-
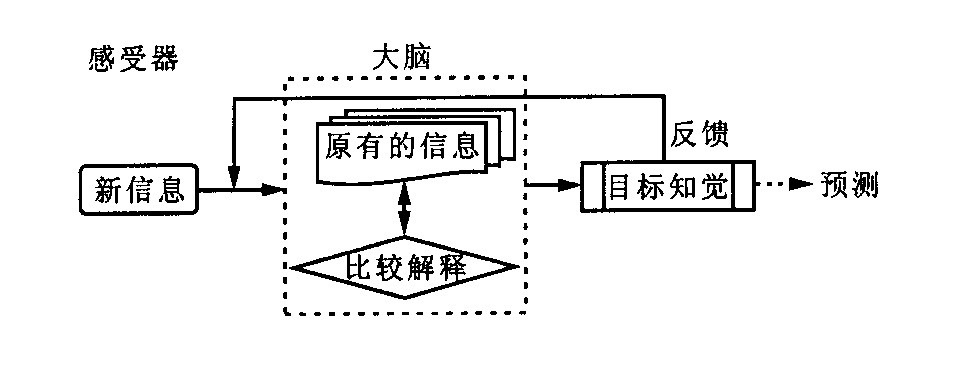
摘要: 通过对驾驶员的反应能力的量化、速度判断过程的分析和对诸如饮酒、服药、电话干扰及疲劳驾驶等外部因素影响下驾驶员行为与跟随车与引导车行驶一致性的研究, 计算与分析行车时的安全距离, 寻求既可避免发生追尾碰撞事故, 又不影响道路通行能力的安全距离恰当值: 当驾驶员和车辆状况良好时, 行车距离保持在速度(以m/s为单位) 的1 /2以上时, 才可能安全; 当驾驶员和车辆状况不良时, 行车距离保持在速度的二倍以上时, 才安全。Abstract: It is pointed out that the traffic accident mostly result in improper driver's action. The driver's capability of response time and speed estimation are studied, and driving performance by car following in traffic is investigated, in order to calculate the appropriate driving safety distance, which assures that neither the rear end collision occurs nor road capacity is affected. If the following distance is S (m), and the following vehicle's velocity is V (m/s), the study results show that when S > V/2, the following is safety under the good condition of driver and vehicle, when S > 2V, the following is safety under the poor operation of driver and vehicle.
-
Key words:
- safety distance /
- response time /
- speed estimation /
- car follwing
-
表 1 道路交通事故类型构成
Table 1. The percentage of traffic accidents & apos; type
事故类型 正面碰撞 侧面碰撞 追尾碰撞 相向刮擦 同向刮擦 碾压 翻车 坠车 撞固定物 失火 其它 事故次数 82653 109552 66154 13603 15854 6369 14191 2769 13118 242 21633 占总数比率 23.88% 31.65% 19.11% 3.93% 4.58% 1.84% 4.10% 0.80% 3.79% 0.07% 6.25% 表 2 交通事故中驾驶员因素
Table 2. Driver & apos; s factor in traffic accidents
国家 驾驶员因素 国家和地区 驾驶员因素 国家和地区 驾驶员因素 国家 驾驶员因素 英国 56.1% 西班牙 92.0% 法国 85.5% 瑞典 81.1% 前苏联 52.7% 日本 40.0% 南美洲 85.7% 南斯拉夫 69.7% 表 3 对光反应的复杂反应时间各阶段的量化
Table 3. Quantifying response time of test in different experiment conditions
年龄组段 反应时间的过程/ms 反应时间/ms 光-视网膜-视中枢 判断时间 动作时间 20-29 40 376 110±4.5 526 30-39 40 371 121±3.7 532 40-49 40 374 135±5.3 549 ≥50 40 383 147±9.3 570 表 4 跟随车与前驱车保持一致性情况
Table 4. Averages and standard deviations of coherence in car-following test
项目 基准条件 电话干扰 连续驾驶2.5 h后 服抗组胺药(10 mg) 服抗组胺药(20 mg) 服抗组胺药(30 mg) 少量饮酒 失眠状态 一致性 0.958±0.059 0.937±0.063 0.937±0.054 0.945±0.071 0.940±0.061 0.943±0.058 0.948±0.037 0.949±0.070 p值 < 0.0570 < 0.0010 < 0.0520 < 0.0030 < 0.0025 < 0.0020 < 0.0051 < 0.0010 表 5 驾驶员信息复杂度β系数[2]
Table 5. Coefficient (β) of complexity of the information which driver deals with
实验条件 β系数 实验条件 β系数 实验条件 β系数 实验条件 β系数 基准条件下 1.0 少量饮酒 1.1 服抗组胺药(10 mg) 1.5 连续驾驶2.5 h后 2.5 服抗组胺药(20 mg) 失眠状态 电话干扰 服抗组胺药(30 mg) -
[1] FU Rui, CHEN Yin-san. Study of truck rear bumper crashworthiness[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2001, 1(2): 41-43. [2] 张殿业. 驾驶员驾驶行为测试技术及安全可靠性研究报告[R]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 1999.1~24. [3] 曹崎. 人机工程学[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 1990.32-39. [4] KAREL Brookuis, DICK De Waard. Measuring driving performance by car-following in traffic[J]. Ergonomics, 1994, 37(3): 427~434. doi: 10.1080/00140139408963661 [5] ZHOU Wei, WANG Bing-gang. Theoretical study about road section capacity[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2001, 1(2): 92-98. [6] 王王宣, 李宏光, 赵航, 等. 现代汽车安全[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1998: 178-200. [7] 郭恩德. 交通法规学[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1991. -





 下载:
下载: