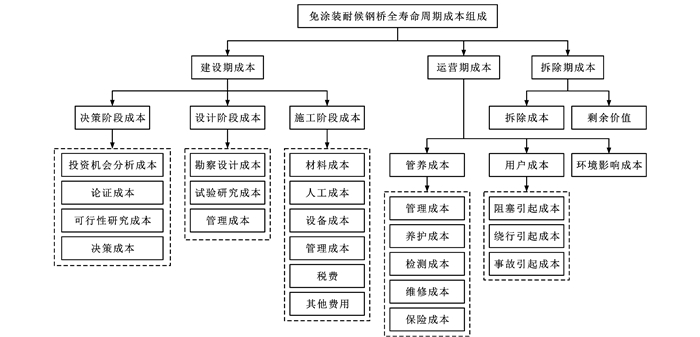
-
摘要: 基于桥梁全寿命周期成本分析理论,系统归纳了长寿命耐候钢桥各阶段成本组成特点,明确了长寿命耐候钢桥全寿命周期经济性评估内容与特征参数,给出了长寿命耐候钢桥成本计算基本假设;从免涂装耐候钢桥与涂装钢桥成本差异出发,对比分析了2种钢桥建设阶段、运营阶段成本计算方法,建立了长寿命耐候钢桥全寿命周期经济性评估模型;以中国3座长寿命免涂装耐候钢组合梁桥为例,计算了长寿命耐候钢桥全寿命周期各阶段成本,明确了涂装、维护方案对长寿命耐候钢桥全寿命周期成本经济性的参数化影响,分析了长寿命免涂装耐候钢桥全寿命周期成本经济性优势。研究结果表明: 免涂装耐候钢桥与涂装钢桥成本差异主要体现在钢材与焊接材料价格、锈层检测成本、涂装维护成本与由此产生的环境及用户成本;与4种涂装钢桥相比,免涂装耐候钢桥全寿命周期成本减少11%~21%,在全寿命周期具有显著的经济性优势;水洗周期对成本具有显著影响,水洗周期从每6年1次增加到每年1次时,增加成本占全寿命周期成本差比的5%~11%;当免涂装耐候钢桥涂装面积达70%左右时,其全寿命周期成本大于涂装钢桥。长寿命耐候钢桥全寿命周期经济性评估模型可为桥梁方案设计与技术经济性比选提供依据,从而促进长寿命耐候钢桥的推广应用。Abstract: Based on the life-cycle cost analysis theory of bridges, the cost characteristics of long lasting weathering steel bridges at different stages were systematically summarized, and the contents and characteristic parameters of the life-cycle economic evaluation of long lasting weathering steel bridges were clarified. Also, the basic assumptions for cost calculation of long lasting weathering steel bridges were provided. Two cost calculation methods at construction and operation stages were analyzed by comparing the cost difference between uncoated weathering steel bridges and coated steel bridges, and a life-cycle economic evaluation model of long lasting weathering steel bridges was established. Three long lasting uncoated weathering steel composite bridges in China were taken as examples to calculate the life-cycle cost of bridges at each stage. The economic parametric influence of coating and maintenance methods on the life-cycle cost of long lasting weathering steel bridges was clarified, and the economic advantage of the life-cycle cost of long lasting uncoated weathering steel bridges was analyzed. Research results show that the cost difference between uncoated weathering steel bridges and coated steel bridges mainly lies in the prices of steel and welding materials, patina detection cost, coating maintenance cost, and resulting environmental and user cost. Compared with four coated steel bridges, the cost of uncoated weathering steel bridges reduces by 11%-21% in the life-cycle, and they have significant economic advantages throughout the life-cycle. Washing cycle has a significant influence on cost that increases by 5%-11% throughout the life-cycle when the cycle changes from once every six years to once every year. When the coating area of uncoated weathering steel bridges reaches about 70%, their life-cycle costs are greater than that of coated steel bridges. The life-cycle economic evaluation model of long lasting weathering steel bridges can provide a basis for bridge scheme design and analysis of techno-economic cost performance, which will promote the promotion and application of long lasting weathering steel bridges.
-
表 1 对比方案参数
Table 1. Comparison scheme parameters
方案 涂装体系 涂装一般维修周期/年 涂装一般维修次数 涂装大维修周期/年 涂装大维修次数 100年 150年 200年 100年 150年 200年 1 免涂装耐候钢桥 2 第5套(溶剂型): 特制环氧富锌防锈底漆-80 μm,棕红云铁环氧中间漆-40 μm,灰铝粉石墨醇酸面漆-70 μm 5.0 16 24 32 25 4 6 8 3 第6套(溶剂型): 特制环氧富锌防锈底漆-80 μm,棕红云铁环氧中间漆-40 μm,灰色丙烯酸脂肪族聚氨酯面漆-70 μm 12.5 4 6 8 25 4 6 8 4 第7套(溶剂型): 特制环氧富锌防锈底漆-80 μm,棕红云铁环氧中间漆-40 μm,氟碳面漆-60 μm 25 4 6 8 5 第7套(水性): 特制环氧富锌防锈底漆-80 μm,棕红云铁环氧中间漆-40 μm,氟碳面漆-60 μm 25 4 6 8 表 2 全寿命周期成本
Table 2. Life-cycle cost
设计使用年限/年 方案1 方案2 方案3 方案4 方案5 100 150 200 100 150 200 100 150 200 100 150 200 100 150 200 眉县常兴二号桥 建设阶段/万元 654.3 654.3 654.3 646.2 646.2 646.2 649.6 649.6 649.6 665.2 665.2 665.2 709.6 709.6 709.6 运营阶段/万元 5.7 5.8 5.8 201.8 210.4 212.3 100.8 105.1 106.1 67.2 70.0 70.7 132.1 137.7 139.0 全寿命周期/万元 660.0 660.1 660.1 848.0 856.6 858.5 750.5 754.7 755.7 732.4 735.3 735.9 841.7 847.3 848.6 成本差比/% 28.5 29.8 30.1 13.7 14.3 14.5 11.0 11.4 11.5 27.5 28.4 28.6 黄延高速K16+ 322.607跨线桥 建设阶段/万元 158.8 158.8 158.8 157.1 157.1 157.1 157.6 157.6 157.6 160.2 160.2 160.2 167.6 167.6 167.6 运营阶段/万元 1.7 1.7 1.8 35.7 37.2 37.6 18.6 19.4 19.6 14.6 15.2 15.3 23.7 24.7 24.9 全寿命周期/万元 160.5 160.5 160.5 192.8 194.3 194.6 176.2 177.0 177.2 174.8 175.4 175.6 191.3 192.3 192.6 成本差比/% 20.1 21.0 21.2 9.8 10.3 10.4 8.9 9.3 9.4 19.2 19.8 20.0 黄延高速K18+ 496.141跨线桥 建设阶段/万元 144.8 144.8 144.8 143.1 143.1 143.1 143.7 143.7 143.7 146.3 146.3 146.3 153.7 153.7 153.7 运营阶段/万元 1.6 1.7 1.7 35.3 36.8 37.1 18.1 18.9 19.1 14.1 14.7 14.9 23.3 24.3 24.5 全寿命周期/万元 146.5 146.5 146.5 178.4 179.9 180.2 161.8 162.6 162.8 160.4 161.0 161.2 177.0 177.9 178.2 成本差比/% 21.8 22.8 23.0 10.5 11.0 11.1 9.5 9.9 10.0 20.8 21.5 21.6 表 3 免涂装耐候钢桥维护成本净现值对比计算
Table 3. Comparative calculation of net present values of maintenance costs for uncoated weathering steel bridges
维护方式 单次水洗或初始涂装成本/万元 涂装维护成本 维护总成本净现值/万元 全寿命周期成本差比/% 一般维护/万元 大涂装维护/万元 水洗周期 每6年1次 0.3 1.3 1.2~1.9 每4年1次 0.3 2.0 1.1~3.2 每2年1次 0.3 4.1 2.2~5.3 每年1次 0.3 8.3 5.2~11.3 涂装体系(涂装面积占比约10%) 第5套 3.2 2.9 4.9 19.4 11.1~28.8 第6套 3.5 3.1 5.2 11.7 7.4~17.1 第7套(溶剂型) 5.1 0.0 6.8 10.6 6.4~15.9 第7套(水性) 9.4 0.0 12.8 19.8 11.9 ~29.8 -
[1] 王春生, 张静雯, 段兰, 等. 长寿命高性能耐候钢桥研究进展与工程应用[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(1): 1-26. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.01.001WANG Chun-sheng, ZHANG Jing-wen, DUAN Lan, et al. Research progress and engineering application of long lasting high performance weathering steel bridges[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(1): 1-26. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.01.001 [2] 陈艾荣, 阮欣. 桥梁维护、安全与运营管理—长寿命与智能化[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2021.CHEN Ai-rong, RUAN Xin. Bridge Maintenance, Safety and Management: Long Life and Intelligence[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2021. (in Chinese) [3] 刘玉擎, 陈艾荣. 耐候钢桥的发展及其设计要点[J]. 桥梁建设, 2003, 33(5): 39-41, 45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2003.05.011LIU Yu-qing, CHEN Ai-rong. Development and design essentials of weathering steel bridges[J]. Bridge Construction, 2003, 33(5): 39-41, 45. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2003.05.011 [4] WALLS J, SMITH M R. Life-cycle cost analysis in pavement design—in search of better investment decisions[R]. Washington DC: Federal Highway Administration, 1998. [5] FRANGOPOL D M, LIN K Y, ESTES A C. Life-cycle cost design of deteriorating structures[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1997, 123(10): 1390-1401. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1997)123:10(1390) [6] FRANGOPOL D M. Bridge Safety and Reliability[M]. Reston: ASCE, 1999. [7] FRANGOPOL D M, KONG J S, GHARAIBEH E S. Reliability- based life-cycle management of highway bridges[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2001, 15(1): 27-34. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3801(2001)15:1(27) [8] KONG J S, FRANGOPOL D M. Life-cycle reliability-based maintenance cost optimization of deteriorating structures with emphasis on bridges[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2003, 129(6): 818-828. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2003)129:6(818) [9] KONG J S, FRANGOPOL D M. Cost-reliability interaction in life-cycle cost optimization of deteriorating structures[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2004, 130(11): 1704-1712. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2004)130:11(1704) [10] LEE K M, CHO H N, CHA C J. Life-cycle cost-effective optimum design of steel bridges considering environmental stressors[J]. Engineering Structures, 2006, 28(9): 1252-1265. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2005.12.008 [11] PETCHERDCHOO A, NEVES L A, FRANGOPOL D M. Optimizing lifetime condition and reliability of deteriorating structures with emphasis on bridges[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2008, 134(4): 544-552. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2008)134:4(544) [12] HONG T, HAN S, LEE S. Simulation-based determination of optimal life-cycle cost for FRP bridge deck panels[J]. Automation in Construction, 2007, 16(2): 140-152. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2006.01.001 [13] MEHRABI A B, LIGOZIO C A, CIOLKO A T, et al. Evaluation, rehabilitation planning, and stay-cable replacement design for the Hale Boggs Bridge in Luling, Louisiana[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2010, 15(4): 364-372. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000061 [14] 叶文亚, 李国平, 范立础. 桥梁全寿命成本初步分析[J]. 公路, 2006(6): 101-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL200606025.htmYE Wen-ya, LI Guo-ping, FAN Li-chu. Preliminary analysis of bridge life-cycle cost[J]. Highway, 2006(6): 101-104. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL200606025.htm [15] 钟卿. 基于全寿命周期成本的桥梁设计理论研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2006.ZHONG Qing. The research on bridge design theory based on the life cycle cost[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2006. (in Chinese) [16] SOLIMAN M, FRANGOPOL D M. Life-cycle cost evaluation of conventional and corrosion-resistant steel for bridges[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2015, 20(1): 06014005. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000647 [17] 贺君, 刘玉擎, 陈艾荣, 等. 耐候性钢桥评估管理系统研究[J]. 桥梁建设, 2009, 39(5): 32-35, 67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLJS200905008.htmHE Jun, LIU Yu-qing, CHEN Ai-rong, et al. Study of evaluation and management system for weathering steel bridges[J]. Bridge Construction, 2009, 39(5): 32-35, 67. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLJS200905008.htm [18] 石振家, 王雷, 陈楠, 等. 耐候钢表面锈层及其稳定化处理现状与发展趋势[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2015, 27(5): 503-508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSFJ201505021.htmSHI Zhen-jia, WANG Lei, CHEN Nan, et al. Present situation and development trend of rust layer on weathering steel surface and its stabilization treatment[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2015, 27(5): 503-508. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSFJ201505021.htm [19] DÍAZ I, CANO H, CHICO B, et al. Some clarifications regarding literature on atmospheric corrosion of weathering steels[J]. International Journal of Corrosion, 2012: 812192. [20] 刘国超, 董俊华, 韩恩厚, 等. 耐候钢锈层研究进展[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2006, 18(4): 268-272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6495.2006.04.010LIU Guo-chao, DONG Jun-hua, HAN En-hou, et al. Progress in research on rust layer of weathering steel[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2006, 18(4): 268-272. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6495.2006.04.010 [21] OKADA H, HOSOI Y, YUKAWA K I, et al. Structure of the rust formed on low alloy steels in atmospheric corrosion[J]. Tetsu to Hagane, 1969, 55(5): 355-365. doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.55.5_355 [22] CRAMPTON D, HOLLOWAY K P, FRACZEK J. Assessment of weathering steel bridge performance in Iowa and development of inspection and maintenance techniques[R]. Des Moines: Iowa Department of Transportation, 2012. [23] HARA S, KAMIMURA T, MIYUKI H, et al. Taxonomy for protective ability of rust layer using its composition formed on weathering steel bridge[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(3): 1131-1142. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2006.06.016 [24] YAMASHITA M, MIYUKI H, MATSUDA Y, et al. The long term growth of the protective rust layer formed on weathering steel by atmospheric corrosion during a quarter of a century[J]. Corrosion Science, 1994, 36(2): 283-299. doi: 10.1016/0010-938X(94)90158-9 [25] FRANGOPOL D M, DONG Y, SABATINO S. Bridge life- cycle performance and cost: analysis, prediction, optimisation and decision-making[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 13(10): 1239-1257. doi: 10.1080/15732479.2016.1267772 [26] WANG Chun-sheng, ZHANG Jing-wen, DUAN Lan, et al. Structural performance and engineering application of a long lasting weathering steel composite bridge with tubular flanges[J]. Structural Engineering International, 2022, 32: 147-158. doi: 10.1080/10168664.2021.2024482 [27] 王春生, 常全禄, 翟晓亮, 等. 管翼缘组合梁桥设计与结构分析[J]. 钢结构, 2015, 30(6): 17-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJIG201506005.htmWANG Chun-sheng, CHANG Quan-lu, ZHAI Xiao-liang, et al. Design and structural analysis of tubular flange composite girder bridge[J]. Steel Construction, 2015, 30(6): 17-21. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJIG201506005.htm [28] YOKOTA H, FRANGOPOL D M. Bridge Maintenance, Safety, Management, Life-Cycle Sustainability and Innovations[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2021. [29] Corus Construction and Industrial. Weathering steel bridges[R]. London: Corus Construction and Industrial, 2010. [30] JIS F, JASB C. Application of weathering steel to bridges[R]. Tokyo: Japan Iron and Steel Federation, 2003. -





 下载:
下载: