Distribution of emergency medical supplies in cities under major public health emergency
-
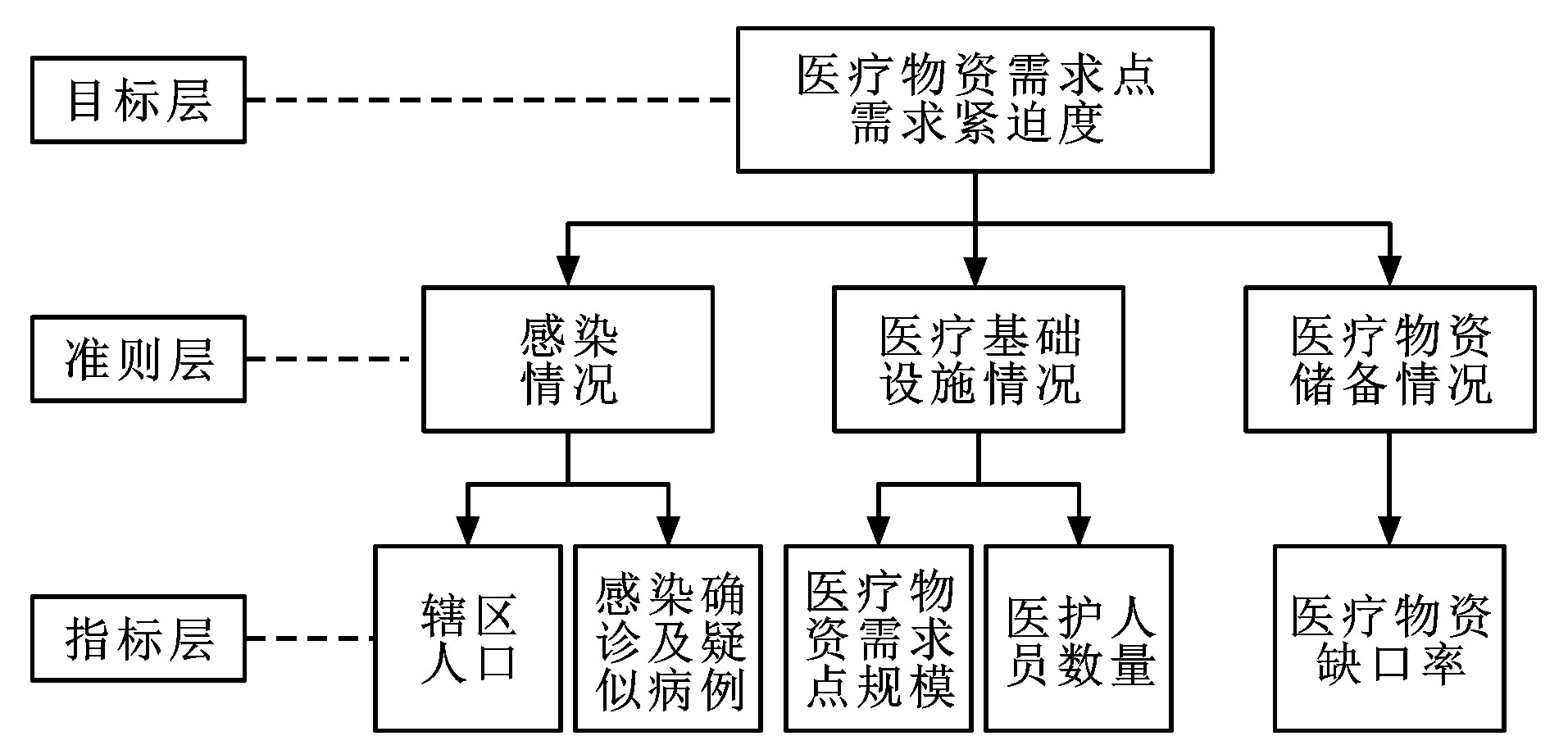
摘要: 为了在发生重大突发公共卫生事件时提高城市医疗物资的应急救援效率, 减少人员伤亡与经济损失, 在分析重大突发公共卫生事件特点与应急物流特征的基础上, 将需求紧迫度作为配送影响因素, 提出以辖区人口、感染确诊及疑似病例、医疗物资需求点规模、医护人员数量和医疗物资缺口率为评价指标的医疗物资需求点需求紧迫度评价指标体系; 针对医疗物资应急物流的特点, 调整医疗物资配送时间窗参数, 建立由车辆行驶成本、配送延误惩罚成本和无配送延误补贴费用组成的总配送费用函数, 并考虑配送车辆载重、配送时间窗、医疗物资需求紧迫度等约束条件, 构建使总配送费用最少与需求紧迫度高的需求点优先配送的双重目标, 优化了医疗物资的配送路径; 依托SPSS、Yaahp和MATLAB软件平台, 结合算例, 利用层次分析法与遗传算法求解考虑与不考虑需求紧迫度的医疗物资应急物流配送路径优化模型。研究结果表明: 重大突发公共卫生事件下, 相对于不考虑需求紧迫度的配送路径, 考虑需求紧迫度的最优配送路径不仅对需求紧迫度较高的医疗物资需求点进行优先配送, 同时还使总配送费用减少了5.8%;需求紧迫度的引入能极大地改善调度的盲目性, 基于配送车辆载重、配送时间窗、医疗物资需求紧迫度等约束条件所构建的双目标优化模型能够有效地提高应急救援效率和减少不必要的调度成本。Abstract: To improve the emergency rescue efficiency of medical supplies and reduce the casualties and economic losses in cities under the major public health emergency, based on the characteristics analyses of major public health emergencies and emergency logistics, the demand urgency was taken as the influencing factor of distribution. The evaluation index system for medical supplies demand points was proposed with the evaluation indexes of population within jurisdictions, confirmed and suspected cases of infection, scale of medical supplies demand point, number of medical staff and gap rate of medical supplies. According to the characteristics of emergency logistics of medical supplies, the time window parameters of medical supplies distribution were adjusted. The total distribution cost function composed of driving cost, penalty cost of distribution delay and subsidy without distribution delay was established. Considering the constraints of vehicle load, distribution time window, and demand urgency of medical supplies, a dual objective of priority distribution for demand points with the minimum total distribution cost and high demand urgency was constructed to optimize the distribution path of medical supplies. Relying on the software platforms of SPSS, Yaahp and MATLAB, and combining with examples, the analytic hierarchy process and genetic algorithm were used to solve the optimization models of emergency logistics distribution path of medical supplies with and without the consideration of demand urgency. Research result shows that under the major public health emergency, the optimal distribution path considering the demand urgency not only gives priority to the medical supplies demand points with higher demand urgency, but also reduces the total distribution cost by 5.8%, comparing with the distribution path without the consideration of demand urgency. The introduction of demand urgency can greatly reduce the blindness of scheduling. The dual objective optimization model restrained by the conditions of vehicle load, distribution time window and demand urgency of medical supplies can effectively improve the emergency rescue efficiency and reduce unnecessary scheduling costs.
-
表 1 各医疗物资需求点信息
Table 1. Information of each medical supplies demand point
需求紧迫度评价指标 辖区人口/万人 感染确诊及疑似病例/人 医疗物资需求点规模/m2 医护人员数量/人 医疗物资缺口率/% 需求点1 1 5 417 10 611 67 40 需求点2 64 268 63 739 90 80 需求点3 144 3 417 35 375 77 70 需求点4 155 3 525 88 078 60 60 需求点5 31 5 801 61 251 90 10 需求点6 13 4 275 20 956 76 30 表 2 各医疗物资需求点标准化信息
Table 2. Standardized information of each medical supplies demand point
需求紧迫度评价指标 辖区人口标准化值 感染确诊及疑似病例标准化值 医疗物资需求点规模标准化值 医护人员数量标准化值 医疗物资缺口率标准化值 需求点1 0.00 0.93 0.00 0.21 0.43 需求点2 0.41 0.00 0.69 0.99 1.00 需求点3 0.93 0.57 0.32 0.57 0.86 需求点4 1.00 0.59 1.00 0.00 0.71 需求点5 0.19 1.00 0.65 0.96 0.00 需求点6 0.08 0.72 0.13 0.55 0.29 表 3 指标得分
Table 3. Scores of indexes
评价指标 辖区人口 确诊及疑似病例 医疗物资需求点规模 医护人员数量 医疗物资缺口率 辖区人口 1 1 4 3 1 确诊及疑似病例 1 1 4 3 1 医疗物资需求点规模 1/4 1/4 1 1 1/5 医护人员数量 1/3 1/3 1 1 1/4 医疗物资缺口率 1 1 5 4 1 表 4 医疗物资需求点参数
Table 4. Medical supplies demand points parameters
参数 物资配送中心0 需求点1 需求点2 需求点3 需求点4 需求点5 需求点6 医疗物资需求/单位质量 0.0 4.0 3.0 1.5 4.5 1.5 2.0 最晚配送时间/h 10 000.0 2.3 0.8 2.5 2.0 2.3 2.3 各需求点相对需求紧迫度 1.00 1.10 1.50 2.06 2.00 1.25 1.00 表 5 其他参数设置
Table 5. Other parameter settings
参数 取值 车辆额定载质量/单位质量 8 延误时单位时间惩罚成本/单位费用 60 无配送延误时单位补贴费用/单位费用 120 车辆单位时间的行驶成本/单位费用 200 表 6 各医疗物资需求点最短距离
Table 6. Minimum distances of each medical supplies demand point
h 需求点 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 0.00 2.00 1.80 2.00 1.50 1.20 0.80 1 2.00 0.00 1.50 1.40 1.80 1.50 1.50 2 1.80 1.50 0.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 3 2.00 1.40 2.00 0.00 1.00 2.00 1.00 4 1.50 1.80 2.00 1.00 0.00 1.50 0.80 5 1.20 1.50 2.00 2.00 1.50 0.00 1.30 6 0.80 1.50 2.00 1.00 0.80 1.30 0.00 表 7 考虑与不考虑需求紧迫度的配送路线
Table 7. Distribution routes considering demand urgency or not
求解结果 考虑需求紧迫度 不考虑需求紧迫度 配送路线1 0-2-1-0 0-1-2-0 配送路线2 0-4-3-6-0 0-6-3-4-0 配送路线3 0-5-0 0-5-0 总配送费用/单位费用 1 732.8 1 840.8 -
[1] 赵飞, 傅承主, 矫涌本, 等. 国内外突发公共卫生事件应急指挥系统建设研究[J]. 中国卫生信息管理杂志, 2012, 9(2): 25-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5166.2012.02.006ZHAO Fei, FU Cheng-zhu, JIAO Yong-ben, et al. Study on the construction of emergency command system for public health emergencies at home and abroad[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Informatics and Management, 2012, 9(2): 25-29. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5166.2012.02.006 [2] 叶冬青, 查震球. 我国突发公共卫生事件的新特点与应对新策略[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2009, 13(1): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ200901002.htmYE Dong-qing, ZHA Zhen-qiu. New characteristics of public health emergencies in China and new strategies to deal with them[J]. Chinese Journal of Disease Control and Prevention, 2009, 13(1): 1-3. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBKZ200901002.htm [3] 黄运夏, 吴广谋, 李骥. 基于Holon的应急物流系统研究[J]. 物流科技, 2009, 24(3): 42-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3100.2009.03.014HUANG Yun-xia, WU Guang-mou, LI Ji. A model of the emergency logistics system based on Holon[J]. Logistics Sci-Tech, 2009, 24(3): 42-44. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3100.2009.03.014 [4] 李菲. 化解公共危机的应急物流研究[J]. 交通企业管理, 2009(2): 53-54. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1006-8864.2009.02.027LI Fei. Urgent logistic study in solving public crisis[J]. Transportation Enterprise Management, 2009(2): 53-54. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1006-8864.2009.02.027 [5] 陈倬. 基于脆弱性分析的城市物流系统安全性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2007.CHEN Zhuo. Security of city logistics system based on vulnerability analysis[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese). [6] CARTER W N. Natural disasters[J]. The Macedon Digest, 1994, 9(4): 32-33. [7] BOMPADRE A, DROR M, ORLIN J B. Improved bounds for vehicle routing solutions[J]. Discrete Optimization, 2006, 3(4): 299-316. doi: 10.1016/j.disopt.2006.04.002 [8] THOMAS A. Supply chain reliability for contingency operations[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium. New York: IEEE, 2002: 61-67. [9] SHAHPARVARI S, ABBASI B. Robust stochastic vehicle routing and scheduling for bushfire emergency evacuation: an Australian case study[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2017, 104: 32-49. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2017.04.036 [10] MORENO A, ALEM D, FERREIRA D. Heuristic approaches for the multiperiod location-transportation problem with reuse of vehicles in emergency logistics[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 2016, 69: 79-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2015.12.002 [11] BALCIK B. Site selection and vehicle routing for post-disaster rapid needs assessment[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2017, 101: 30-58. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2017.01.002 [12] SAKURABA C S, SANTOS A C, PRINS C, et al. Road network emergency accessibility planning after a major earthquake[J]. Euro Journal on Computational Optimization, 2016, 4: 1-22. doi: 10.1007/s13675-016-0064-0 [13] BRUNI M E, BERALDI P, KHODAPARASTI S. A fast heuristic for routing in post-disaster humanitarian relief logistics[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2018, 30: 304-313. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2018.09.033 [14] BOUCHRA B, BTISSAM D, MOHAMMAD C. A hybrid genetic algorithm for the static and dynamic vehicle routing problem with soft time windows[C]//IEEE. The 3rd International Conference on Logistics Operations Management. New York: IEEE, 2016: 1-9. [15] 李创. 国内外应急物流研究综述[J]. 华东经济管理, 2013, 27(6): 166-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDJJ201306032.htmLI Chuang. Review on domestic and foreign research on emergency logistics[J]. East China Economic Management, 2013, 27(6): 166-171. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDJJ201306032.htm [16] 王宗喜. 大力推进应急物流建设与发展[J]. 中国流通经济, 2009(24): 37-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGLT200907006.htmWANG Zong-xi. Vigorously promoting construction and development of emergency logistics[J]. China Business and Market, 2009(24): 37-39. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGLT200907006.htm [17] 邹志云, 宋程, 虢向阳. 基于灰色理论的应急物流最优路径选择[J]. 物流技术, 2007, 27(1): 46-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLJS200801016.htmZOU Zhi-yun, SONG Cheng, GUO Xiang-yang. How to select the optimal emergent logistics route based on grey theory[J]. Logistics Technology, 2007, 27(1): 46-48. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLJS200801016.htm [18] 程碧荣, 赵晓波, 秦进. 考虑供应不足的应急物流车辆路径优化模型及算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2016, 33(6): 1682-1685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.06.018CHENG Bi-rong, ZHAO Xiao-bo, QIN Jin. Optimization model and algorithm of emergency vehicle route with insufficiency supply[J]. Computer Application Research, 2016, 33(6): 1682-1685. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.06.018 [19] HUANG Xiao-xia, SONG Li-ying. An emergency logistics distribution routing model for unexpected events[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2018, 269(6): 1-17. [20] 宋英华, 艾艳芳, 王喆, 等. 考虑商业物流资源的应急物流定位-分配问题模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(11): 157-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201611032.htmSONG Ying-hua, AI Yan-fang, WANG Zhe, et al. Research on LAP model of emergency logistics considering commercial logistics resources[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(11): 157-162. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201611032.htm [21] 杨郑. 考虑需求紧迫度的应急物流车辆路径问题研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018.YANG Zheng. Research on vehicle routing problem of emergency logistics considering the demand urgency[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2018. (in Chinese). [22] 崔岩, 张子祥, 时新, 等. 考虑顾客时间紧迫度的生鲜电商配送路径优化问题[J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版), 2017, 38(6): 59-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZGY201706012.htmCUI Yan, ZHANG Zi-xiang, SHI Xin, et al. Fresh agricultural product e-commerce distribution routing problem considering time demand of customer[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2017, 38(6): 59-63. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZGY201706012.htm [23] 张玉州, 徐廷政, 郑军帅, 等. 考虑紧急度的救灾车辆路径问题建模与优化[J]. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(8): 2444-2449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201908043.htmZHANG Yu-zhou, XU Ting-zheng, ZHENG Jun-shuai, et al. Modeling and optimization of disaster relief vehicle routing problem considering urgency[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(8): 2444-2449. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201908043.htm [24] 黄敏芳, 刘敬, 郭琼. 带时间窗的电动汽车物流配送车辆路径问题研究[J]. 物流技术, 2019, 38(5): 66-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLJS201905018.htmHUANG Min-fang, LIU Jing, GUO Qiong. Research on routing problem of electric distribution vehicles with time window[J]. Logistics Technology, 2019, 38(5): 66-72. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLJS201905018.htm [25] 李珍萍, 张煜炜. 带时间窗和服务顺序约束的多需求车辆路径问题[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(7): 1565-1570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201907032.htmLI Zhen-ping, ZHANG Yu-wei. Multiple demands vehicle routing problem with time windows and service order constraints[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(7): 1565-1570. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201907032.htm [26] 胡大伟, 陈希琼, 高扬. 定位-路径问题综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2018, 18(2): 111-129. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201801011HU Da-wei, CHEN Xi-qiong, GAO Yang. Review on location-routing problem[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2018, 18(2): 111-129. (in Chinese). http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201801011 [27] 曲冲冲, 王晶, 黄钧, 等. 考虑时效与公平性的震后应急物资动态配送优化研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2018, 26(6): 178-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGK201806018.htmQU Chong-chong, WANG Jing, HUANG Jun, et al. Study on optimization of dynamic distribution of emergency materials after earthquake considering timeliness and fairness[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2018, 26(6): 178-187. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGK201806018.htm [28] 王婧, 王海军. 应急救援中应急物资需求紧迫性分级研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2013, 49(5): 4-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201305003.htmWANG Jing, WANG Hai-jun. Gradation for demand urgency of emergency materials in emergency relief[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2013, 49(5): 4-7. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201305003.htm [29] 郭金玉, 张忠彬, 孙庆云. 层次分析法的研究与应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2008, 18(5): 148-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK200805026.htmGUO Jin-yu, ZHANG Zhong-bin, SUN Qing-yun. Study and applications of analytic hierarchy process[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2008, 18(5): 148-153. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK200805026.htm [30] 赵诗奎. 基于遗传算法的柔性资源调度优化方法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013.ZHAO Shi-kui. Research on the optimization method for flexible resource scheduling based on genetic algorithm[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013. (in Chinese). [31] 王正武, 陈涛, 宋名群. 同时接送模式下响应型接驳公交运行路径与调度的协调优化[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2019, 19(5): 139-149. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201905014WANG Zheng-wu, CHEN Tao, SONG Ming-qun. Coordinated optimization of operation routes and schedules for responsive feeder transit under simultaneous pick-up and delivery mode[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2019, 19(5): 139-149. (in Chinese). http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201905014 [32] 张铃, 张钹. 遗传算法机理的研究[J]. 软件学报, 2000, 11(7): 945-952. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB200007011.htmZHANG Ling, ZHANG Ba. Differentiated services for the internet based on dynamic buffer thresholds[J]. Journal of Software, 2000, 11(7): 945-952. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJXB200007011.htm [33] 余朝军, 江驹, 徐海燕, 等. 基于改进遗传算法的航班-登机口分配多目标优化[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(2): 121-130. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.010YU Chao-jun, JIANG Ju, XU Hai-yan, et al. Multi-objective optimization of flight-gate assignment based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(2): 121-130. (in Chinese). doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.010 [34] HU Hui, HE Jing, HE Xiong-fei, et al. Emergency material scheduling optimization model and algorithms: a review[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2019, 6(5): 441-454. -





 下载:
下载: