Data-driven equivalent scaled model of coupler-buffer device design for subway vehicles
-
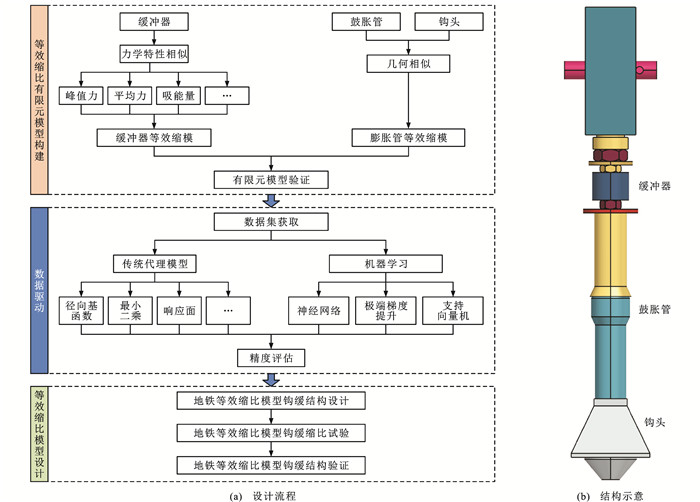
摘要: 为了快速获取地铁车辆碰撞中钩缓结构碰撞特性,研究了地铁车辆钩缓结构设计,提出了一种基于数据驱动的地铁车辆等效缩比模型钩缓结构设计方法;以钩缓结构中橡胶缓冲器为研究对象,建立等效缩比橡胶缓冲器有限元模型并进行缩比试验验证,构建了等效缩比橡胶缓冲器几何参数与力学特性响应面代理模型;以钩缓结构中鼓胀管为研究对象,建立了1/8缩比鼓胀管有限元模型并通过准静态压缩试验验证,构建了基于缩比鼓胀管几何参数耐撞性指标预测模型;为了验证方法的有效性,基于某型地铁头车钩缓结构碰撞试验,针对钩头、缓冲器、鼓胀管开展等效缩比模型设计,开展1/8缩比地铁头车碰撞试验,获得等效缩比钩缓结构力学特性曲线后,将其还原与地铁头车全尺寸有限元仿真结果进行比较。研究结果表明:构建的等效缩比橡胶缓冲器冲击峰值力和平均力响应面代理模型的决定系数分别为0.994和0.992;建立的1/8缩比鼓胀管多种几何参数耐撞性指标预测模型中,多层感知机模型冲击平台力和比吸能的预测结果决定系数均达到0.999;开展的地铁车辆等效缩比模型钩缓结构试验与地铁头车全尺寸有限元仿真结果中,缩比试验与仿真力-位移曲线趋势基本一致,缓冲器的平均力、冲击峰值力误差分别为1.11%、5.62%,鼓胀管冲击平台力、比吸能误差分别为0.59%、2.51%。可见,基于数据驱动的地铁车辆等效缩比模型钩缓结构设计方法能较好地设计等效缩比钩缓结构,在确保缩比模型精确度的同时,降低钩缓结构研究和设计成本。Abstract: In order to quickly obtain the collision characteristics of the coupler-buffer device in the subway vehicle collision, the design of the coupler-buffer device was studied, and the data-driven equivalent scaled model design method of the coupler-buffer device was proposed. By taking the rubber buffer in the coupler-buffer device as the research object, the equivalent scaled finite element model of the rubber buffer was established and verified by scaled tests. The response surface proxy models of the geometrical parameter and mechanical characteristic in the equivalent scaled rubber buffer were constructed. The expansion tubes in the coupler-buffer device were taken as the research object, and a finite element model of the 1/8 scaled expansion tube was established and verified by quasi-static compression tests. A crashworthiness index prediction model based on the geometrical parameters of the scaled expansion tube was constructed. Based on the collision test of the coupler-buffer device for a type of subway head car, the equivalent scaled model designs of the couple head, buffer, and expansion tube were carried out to verify the validity of the method. A 1/8 equivalent scaled subway head car collision test was carried out to obtain the mechanical property curves, which were then restored and compared with the full-scale subway head car finite element simulation results. Research results show that the determination coefficients of the response surface proxy models of the peak crushing force and total mean force in the equivalent scaled rubber buffer are 0.994 and 0.992, respectively. In the crashworthiness index prediction models of the 1/8 scaled expansion tube, the determination coefficients of the platform mean force and specific energy absorption in the multilayer perceptron mode are both 0.999. In the results of the equivalent scaled coupler-buffer device for the subway vehicle test and the full-scale subway head car finite element simulation, the trends of force-displacement curves of the scaled test and the simulation test are the same, and the errors of total mean force, peak crushing force of the buffer are 1.11% and 5.62%, and the errors of platform mean force and specific energy absorption of the expansion tube are 0.59% and 2.51%, respectively. It can be seen that the data-driven design method based on the coupler-buffer device for subway vehicles can better be applied to the design of the equivalent scaled coupler-buffer device, reducing the cost of research and design in the coupler-buffer device while ensuring the accuracy of the equivalent scaled model.
-
Key words:
- subway vehicle /
- coupler-buffer device /
- data-drive /
- equivalent scaled model /
- numerical simulation /
- parameter design
-
表 1 鼓胀管原模型及缩比模型几何结构参数
Table 1. Geometrical structure parameters of original model and scaled model of expansion tube
几何参数 原模型 缩比模型 锥管长度/mm 320 40 锥管锥角/(°) 25 25 锥管外半径/mm 68.0 8.5 胀管长度/mm 280 35 胀管内半径/mm 61.0 7.6 胀管壁厚/mm 9.6 1.2 表 2 响应面模型误差分析
Table 2. Error analysis of response surface model
耐撞性指标 DMRE/% DRMSE/kN DMAE/kN R2 FPCF 3.77 1.272 1.052 0.994 FTMF 4.16 0.758 0.606 0.992 表 3 DOE设计变量基本信息
Table 3. Basic informations of DOE design variables
变量 初始值 变化范围 锥管锥角/(°) 25 [20, 30] 锥管外半径/mm 8.5 [8.5,9.5] 胀管内半径/mm 7.6 [7.6,8.4] 胀管壁厚/mm 1.2 [1.2,2.4] 表 4 三种机器学习模型预测精度对比
Table 4. Prediction accuracy comparison of three machine learning models
模型 指标 FPMF ESEA 训练集 测试集 训练集 测试集 MLP R2 0.999 0.999 0.999 0.999 DMSE /10-5 kN2 3.31 2.45 2.93 1.82 DMAE /10-3 kN 3.01 2.67 3.92 2.81 XGBoost R2 0.975 0.965 0.966 0.959 DMSE /10-5 kN2 5.01 4.88 6.52 5.99 DMAE/10-3 kN 4.08 4.01 5.22 5.02 SVM R2 0.960 0.952 0.953 0.955 DMSE/10-5 kN2 8.01 9.52 7.06 7.61 DMAE/10-3 kN 7.21 8.30 5.88 6.20 表 5 钩缓结构全尺寸模型和缩比模型耐撞性指标
Table 5. Crashworthiness indexes of full-scale and scaled models for coupler-buffer device
钩缓结构 缓冲器 鼓胀管 FPCF/kN FTMF/kN FPMF/kN ESEA/(J·g-1) 全尺寸模型 1 267.17 699.92 1 118.21 12.48 缩比模型 19.80 10.93 17.47 12.48 表 6 等效缩比模型钩缓结构几何尺寸
Table 6. Geometry of equivalent scaled model coupler-buffer device
钩缓结构 缓冲器 鼓胀管 参数 半径/mm 高度/mm 锥管锥角/(°) 锥管外半径/mm 胀管壁厚/mm 胀管内半径/mm 数值 14.0 22.5 28.0 9.0 1.6 8.0 -
[1] 周子凯, 丁伟, 周宝宪. 基于数据驱动的铁路货运事故致因分析及预防对策[J]. 物流技术, 2023, 42(1): 6-9, 19.ZHOU Zi-kai, DING Wei, ZHOU Bao-xian. Data-driven cause analysis and prevention measures for railway freight transportation accidents[J]. Logistics Technology, 2023, 42(1): 6-9, 19. (in Chinese) [2] 王成全, 周雄飞, 刘磊, 等. 正面斜碰撞下列车脱轨行为与机理研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2023, 20(5): 1821-1832.WANG Cheng-quan, ZHOU Xiong-fei, LIU Lei, et al. Derailment behavior and mechanism of a train under frontal oblique collisions[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(5): 1821-1832. (in Chinese) [3] 王科飞, 张春玉, 杨青, 等. Hybrid Ⅲ-50th-RS假人上腹部冲击试验探究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(7): 2072-2079.WANG Ke-fei, ZHANG Chun-yu, YANG Qing, et al. Probe into the impact test of the upper abdomen of the hybrid Ⅲ-50th-RS dummy[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(7): 2072-2079. (in Chinese) [4] 肖守讷, 张志新, 阳光武, 等. 列车碰撞仿真中钩缓装置模拟方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(5): 831-836. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.05.014XIAO Shou-ne, ZHANG Zhi-xin, YANG Guang-wu, et al. Simulation method for couplers and buffers in train collision calculations[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(5): 831-836. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.05.014 [5] QI Zhao-hui, HUANG Zhi-hao, KONG Xian-chao. Simulation of longitudinal dynamics of long freight trains in positioning operations[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2012, 50(9): 1409-1433. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2012.661063 [6] WU Qing, SPIRYAGIN M, COLE C. Advanced dynamic modelling for friction draft gears[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2015, 53(4): 475-492. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2014.1002504 [7] DOU Wei-yuan, ZHANG Le-le, CHEN Geng, et al. A boundary- condition-transfer method for shell-to-solid submodeling and its application in high-speed trains[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 177: 105542. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105542 [8] 聂天琦, 任尊松, 孙守光, 等. 高速动车组碰撞安全性研究[J]. 铁道机车车辆, 2015, 35(4): 11-15.NIE Tian-qi, REN Zun-song, SUN Shou-guang, et al. Research on collision safety of high-speed EMU[J]. Railway Locomotive and Car, 2015, 35(4): 11-15. (in Chinese) [9] 高广军, 舒康, 关维元, 等. 列车收缩管吸能防爬器耐撞性研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(2): 520-527.GAO Guang-jun, SHU Kang, GUAN Wei-yuan, et al. Crashworthiness analysis of shrink circular tube energy absorbers with an anti-clamber for trains[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(2): 520-527. (in Chinese) [10] 刘财芝, 唐国金, 周利霖. 运载火箭1/5动力学缩比模型设计[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2017, 39(2): 27-31.LIU Cai-zhi, TANG Guo-jin, ZHOU Li-lin. 1/5 dynamic scaled model design of launch vehicle[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2017, 39(2): 27-31. (in Chinese) [11] YAO Shu-jian, ZHANG Duo, LU Fang-yun, et al. A combined experimental and numerical investigation on the scaling laws for steel box structures subjected to internal blast loading[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 102: 36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.12.003 [12] 张凯, 许平, 姚曙光. 基于列车纵向缩比模型的摩擦力尺寸效应研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(3): 51-57.ZHANG Kai, XU Ping, YAO Shu-guang. Research on friction size effects based on scaled train model in longitudinal direction[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(3): 51-57. (in Chinese) [13] 王晋乐, 田洪雷, 赵士忠, 等. 蜂窝填充梯度吸能结构力学特性试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(5): 1904-1917.WANG Jin-le, TIAN Hong-lei, ZHAO Shi-zhong, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of honeycomb-filled gradient energy absorption structure[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2022, 53(5): 1904-1917. (in Chinese) [14] YU Yao, GAO Guang-jun, GUAN Wei-yuan, et al. Scale similitude rules with acceleration consistency for trains collision[J]. Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2018, 232(10): 2466-2480. doi: 10.1177/0954409718773562 [15] LIU Xiu-juan, XU Peng-cheng, ZHAO Juan-juan, et al. Material machine learning for alloys: applications, challenges and perspectives[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 921: 165984. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165984 [16] CHALLAPALLI A, KONLAN J, PATEL D, et al. Discovery of cellular unit cells with high natural frequency and energy absorption capabilities by an inverse machine learning framework[J]. Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 7: 779098. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2021.779098 [17] 车全伟, 雷成, 李玉如, 等. 基于神经网络的数据挖掘模型在吸能装置上的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(5): 995-1001.CHE Quan-wei, LEI Cheng, LI Yu-ru, et al. Data mining model based on neural network and its application on anti-climber device[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(5): 995-1001. (in Chinese) [18] 张国恒, 高锋阳, 石岩, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络的牵引逆变器开路故障多特征融合诊断方法[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020, 17(3): 732-740.ZHANG Guo-heng, GAO Feng-yang, SHI Yan, et al. Multi-feature fusion diagnosis method of open circuit fault for traction inverter based on Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(3): 732-740. (in Chinese) [19] PONTIROLI C, ROUQUAND A, DAUDEVILE L, et al. Soft projectile impacts analysis on thin reinforced concrete slabs: tests, modelling and simulations[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2012, 16(9): 1058-1073. [20] LU Si-si, XU Ping, YAN Kai-bo, et al. A force/stiffness equivalence method for the scaled modelling of a high-speed train head car[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2019, 137: 129-142. [21] SHAO Heng, XU Ping, YAO Shu-guang, et al. Improved multibody dynamics for investigating energy dissipation in train collisions based on scaling laws[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2016, 2016: 1-11. [22] LI Rui, XU Ping, PENG Yong, et al. Scaled tests and numerical simulations of rail vehicle collisions for various train sets[J]. Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2015, DOI: 10.1177/0954409715605126. [23] XU Ping, WANG Ao, YANG Li-ting, et al. Correlation study between the mechanical property of the square cone energy-absorbing structure and collision energy distribution for urban rail trains[J]. Machines, 2022, 10: 747. [24] 石越卿, 秦睿贤, 陈秉智. 列车防撞柱结构耐撞性设计与优化[J]. 机械强度, 2022, 44(5): 1134-1140.SHI Yue-qing, QIN Rui-xian, CHEN Bing-zhi. Crashworthiness design and optimization of train collision post of train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2022, 44(5): 1134-1140. (in Chinese) [25] 陈征, 黎青青, 肖乃松, 等. 基于GA-BP神经网络的柴油喷雾贯穿距预测[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(1): 247-252.CHEN Zheng, LI Qing-qing, XIAO Nai-song, et al. Prediction of diesel spray penetration length based on GA-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2018, 49(1): 247-252. (in Chinese) [26] 陈劼昊, 梁习锋, 许平, 等. 高速列车吸能结构开孔设计及结构优化[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 19(6): 1502-1510.CHEN Jie-hao, LIANG Xi-feng, XU Ping, et al. Windowed design and structure optimization of energy absorbing structure of high-speed train[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(6): 1502-1510. (in Chinese) [27] 张伟光, 钟靖涛, 于建新, 等. 基于机器学习和图像处理的路面裂缝检测技术研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(7): 2402-2415.ZHANG Wei-guang, ZHONG Jing-tao, YU Jian-xin, et al. Research on pavement crack detection technology based on convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2021, 52(7): 2402-2415. (in Chinese) [28] XU Tuo, XU Ping, ZHAO Hui, et al. Vehicle running attitude prediction model based on artificial neural network-parallel connected (ANN-PL) in the single-vehicle collision[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2023, 175: 103356. [29] DI BENEDETTO R M, BOTELHO E C, JANOTTI A, et al. Development of an artificial neural network for predicting energy absorption capability of thermoplastic commingled composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 257: 113131. [30] XU Ping, QU Cheng-ju, YAO Shu-guang, et al. Numerical optimization for the impact performance of a rubber ring buffer of a train coupler[J]. Machines, 2021, 9: 225. [31] 胡昌明, 贺红亮, 胡时胜. 45号钢的动态力学性能研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(2): 188-192.HU Chang-ming, HE Hong-liang, HU Shi-sheng. A study on dynamic mechanical behaviors of 45 steel[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(2): 188-192. (in Chinese) [32] BAROUTAJI A, GILCHHRIST M D, SMYTH D, et al. Analysis and optimization of sandwich tubes energy absorbers under lateral loading[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 82: 74-88. [33] WANG Shi-ming, PENG Yong, WANG Tian-tian, et al. Collision performance and multi-objective robust optimization of a combined multi-cell thin-walled structure for high speed train[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2019, 135: 341-355. [34] XU Ping, XING Jie, YAO Shu-guang, et al. Energy distribution analysis and multi-objective optimization of a gradual energy-absorbing structure for subway vehicles[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2017, 115: 255-263. [35] YAO Shu-guang, ZHU Hui-fen, LIU Ming-yang, et al. A study on the frontal oblique collision-induced derailment mechanism in subway vehicles[J]. Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2019, 234: 584-595. -





 下载:
下载: