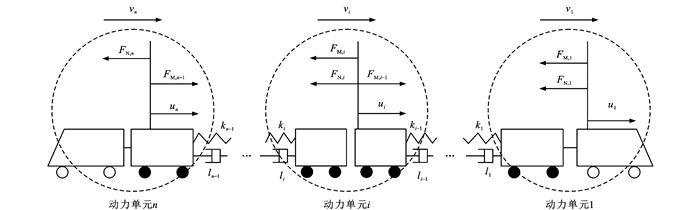
-
摘要: 为了提高列控系统跟踪精度与平稳运行,提出了一种改进的多输入多输出(MIMO)无模型自适应控制(MFAC)方法;基于动态线性化技术,将系统各动力单元输入输出数据等效成更符合高速动车组实际运行特性的全格式动态线性化(FFDL)数据模型;通过在目标准则函数中加入输出误差率,并对输出误差和输出误差率进行加权融合,推导出新的带有输出误差率的无模型自适应控制(MFAC-OER)方案;通过对FFDL数据模型的外界扰动、参数误差等不确定项进行延时估计,进一步提升了算法的控制性能和对系统的等价描述程度;以实验室配备的CRH380A型动车组半实物试验平台对该方法进行仿真测试,使其跟踪济南—徐州的实际速度-位移曲线,并与传统算法进行对比。仿真结果表明:通过MFAC-OER方法得到的动车组各动力单元速度误差为[-0.151, 0.136] km·h-1,控制力和加速度分别在[-48, 42] kN和[-0.785, 0.687] m·s-2以内且变化平稳,控制性能优于比例积分微分方法和传统MFAC方法;整体仿真结果证明了MFAC-OER方法不仅能快速到达系统稳态并且具有良好的抗外界干扰特性,满足动车组跟踪精度与安全要求。Abstract: To improve the tracking accuracy and stable operation of the train control system, an improved multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) model-free adaptive control (MFAC) method was proposed. Based on the dynamic linearization technology, the input-output data of each power unit of the system were equivalently transformed into a full form dynamic linearization (FFDL) data model that better fitted the actual operation characteristics of high-speed electric multiple units (EMUs). By incorporating the output error rates into the objective criterion function and weighting the fusion of output errors and output error rates, a new model-free adaptive control scheme with output error rates (MFAC-OER) was derived. The control performance of the algorithm and the equivalent description degree of the system were further improved by delayed estimation of uncertainty factors, such as external disturbances and parameter errors in the FFDL data model. The proposed method was simulated and tested on a CRH380A high-speed EMUs semi-physical test platform equipped in the laboratory to track the actual speed-displacement curve from Jinan to Xuzhou and compare it with some traditional algorithms. Simulation results show that the speed errors of each power unit of EMUs obtained by the MFAC-OER method are within [-0.151, 0.136] km·h-1, with the control force and acceleration smoothly varying in the ranges of [-48, 42] kN and [-0.785, 0.687] m·s-2, respectively. The proposed method outperforms the proportional-integral-derivative (PID) and traditional MFAC methods in the control performance. The overall simulation results show that the MFAC-OER method can not only quickly reach the steady state of the system but also possesses good resistance to external disturbances, meeting the tracking accuracy and safety requirements of the EMUs.
-
表 1 CRH380A型动车组模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters of CRH380A EMUs
参数 数值 动力单元1质量/kg 1.836×105 动力单元2质量/kg 1.123×105 动力单元3质量/kg 1.836×105 列车阻力系数ai/(N·kg-1) 5.2 列车阻力系数bi/[N·s2·(kg·m)-1] 3.6×10-2 列车阻力系数ci/[N·s2·(kg·m2)-1] 1.2×10-3 车钩弹性系数ki/(N·m-1) 2.0×107 车钩阻尼系数li/(N·s·m-1) 5.0×106 表 2 正常运行时各个控制方法的性能指标
Table 2. Performance indexes of each control method in normal operation
参数 MSE IAE MA MFAC-OER方法 0.048 317 0.785 MFAC方法 0.156 918 0.825 PID方法 0.374 1 812 0.906 表 3 参数突变时各个控制方法的性能指标
Table 3. Performance indexes of each control method in case of parameter mutation
s 方法 PID方法 MFAC方法 MFAC-OER方法 上升时间 6 4 2 调节时间 55 27 13 -
[1] 李中奇, 周靓, 杨辉, 等. 基于预测控制的动车组迭代学习控制方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(1): 280-290. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.01.021LI Zhong-qi, ZHOU Liang, YANG Hui, et al. Iterative learning control method for EMUs based on predictive control[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(1): 280-290. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.01.021 [2] ZHANG Kun-peng, JIANG Bin, CHEN Fu-yang. Multiple-model based diagnosis of multiple faults with high speed train applications using second level adaptation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(7): 6257-6266. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2994867 [3] YUAN Han, HUANG De-qing, LI Xue-fang. Adaptive speed tracking control for high speed trains under stochastic operation environments[J]. Automatica, 2023, 147: 110674. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110674 [4] CHEN Yao, DONG Hai-rong, LU Jin-hu, et al. A super- twisting-like algorithm and its application to train operation control with optimal utilization of adhesion force[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(11): 3035-3044. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2539361 [5] 李中奇, 丁俊英, 杨辉, 等. 基于控制器匹配的高速列车广义预测控制方法[J]. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(9): 82-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201809013.htmLI Zhong-qi, DING Jun-ying, YANG Hui, et al. Generalized predictive control tuning for high-speed train based on controller matching method[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(9): 82-89. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201809013.htm [6] 贾超. 考虑安全约束的列车自动驾驶多质点非线性预测控制[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020.JIA Chao. Nonlinear predictive control for automatic train operation with consideration of safety constraints and multi-point model[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese) [7] 徐传芳, 陈希有, 郑祥, 等. 基于动态面方法的高速列车蠕滑速度跟踪控制[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(2): 41-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202002006.htmXU Chuan-fang, CHEN Xi-you, ZHENG Xiang, et al. Slip velocity tracking control of high-speed train using dynamic surface method[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(2): 41-49. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202002006.htm [8] 杨杰, 陈昱圻, 王盼盼. 基于改进粒子群算法的列车速度跟踪自抗扰控制器设计[J]. 铁道学报, 2021, 43(7): 40-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202107006.htmYANG Jie, CHEN Yu-qi, WANG Pan-pan. Design of active disturbance rejection controller for train speed tracking based on improved particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2021, 43(7): 40-46. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202107006.htm [9] YANG Hui, FU Ya-ting, WANG Dian-hui. Multi-ANFIS model based synchronous tracking control of high-speed electric multiple unit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(3): 1472-1484. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2725819 [10] 杨辉, 张芳, 张坤鹏, 等. 基于分布式模型的动车组预测控制方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 1912-1921. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201411027.htmYANG Hui, ZHANG Fang, ZHANG Kun-peng, et al. Predictive control using a distributed model for electric multiple unit[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 1912-1921. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201411027.htm [11] ZHOU Liang, LI Zhong-qi, YANG Hui, et al. Data-driven model-free adaptive sliding mode control based on FFDL for electric multiple units[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(21): 10983. doi: 10.3390/app122110983 [12] HOU Zhong-sheng, JIN Shang-tai. A novel data-driven control approach for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2011, 19(6): 1549-1558. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2010.2093136 [13] MA Yong-sheng, CHE Wei-wei, DENG Chao, et al. Distributed model-free adaptive control for learning nonlinear MASs under DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(3): 1146-1155. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3104978 [14] MA Yong-sheng, CHE Wei-wei, DENG Chao. Dynamic event- triggered model-free adaptive control for nonlinear CPSs under aperiodic DoS attacks[J]. Information Sciences, 2022, 589: 790-801. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.01.009 [15] LIN C J, LAI C C, HSIA K H, et al. Apply model-free adaptive control approach for mobile robot path following[J]. Journal of Robotics, Networking and Artificial Life, 2020, 7(3): 190-193. doi: 10.2991/jrnal.k.200909.010 [16] WANG Huai-zhen, FANG Li-jin, SONG Tang-zhong, et al. Model-free adaptive sliding mode control with adjustable funnel boundary for robot manipulators with uncertainties[J]. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(6): 065101. doi: 10.1063/5.0037054 [17] LIU Shi-da, HOU Zhong-sheng, ZHANG Xin, et al. Model-free adaptive control method for a class of unknown MIMO systems with measurement noise and application to quadrotor aircraft[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2020, 14(15): 2084-2096. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2020.0073 [18] 潘晓龙, 鲜斌. 小型无人直升机的无模型自适应鲁棒控制设计[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2017, 34(9): 1171-1178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201709006.htmPAN Xiao-long, XIAN Bin. Model-free adaptive robust control design for a small unmanned helicopter[J]. Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 34(9): 1171-1178. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201709006.htm [19] 石卫师. 基于无模型自适应控制的城轨列车自动驾驶研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2016, 38(3): 72-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201603014.htmSHI Wei-shi. Research on automatic train operation based on model-free adaptive control[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38(3): 72-77. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201603014.htm [20] WANG Hao-jun, HOU Zhong-sheng, JIN Shang-tai. Model-free adaptive fault-tolerant control for multiple point-mass subway trains with speed and traction/braking force constraints[J]. IFAC PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(2): 3916-3921. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.2239 [21] 李中奇, 周靓, 杨辉. 高速动车组数据驱动无模型自适应控制方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 437-447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202401015.htmLI Zhong-qi, ZHOU Liang, YANG Hui. Data-driven model-free adaptive control method for high-speed electric multiple unit[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 437-447. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202401015.htm [22] WANG Hao-jun, HOU Zhong-sheng. Model-free adaptive fault-tolerant control for subway trains with speed and traction/braking force constraints[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2020, 14(12): 1557-1566. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2019.1161 [23] 王海, 刘根锋, 侯忠生. 高速列车数据驱动无模型自适应容错控制[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(5): 1127-1136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC202205004.htmWANG Hai, LIU Gen-feng, HOU Zhong-sheng. Data-driven model-free adaptive fault tolerant control for high-speed trains[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(5): 1127-1136. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC202205004.htm [24] XIONG Shuang-shuang, HOU Zhong-sheng. Model-free adaptive control for unknown MIMO nonaffine nonlinear discrete-time systems with experimental validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(4): 1727-1739. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3043711 [25] HOU Zhong-sheng, XIONG Shuang-shuang. On model-free adaptive control and its stability analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4555-4569. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2894586 [26] DONG Na, LYU Wen-jin, ZHU Shuo, et al. Model-free adaptive nonlinear control of the absorption refrigeration system[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, 107(2): 1623-1635. doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-06964-5 [27] XU Qing-song. Digital integral terminal sliding mode predictive control of piezoelectric-driven motion system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(6): 3976-3984. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2504343 [28] 李中奇, 周靓, 杨辉. 高速动车组数据驱动无模型自适应积分滑模预测控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(1): 194-210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202401015.htmLI Zhong-qi, ZHOU Liang, YANG Hui. Data-driven model-free adaptive integral sliding mode predictive control for high-speed electric multiple unit[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 194-210. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202401015.htm [29] 王龙生. 基于多质点模型的高速列车自动驾驶预测控制[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2016.WANG Long-sheng. Predictive control for automatic operation of high-speed trains based on multi-point model[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese) [30] ZHOU Liang, LI Zhong-qi, YANG Hui, et al. Adaptive terminal sliding mode control for high-speed EMU: a MIMO data-driven approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, DOI: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3373037. -





 下载:
下载: