Review of convolutional neural network and its application in intelligent transportation system
-
摘要: 从特征传输方式、空间维度、特征维度3个角度,论述了近年来卷积神经网络结构的改进方向,介绍了卷积层、池化层、激活函数、优化算法的工作原理,从基于值、等级、概率和转换域四大类总结了近年来池化方法的发展,给出了部分具有代表性的激活函数对比、梯度下降算法及其改进型和自适应优化算法的工作原理和特点;梳理了卷积神经网络在车牌识别、车型识别、交通标志识别、短时交通流预测等智能交通领域中的应用和国内外研究现状,并将卷积神经网络算法与支持向量机、差分整合移动平均回归模型、卡尔曼滤波、误差反向传播神经网络、长短时记忆网络算法从优势、劣势和在智能交通领域的主要应用场景三方面进行了对比;分析了卷积神经网络在智能交通领域面临的鲁棒性不佳和实时性较差等问题,并从算法优化、并行计算层面和有监督学习到无监督学习方向研判了卷积神经网络的发展趋势。研究结果表明:卷积神经网络在视觉领域具有较强优势,在智能交通系统中主要应用于交通标志、车牌、车型识别、交通事件检测、交通状态预测;相比其他算法,卷积神经网络所提取的特征更加全面,有效地提高了识别准确度与速度,具有较大的应用价值;卷积神经网络未来将通过网络结构的优化、算法的改进、算力的提升以及基准数据集的增强,为智能交通带来新的突破。Abstract: From the perspectives of feature transmission mode, spatial dimension and feature dimension, the improvement directions of convolution neural network structure in recent years were reviewed. The working principles of the convolution layer, pooling layer, activation function and optimization algorithm were introduced, and the recent developments of pooling methods in terms of value, level, probability, and transformation domain were summarized. The comparison of some representative activation functions, and the working principle and characteristics of the gradient descent algorithm and its improved and adaptive optimization algorithm were given. The application and research status of convolutional neural network in intelligent transportation fields such as license plate recognition, vehicle type recognition, traffic sign recognition, and short-term traffic flow prediction were reviewed. The convolutional neural network algorithm was compared with the support vector machine, differential integrated moving average regression model, Kalman filter, error back propagation neural network, and long-term and short-term memory network algorithms from the advantages and disadvantages and main application scenarios in the field of intelligent transportation. The issues of poor robustness and poor real-time performance of convolutional neural network in the field of intelligent transportation were analyzed. The development trend of convolutional neural network was evaluated in terms of algorithm optimization, parallel computing, and supervised learning to unsupervised learning. Research results show that the convolutional neural network has strong advantages in the field of vision. It is mainly used for traffic sign, license plate, vehicle type recognition, traffic event detection, and traffic state prediction in intelligent transportation system. Compared with other algorithms, the convolutional neural network can extract more comprehensive features. It can effectively improve the recognition accuracy and speed and has great application value. The convolutional neural network will bring new breakthroughs to intelligent transportation in the future through the optimization of network structure, the improvement of algorithm and computing power, and the enhancement of benchmark data sets. 5 tabs, 3 figs, 146 refs.
-
表 1 基于空间维度、特征维度、特征传输方式的网络结构
Table 1. Network structure based on spatial dimensions, characteristic dimensions, and characteristic transmission methods
分类标准 方法 代表性网络 空间维度 (1)用多个小卷积核代替大卷积核 VGGNet[24] (2)多尺度非线性,单一尺寸卷积核用多尺寸卷积核代替,使用1×1卷积核 Inception系列[25, 28-30] (3)固定形状卷积核趋于使用可变形卷积核 可变形卷积网络[31] (4)空洞卷积 FCN[32] (5)反卷积 ZFNet[23] 特征维度 (1)深度可分离卷积,每个通道使用不同卷积操作 Xception[33] (2)使用分组卷积 AlexNet[17] (3)分组卷积前对通道随机分组 ShuffleNet[34] (4)通道加权计算 SE-Net[35] 特征传输方式 (1)使用跳跃连接,让模型更深 ResNet[26] (2)密集连接,使每一层都融合上其他层的特征输出 DenseNet[27] 表 2 基于值、等级、概率和转换域的池化方法
Table 2. Pooling methods based on values, rank, probabilities and transformed domains
分类标准 代表性方法 基于值的池化方法 基于显著性特征 最大池化[47]、平均池化[48]、混合池化[50]、全局平均池化[51]、跳跃池化[52]、空间金字塔池化[53]、内核池化[54]、动态相关池化[55]、多激活池化[56]、联合池化[57]、细节保留池化[58]、同心圆池化[59] 基于补丁 补丁子类池化[60]、系列多池化[61]、部分平均池化[62] 多采样方法 多采样棋盘池化[63]、并行网格池化[64] 基于等级的池化方法 多级池化[65]、顺序池化[66]、全局加权排名池化[67] 基于排名的平均池化[68]、基于排名的加权合并池化[68]、基于等级的随机池化[68] 基于概率的池化方法 随机空间采样池化[69]、混合池化[70]、随机池化[71] 丢弃最大池化[72]、稀疏随机池化[73] 基于转换域的池化方法 基于时域的池化[74]、基于频域的池化[75]、基于小波域的池化[76] 表 3 部分具有代表性的激活函数对比
Table 3. Contrast of some representative activation functions
激活函数 数学表达形式 优点 缺点 Sigmoid $ {f_1}(x) = \frac{1}{{1 + {{\rm{e}}^{ - x}}}}$ 具有连续可微分性的特征,曾是激活函数的最优选择 不具有稀疏特性,容易梯度弥散,不关于原点对称,收敛速度较慢,且计算复杂 Tanh ${f_2}(x) = \frac{{{{\rm{e}}^x}{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{e}}^{ - x}}}}{{{{\rm{e}}^x} + {{\rm{e}}^{ - x}}}} $ 关于原点对称,比Sigmoid函数收敛速度快 无法解决梯度弥散的问题,且计算复杂 ReLU[87] f3(x)=max{0, x} 解决了梯度弥散问题,收敛速度快,更加接近生物神经元的激活模型[89],且计算简单 稀疏性过强,易出现神经元死亡现象[90] Softplus[88] f4(x)=ln(1+ex) 避免ReLU强制性稀疏的缺点,对全部数据进行非线性映射,避免有价值的信息丢失 欠缺对样本模型的表达能力,收敛速度较慢 Maxout[91] $\begin{array}{l} {f_5}(x) = \mathop {max\;{s_{qg}}}\limits_{g \in [1,G]} \\ {s_{qg}} = \sum\limits_{q = 1}^N {{w_{qg}}{x_q} + {v_g}} \; \end{array} $ 克服了ReLU的缺点 增加了参数量[92] ELU[93] ${f_6}(x) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {x\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;x > 0}\\ {{\alpha _6}({{\rm{e}}^x} - 1)\;\;x \le 0} \end{array}} \right. $ 缓解神经元死亡现象,具有一定抗干扰能力,输出均值接近于0,收敛速度更快 会发生梯度弥散,计算复杂 Leaky ReLU[94] ${f_7}(x) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {x\;\;\;\;\;x > 0}\\ {{\alpha _7}x\;\;x \le 0} \end{array}} \right. $ 缓解ReLU的神经元死亡现象,具有一定稀疏性 欠缺对样本模型的表达能力,需调整超参数α PReLU[95] ${f_8}(x) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {x\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;x > 0}\\ {{\alpha _8}(x)\;\;x \le 0} \end{array}} \right. $ 继承了Leaky ReLU的优点,且较Leaky ReLU效果更好 欠缺对样本模型的表达能力,需调整超参数α,模型训练难度有所提高 SeLU[96] $\begin{array}{l} {f_9}(x) = \lambda \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {x\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;x > 0}\\ {{\alpha _9}{{\rm{e}}^x} - {\alpha _9}\;\;x \le 0} \end{array}} \right.\\ {\alpha _9} \approx 1.6733,\lambda \approx 1.0507 \end{array} $ 确保训练过程中梯度不会爆炸或消失,自动将样本分布归一化到0均值和单位方差 表 4 优化算法类别
Table 4. Classification of optimization algorithms
表 5 卷积神经网络与其他ITS常用算法对比
Table 5. Comparison among convolutional neural network and other ITS common algorithms
算法名称 算法优势 算法劣势 应用方向 卷积神经网络(CNN) 自主学习进行特征提取、分类,识别率高 训练数据集庞大、对硬件要求较高 交通标志识别、车牌识别、车型识别、交通事件检测、交通状态预测 支持向量机(SVM) 可以解决高维数据和非线性问题 处理多分类问题以及数据量较大时效果不佳、核函数参数确定困难 交通标志识别 差分整合移动平均回归模型(Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Model,ARIMA) 模型体量较小,便于计算 时间序列需要稳定、非线性问题预测性能差、对数据敏感、数据不可缺失稀疏 客流量预测等回归问题 卡尔曼滤波(Kalman Filtering) 非线性问题处理性能佳、精度高 计算量大、模型复杂、易受噪声数据干扰 客流量预测、交通标志识别 误差反向传播神经网络(Back Propagation Feed-Forward Neural Network, BPNN) 模型收敛较快,数据的内部规律不需深入了解 随机初始化权值参数、易陷入局部最优 客流量预测、交通状态判别 长短时记忆网络(Long Short-Term Memory Networks, LSTM) 很好地利用了数据中心的时间特征、鲁棒性较强 训练数据集庞大、对数据敏感、数据不可缺失稀疏、结构复杂、收敛速度较慢 客流量预测等回归问题 -
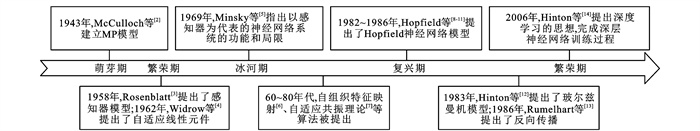
[1] 周飞燕, 金林鹏, 董军. 卷积神经网络研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40(6): 1229-1251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201706001.htmZHOU Fei-yan, JIN Lin-peng, DONG Jun. Review of convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(6): 1229-1251. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201706001.htm [2] MCCULLOCH W S, PITTS W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 1943, 5: 115-133. doi: 10.1007/BF02478259 [3] ROSENBLATT F. The perceptron: a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain[J]. Psychological Review, 1958, 65(6): 386-408. doi: 10.1037/h0042519 [4] WIDROW B, HOFF M E. Associative storage and retrieval of digital information in networks of adaptive "neurons"[J]. Biological Prototypes and Synthetic Systems, 1962: 160-166. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-1716-6_25 [5] MINSKY M L, PAPERT S A. Perceptrons[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1969. [6] KOHONEN T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1982, 43: 59-69. doi: 10.1007/BF00337288 [7] CARPENTER G A, GROSSBERG S. The ART of adaptive pattern recognition by a self-organizing neural network[J]. IEEE Computer, 1988, 21(3): 77-88. doi: 10.1109/2.33 [8] HOPFIELD J J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1982, 79(8): 2554-2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2554 [9] HOPFIELD J J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1984, 81(10): 3088-3092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3088 [10] HOPFIELD J J, TANK D W. "Neural" computation of decisions in optimization problems[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1985, 52: 141-152. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10000046381 [11] HOPFIELD J J, TANK D. Computing with neural circuits: a model[J]. Science, 1986, 233(4764): 625-633. doi: 10.1126/science.3755256 [12] HINTON G E, SEJNOWSKI T J. Optimal perceptual inference[C]//IEEE. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. New York: IEEE, 1983: 448-453. [13] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323: 533-536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [14] HINTON G E, SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [15] BENGIO Y, LAMBLIN P, DAN P, et al. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks[C]//NeurIPS. 20th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. San Diego: NeurIPS, 2006: 153-160. [16] VINCENT P, LAROCHELLE H, LAJOIE I, et al. Stacked denoising autoencoders: learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11: 3371-3408. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1953039 [17] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [18] 张晓男, 钟兴, 朱瑞飞, 等. 基于集成卷积神经网络的遥感影像场景分类[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1128001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201811042.htmZHANG Xiao-nan, ZHONG Xing, ZHU Rui-fei, et al. Scene classification of remote sensing images based on integrated convolutional neural networks[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(11): 1128001. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201811042.htm [19] LECUN Y L, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [20] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database[C]//IEEE. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2009: 248-255. [21] HUBEL D H, WIESEL T N. Receptive fields binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex[J]. Journal of Physiology, 1962, 160: 106-154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837 [22] FUKUSHIMA K. Neocognitron: a self- organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1980, 36: 193-202. doi: 10.1007/BF00344251 [23] ZEILER M D, FERGUS R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]//Springer. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 818-833. [24] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//ICLR. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2015: 1-14. [25] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yang-qing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//IEEE. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-9. [26] HE Kai-ming, ZHANG Xiang-yu, REN Shao-qing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. [27] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2017: 2261-2269. [28] IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//ICML. 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. San Diego: ICML, 2015: 448-456. [29] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 2818-2826. [30] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]//AAAI. Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2017: 4278-4284. [31] DAI Ji-feng, QI Hao-zhi, XIONG Yue-wen, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2017: 764-773. [32] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640-651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [33] CHOLLET F. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 1800-1807. [34] ZHANG Xiang-yu, ZHOU Xin-yu, LIN Meng-xiao, et al. ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]//IEEE. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 6848-6856. [35] HU Jie, SHEN Lin, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011-2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [36] 高鑫, 李慧, 张义, 等. 基于可变形卷积神经网络的遥感影像密集区域车辆检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(12): 2812-2819. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201812003.htmGAO Xin, LI Hui, ZHANG Yi, et al. Vehicle detection in remote sensing images of dense areas based on deformable convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2018, 40(12): 2812-2819. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201812003.htm [37] YU F, KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[C]//ICLR. 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2016: 1-13. [38] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs[C]//ICLR. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2015: 1-14. [39] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [40] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2017, DOI: arXiv:1706.05587. [41] CHEN L C, ZHU Y K, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]//Springer. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 833-851. [42] KAIMING H, GEORGIA G, PIOTR D, et al. Mask R-CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 386-397. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2844175 [43] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [44] LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Hai-fang, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//IEEE. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 8759-8768. [45] HUANG Zhao-jin, HUANG Li-chao, GONG Yong-chao, et al. Mask scoring R-CNN[C]//IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2019: 6402-6411. [46] SARIGUL M, OZYILDIRIM B M, AVCI M. Differential convolutional neural network[J]. Neural Networks, 2019, 116: 279-287. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.04.025 [47] ZEILER M D, FERGUS R. Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks[C]//ICLR. 1st International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2013: 1-9. [48] FEI Jian-chao, FANG Hu-sheng, YIN Qin, et al. Restricted stochastic pooling for convolutional neural network[C]//ACM. 10th International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service. New York: ACM, 2018: 1-4. [49] AKHTAR N, RAGAVENDRAN U. Interpretation of intelligence in CNN-pooling processes: a methodological survey[J]. Neural Computing and Application, 2020, 32(3): 879-898. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04296-5 [50] YU D, WANG H, CHEN P, et al. Mixed pooling for convolutional neural networks[C]//Springer. 9th International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 364-375. [51] LIN Min, CHEN Qiang, YAN Shui-cheng. Network in network[C]//ICLR. 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2014: 1-10. [52] SUN Man-li, SONG Zhan-jie, JIANG Xiao-heng, et al. Learning pooling for convolutional neural network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 224: 96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.10.049 [53] HE Kai-ming, ZHANG Xiang-yu, REN Shao-qing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [54] CUI Yin, ZHOU Feng, WANG Jiang, et al. Kernel pooling for convolutional neural networks[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2017: 3049-3058. [55] CHEN Jun-feng, HUA Zhou-dong, WANG Jing-yu, et al. A convolutional neural network with dynamic correlation pooling[C]//IEEE. 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (CIS). New York: IEEE, 2017: 496-499. [56] ZHAO Qi, LYU Shu-chang, ZHANG Bo-xue, et al. Multiactivation pooling method in convolutional neural networks for image recognition[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018, 2018: 8196906. doi: 10.1155/2018/8196906 [57] ZHANG Jian-ming, HUANG Qian-qian, WU Hong-lin, et al. A shallow network with combined pooling for fast traffic sign recognition[J]. Information, 2017, 8(2): 45. doi: 10.3390/info8020045 [58] SAEEDAN F, WEBER N, GOESELE M, et al. Detail- preserving pooling in deep networks[C]//IEEE. 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 9108-9116. [59] QI Kun-lun, GUAN Qing-feng, YANG Chao, et al. Concentric circle pooling in deep convolutional networks for remote sensing scene classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 934. doi: 10.3390/rs10060934 [60] LONG Yang, ZHU Fan, SHAO Ling, et al. Face recognition with a small occluded training set using spatial and statistical pooling[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 430/431: 634-644. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.042 [61] WANG Feng, HUANG Si-wei, SHI Lei, et al. The application of series multi-pooling convolutional neural networks for medical image segmentation[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2017, 13(12): 1-10. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/322033622_The_application_of_series_multi-pooling_convolutional_neural_networks_for_medical_image_segmentation [62] ZHI Tian-cheng, DUAN Ling-yu, WANG Yi-tong, et al. Two-stage pooling of deep convolutional features for image retrieval[C]//IEEE. 23rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. New York: IEEE, 2016: 2465-2469. [63] SADIGH S, SEN P. Improving the resolution of CNN feature maps efficiently with multisampling[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2018, DOI: arXiv:1805.10766. [64] TAKEKI A, IKAMI D, IRIE G, et al. Parallel grid pooling for data augmentation[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2018, DOI: arXiv:1803.11370. [65] SHAHRIARI A, PORIKLI F. Multipartite pooling for deep convolutional neural networks[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2017, DOI: arXiv:1710.07435. [66] KUMAR A. Ordinal pooling networks: for preserving information over shrinking feature maps[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2018, DOI: arXiv:1804.02702. [67] KOLESNIKOV A, LAMPERT C H. Seed, expand and constrain: three principles for weakly- supervised image segmentation[C]// Springer. 21st ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 695-711. [68] SHI Zeng-lin, YE Yang-ding, WU Yun-peng. Rank-based pooling for deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2016, 83: 21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2016.07.003 [69] ZHAI Shuang-fei, WU Hui, KUMAR A, et al. S3Pool: pooling with stochastic spatial sampling[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2017: 4003-4011. [70] TONG Zhi-qiang, AIHARA K, TANAKA G. A hybrid pooling method for convolutional neural networks[C]//Springer. International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 454-461. [71] TURAGA S C, MURRAY J F, JAIN V, et al. Convolutional networks can learn to generate affinity graphs for image segmentation[J]. Neural Computation, 2010, 22(2): 511-538. doi: 10.1162/neco.2009.10-08-881 [72] WU Hai-bing, GU Xiao-dong. Max-pooling dropout for regularization of convolutional neural networks[C]//Springer. 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 46-54. [73] SONG Zhen-hua, LIU Yan, SONG Rong, et al. A sparsity-based stochastic pooling mechanism for deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2018, 105: 340-345. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.05.015 [74] WANG P, LI W, GAO Z, et al. Depth pooling based large-scale 3D action recognition with convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(5): 1051-1061. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2818329 [75] RIPPEL O, SNOEK J, ADAMS R P. Spectral representations for convolutional neural networks[C]//NeurIPS. 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. San Diego: NeurIPS, 2015: 2449-2457. [76] WILLIAMS T, LI R. Wavelet pooling for convolutional neural networks[C]//ICLR. 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2018: 1-12. [77] SAINATH T N, KINGSBURY B, MOHAMED A R, et al. Improvements to deep convolutional neural networks for LVCSR[C]//IEEE. 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding. New York: IEEE, 2013: 315-320. [78] 白琮, 黄玲, 陈佳楠, 等. 面向大规模图像分类的深度卷积神经网络优化[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(4): 1029-1038. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB201804012.htmBAI Cong, HUANG Ling, CHEN Jia-nan, et al. Optimization of deep convolutional neural network for large scale image classification[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(4): 1029-1038. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB201804012.htm [79] EOM H, CHOI H. Alpha—integration pooling for convolutional neural networks[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2018, DOI: arXiv:1811.03436. [80] 刘万军, 梁雪剑, 曲海成. 不同池化模型的卷积神经网络学习性能研究[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2016, 21(9): 1178-1190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB201609007.htmLIU Wan-jun, LIANG Xue-jian, QU Hai-cheng. Learning performance of convolutional neural networks with different pooling models[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2016, 21(9): 1178-1190. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB201609007.htm [81] ZHANG Bo-xue, ZHAO Qi, FENG Wen-quan, et al. AlphaMEX: a smarter global pooling method for convolutional neural networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 321: 36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.07.079 [82] JOSE A, LOPEZ R D, HEISTERKLAUS I, et al. Pyramid pooling of convolutional feature maps for image retrieval[C]//IEEE. 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. New York: IEEE, 2018: 480-484. [83] WAIBEL A, HANAZAWA T, HINTON G, et al. Phoneme recognition using time-delay neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(3): 328-339. doi: 10.1109/29.21701 [84] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [85] WANG Ze-long, LAN Qiang, HUANG Da-fei, et al. Combining FFT and spectral-pooling for efficient convolution neural network model[C]//Advances in Intelligent Systems Research. 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Engineering. Paris: Atlantis Press, 2016: 203-206. [86] SMITH J S, WILAMOWSKI B M. Discrete cosine transform spectral pooling layers for convolutional neural networks[C]//Springer. 17th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 235-246. [87] NAIR V, HINTON G E. Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines[C]//ICML. 27th International Conference on Machine Learning. San Diego: ICML, 2010: 807-814. [88] GLOROT X, BORDES A, BENGIO Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 15: 315-323. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/319770387_Deep_Sparse_Rectifier_Neural_Networks [89] LI Y, DING P, LI B. Training neural networks by using power linear units (PoLUs)[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2018, DOI: arXiv:1802.00212. [90] DOLEZEL P, SKRABABEK P, GAGO L. Weight initialization possibilities for feed forward neural network with linear saturated activation functions[J]. IFAC—Papers on Line, 2016, 49(25): 49-54. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405896316326453 [91] GOODFELLOW I J, WARDE-FARLEY D, MIRZA M, et al. Maxout networks[C]//ICML. 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. San Diego: ICML, 2013: 2356-2364. [92] CASTANEDA G, MORRIS P, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M. Evaluation of maxout activations in deep learning across several big data domains[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2019, DOI: 10.1186/s40537-019-0233-0. [93] CLEVERT D A, UNTERTHINER T, HOCHREITER S. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (ELUs)[C]//ICLR. 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2016: 1-14. [94] MAAS A L, HANNUN A Y, NG A Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[C]//ACM. 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2013: 456-462. [95] HE Kai-ming, ZHANG Xiang-yu, REN Shao-qing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]//IEEE. 15th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2015: 1026-1034. [96] KLAMBAUER G, UNTERTHINER T, MAYR A, et al. Self-normalizing neural networks[C]//NeurIPS. 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. San Diego: NeurIPS, 2017: 972-981. [97] 杨观赐, 杨静, 李少波, 等. 基于Dopout与ADAM优化器的改进CNN算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(7): 122-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201807023.htmYANG Guan-ci, YANG Jing, LI Shao-bo, et al. Modified CNN algorithm based on Dropout and ADAM optimizer[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(7): 122-127. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201807023.htm [98] KINGMA D P, BA J L. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]//ICLR. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2015: 1-15. [99] ROBBINS H, MONRO S. A stochastic approximation method[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1951, 22(3): 400-407. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177729586 [100] 石琪. 基于卷积神经网络图像分类优化算法的研究与验证[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2017.SHI Qi. Research and verification of image classification optimization algorithm based on convolutional neural network[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017. (in Chinese) [101] 王红霞, 周家奇, 辜承昊, 等. 用于图像分类的卷积神经网络中激活函数的设计[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2019, 53(7): 1363-1373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201907016.htmWANG Hong-xia, ZHOU Jia-qi, GU Cheng-hao, et al. Design of activation function in CNN for image classification[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2019, 53(7): 1363-1373. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201907016.htm [102] POLYAK B T. Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods[J]. USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics, 1964, 4(5): 1-17. doi: 10.1016/0041-5553(64)90137-5 [103] SUTSKEVER I, MARTENS J, DAHL G, et al. On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning[C]// ACM. 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2013: 2176-2184. [104] DUCHI J, HAZAN E, SINGER Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2121-2159. http://web.stanford.edu/~jduchi/projects/DuchiHaSi10.html [105] ZEILER M D. Adadelta: an adaptive learning rate method[J]. ArXiv E-Print, 2012, DOI: arXiv:1212.5701. [106] JI Shi-hao, VISHWANATHAN S V N, SATISH N, et al. BlackOut: speeding up recurrent neural network language models with very large vocabularies[C]//ICLR. 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2016: 1-4. [107] LOUIZOS C, WELLING M, KINGMA D P. Learning sparse neural networks through L0 regularization[C]//ICLR. 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2018: 1-13. [108] DOZAT T. Incorporating nesterov momentum into adam[C]//ICLR. 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2016: 1-4. [109] LUO Liang-chao, XIONG Yuan-hao, LIU Yan, et al. Adaptive gradient methods with dynamic bound of learning rate[C]//ICLR. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations. La Jolla: ICLR, 2019: 1-19. [110] WANG Di, TIAN Yu-min, GENG Wen-hui, et al. LPR-Net: recognizing Chinese license plate in complex environments[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 130: 148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2018.09.026 [111] 李祥鹏, 闵卫东, 韩清, 等. 基于深度学习的车牌定位和识别方法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(6): 979-987. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201906014.htmLI Xiang-peng, MIN Wei-dong, HAN Qing, et al. License plate location and recognition based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(6): 979-987. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201906014.htm [112] LIN Hui, WANG Peng, YOU Chun-hua, et al. Reading car license plates using deep neural networks[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2018, 72: 14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2018.02.002 [113] XIANG Han, ZHAO Yong, YUAN Yu-le, et al. Lightweight fully convolutional network for license plate detection[J]. Optik, 2019, 178: 1185-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.10.098 [114] ASIF M R, QI Chun, WANG Tie-xiang, et al. License plate detection for multi-national vehicles: an illumination invariant approach in multi-lane environment[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2019, 78: 132-147. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2019.07.012 [115] PUARUNGROJ W, BOONSIRISUMPUN N. Thai license plate recognition based on deep learning[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 135: 214-221. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.08.168 [116] CAO Yu, FU Hui-yuan, MA Hua-dong. An end-to-end neural network for multi-line license plate recognition[C]//IEEE. 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 3698-3703. [117] 赵汉理, 刘俊如, 姜磊, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的双行车牌分割算法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(8): 1320-1329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201908007.htmZHAO Han-li, LIU Jun-ru, JIANG Lei, et al. Double-row license plate segmentation with convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(8): 1320-1329. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201908007.htm [118] 张秀玲, 张逞逞, 周凯旋. 基于感兴趣区域的CNN-Squeeze交通标志图像识别[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2019, 19(3): 48-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT201903008.htmZHANG Xiu-ling, ZHANG Cheng-cheng, ZHOU Kai-xuan. Traffic sign image recognition via CNN-Squeeze based on region of interest[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2019, 19(3): 48-53. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT201903008.htm [119] 王方石, 王坚, 李兵, 等. 基于深度属性学习的交通标志检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 319-329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201801039.htmWANG Fang-shi, WANG Jian, LI Bing, et al. Deep attribute learning based traffic sign detection[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(1): 319-329. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201801039.htm [120] 李旭东, 张建明, 谢志鹏, 等. 基于三尺度嵌套残差结构的交通标志快速检测算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(5): 1022-1036. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ202005011.htmLI Xu-dong, ZHANG Jian-ming, XIE Zhi-peng, et al. A fast traffic sign detection algorithm based on three-scale nested residual structures[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(5): 1022-1036. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ202005011.htm [121] 宋青松, 张超, 田正鑫, 等. 基于多尺度卷积神经网络的交通标志识别[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(8): 131-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX201808018.htmSONG Qing-song, ZHANG Chao, TIAN Zheng-xin, et al. Traffic sign recognition based on multi-scale convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 45(8): 131-137. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX201808018.htm [122] 孙伟, 杜宏吉, 张小瑞, 等. 基于CNN多层特征和ELM的交通标志识别[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2018, 47(3): 343-349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.03.004SUN Wei, DU Hong-ji, ZHANG Xiao-rui. et al. Traffic sign recognition method based on multi-layer feature CNN and extreme learning machine[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018, 47(3): 343-349. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2018.03.004 [123] 张淑芳, 朱彤. 基于残差单发多框检测器模型的交通标志检测与识别[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2019, 53(5): 940-949. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201905015.htmZHANG Shu-fang, ZHU Tong. Traffic sign detection and recognition based on residual single shot multibox detector model[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2019, 53(5): 940-949. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201905015.htm [124] LIU Zhi-gang, LI Dong-yu, GE Shu-zhi, et al. Small traffic sign detection from large image[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2020, 50(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1007/s10489-019-01511-7 [125] 张建明, 王伟, 陆朝铨, 等. 基于压缩卷积神经网络的交通标志分类算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(1): 103-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201901019.htmZHANG Jian-ming, WANG Wei, LU Chao-quan, et al. Traffic sign classification algorithm based on compressed convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(1): 103-108. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201901019.htm [126] SONG Shi-jin, QUE Zhi-qiang, HOU Jun-jie, et al. An efficient convolutional neural network for small traffic sign detection[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2019, 97: 269-277. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2019.01.012 [127] ZHANG Qiang, ZHOU Li, LI Jia-feng, et al. Vehicle color recognition using multiple-layer feature representations of lightweight convolutional neural network[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 147(7): 146-153. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=c838aa91d4c92e3df3fe0f0f55425b12 [128] FU Hui-yuan, MA Hua-dong, WANG Gao-ya, et al. MCFF-CNN: multiscale comprehensive feature fusion convolutional neural network for vehicle color recognition based on residual learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 395: 178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.02.111 [129] LI Su-hao, LIN Jin-zhao, LI Guo-quan, et al. Vehicle type detection based on deep learning in traffic scene[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 131: 564-572. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.04.281 [130] HU Bin, LAI Jian-huang, GUO Chun-chao. Location-aware fine-grained vehicle type recognition using multi-task deep networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 243: 60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.085 [131] XIANG Ye, FU Ying, HUANG Hua. Global relative position space based pooling for fine-grained vehicle recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 367: 287-298. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.098 [132] 余烨, 傅云翔, 杨昌东, 等. 基于FR-ResNet的车辆型号精细识别研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(5): 1125-1136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202105014.htmYU Ye, FU Yun-xiang, YANG Chang-dong, et al. Fine-grained car model recognition based on FR-ResNet[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(5): 1125-1136. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202105014.htm [133] 杨娟, 曹浩宇, 汪荣贵, 等. 基于语义DCNN特征融合的细粒度车型识别模型[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(1): 141-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201901018.htmYANG Juan, CAO Hao-yu, WANG Rong-gui, et al. Fine-grained car recognition model based on semantic DCNN features fusion[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(1): 141-157. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201901018.htm [134] 蒋行国, 万今朝, 蔡晓东, 等. 奇异值分解与中心度量的细粒度车型识别算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(3): 82-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD201903019.htmJIANG Xing-guo, WAN Jin-zhao, CAI Xiao-dong, et al. Algorithm for identification of fine-grained vehicles based on singular value decomposition and central metric[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(3): 82-88. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD201903019.htm [135] 杨娟, 曹浩宇, 汪荣贵, 等. 区域建议网络的细粒度车型识别[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(6): 837-845. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB201806006.htmYANG Juan, CAO Hao-yu, WANG Rong-gui, et al. Fine-grained car recognition method based on region proposal networks[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(6): 837-845. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB201806006.htm [136] 罗文慧, 董宝田, 王泽胜. 基于CNN-SVR混合深度学习模型的短时交通流预测[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2017, 17(5): 68-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT201705010.htmLUO Wen-hui, DONG Bao-tian, WANG Ze-sheng. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on CNN-SVR hybrid deep learning model[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2017, 17(5): 68-74. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT201705010.htm [137] 石敏, 蔡少委, 易清明. 基于空洞-稠密网络的交通拥堵预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2021, 55(2): 124-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT202102003.htmSHI Min, CAI Shao-wei, YI Qing-ming. A traffic congestion prediction model based on dilated-dense network[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(2): 124-130. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT202102003.htm [138] DENG Shao-jiang, JIA Shu-yuan, CHEN Jing. Exploring spatial-temporal relations via deep convolutional neural networks for traffic flow prediction with incomplete data[J]. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 2019, 78: 712-721. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.09.040 [139] AN Ji-yao, FU Li, HU Meng, et al. A novel fuzzy-based convolutional neural network method to traffic flow prediction with uncertain traffic accident information[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 12: 2169-3536. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8639012/ [140] HAN Dong-xiao, CHEN Juan, SUN Jian. A parallel spatiotemporal deep learning network for highway traffic flow forecasting[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2019, 15(2): 1-12. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/331379923_A_parallel_spatiotemporal_deep_learning_network_for_highway_traffic_flow_forecasting [141] ZHANG Wei-bin, YU Ying-hao, QI Yong, et al. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on spatio-temporal analysis and CNN deep learning[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2019, 15(2): 1688-1711. doi: 10.1080/23249935.2019.1637966 [142] GUO Sheng-nan, LIN You-fang, FENG Ning, et al. Attention based spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks for traffic flow forecasting[C]//AAAI. 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2019: 922-929. [143] WU Yuan-kai, TAN Hua-chun, QIN Ling-qiao, et al. A hybrid deep learning based traffic flow prediction method and its understanding[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 90: 166-180. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=d7a038c4f0d3776bcead726010596c60 [144] 赵海涛, 程慧玲, 丁仪, 等. 基于深度学习的车联边缘网络交通事故风险预测算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 50-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX202001006.htmZHAO Hai-tao, CHENG Hui-ling, DING Yi, et al. Research on traffic accident risk prediction algorithm of edge internet of vehicles based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 50-57. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX202001006.htm [145] 朱虎明, 李佩, 焦李成, 等. 深度神经网络并行化研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(8): 1861-1881. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201808011.htmZHU Hu-ming, LI Pei, JIAO Li-cheng, et al. Review of parallel deep neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(8): 1861-1881. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX201808011.htm [146] CHETLUR S, WOOLLEY C, VANDERMERSCH P, et al. cuDNN: efficient primitives for deep learning[J]. arXiv e-Print, 2012, DOI: arXiv:1410.0759. -





 下载:
下载: