Optimal route arithmetic with multigoals in highway network based on travel decision-making
-
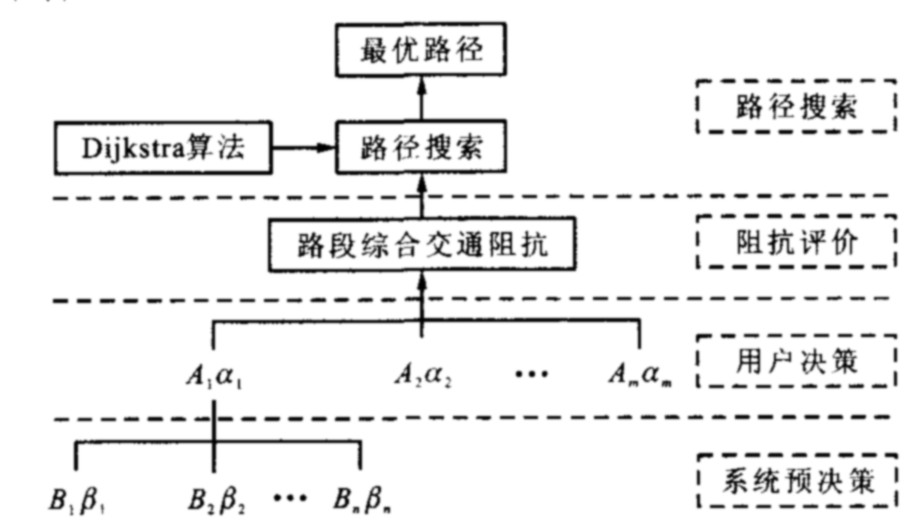
摘要: 为使公路网静态最优出行路径能综合表达道路环境影响因素与出行者的路径选择偏好, 研究了GIS环境下的用户-系统最优出行路径决策模式。基于层次分析法, 构建了综合考虑行程时间、舒适安全性与行程费用的公路网路段交通阻抗评价指标体系, 提出了对定性与定量化参评指标进行综合一致性处理的方法。通过用户-系统共同决定的路段交通阻抗的综合评价过程, 将最优路径问题转化为最短路径问题, 采用各路段各出行目标的标准化值之和作为评价指标, 采用Dijkstra算法实现最优路径的搜索。实例验证结果表明: 最优路径比距离最短路径出行距离增加8%, 出行时间减少7%, 舒适安全性提高17%, 出行费用增加13%, 所得最优路径是针对特定用户的多目标路径, 明显异于单目标最短路径, 表明该方法可行。Abstract: To synthetically consider the correlative influence factors of road environment and special user's desires of optimal route selection in the static optimal route search with multigoals in highway network, user-system decision-making model of optimal route search under GIS environment was studied.Based on AHP theory, the evaluation indices system of link impedance was presented involving travel time, safety, comfort and travel expenditure, and the methods of standardized process for the indices were raised. Through the synthetical evaluation process of link impedance determined by user-system, the optimal route problem was transformed into the shortest route problem, the sum of standardized values of link travel goals was taken as the evaluation index, and the optimal route could be found by using Dijkstra algorithm. Test result shows that the optimal route is different from the shortest path, its travel distance increases by 8%, its travel time decreases by 7%, its comfort and safety improve by 17%, its travel charge increases by 13%, the searched optimal route with user-aimed multigoals is better than the shortest route with single goal, so the arithmetic is feasible.
-
表 1 综合评价指标权重
Table 1. Indices weights of integrated evaluation
评价准则 评价指标及权重 指标相对于准则层组合权重 指标的度量 行程时间α1 行程时间1.000 1.000 h 行程费用α2 综合费用1.000 1.000 元·veh-1 舒适安全α3 交通负荷0.164 0.164 V/C 路面状况0.332 行驶质量0.534 0.177 RRQI 破损状况0.267 0.089 PPCI 抗滑评价等级0.199 0.066 优、良、中、次、差 交通安全0.464 交通事故率1.000 0.464 AAH/(次·亿车公里-1) 沿途景观0.040 0.040 优、良、中、次、差 表 2 用户出行决策量化表示
Table 2. Measurable disposal of user's travel decision-making
重要性 很重要 重要 不重要 很重要 0 1 2 重要 -1 0 1 不重要 -2 -1 0 表 3 交通阻抗属性
Table 3. Attribute of traffic impedance
ID 路线编码 路段编码 起点里程 终点里程 Time字段 Cost字段 Comfort字段 Integration字段 1 G020000000 G020120111001 K0+000 K0+370 0.006 1 0.006 8 0.358 0 0.104 7 2 G020000000 G020120111002 K0+370 K12+247 0.196 0 0.217 1 0.456 0 0.272 1 3 G020000000 G020120223003 K12+247 K12+648 0.006 6 0.007 3 0.395 0 0.115 5 4 G020000000 G020120223004 K12+648 K52+045 0.650 0 0.720 0 0.682 0 0.670 0 5 G020000000 G020120223005 K52+045 K52+320 0.004 5 0.005 0 0.715 0 0.203 5 -
[1] 孙燕, 陈森发, 黄鹍. 基于灰色评价理论的自适应最优路径选择[J]. 中国公路学报, 2003, 16(4): 87-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200304019.htmSun Yan, Chen Sen-fa, Huang Kun. Adaptive optimal route selection based on gray evaluation theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2003, 16(4): 87-90. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200304019.htm [2] 陆锋, 周成虎, 万庆. 基于层次空间推理的交通网络行车最优路径算法[J]. 武汉测绘科技大学学报, 2000, 25(3): 226-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH200003007.htmLu Feng, Zhou Cheng-hu, Wan Qing. An optimum vehicular path algorithm for traffic network based on hierarchical spatial reasoning[J]. Journal of Wuhan Technical University ofSurveying and Mapping, 2000, 25(3): 226-232. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH200003007.htm [3] 陈松岩, 今井昭夫. 物流网络选址与路径优化问题的模型与启发式解法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2006, 6(3): 118-121. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200603025Chen Song-yan, I mai Akio. Model and heuristic solution for location routing problems of logistics network[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2006, 6(3): 118-121. (in Chinese) http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200603025 [4] Pang G K H, Takabashi K, Yokota T, et al. Adaptive route selection for dynamic route guidance system based on fuzzyneural approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1999, 48(6): 2 028-2 041. doi: 10.1109/25.806795 [5] 胡刚, 金振伟, 司小平, 等. 车载导航技术现状及其发展趋势[J]. 系统工程, 2006, 24(1): 41-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCXT200601007.htmHu Gang, Jin Zhen-wei, Si Xiao-ping, et al. The actuality and trend of in-vehicle navigation technologies[J]. System Engineering, 2006, 24(1): 41-47. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCXT200601007.htm [6] 杨瑞臣, 周永付, 云庆霞. 寻找车辆最优路径的混合算法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2005, 5(1): 102-105. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200501024Yang Rui-chen, Zhou Yong-fu, Yun Qing-xia. Hybrid algorithmof vehicle's optimal route[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2005, 5(1): 102-105. (in Chi-nese). http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200501024 [7] 马永锋. 公路网GIS数据组织方法及公路网多目标最优出行路径研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2004. [8] 王炜, 邓卫, 杨琪. 公路网络规划建设与管理方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. [9] 黎茂盛, 王炜, 史峰. 降级路网的认知及交通流平衡分析模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(6): 87-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200606016.htmLi Mao-sheng, Wang Wei, Shi Feng. Cognition of degraded road network and equilibrium analysis model on traffic flow[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2006, 19(6): 87-91. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200606016.htm [10] 王莲芬, 许树柏. 层次分析法引论[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 1990. [11] 徐泽水. 层次分析新标度法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 1998, 18(10): 74-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL810.009.htmXu Ze-shui. A new scale method in analytic hierarchy process[J]. System Engineering Theory and Application, 1998, 18(10): 74-77. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL810.009.htm [12] 张渭军, 王华. 城市道路最短路径的Dijkstra算法优化[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 25(6): 62-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200506014.htmZhang Wei-jun, Wang Hua. Optimination Dijkstra arithmetic for shortest path of urban traffic net[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2005, 25(6): 62-65. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200506014.htm -





 下载:
下载: