-
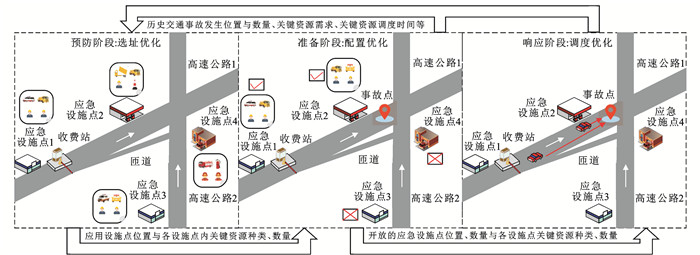
摘要: 定义了高速公路应急关键资源,根据高速公路交通事故应急救援的预防、准备、响应阶段,将高速公路应急关键资源调配分为应急设施点选址、应急关键资源配置与调度,系统回顾了这三方面的研究成果,探讨了目前存在的问题与后续研究方向。研究结果表明:在应急设施点选址方面,现有研究多面向高速公路规划初期场景,选址结果也较为固定,有必要研究面向道路运营阶段的路侧小型和微型应急设施点选址方法,受限于模型求解性能,现有研究较少考虑大规模应急设施点选址,组合式求解算法有望在此取得突破;在应急关键资源配置方面,现有研究假设在事故初期就可获得完备的事故信息,与实际情况不符,利用静态资源配置方案设计动态资源配置策略更贴合实际;在应急关键资源调度方面,交通事故后的不确定性为应急关键资源调度带来了挑战,应研究鲁棒性强的交通状态估计方法,事故后交通状态的时变特性对应急车速有较大影响,应研究融合动态路径规划与交通控制策略的应急关键资源调度方法,面向未来,有必要研究混合交通流与智能网联汽车环境下的应急关键资源调度方法,深入探究应急车辆调度过程中车速的动态变化规律;在三者融合方面,高速公路场景下的一体化优化研究尚未开展,有必要研究面向桥梁、山区等特殊场景的陆海空天立体化应急关键资源调配理论和验证方法,进一步提升高速公路运输网络韧性。Abstract: The key emergency resources for expressways were defined. In terms of the prevention, preparation, and response stages of emergency rescue for expressway traffic accidents, the key emergency resource deployment for expressways was divided into emergency facility location selection, allocation and dispatching of key emergency resources. The research achievements in the three aspects were systematically reviewed, and the existing problems and future research directions were discussed. Research results show that in terms of the location selection for emergency facility, current research is mostly oriented to the initial scenario of expressway planning, and the location selection result is relatively fixed. It is necessary to study the location selection methods for small and miniature emergency facilities oriented towards the stage of road operation. Limited by the model’s solving performance, existing research seldom considers the location selection for large-scale emergency facility. The combined solving algorithm that integrates multiple optimization algorithms is expected to make breakthroughs. In terms of the key emergency resource allocation, current research assumes that the complete accident information is available during the initial phase of the accident, which is inconsistent with actual condition. Using a static allocation scheme to design a dynamic resource allocation strategy is more realistic. In terms of the key emergency resource dispatching, uncertainty after traffic accidents brings challenges. Robust methods estimating the traffic state should be studied. The time-varying characteristics of traffic state after traffic accidents have great impact on the speeds of emergency vehicles. The key emergency resource dispatching methods integrating the dynamic path planning and traffic control strategies should be studied. Looking toward the future, it is necessary to study the key emergency resource dispatching method in the environment with mixed traffic flow and intelligent and connected vehicles. The dynamic change law of vehicle speed in the process of emergency vehicle dispatching should be deeply explored. In terms of the integration, the research on the integrated optimization of expressway scenarios has not yet been studied. Therefore, it is necessary to study the theory and verification methods of key emergency resource deployment for land-sea-air-space oriented towards special scenarios, such as bridges and mountainous areas, so as to improve the resilience of expressway transportation network.
-
表 1 应急设施点选址模型
Table 1. Location selection models for emergency facility
文献 模型 优化目标 约束条件 适应性 ① ② ③ [22] LSCP 最小化响应时间 应急设施点数量 确保在有限应急设施点数量下的救援响应时间 √ [24] MCLP 最大化覆盖率 应急设施点数量、服务能力 确保在有限应急设施点数量与服务能力下的设施覆盖率 √ [28] DSM 最大化覆盖率 应急车辆数、服务可靠性 确保在有限应急车辆数与服务可靠性下的应急车辆覆盖率 √ √ [37] HQM 最小化响应时间 应急车辆数 确保在有限应急车辆数下的救援响应时间 √ √ [43] DACL 最小化应急车辆数 覆盖范围、服务可靠性 时间周期内确保在不同覆盖范围和有限服务可靠性下的应急车辆数 √ √ [45] 双层选址-路径-配给 最小化响应时间、最大化综合满意度、公平性 应急车辆数、设施点容量、供给能力 时间周期内确保在有限应急车辆数、设施点容量与供给能力下的响应时间、满意度与公平性 √ √ √ [46] DMOCM 最小化响应时间、最小化资源短缺数量 事故点需求、应急设施点服务能力 时间周期内确保在不确定事故需求及应急设施点服务能力下的响应时间、资源短缺数量,使用资源短缺数量表征救援公平性 √ √ [42] 随机规划(Stochastic Programming, SP) 最小化救援总成本 服务能力及计算时间 确保在有限设施点服务能力和模型求解时间下的应急救援成本 √ √ [47] DMOCM 最大化覆盖率、最小化救援时间、最小化建设成本 应急设施点数量、计算次数 时间周期内确保在有限应急设施点数量和计算次数下的覆盖率、救援时间及建设成本 √ √ [48] 多目标鲁棒优化(Robust Optimization, RO) 最小化救援总成本、服务公平性 应急设施点供给能力、应急车辆数 时间周期内确保在有限应急设施点供给能力及应急车辆数下的救援成本与公平性 √ √ [49] 两阶段RO 最小化总成本 应急设施点容量、服务公平性 时间周期内确保在有限应急设施点容量与服务公平性下的救援总成本 √ √ 表 2 应急设施点选址模型求解算法
Table 2. Solving algorithms of location selection models for emergency facility
文献 模型 求解算法 算法类型 算例数 算例规模 [46] 多目标位置-分配(Location-Allocation, LA) 多目标超启发式算法 启发式算法 6 最大8个应急设施点、8个需求点 [52] BLM 粒子群算法 启发式算法 1 67个应急设施点、8个高速公路路段 [54] BLM 禁忌搜索算法 启发式算法 1 7个应急设施点、7个需求点 [65] MCLP 遗传算法 启发式算法 1 84个应急设施点、459个需求点 [66] 多目标非线性整数规划(Nonlinear Integer Programming, NLIP) 帕累托遗传算法 启发式算法 1 14个应急设施点 [60] 多目标LA ε约束法 精确式算法 4 最大4个应急设施点、45个需求点 [67] LA 分支定界算法 精确式算法 2 最大10个应急设施点、40个需求点 [63] 分层设施选址 混合粒子群算法+禁忌搜索算法 组合式算法 1 10个应急设施点、24个需求点 [64] BLM 免疫算法+蚁群算法 组合式算法 1 3个应急设施点、13个需求点 表 3 静态应急关键资源配置模型
Table 3. Static key emergency resource allocation models
文献 模型 考虑因素 试验地点 应急关键资源 [68] 模糊分类+基于规则的网络模型 各部门对资源需求度 安徽省高速公路 交警:60个锥形桶、4辆车、4名人员、10个警戒带、6个警示标志、10个闪光灯;
医疗:20个急救箱、3辆救护车、6名医生、6名护士、10 000个血袋;
消防:8名人员、2个消防泵、1个灭火器、2辆危化品救援车、2台液压切割机、2个回收灌;
路政与养护:3辆清障车、2台起重机,3辆拖车、30件雨衣[69] SP模型 资源配置时间、配置成本、事故资源需求随机度 南京市高速公路 交警、高速公路管理局、消防、养护、医疗部门,清障车、拖车、消防车、救护车 [70] 四叉树+多目标配置模型 资源需求空间分布 台湾省新北市 救护车 [71] 改进事故频数法+三阶段随机遗憾最小化模型 应急响应时间、救援成本、需求属性遗憾值 潍坊、日照、临沂 清障车 表 4 应急关键资源配置概况
Table 4. Overview of key emergency resource allocation
文献 优化目标 模型 求解算法 算例规模 可持续发展 [74] 资源需求率、不利环境影响、经济成本 随机双层优化模型 样本平均近似法、全局准则混合算法 2个应急设施点、3个需求点 是 [75] 公平性、配置时间 MIP模型 6个应急设施点、5类应急关键资源 是 [76] 配置时间 整数规划模型 自适应遗传算法 5~10类应急关键资源,每类资源需求最大20个 否 [79] 配置成本 MIP模型 基于局部搜索的线性规划算法 10个应急设施点、5个需求点、3个二次事故点、46类应急关键资源 否 [81] 配置时间 动态规划模型 5辆应急车辆、30 km高速公路 否 [82] 配置成本、碳排放量 单层多目标SP模型 矩阵编码的遗传算法 5个应急设施点、4类应急关键资源 是 [84] 配置成本 两阶段SP模型 粒子群算法 41个应急设施点、3类应急关键资源 否 [85] 配置成本、资源需求率 分布式RO模型 平均绝对偏差的模糊集与近似方法结合 4个应急设施点、4类应急关键资源 否 [86] 配置延时、配置成本 基于智能体的车辆派遣模型 启发式算法 4个应急设施点、2个需求点、35辆应急车辆 否 表 5 考虑不同优化目标下的应急关键资源调度模型
Table 5. Key emergency resource dispatching models considering different optimization objectives
目标个数 文献 模型 优化目标 求解算法 决策方式 单目标优化 [95] 无向图模型 最短调度时间 改进的Dijkstra算法 动态 [99] 时序协同进化模型 最短调度时间 改进波纹扩散算法 动态 [105] 无向图模型 最短路径 Dijkstra算法 静态 [106] 时间依赖图模型 最短路径 双向A*算法 动态 [107] 动态规划模型 最短路径 粒子群算法 动态 [108] 选址-路径问题(Location-Routing Problem, LRP)模型 最短调度时间 静态 多目标优化 [46] MINLP模型 最小救援成本、最少资源 多目标超启发式算法 动态 [109] 混合整数线性规划(Mixed Integer Linear Programming, MILP)模型 最少资源、最大路径可靠性 多目标进化算法 动态 [110] 整数非线性规划模型 最短救援时间、最小延迟时间、最少救援车辆 改进引力搜索算法 静态 [111] MILP模型 最少资源、最小救援成本、最大路径可靠性 改进樽海鞘算法 动态 表 6 应急关键资源调度研究概况
Table 6. Overview of research on key emergency resource dispatching
文献 建模环境 上层目标函数 下层目标函数 决策方式 算例规模 描述 [98] 拥堵 最小化出行距离 最小化出行成本 分散 43个节点、197个路段、50辆车 采用动态拥堵信息更新机制将拥堵代价纳入模型 [102] 拥堵 最小化车辆出行时间 最小化拥堵程度 分散 46个节点、85个路段、8辆应急车辆 构建交通拥堵程度函数并作为优化目标 [116] 潜在事故 最小化救援成本 集中 3个应急设施点、3个潜在事故点、1个事故点 以历史事故数据计算潜在事故发生概率并纳入优化模型 [117] 潜在事故 最小化救援时间 最小化救援成本 分散 46个节点、85个路段、8辆应急车辆、3个潜在事故点 实时更新行驶速度函数,确保应急车辆不通过发生事故的路段 [119] 多事故点 最小化救援时间 最小化运输成本 分散 3个事故点、9个应急设施点 引入理想点法求解,以期平衡多事故点的需求 [120] 事故优先级 最小化应急设施点 最小化救援时间 分散 2个事故点、9个应急设施点 构建事故影响程度评价函数,确定事故优先级 [101] 事故优先级 最小化救援延误 集中 10个节点、15个路段、2个事故点 根据事故严重程度确定事故优先级 [121] 不确定性 最大化救援可靠性 最小化救援时间 分散 16个节点、3辆应急车辆 使用RO模型转化不确定参数约束 [124] 不确定性 最小化救援成本 最大化响应需求 分散 15辆应急车辆 使用情景分析法处理需求不确定,使用时间窗口解决交通流不确定性 [125] 不确定性 最大化救援点需求 最小化救援时间 分散 4个事故点、4个应急设施点 使用模糊理论处理不确定性 [128] 不确定性 最小化救援时间 最小化救援成本 分散 10个节点、4辆应急车辆、4个事故点 使用RO模型转化不确定参数约束 -
[1] 杨惠敏, 陈雨人, 方守恩, 等. 高速公路交通事故救援时间与生存率关系模型研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2015, 33(4): 82-86.YANG Hui-min, CHEN Yu-ren, FANG Shou-en, et al. A study of the relationship between rescue time and survival rate of traffic accidents on freeways using a Cox regression model[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2015, 33(4): 82-86. (in Chinese) [2] PAL C, HIRAYAMA S, NARAHARI S, et al. An insight of World Health Organization (WHO) accident database by cluster analysis with self-organizing map (SOM)[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2018, 19(S1): 15-20. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2017.1370089?needAccess=true [3] WANG Duo, YANG Kai, YANG Li-xing, et al. Distributional robustness and lateral transshipment for disaster relief logistics planning under demand ambiguity[J]. International Transactions in Operational Research, 2024, 31(3): 1736-1761. doi: 10.1111/itor.13227 [4] PRODHON C, PRINS C. A survey of recent research on location-routing problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2014, 238(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2014.01.005 [5] ARINGHIERI R, BRUNI M E, KHODAPARASTI S, et al. Emergency medical services and beyond: addressing new challenges through a wide literature review[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 2017, 78: 349-368. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2016.09.016 [6] DÖNMEZ Z, KARA B Y, KARSU Ö, et al. Humanitarian facility location under uncertainty: critical review and future prospects[J]. Omega, 2021, 102: 102393. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2021.102393 [7] LIU Yang, YUAN Yun, SHEN Jie-yi, et al. Emergency response facility location in transportation networks: a literature review[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2021, 8(2): 153-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2021.03.001 [8] SHEN Jin-xing, LIU Kun, MA Chang-xi, et al. Bibliometric analysis and system review of vehicle routing optimization for emergency material distribution[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2022, 9(6): 893-911. doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2022.10.001 [9] RAND G K. Methodological choices in depot location studies[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 1976, 27(1): 241-249. doi: 10.1057/jors.1976.39 [10] SALHI S, RAND G K. The effect of ignoring routes when locating depots[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1989, 39(2): 150-156. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(89)90188-4 [11] BOLOORI ARABANI A, FARAHANI R Z. Facility location dynamics: an overview of classifications and applications[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2012, 62(1): 408-420. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/1983610497 [12] IWAKATA M, OKAMOTO N, ISHIDA H, et al. A study of freight facility location in Tokyo Metropolitan and its future[J]. Journal of the Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, 2015, 11: 722-738. [13] CELIK TURKOGLU D, EROL GENEVOIS M. A comparative survey of service facility location problems[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2020, 292(1): 399-468. doi: 10.1007/s10479-019-03385-x [14] ZHAO Ming, CHEN Qiu-wen, MA Jian, et al. Optimizing temporary rescue facility locations for large-scale urban environmental emergencies to improve public safety[J]. Journal of Environmental Informatics, 2017, 29(1): 61-73. [15] 田德红, 何建敏, 孙海信. 基于Multi-Agent的应急物资储存点布局优化研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报(社会科学版), 2019, 21(1): 67-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-105x.2019.01.006TIAN De-hong, HE Jian-min, SUN Hai-xin. Research on the optimal layout of emergency material storages based on multi-agent system[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology (Social Sciences), 2019, 21(1): 67-81. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-105x.2019.01.006 [16] MLADINEO N, KNEZIC S, JAJAC N. Decision support system for emergency management on motorway networks[J]. Transportmetrica, 2011, 7(1): 45-62. doi: 10.1080/18128600903244669 [17] RODRIGUES L F, MORABITO R, CHIYOSHI F Y, et al. Towards hypercube queuing models for dispatch policies with priority in queue and partial backup[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 2017, 84: 92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2017.02.021 [18] AKDOGAN M A, BAYINDIR Z P, IYIGUN C. Location analysis of emergency vehicles using an approximate queueing model[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2017, 22: 430-439. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2017.03.018 [19] CHANTA S, MAYORGA M E, KURZ M E, et al. The minimum p-envy location problem: a new model for equitable distribution of emergency resources[J]. IIE Transactions on Healthcare Systems Engineering, 2011, 1(2): 101-115. doi: 10.1080/19488300.2011.609522 [20] TORO-DÍAZ H, MAYORGA M E, CHANTA S, et al. Joint location and dispatching decisions for emergency medical services[J]. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2013, 64(4): 917-928. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2013.01.002 [21] TOREGAS C, SWAIN R, REVELLE C, et al. The location of emergency service facilities[J]. Operations Research, 1971, 19(6): 1363-1373. doi: 10.1287/opre.19.6.1363 [22] ZOGRAFOS K G, NATHANAIL T, MICHALOPOULOS P. Analytical framework for minimizing freeway-incident response time[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 1993, 119(4): 535-549. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(1993)119:4(535) [23] TANSEL B C, FRANCIS R L, LOWE T J. State of the art- location on networks: a survey. Part: the p-center and p-median problems[J]. Management Science, 1983, 29(4): 482-497. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.29.4.482 [24] CHURCH R, REVELLE C. The maximal covering location problem[J]. Papers of the Regional Science Association, 1974, 32(1): 101-118. doi: 10.1111/j.1435-5597.1974.tb00902.x [25] NELAS J, DIAS J. Optimal emergencyvehicles location: an approach considering the hierarchy and substitutability of resources[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2020, 287(2): 583-599. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2020.03.067 [26] ALSALLOUM O I, RAND G K. A goal-programming model applied to the EMS system at Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia[R]. Lancaster: Lancaster University, 2003. [27] ALSALLOUM O I, RAND G K. Extensions to emergency vehicle location models[J]. Computersand Operations Research, 2006, 33(9): 2725-2743. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2005.02.025 [28] LIU Yi, LI Zhong-zhi, LIU Jing-xian, et al. A double standard model for allocating limited emergency medical service vehicle resources ensuring service reliability[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 69: 120-133. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2016.05.023 [29] 濮居一. 高速公路交通应急救援资源调配决策方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019.PU Ju-yi. Research on decision-making method of freeway traffic emergency rescue resource deployment[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019. (in Chinese) [30] 胡安兵. 基于遗传算法的高速公路应急站点选址模型及应用[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2013, 31(5): 104-106, 111. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2013.05.020HU An-bing. Freeway emergency location model and application using genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2013, 31(5): 104-106, 111. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2013.05.020 [31] SHAVARANI S M. Multi-level facility location-allocation problem for post-disaster humanitarian relief distribution: a case study[J]. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management, 2019, 9(1): 70-81. doi: 10.1108/JHLSCM-05-2018-0036 [32] DASKIN M S. A maximum expected covering location model: formulation, properties and heuristic solution[J]. Transportation Science, 1983, 17(1): 48-70. doi: 10.1287/trsc.17.1.48 [33] REPEDE J F, BERNARDO J J. Developing and validating a decision support system for locating emergency medical vehicles in Louisville, Kentucky[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1994, 75(3): 567-581. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(94)90297-6 [34] BHARSAKADE R S, KULKARNI O S. Analysis of and modeling for emergency medical services facility location for road accidents on highway[J]. International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development, 2018, 8(1): 595-604. doi: 10.24247/ijmperdfeb201866 [35] YU De-jian, ZHOU De-qun, HE Xiao-rong. A weighted grey target theory-based strategy model for emergency facility location[C]//IEEE. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Grey Systems and Intelligent Services (GSIS). New York: IEEE, 2009: 1158-1162. [36] PARK H, SHAFAHI A, HAGHANI A. A stochastic emergency response location model considering secondary incidents on freeways[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(9): 2528-2540. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2519043 [37] TAKEDA R A, WIDMER J A, MORABITO R. Analysis of ambulance decentralization in an urban emergency medical service using the hypercube queueing model[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 2007, 34(3): 727-741. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2005.03.022 [38] MENDONÇA F C, MORABITO R. Analysing emergency medical service ambulance deployment on a Brazilian highway using the hypercube model[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2001, 52(3): 261-270. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601097 [39] GEROLIMINIS N, KEPAPTSOGLOU K, KARLAFTIS M G. A hybrid hypercube-genetic algorithm approach for deploying many emergency response mobile units in an urban network[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 210(2): 287-300. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2010.08.031 [40] DAVOUDPOUR H, MORTAZ E, HOSSEINIJOU S A. A new probabilistic coverage model for ambulances deployment with hypercube queuing approach[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 70(5-8): 1157-1168. doi: 10.1007/s00170-013-5336-8 [41] WANG Qing-yi, NIE Xiao-feng. A stochastic programming model for emergency supply planning considering traffic congestion[J]. IISE Transactions, 2019, 51(8): 910-920. doi: 10.1080/24725854.2019.1589657 [42] NOGUEIRA L C, PINTO L R, SILVA P M S. Reducing emergency medical service response time via the reallocation of ambulance bases[J]. Health Care Management Science, 2016, 19(1): 31-42. doi: 10.1007/s10729-014-9280-4 [43] RAJAGOPALAN H K, SAYDAM C, XIAO J. A multiperiod set covering location model for dynamic redeployment of ambulances[J]. Computersand Operations Research, 2008, 35(3): 814-826. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2006.04.003 [44] GENDREAU M, LAPORTE G, SEMET F. The maximal expected coverage relocation problem for emergency vehicles[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2006, 57(1): 22-28. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601991 [45] 郭鹏辉, 朱建军, 王翯华. 考虑异质物资合车运输的灾后救援选址-路径-配给优化[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2019, 39(9): 2345-2360.GUO Peng-hui, ZHU Jian-jun, WANG He-hua. Location-routing-allocation problem with consolidated shipping of heterogeneous relief supplies in post-disaster rescue[J]. Systems Engineering—Theory and Practice, 2019, 39(9): 2345-2360. (in Chinese) [46] WANG Zheng, LENG Long-long, DING Jun-jie, et al. Study on location-allocation problem and algorithm for emergency supplies considering timeliness and fairness[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2023, 177: 109078. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2023.109078 [47] ZENG Ling-tai, LIU Yu-gang, TANG Yu-tian, et al. Study of the dynamic location of emergency rescue facilities for urban bus considering rescue urgency[C]//IEEE. The 5th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety. New York: IEEE, 2019: 868-874. [48] ESHGHI A A, TAVAKKOLI-MOGHADDAM R, EBRAHIMNEJAD S, et al. Multi-objective robust mathematical modeling of emergency relief in disaster under uncertainty[J]. Scientia Iranica, 2022, 29(5): 2670-2695. [49] QI Ming-yao, YANG Ying, CHENG Chun. Location and inventory pre-positioning problem under uncertainty[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2023, 177: 103236. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2023.103236 [50] IANNONI A P, MORABITO R, SAYDAM C. A hypercube queueing model embedded into a genetic algorithm for ambulance deployment on highways[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2008, 157(1): 207-224. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034490719410_1a45.html [51] TAN Zhe-yi, ZHANG Qian, DENG Wei-liang, et al. A simulation-based optimization for deploying multiple kinds road rescue vehicles in urban road networks[J]. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2023, 181: 109333. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2023.109333 [52] ANGULO E, CASTILLO E, GARCÍA-RÓDENAS R, et al. A continuous bi-level model for the expansion of highway networks[J]. Computers and operations research, 2014, 41: 262-276. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2013.02.022 [53] SALMAN F S, YVCEL E. Emergency facility location under random network damage: insights from the Istanbul case[J]. Computersand Operations Research, 2015, 62: 266-281. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2014.07.015 [54] BAŞAR A, ÇATAY B, VNLVYURT T. A multi-period double coverage approach for locating the emergency medical service stations in Istanbul[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2011, 62(4): 627-637. doi: 10.1057/jors.2010.5 [55] MRKELA L, STANIMIROVI AC'G Z. A variable neighborhood search for the budget-constrained maximal covering location problem with customer preference ordering[J]. Operational Research, 2022, 22(5): 5913-5951. doi: 10.1007/s12351-021-00652-3 [56] BERESNEV V, MELNIKOV A. Exact method for the capacitated competitive facility location problem[J]. Computersand Operations Research, 2018, 95: 73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2018.02.013 [57] PARRAGH S N, TRICOIRE F. Branch-and-bound for bi-objective integer programming[J]. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 2019, 31(4): 805-822. doi: 10.1287/ijoc.2018.0856 [58] ÁLVAREZ-MIRANDA E, FERNÁNDEZ E, LJUBIĆ I. The recoverable robust facility location problem[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2015, 79: 93-120. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2015.06.001 [59] LIN Yun-hui, TIAN Qing-yun. Branch-and-cut approach based on generalized benders decomposition for facility location with limited choice rule[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2021, 293(1): 109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2020.12.017 [60] ABOUNACER R, REKIK M, RENAUD J. An exact solution approach for multi-objective location-transportation problem for disaster response[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 2014, 41: 83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2013.08.001 [61] HAMMAD A W A, AKBARNEZHAD A, REY D. Sustainable urban facility location: minimising noise pollution and network congestion[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2017, 107: 38-59. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2017.09.005 [62] GENDRON B, KHUONG P V, SEMET F. A lagrangian-based branch-and-bound algorithm for the two-level uncapacitated facility location problem with single-assignment constraints[J]. Transportation Science, 2016, 50(4): 1286-1299. doi: 10.1287/trsc.2016.0692 [63] OUYANG Chao, ANSARI R. Applying a hybrid particle swarm optimization-tabu search algorithm to a facility location case in Jakarta[J]. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 2017, 34(3): 199-212. doi: 10.1080/21681015.2016.1243167 [64] XI Jian-feng, MU Kai, DING Tong-qiang, et al. A macroscopic and hierarchical location model of regional road traffic disaster relief material repository[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 11(1): 1-9. [65] JARAMILLO J H, BHADURY J, BATTA R. On the use of genetic algorithms to solve location problems[J]. Computersand Operations Research, 2002, 29(6): 761-779. doi: 10.1016/S0305-0548(01)00021-1 [66] 马昌喜, 石褚巍, 杜波. 轴辐式应急救援网络规划[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(3): 198-208. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.03.015 MA Chang-xi, SHI Chu-wei, DU Bo. Hub-and-spoke emergency rescue network planning[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(3): 198-208. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.03.015 [67] AKYVZ M H, ALTıNELI K, ÖNCAN T. Location and allocation based branch and bound algorithms for the capacitated multi-facility Weber problem[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2014, 222(1): 45-71. doi: 10.1007/s10479-012-1221-3 [68] YAN Song, WANG Jun-li, ZHU Yin. Road emergency events resources optimization and allocation model[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 392: 062128. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/392/6/062128 [69] CHAI Gan, SUN Ying-ying, ZHU Cang-hui. Particle swarm optimization algorithm for emergency resource allocation on expressway[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the first ACM/SIGEVO Summit on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. New York: ACM, 2009: 135-140. [70] TSAI Y, CHANG K W, YIANG G T, et al. Demand forecast and multi-objective ambulance allocation[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 32(7): 1859011. doi: 10.1142/S0218001418590115 [71] LUAN Si-liang, YANG Qing-fang, WANG Wei, et al. Random regret-minimization model for emergency resource preallocation at freeway accident black spots[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2018, 2018: 3513058. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2896061676 [72] SU Dong-lan, GUO Zhong-yin, LI Zhi-yong, et al. Operation risk model and monitoring-warning system of expressway tunnels[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2016, 14: 1315-1324. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2016.05.204 [73] TAKANO K, KIRIHARA K, KAWAGUCHI K, et al. Highway facilities on the Joban expressway to contribute to the reconstruction of the Tohoku Region[C]//IEEE. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1-5. [74] LIU Ming, LIN Tao, CHU Feng, et al. A new stochastic bi-level optimization model for post-disaster relief scheduling problem in sustainable Humanitarian supply chains with uncertain relief supplies and demands[J]. IFAC PapersOnLine, 2022, 55(10): 2481-2486. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2022.10.081 [75] AHMADI G, TAVAKKOLI-MOGHADDAM R, BABOLI A, et al. A decision support model for robust allocation and routing of search and rescue resources after earthquake: a case study[J]. Operational Research, 2022, 22(2): 1039-1081. doi: 10.1007/s12351-020-00591-5 [76] YAN Yuan-kun, KONG Yan, FU Zhang-jie. Dynamic resource scheduling in emergency environment[J]. Journal of Information Hiding and Privacy Protection, 2019, 1(3): 143-155. doi: 10.32604/jihpp.2019.07772 [77] 柴干, 赵倩, 黄琪, 等. 高速公路交通应急救援资源的配置[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2010, 20(1): 165-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2010.01.028CHAI Gan, ZHAO Qian, HUANG Qi, et al. Allocation of emergency rescue resources for freeway traffic[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2010, 20(1): 165-170. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2010.01.028 [78] 濮居一, 柴干, 过秀成. 考虑救援路径拥挤状态的交通应急资源派遣方法[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(6): 1102-1107.PU Ju-yi, CHAI Gan, GUO Xiu-cheng. Dispatching method for traffic emergency resource considering congestion state of rescue route[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1102-1107. (in Chinese) [79] ZHANG Jiang-hua, LI Jin, LIU Zhi-ping. Multiple-resource and multiple-depot emergency response problem considering secondary disasters[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(12): 11066-11071. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.03.016 [80] BOUYAHIA Z, HADDAD H, JABEUR N, et al. A two-stage road traffic congestion prediction and resource dispatching toward a self-organizing traffic control system[J]. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 2019, 23(5): 909-920. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000042271083599_f56c.html [81] PARK H, WADDELL D, HAGHANI A. Online optimization with look-ahead for freeway emergency vehicle dispatching considering availability[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 109: 95-116. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2019.09.016 [82] CAO Ce-jun, LI Cong-dong, YANG Qin, et al. A novel multi-objective programming model of relief distribution for sustainable disaster supply chain in large-scale natural disasters[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 174: 1422-1435. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.037 [83] ZAREI M H, CARRASCO-GALLEGO G R, RONCHI S. On the role of regional hubs in the environmental sustainability of humanitarian supply chains[J]. Sustainable Development, 2019, 27(5): 846-859. doi: 10.1002/sd.1945 [84] WANG Bo-chen, DENG Wei-liang, TAN Zhe-yi, et al. A two-stage stochastic optimization for disaster rescue resource distribution considering multiple disasters[J]. Engineering Optimization, 2024, 56(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2022.2144277 [85] ZHANG Jiang-hua, LI Yu-chen, YU Guo-dong. Emergency relief network design under ambiguous demands: a distributionally robust optimization approach[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 208: 118139. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118139 [86] 朱苍晖, 李兴华, 柴干. 基于agent的高速公路救援车辆动态派遣方法[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 41(增): 68-73.ZHU Cang-hui, LI Xing-hua, CHAI Gan. Agent-based dynamic dispatch of traffic rescue vehicles in expressway network[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 41(S): 68-73. (in Chinese) [87] 李建斌. 高速公路突发事件紧急救援关键技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012.LI Jian-bin. Research on key technology of freeway incident emergency respond[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2012. (in Chinese) [88] DIJKSTRA E W. A note on two problems inconnexion with graphs[J]. Numerische Mathematik, 1959, 1(1): 269-271. doi: 10.1007/BF01386390 [89] BELLMAN R. On a routing problem[J]. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 1958, 16(1): 87-90. doi: 10.1090/qam/102435 [90] HART P E, NILSSON N J, RAPHAEL B. Aformal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and Cybernetics, 1968, 4(2): 100-107. doi: 10.1109/TSSC.1968.300136 [91] HAMDI S, PRIHANDOKO P. Analisis algoritma Dijktra dan algoritma Bellman-Ford sebagai penentuan jalur terpendek menuju lokasi kebakaran (studi kasus: Kecamatan Praya Kota)[J]. Energy-Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu-Ilmu Teknik, 2018, 8(1): 26-32. [92] SHI Liu-hong, YANG Bin. An emergency routing model based on fuzzy road connectivity[C]//IEEE. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Automation Engineering. New York: IEEE, 2011: 465-469. [93] KIRONO S, ARIFIANTO M I, PUTRA R E, et al. Graph-based modeling and Dijkstra algorithm for searching vehicle routes on highways[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 2018, 9(8): 1273-1280. [94] YAO Jiao, DAI Ya-xuan, NI Yi-ling, et al. Deep characteristics analysis on travel time of emergency traffic[J]. International Journal of Computational Science and Engineering, 2020, 22(1): 162-169. doi: 10.1504/IJCSE.2020.107271 [95] WEI Xiao-ge, WEI Lyu, SONG Wei-guo. Rescue route reselection model and algorithm for the unexpected accident[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2013, 62: 532-537. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2013.08.097 [96] YANG Di, YANG Shun-xin, JIN Yu-heng, et al. Design of deploying expressway incident response trucks in regional expressway networks: a case study in Shanxi Province[C]//ASCE. 15th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals. Reston: ASCE, 2015: 2135-2145. [97] ZHAO Mu-hua, LIU Jian, HU Xiao-jian. A path selection method for traffic accident emergency rescue on expressway network[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Transportation, Mechanical, and Electrical Engineering. New York: IEEE, 2011: 1861-1866. [98] ALVAREZ P, LERGA I, SERRANO-HERNANDEZ A, et al. The impact of traffic congestion when optimising delivery routes in real time. A case study in Spain[J]. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 2018, 21(5): 529-541. doi: 10.1080/13675567.2018.1457634 [99] WEN Hui-ying, WU Jia-bin, DUAN Yu-chen, et al. A methodology of timing co-evolutionary path optimization for accident emergency rescue considering future environmental uncertainty[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 131459-131472. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2940315 [100] LI Jing-quan, MIRCHANDANI P B, BORENSTEIN D. A Lagrangian heuristic for the real-time vehicle rescheduling problem[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2009, 45(3): 419-433. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2008.09.002 [101] NIU Yu-xin. A novel model and GA-based solution for resource scheduling in highway emergency rescue[C]//Atlantis Press. Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development. Dordrecht: Atlantis Press, 2018: 1549-1553. [102] ZHAO Jian-dong, GUO Yu-jie, DUAN Xiao-hong. Dynamic path planning of emergency vehicles based on travel time prediction[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2017, 2017: 9184891. [103] HE Feng, HE Rui-chun, SUN Sheng-nan, et al. Research on the model of emergency fire rescue vehicle routing selection and resource allocation[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 641/642: 824-828. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.641-642.824 [104] GHANNADPOUR S F, NOORI S, TAVAKKOLI-MOGHADDAM R, et al. A multi-objective dynamic vehicle routing problem with fuzzy time windows: model, solution and application[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2014, 14: 504-527. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2013.08.015 [105] YAMADA T. A network flow approach to a city emergency evacuation planning[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 1996, 27(10): 931-936. doi: 10.1080/00207729608929296 [106] NANNICINI G, DELLING D, SCHULTES D, et al. Bidirectional A* search on time-dependent road networks[J]. Networks, 2012, 59(2): 240-251. doi: 10.1002/net.20438 [107] ZHAO Jian-dong, DUAN Xiao-hong. A novel particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving the shortest path problem in highway network[J]. Advances in Transportation Studies, 2015, 4(2): 97-106. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303575789_A_novel_particle_swarm_optimization_algorithm_for_solving_the_shortest_path_problem_in_highway_network [108] 赵扬, 王雷, 赵秋红. 考虑时间延误的高速公路应急救援模型研究[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2020, 40(5): 844-856.ZHAO Yang, WANG Lei, ZHANG Qiu-hong. Study on emergency rescue model of expressway with time delay[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical Sciences, 2020, 40(5): 844-856. (in Chinese) [109] ZHOUYa-wen, LIU Jing, ZHANG Yu-tong, et al. A multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for multi-period dynamic emergency resource scheduling problems[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2017, 99: 77-95. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2016.12.011 [110] TIAN Guang-dong, FATHOLLAHI-FARD A M, REN Ya-ping, et al. Multi-objective scheduling of priority-based rescue vehicles to extinguish forest fires using a multi-objective discrete gravitational search algorithm[J]. Information Sciences, 2022, 608: 578-596. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.06.052 [111] WAN Meng-ran, YE Chun-ming, PENG Da-jiang. Multi-period dynamic multi-objective emergency material distribution model under uncertain demand[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 117: 105530. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105530 [112] ZHU Cang-hui, LI Xing-hua, CHAI Gan. The optimization approach for traffic rescue resource dispatch on expressway based on fuzzy programming[C]//CAO Bing-yuan, WANG Guo-jun, GUO Si-zong, et al. Fuzzy Information and Engineering 2010: Volume I. Berlin: Springer, 2010: 313-326. [113] CHAI Gan, WANG Xi-ying, GUO Jian-hua. Optimized dispatch of expressway block removal and rescue resources based on genetic algorithms[C]//ASCE. International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety. Reston: ASCE, 2011: 802-815. [114] CHAI Gan, CAO Jin-de, HUANG Wei, et al. Optimized traffic emergency resource scheduling using time varying rescue route travel time[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 1567-1575. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.09.086 [115] PU Ju-yi, GUO Xiu-cheng, CHAI Gan, et al. Emergency rescue resource dispatch of expressway based on potential accidents and GA: case study of Henan, China[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 409/410: 1262-1268. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.409-410.1262 [116] 龚静. 多事故点救援车辆综合派遣问题研究[J]. 交通与运输, 2014, 30(1): 199-202.GONG Jing. Research on the rescue vehicle consolidated dispatching of multiple accident points[J]. Trafficand Transportation, 2014, 30(1): 199-202. (in Chinese) [117] DUAN Xiao-hong, NIU Tian-yong, HUANG Qi. An improved shuffled frog leaping algorithm and its application in dynamic emergency vehicle dispatching[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018, 2018: 7896926. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2794570847 [118] LI Yan-rong, LI Xiao-yong, HOU Li-yang, et al. A multi-objective emergency resource scheduling method based on MOEA/D[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Algorithms, Computing and Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2019: 219-224. [119] WANG Wei, HUANG Li, GUO Zhao-xia. Optimization of emergency material dispatch from multiple depot locations to multiple disaster sites[J]. Sustainability, 2017, 9(11): 1978-1985. doi: 10.3390/su9111978 [120] XU Sheng, XU Zhou-hua, LIU Yi. Optimal dispatch of oil spill resources considering resource priority[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Engineering. New York: IEEE, 2016: 76-79. [121] 刘波, 李砚. 应急物资车辆调度的鲁棒双层优化模型[J]. 系统工程, 2016, 34(5): 77-81.LIU Bo, LI Yan. Robust bilevel optimization model for vehicle routing of emergency commodities[J]. Systems Engineering, 2016, 34(5): 77-81. (in Chinese) [122] SUN Hua-li, WANG Yang, XUE Yao-feng. A bi-objective robust optimization model for disaster response planning under uncertainties[J]. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2021, 155: 107213. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107213 [123] AKBARPOUR M, ALI TORABI S A, GHAVAMIFAR A. Designing an integrated pharmaceutical relief chain network under demand uncertainty[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2020, 136: 101867. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2020.101867 [124] WANG Wei, WANG Shuai-an, ZHEN Lu, et al. EMS location-allocation problem under uncertainties[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2022, 168: 102945. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2022.102945 [125] TANG Zhao-ping, QIN Jin, SUN Jian-ping. Railway emergency resource dispatching optimization based on fuzzy satisfaction degree under the priority principle[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 33(5): 2677-2686. doi: 10.3233/JIFS-169317 [126] ZHOU Ya-wen, LIU Jing. A multi-agent genetic algorithm for multi-period emergency resource scheduling problems in uncertain traffic network[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. New York: IEEE, 2017: 43-50. [127] ZHANG Jiang-hua, LONG Daniel-zhuoyu, LI Yu-chen. A reliable emergency logistics network for COVID-19 considering the uncertain time-varying demands[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2023, 172: 103087. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2023.103087 [128] ADARANG H, BOZORGI-AMIRI A, KHALILI-DAMGHANI K, et al. A robust bi-objective location-routing model for providing emergency medical services[J]. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management, 2020, 10(3): 285-319. doi: 10.1108/JHLSCM-11-2018-0072 -





 下载:
下载: