3): 04015065-1-10. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000823 [12] KAINUMA S, YANG Mu-ye, JEONG Young-soo, et al. Experimental investigation for structural parameter effects on fatigue behavior of rib-to-deck welded joints in orthotropic steel decks[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2017, 79: 520-537. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.04.028 [13] 唐亮, 黄李骥, 刘高, 等. 正交异性钢桥面板顶板贯穿型疲劳裂纹研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2012, 29 (2): 59-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2012.02.011TANG Liang, HUANG Li-ji, LIU Gao, et al. Research on fatigue cracks through deck-plate in orthotropic steel deck[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2012, 29 (2): 59-66. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2012.02.011 [14] 吉伯海, 陈祥, 刘荣, 等. 钢桥面板顶板与U肋接头疲劳效应分析[J]. 建筑钢结构进展, 2014, 16 (6): 56-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9379.2014.06.007JI Bo-hai, CHEN Xiang, LIU Rong, et al. A numerical study on the fatigue effect of trough-deck plate weld joint to steel bridge deck system[J]. Progress in Steel Building Structures, 2014, 16 (6): 56-62. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9379.2014.06.007 [15] 王春生, 翟慕赛, 唐友明, 等. 钢桥面板疲劳裂纹耦合扩展机理的数值断裂力学模拟[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30 (3): 82-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.009WANG Chun-sheng, ZHAI Mu-sai, TANG You-ming, et al. Numerical fracture mechanical simulation of fatigue crack coupled propagation mechanism for steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30 (3): 82-95. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.009 [16] 蒲黔辉, 高立强, 刘振标, 等. 基于热点应力法的正交异性钢桥面板疲劳验算[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2013, 48 (3): 395-401. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.03.001PU Qian-hui, GAO Li-qiang, LIU Zhen-biao, et al. fatigue assessment of orthotropic steel bridge deck based on hot spot stress method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48 (3): 395-401. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.03.001 [17] 王春生, 付炳宁, 张芹, 等. 正交异性钢桥面板足尺疲劳试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26 (2): 69-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2013.02.011WANG Chun-sheng, FU Bing-ning, ZHANG Qin, et al. Fatigue test on full-scale orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26 (2): 69-76. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2013.02.011 [18] 赵秋, 吴冲. U肋加劲板焊接残余应力数值模拟分析[J]. 工程力学, 2012, 29 (8): 262-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201208042.htmZHAO Qiu, WU Chong. Numerical analysis of welding residual stress of U-rib stiffened plate[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29 (8): 262-268. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201208042.htm [19] 卫星, 邹修兴, 姜苏, 等. 正交异性钢桥面肋-板焊接残余应力的数值模拟[J]. 桥梁建设, 2014, 44 (4): 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLJS201404005.htmWEI Xing, ZOU Xiu-xing, JIANG Su, et al. Numerical simulation of residual stress in rib-to-top plate welding of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. Bridge Construction, 2014, 44 (4): 27-33. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLJS201404005.htm [20] LIU Rong, JI Bo-hai, WANG Man-man, et al. Numerical evaluation of toe-deck fatigue in orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2015, 29 (6): 04014180-1-10. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0000677 [21] 黄卫. 大跨径桥梁钢桥面铺装设计[J]. 土木工程学报, 2007, 40 (9): 65-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200709012.htmHUANG Wei. Design of deck pavement for long-span steel bridges[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2007, 40 (9): 65-77. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200709012.htm [22] 陈磊磊, 钱振东. 基于简单性能试验的环氧沥青混合料动态模量研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2013, 16 (2): 341-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZCX201302031.htmCHEN Lei-lei, QIAN Zhen-dong. Study on dynamic modulus of epoxy asphalt mixture based on simple performance test[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2013, 16 (2): 341-344. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZCX201302031.htm [23] 吴冲, 刘海燕, 张志宏, 等. 桥面铺装温度对正交异性钢桥面板疲劳的影响[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 41 (8): 1213-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ201308017.htmWU Chong, LIU Hai-yan, ZHANG Zhi-hong, et al. Influence of pavements temperature on fatigue life of orthotropic deck of steel bridge[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2013, 41 (8): 1213-1218. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ201308017.htm [24] 傅中秋, 吉伯海, 王满满, 等. 考虑桥面铺装作用的正交异性钢桥面板应力幅分析[J]. 工业建筑, 2015, 45 (5): 143-145, 151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYJZ201505031.htmFU Zhong-qiu, JI Bo-hai, WANG Man-man, et al. Stress amplitude analysis of orthotropic steel bridge deck with pavement[J]. Industrial Construction, 2015, 45 (5): 143-145, 151. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYJZ201505031.htm [25] 中交公路规划设计院有限公司. 广东虎门二桥工可研究阶段公路桥梁车辆荷载专题研究[R]. 北京: 中交公路规划设计院有限公司, 2015.CCCC Highway Consultants Co., Ltd. Monographic study on highway bridge vehicle loads of the Second Humen Bridge in the project feasibility stage[R]. Beijing: CCCC Highway Consultants Co., Ltd., 2015. (in Chinese). [26] YA S, YAMADA K, ISHIKAWA T. Fatigue evaluation of rib-to-deck welded joints of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2011, 16 (4): 492-499. [27] 陈一馨, 吕彭民, 郭成军, 等. 钢桥面板U肋与盖板焊缝构造细节疲劳性能评估[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 34 (1): 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201401010.htmCHEN Yi-xin, LU Peng-min, GUO Cheng-jun. Study on fatigue performance of orthotropic steel bridge deck U-rib and cover weld structure[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2014, 34 (1): 49-55. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201401010.htm [28] FU Zhong-qiu, JI Bo-hai, ZHANG Cheng-yi, et al. Fatigue performance of roof and U-rib weld of orthotropic steel bridge deck with different penetration rates[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2017, 22 (6): 04017016-1-12. -





 下载:
下载: