Simulation analysis for collision characteristics of concrete barriers on montane highway
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
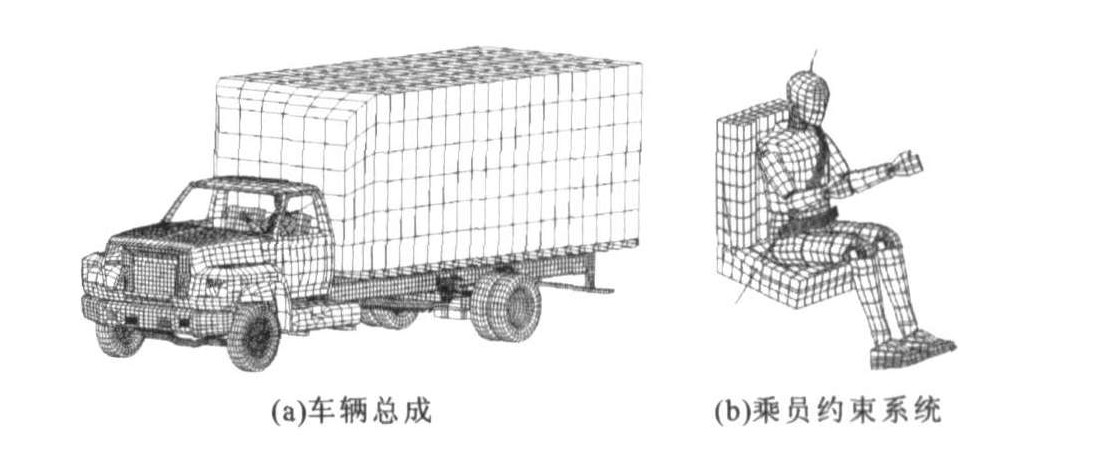
摘要: 为探明山区公路上常用的间断式混凝土护栏及连续式混凝土护栏的碰撞特性, 基于动态显式有限元方法及VPG软件, 建立了完整的汽车-护栏-乘员-座椅-安全带一体化模型, 对四种典型山区公路护栏进行了碰撞仿真分析。发现汽车撞击间断式混凝土护栏时, 出现混凝土墩拌阻车轮的现象, 甚至出现汽车的右前轮被护栏完全刮脱的情况, 不仅假人头部及胸部遭受剧烈冲击, 而且驾驶室变形严重; 而汽车撞击连续式混凝土护栏时, 车辆的左后轮出现了明显的抬高现象, 表明车辆存在倾翻的趋势, 但车辆尾部的高度变化曲线表明, 车辆左后轮在抬高到一定高度后, 将不再继续抬高, 并逐步返回地面, 说明车辆尾部的高度变化趋势是趋于稳定的; 当护栏底部凸缘高为80mm时, 出现前轮可以顺利爬上并溜下护栏斜坡, 而后轮无法爬上护栏斜坡的现象; 当护栏底部凸缘高为150mm时, 则车辆的前、后轮均不能爬上护栏斜坡。结果表明, 间断式混凝土护栏存在的主要问题是对失控车辆的诱导能力不足; 连续式混凝土护栏存在的主要问题是护栏底部的凸缘太高, 护栏的主要尺寸参数需要优化。Abstract: In order to explore the collision characteristics of interrupted type and continuous type concrete barriers on montane highway, a integrated model of automobile-barrier-passenger-seat-safety belt was established by dynamic explicit finite element method(EFEM) and VPG software. The collision process analysis for four kinds of typical montane highway concrete barriers was carried out. It is pointed that when interrupted type concrete barrier is crashed by truck, concrete frusta blocks wheel, even right front wheel is divorced from truck, dummy's head and chest suffer from violent impact, and cab deformation is severe; however, when continuous type concrete barrier is crashed by truck, the hoist phenomenon of left rear wheel and the turning over trend of truck are obvious, but the height variety curve of truck tail shows that the hoist of left rear wheel does not continue over a certain height, and the wheel return to ground gradually, that's to say, the height variety trend of truck tail is stability; as the height of convex barrier flange at bottom is 80 mm, the front wheel of truck can smoothly climb up and slip away concrete barrier slope, but the rear wheel of truck can't climb up concrete barrier slope; while the height of convex barrier flange at bottom is 150 mm, the front wheel and rear wheel of truck can't climb up concrete barrier slope. Analysis result indicates that interrupted type concrete barrier is short of inducing ability to losing control vehicle, the convex flange of continuous type concrete barrier at bottom is too high to be climbed by truck, and it's necessary to optimize its main structure parameters.
-
Key words:
- traffic safety /
- concrete barrier /
- simulation /
- collision /
- montane highway
-
表 1 混凝土护栏
Table 1. Concrete barriers
序号 护栏型式 基本特征 1 中部连续式钢管+混凝土墩 混凝土墩间距为1 m; 混凝土墩之间采用整体钢管相连, 即钢管穿越全部混凝土墩 2 顶部钢管+中部间断式钢管+混凝土墩 混凝土墩间距为1 m; 混凝土墩之间采用钢管相连, 钢管长为1.3 m, 钢管插入混凝土墩的深度为每侧0.15 m; 顶部钢管将混凝土墩连成整体 3 连续式混凝土护栏 混凝土连续式布置 4 顶部钢管+连续式混凝土护栏 混凝土连续式布置; 顶部钢管用于防止车辆跨越护栏, 并增加美感 -
[1] 雷正保, 谢玉洪, 李海侠. 大变形结构的耐撞性[M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 2005. [2] 雷正保, 杨兆. 汽车-护栏碰撞系统的安全性研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2006, 28(2): 152-158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-680X.2006.02.011Lei Zheng-bao, Yang Zhao. Astudy on the safetyin vehicle-guardrail impact[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2006, 28(2): 152-158. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-680X.2006.02.011 [3] 雷正保, 杨兆. 三波护栏的耐撞性研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2006, 23(7): 130-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2006.07.031Lei Zheng-bao, Yang Zhao. Study on crashworthiness of three-beam guardrail structure[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2006, 23(7): 130-136. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2006.07.031 [4] 雷正保, 杨兆. 汽车撞击护栏时乘员的安全性研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2006, 25(2): 5-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2006.02.002Lei Zheng-bao, Yang Zhao. Study on the passenger safety during the impact process of automobile against fence[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2006, 25(2): 5-11. (in Chi-nese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2006.02.002 [5] 雷正保, 周屏艳, 颜海棋, 等. 汽车-护栏系统耐撞性研究的有限元模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2006, 16(8): 9-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.08.002Lei Zheng-bao, Zhou Ping-yan, Yan Hai-qi, et al. Finite element model for crashworthiness study of vehicle crash barrier system[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2006, 16(8): 9-16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.08.002 [6] 雷正保, 周屏艳, 颜海棋. 护拦防护重型车辆撞击的能力[J]. 长沙理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 3(3): 65-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9331.2006.03.010Lei Zheng-bao, Zhou Ping-yan, Yan Hai-qi. The crashworthiness of guardrail to defend the impact of heavyvehicle[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science and Technology: Natural Science, 2006, 3(3): 65-73. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9331.2006.03.010 [7] 李文权. 高速公路路侧标志遮挡问题[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2006, 6(3): 97-102. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200603021Li Wen-quan. Blocking problemof freeway side traffic signs[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2006, 6(3): 97-102. (in Chinese) http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200603021 [8] 任卫群, 张云清, 金国栋. 公路车辆对道路破坏性研究的系统化方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2005, 18(4): 110-114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2005.04.023Ren Wei-qun, Zhang Yun-qing, Jin Guo-dong. Systematic research method for vehicle-generated road damage[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2005, 18(4): 110-114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2005.04.023 [9] ETA-Engineering Technology Associates. VPG/safety tuto-rial: process guidance for vehicle impact and safety analysis model creation[R]. Miami: ETA-Engineering Technology Associates, 2004. [10] Hallquist J O. LS-DYNA theoretical manual[R]. California: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2006. [11] Livermore Software Technology Corporation. LS-DYNA ke-yword user's manual[R]. California: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2006. [12] JTG D81-2006, 公路交通安全设施设计规范[S]. [13] 罗云飞, 刘振闻, 李光耀, 等. 受冲薄壁结构动力效应的显式有限元分析[J]. 力学学报, 2000, 32(1): 70-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB200001007.htmLuo Yun-fei, Liu Zhen-wen, Li Guang-yao, et al. Finite element method for the evaluation of dynamic effects of thin-walled structure in impacting processes[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical Applied Mechanics, 2000, 32(1): 70-77. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB200001007.htm [14] 雷正保. 汽车纵向碰撞控制结构设计的理论与方法[M]. 长沙: 湖南大学出版社, 2001. [15] 雷正保. 汽车覆盖件冲压成形CAE技术[M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 2003. -





 下载:
下载: