Monitoring method of safety computer condition for railway signal system
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
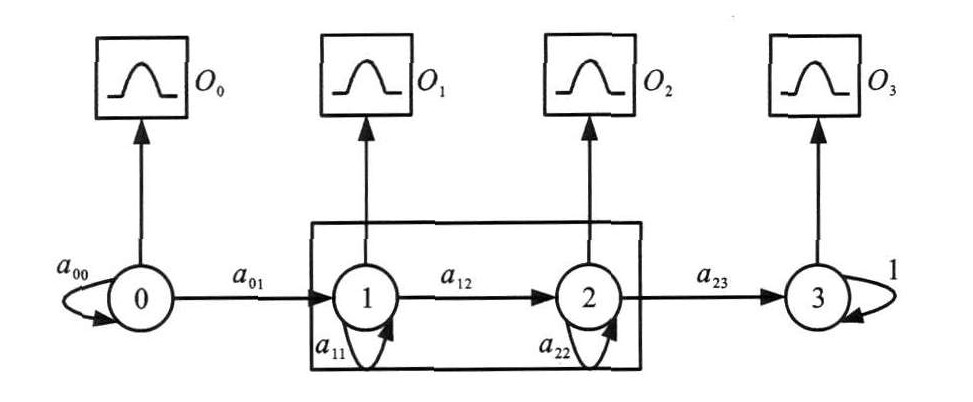
摘要: 基于隐马尔科夫模型(Hidden Markov Model, HMM)提出了状态监测和故障诊断的原理与基本流程。通过观测数据的提取与降维, 正常态模型训练与改进, 故障态模型训练等一系列措施, 实现了两模冗余安全计算机的状态监测, 对正常态与时钟偏离1%~10%等7种不同条件进行监测。监测结果表明: 对数似然概率均值从-228.98降至-1 385.60, 健康状态不断恶化。对1号处理单元(PU1)故障状态进行仿真监测时, 将PU1故障与PU1故障态、正常态、安全容错管理单元(FTSM)故障态、通信控制器(CC)故障态以及系统受扰故障态进行比较, 得到对数似然概率均值分别为-161.95、-13.72、-14.13、-40.17及-35.69, 证明了系统所发生的故障是因PU1所致。监测方法能够有效实现安全计算机健康状态的检测, 为铁道信号安全计算机监测技术提供理论支撑。Abstract: The principle and primal procedure of condition monitoring and fault detection were proposed based on hidden Markov model(HMM).The condition monitoring for two-mode redundant safety computer was carried out by using a number of ways, including the extraction and dimensionality reduction of observed data, the training and improvement of normal status model, the training of fault status model and so on. 7 different conditions of normal statuses and statuses with 1%-10% clock offsets were monitored.Monitoring result shows that average logarithmic likelihood probability reduces from -228.98 to -1 385.60, which indicates the degrading of health status.When the monitoring of PU1(process unit 1) faults is conducted by simulation, the average logarithmic likelihood probabilities of fault status compared with PU1 fault, normal status, fault tolerance and safety management(FTSM) fault, communication controller(CC) fault, and system interference fault are -161.95, -13.72, -14.13, -40.17 and -35.69, respectively, which verifies that the system fault is resulted from PU1. So the proposed monitoring method is effective in safety computer monitoring, and it will give a theoretical support to the monitoring of railway signal safety computer.
-
Key words:
- railway signal /
- system safety /
- hidden Markov model /
- fault monitoring /
- health management
-
[1] 曹源, 唐涛, 徐田华, 等. 形式化方法在列车运行控制系统中的应用[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2010, 10(1): 112-126. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201001020CAO Yuan, TANG Tao, XU Tian-hua, et al. Application of formal methods in train control system[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2010, 10(1): 112-126. (in Chinese). http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201001020 [2] 陈珊, 王太勇, 王国锋, 等. 机械设备智能诊断与预测维修系统[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2003, 38(5): 540-543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2003.05.013CHEN Shan, WANG Tai-yong, WANG Guo-feng, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis, prediction and maintenance system of mechanical equipment[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2003, 38(5): 540-543. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2003.05.013 [3] VICHARE N M, PECHT M G. Prognostics and health management of electronics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components and Packaging Technologies, 2006, 29(1): 222-229. doi: 10.1109/TCAPT.2006.870387 [4] OWSLEY L M D, ATLASL E, BERNARD G D. Self-organizing feature maps and hidden Markov models formachine-tool monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(11): 2787-2798. doi: 10.1109/78.650105 [5] SMYTH P. Hidden Markov models and neural networks for fault detection in dynamic systems[C]∥IEEE. Proceedings of Neural Networks for Signal Processing. Boise: IEEE, 1993: 582-592. [6] ATLAS L, OSTENDORF M, BERNARD G D. Hidden Markov models for monitoring machining tool-wear[C]∥IEEE. Proceedings of the Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Istanbul: IEEE, 2000: 3887-3890. [7] OCAK H, LOPARO K A. A new bearing fault detection and diagnosis scheme based on hidden Markov modeling of vibration signals[C]∥IEEE. Proceedings of the Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2001: 3141-3144. [8] ZHAO Yun-xin, ATLAS L E, ZHUANG Xin-hua. Application of the gibbs distribution to hidden Markov modeling in speaker independent isolated word recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1991, 39(6): 1291-1299. doi: 10.1109/78.136535 [9] 林果园, 郭山清, 黄皓, 等. 基于动态行为和特征模式的异常检测模型[J]. 计算机学报, 2006, 29(9): 1553-1560. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2006.09.006LIN Guo-yuan, GUO Shan-qing, HUANG Hao, et al. An anomaly detection model based on dynamic behavior and character patterns[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2006, 29(9): 1553-1560. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2006.09.006 [10] 冯长建. HMM动态模式识别理论、方法以及在旋转机械故障诊断中的应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2002.FENG Chang-jian. HMM dynamical pattern recognition the-ories, methods and applications in faults diagnosis of rotating machine[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2002. (in Chinese). [11] 王剑, 张辉, 蔡伯根, 等. 基于HMM的列车轨道占用自动识别算法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2009, 31(3): 54-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB200903011.htmWANG Jian, ZHANG Hui, CAI Bai-gen, et al. The algorithm of automatic track occupying identification based on HMM[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2009, 31(3): 54-58. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB200903011.htm [12] QIAO Y, XIN X W, BIN Y, et al. Anomaly intrusion detection method based on HMM[J]. Electronics Letters, 2002, 38(13): 663-664. doi: 10.1049/el:20020467 [13] 宋雪萍, 马辉, 刘杰, 等. 基于HMM的故障诊断特征提取和聚类技术[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2006, 26(2): 92-96, 157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCS200602001.htmSONG Xue-ping, MA Hui, LIU Jie, et al. Feature extraction and clustering technique of rotating machinery fault diagnose based on HMM[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement and Diagnosis, 2006, 26(2): 92-96, 157. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCS200602001.htm [14] RABINER L R, JUANG B H. An introduction to hidden Markov models[J]. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 1986, 3(1): 4-16. [15] PECK R, NESS J. The use of shrinkage estimators in linear discriminant analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1982, 4(5): 530-537. -





 下载:
下载: