Toll Model and Algorithm of Road Jammed with Traffic Based on Elastic Demand
-
摘要: 拥挤道路收费作为交通需求管理的一种有效措施在许多国家和地区开始提倡。研究了弹性需求下的拥挤道路收费问题, 建立了双层规划模型, 其中上层模型以用户盈余最大化为目标, 下层模型满足弹性需求下的随机用户平衡(SUE)。基于双层模型求解的复杂性, 设计了一个基于步长加速法和惩罚函数法的启发式算法, 实例计算表明该模型与算法是有效的。Abstract: Collecting toll for road jammed with traffic as an effective measure was adopted for managing traffic demand in many conutries and areas. The bi level programming model of the toll road was developed. The upper objective is consumer surplus which belongs to economics, while the lower is stochastic user equilibrium with elastic demand.Because of complex property, a heuristic algorithm which is based on step acceleration method and penalty function method is proposed, and a numerical example is given.
-
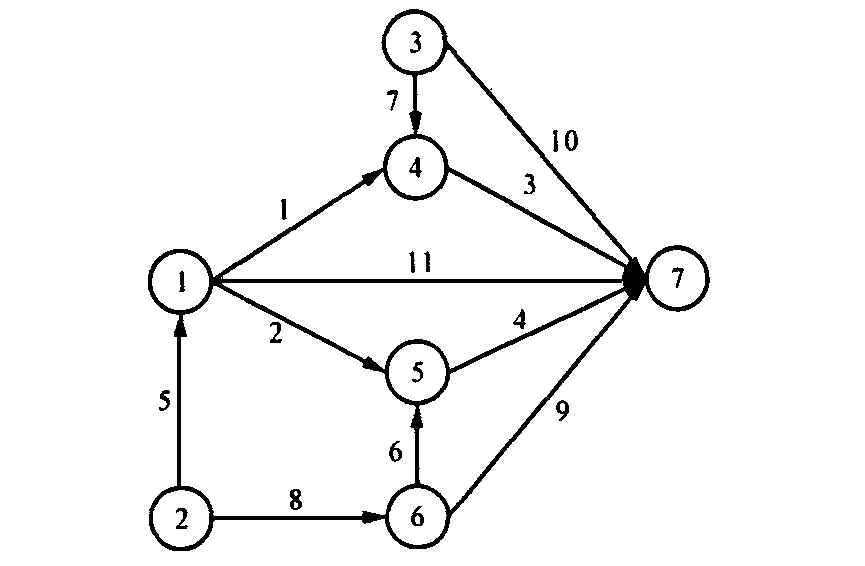
表 1 OD对需求函数的参数数据
OD对 (1, 7) (2, 7) (3, 7) (6, 7) 500 400 300 300 πω 0.05 0.05 0.04 0.03 表 2 路段旅行时间函数的参数数据
路段a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 t 6 5 6 7 6 1 4 10 9 11 13 Ba 200 200 200 200 100 100 200 150 200 200 250 表 3 不同的η及δ下的求解结果
η 0.03 0.05 0.06 0.03 0.03 0.05 δ 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 u (1, 4) 0.4000 0.7312 0.8500 0.6094 1.0000 1.0000 u (1, 5) 0.45000 0 0.20000 0.22500 0.06875 0.50000 u (1, 7) 0.2000 0.4250 0.5063 0.2531 0 0.4453 u (2, 1) 0.5000 0.9500 1.0630 0.7031 1.6000 0.8125 u (2, 6) 0.4000 0.8687 1.2000 0.6000 0.8812 0.5234 u (3, 4) 0.8938 1.5190 1.3440 1.5280 1.8060 1.2580 u (3, 7) 0.7063 1.2560 1.0560 1.0870 0.6625 0.7734 u (4, 7) 0.8500 0.6937 0.6563 0.6563 0 0.5000 u (5, 7) 1.100 1.781 1.656 1.397 1.100 1.250 u (6, 5) 0.8000 0.4000 0.4000 0.6000 0.8438 1.0000 u (6, 7) 0.4500 0.9750 0.8437 0.6000 0.2875 1.0470 Z -20640 -20660 -206650 -20630 -20610 -20660 q (1, 7) 246.8 238.0 237.1 251.4 256.0 237.8 q (2, 7) 142.3 133.4 131.9 144.1 145.8 135.4 q (3, 7) 186.8 184.1 185.2 184.4 186.3 186.7 q (6, 7) 217.1 213.3 215.1 216.0 217.1 211.7 num.SUE 612 1431 1023 1510 907 663 num.i 2 6 2 2 2 3 注: 在每种情形下, u (0) =0, α=1.95, ε=0.01, num.SUE为模型求解过程中SUE的总迭代数, num.i为惩罚迭代次数。 表 4 OD需求函数参数πω变化下的计算结果
πω 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.08 0.10 q (1, 7) 287.3 266.6 220.6 175.8 147.0 q (2, 7) 169.00 146.60 128.70 83.37 62.39 q (3, 7) 182.9 173.0 146.0 124.0 107.5 q (4, 7) 186.4 180.2 166.7 140.0 123.9 TD 825.60 766.40 662.00 523.17 440.79 Z -21910 -15560 -11550 -6875 -4378 注: 在每种情形下, u (0) =0, α=1.95, ε=0.08, δ=0.4, TD为网络所有OD对的总实际需求量, 不同OD对的需求函数参数πω均相同。 -
[1] YANG H, LAM W HK. Optimal road tolls under conditions of queuing and congestion[J]. Transportation Researh A, 1996, 30: 319-332. [2] YANG H, BELL M G H. Traffic restraint, road pricing and network equivibrium[J]. Transportation Research B, 1997, 31: 303-314. doi: 10.1016/S0191-2615(96)00030-6 [3] LAM W H K, GAO Z Y, CHAN K S, YANG H. A stochasticuser equilibrium assignment model for congested transit networks[J]. Transportation Research, 1999, 33B: 358-361. [4] FERRARI P. Capacity constraints in urban transport networks[J]. Transportation Research, 1997, 31B: 291-301. [5] YANG H, HUANG H J. Principle of marginal-cost pricing: how does it work in a general road network[J]. Transportation Research, 1998, 32A: 45-54. [6] 黄海军. 城市交通网络平衡分析理论与实践[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1994. -





 下载:
下载: