Concept, architecture and challenging technologies of ubiquitous traffic information service system
-
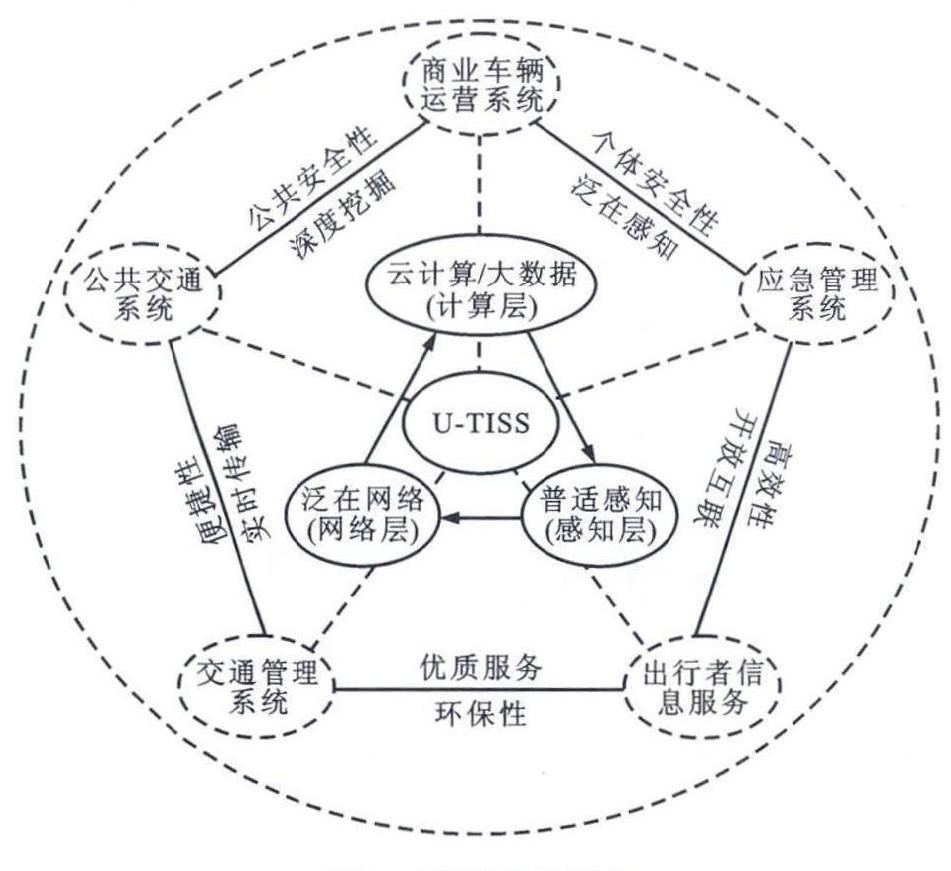
摘要: 分析了现有交通信息服务系统存在的感知能力有限、服务方式单一和动态信息更新不及时的问题, 围绕当前交通工程和信息技术领域的研究发展趋势, 提出了一种泛在交通信息服务系统(U-TISS)的架构, 将先进的协同感知、泛在网络、云计算、大数据等技术综合运用于交通信息服务领域, 实现交通信息服务系统与交通物理系统的深度融合。U-TISS架构包括感知、网络、计算和服务4层次。感知层主要通过传感器、射频标签、识读器、摄像头、全球定位系统、车载智能终端设备等, 实现对人、车、路、环境的全面感知; 网络层是以ZigBee、蓝牙、DSRC等短程通信为主的末梢节点通信与以3G/4G或有线通信链路为主的承载网络通信, 通过车路短程通信和自组织网络、路侧与感知中心的承载网络实时采集和传输各种交通信息, 构建交通要素信息的精准获取与发布体系; 计算层利用云计算技术实现有效的交通富信息挖掘与提取, 提升交通信息服务质量; 服务层构建基于泛在网络和云计算的交通信息服务平台, 通过移动智能终端、车载终端、资讯广播、可变信号板等信息发布方式, 为交通参与者提供实时动态的交通信息服务和丰富全面的辅助决策支持, 实现交通信息服务的智能化与个性化。基于U-TISS架构, 分析了实现U-TISS的关键技术, 包括智能终端的普适感知与交互、车辆精确定姿与定位、交通信息路侧协同感知、车车/车路短程通信与组网、车载移动互联、交通信息云管理、交通大数据分析与挖掘、信息安全与隐私保护。分析结果表明: U-TISS具有泛在感知、开放互联、实时传输、深度挖掘与优质服务的特点, 能够从安全性、高效性、便捷性和环保性4方面改进与提升现有交通信息服务系统的服务水平。在安全性方面, 基于DSRC的车车/车路通信与组网技术使驾驶人可以获取超越视距、超车载感知能力范围与多时空尺度的交通信息, 增强车车/车路间的协同能力; 在高效性方面, 借助泛在感知的海量路网运行信息和云计算平台提供的大数据分析技术, 通过精细化的管理实现交通系统的高效运行; 在便捷性方面, 通过智能终端能够为公众出行路线、方式和出发时间的个性化定制提供支持; 在环保性方面, 通过对车辆控制系统提供更多的行车环境信息实现车辆控制的优化, 通过大数据或社交网络提高驾驶人对环保驾驶的认知, 实现绿色出行。U-TISS关键技术的深入研究、推广与应用, 及相关行业标准与规范的出台, 将引起交通信息服务类应用商业模式的创新与变革, 最终实现协作式智慧交通。Abstract: The limited awareness abilities, simple service modes and long delays of updating dynamic informatioh of most existing traffic information service systems were analyzed.A novel framework of ubiquitous traffic information service system(U-TISS) was proposed based on the current TISSs, and the research and development tendencies of traffic engineering and information science.U-TISS integrated advanced cooperative sensing, ubiquitous network, cloud computation and big data to realize the deep fusion between TISSs and traffic cyber physical systems.The architecture of U-TISS mainly consisted of four layers, including sensing, network, computation and service.In sensing layer, a comprehensive sensing on pedestrians, vehicles, roads and environments were carried out by sensors, RFIDs, readers, cameras, GPS, vehicle intelligent terminals, etc.In network layer, peripheral communication and carrying network communication were implemented, such as ZigBee, bluetooth, DSRC, 3G/4G, and wired link, and an accurate capture and release system was built to timely collect and transmit traffic information by short-range communication between roads and cars, self-organizing network, and carrying network between roadsides and monitor centers.In computation layer, cloud computation extracted traffic information effectively to enhance the service quality of traffic information.In service layer, a service platform was constructed based on ubiquitous network and cloud computation.Its information was released timely by mobile intelligent terminals, vehicular terminals, information broadcasts and variable signal boards, and the auxiliary decision support was provided to realize the intelligentization and individuation of information service.The key technologies of U-TISS implementation were analyzed, including pervasive sensing and interaction of smart devices, accurate measurement of vehicle position and orientation, cooperative sensing of traffic information with road side units, communication and networking of vehicle-to-vehicle/vehicle-to-infrastructure, on-board mobile internet, traffic information management in the cloud, analysis and excavation of traffic big data, and information security and privacy protection.Analysis result shows that the characteristics of U-TISS are ubiquitous sensing, open interconnection, real-time transmission, deep mining and high quality service, and can improve the service level of TISS in safety, high efficiency, convenience and environmental protection.In term of safety, wireless communication and networking technology provide drivers with multi-scale tempo-spatial traffic information beyond the line of sight and the sensing capability of vehicles.In term of high efficiency, ubiquitous sensing of massive traffic information and big data analysis based on cloud computing techniques can achieve the efficient operation of transportation systems with refinement of management.In term of convenience, the public can get personalized and customized travel information through smart devices.In term of environmental protection, vehicle control systems can be optimized by the information of driving environment, and the awareness of ecodriving behaviors can be raised by big data and social network, so that green travel is realized.With the breakthrough of key technologies and the issuing of related standards and norms, the innovation and change of business mode will occur in the field of traffic information service, which will lead to collaborative intellieent transDortation.
-
表 1 典型交通信息服务系统研究与应用现状
Table 1. Researches and application statuses of typical TISSs

表 2 安全性方面应用
Table 2. Application in safety

表 3 高效性方面应用
Table 3. Application in high efficiency

表 4 便捷性方面应用
Table 4. Application in convenience

表 5 环保性应用
Table 5. Application in environmental conservation

-
[1] 王笑京. 新一代智能交通系统的技术特点和发展建议[J]. 工程研究——跨学科视野中的工程, 2014, 6(1): 37-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKG201401006.htmWANG Xiao-jing. The technical features and development suggestions of the next generation intelligent transportation system[J]. Journal of Engineering Studies, 2014, 6(1): 37-42. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKG201401006.htm [2] DIMITRAKOPOULOS G, DEMESTICHAS P. Intelligent transportation systems: systems based on cognitive networking principles and management functionality[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2010, 5(1): 77-84. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2009.935537 [3] JAYAKRISHNAN R, MAHMASSANI H S, HU T Y. An evaluation tool for advanced traffic information and management systems in urban networks[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 1994, 2(3): 129-147. doi: 10.1016/0968-090X(94)90005-1 [4] WISCHHOF L, EBNER A, ROHLING H. Information dissemination in self-organizing intervehicle networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2005, 6(1): 90-101. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2004.842407 [5] 张平, 苗杰, 胡铮, 等. 泛在网络研究综述[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2010, 33(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJYD201005002.htmZHANG Ping, MIAO Jie, HU Zheng, et al. A survey of ubiquitous network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2010, 33(5): 1-6. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJYD201005002.htm [6] LEE C S, LEE G M, RHEE W S. Standardization and challenges of smart ubiquitous networks in 1TU-T[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2013, 51(10): 102-110. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2013.6619572 [7] LEE C S, LEE G M, RHEE W S. Smart ubiquitous networks for future telecommunication environments[J]. Computer Standards and Interfaces, 2014, 36(2): 412-422. doi: 10.1016/j.csi.2013.08.012 [8] 杨晓光. 中国交通信息系统基本框架体系研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2000, 17(5): 50-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2000.05.016YANG Xiao-guang. Studies on architecture of transportation information systems in China[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2000, 17(5): 50-55. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2000.05.016 [9] 史新宏, 蔡伯根, 穆建成. 智能交通系统的发展[J]. 北方交通大学学报, 2002, 26(1): 29-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8106.2002.01.006SHI Xin-hong, CAI Bo-gen, MU Jian-cheng. Development of intelligent transportation system[J]. Journal of Northern Jiaotong University, 2002, 26(1): 29-34. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8106.2002.01.006 [10] KRAGE M K. The TravTek driver information system[C]//IEEE. 1991 Vehicle Navigation and Information Systems Conference. New York: IEEE, 1991: 739-748. [11] REMER M, ATGHERTON T, GARDNER W. ITS benefits, evaluation and costs; results and lessons from the Minnesota Guidestar TravLink operational test[C]//Institute of Transportation Engineers(ITE). Compendium of Technical Papers for the 66th ITE Annual Meeting. Minneapolis: Institute of Transportation Engineers, 1996: 3-7. [12] HORAN T A, ABHICHANDANl T, RAYALU R. Assessing user satisfaction of E-government services: development and testing of quality-in-use satisfaction with advanced traveler information systems(ATIS)[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of the39th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Hawaii: IEEE, 2006: 1-10. [13] AMANNA A. Overview of IntelliDrive/vehicle infrastructure integration(VII)[R]. Blacksburg: Vriginia Tech Transportation Institute, 2009. [14] SENGUPTA R, MISENER J, AHERN K, et al. SafeTrip-21: connected traveler[R]. Berkeley: University of California, 2010. [15] CATLING I, OP DE BEEK F. SOCRATES: system of cellular radio for traffic efficiency and safety[C]//IEEE. 1991 Vehicle Navigation and Information Systems Conference. New York; IEEE, 1991: 147-150. [16] BOUWER M C. EUROAD concept for RDS-TMC in ACCEPT[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE-IEE Vehicle Navigation and Information Systems Conference, 1993. Ottawa: IEEE, 1993: 104-107. [17] TOULMINET G, BOUSSUGE J, LAURGEAU C. Comparative synthesis of the 3 main European projects dealing with-cooperative systems(CVIS, SAFESPOT and COOPERS)and description of COOPERS demonstration site 4[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of 11th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Beijing: IEEE, 2008: 809-814. [18] FESTAG A, LE L, GOLEVA M. Field operational tests for cooperative systems: a tussle between research, standardization and deployment[J]//IEEE. Proceedings of the Eighth ACM International Workshop on Vehicular Inter-networking. Las Vegas, IEEE, 2011: 73-78. [19] YAMADA S. The strategy and deployment plan for VICS[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 1996, 34(10): 94-97. doi: 10.1109/35.544328 [20] KANOSHIMA H, HATAKENAKA H. Development of nextgeneration road services by public and private joint research[C]//IEEE. 8th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications. Phuket: IEEE, 2008: 404-407. [21] 关积珍. 对北京奥运公众交通信息服务的探讨[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2008, 8(6): 61-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2008.06.009GUAN Ji-zhen. Public service of traffic information during the Beijing Olympics[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2008, 8(6): 61-66. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2008.06.009 [22] 王博彬, 邵春福, 孙轶轩, 等. 多方式交通信息条件下节假日出行行为研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2014, 14(1): 229-234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2014.01.035WANG Bo-bin, SHAO Chun-fu, SUN Yi-xuan, et al. Holiday travel behavior analysis under integrated multimodal travel information service[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2014, 14(1): 229-234. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2014.01.035 [23] 俄文娟. 无信号交叉口车车冲突检测与消解算法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012.E Werrjuan. Research on vehicle conflict detection and resolution algorithm at unsignalized intersection[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012. (in Chinese). [24] HOFS W, LAPPIN J, SCHAGRIN M, et al. International deployment of cooperative intelligent transportation systemsbilateral efforts of the European Commission and United States Department of Transportation[R]. Washington DC: U S Department of Transportation, 2012. [25] 孙棣华, 李永福, 刘卫宁, 等. 交通信息物理系统及其关键技术研究综述[j]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(1): 144-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2013.01.020SUN Di-hua, LI Yong-fu, LIU Wei-ning, et al. Research summary on transportation cyber physical systems and the challenging technologies[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(1): 144-155. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2013.01.020 [26] ESTRIN D, CHANDY K M, YOUNG R M, et al. Participatory sensing: applications and architecture[J]. IEEE Internet Computing, 2010, 14(1): 12-42. doi: 10.1109/MIC.2010.12 [27] RUGE L, ALTAKROURI B, SCHRADER A. SoundOfTheCityContinuous noise monitoring for a healthy city[C]//IEEE. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops(PERCOM Workshops). San Diego: IEEE, 2013: 670-675. [28] SCHNEIDER W. Mobile phones as a basis for traffic state information[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of the 8th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Vienna, IEEE, 2005: 782-784. [29] 张绍阳, 葛丽娟, 安毅生, 等. 交通运输数据标准研究现状与发展[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2014, 14(2): 112-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2014.02.019ZHANG Shao-yang, GE Li-juan, AN Yi-sheng, et al. Research status and development of transportation data standards[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2014, 14(2): 112-126. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2014.02.019 [30] FIRE M, KAGAN D, PUZIS R, et al. Data mining opportunities in geosocial networks for improving road safety[C]//IEEE. IEEE 27th Convention of Electrical Electronics Engineers in Israel(IEEEI). Eilat: IEEE, 2012: 1-4. [31] KARAGIANNISG, ALTINTAS O, EKICI E, et al. Vehicular networking: a survey and tutorial on requirements, architectures, challenges, standards and solutions[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2011, 13(4): 584-616. doi: 10.1109/SURV.2011.061411.00019 [32] CHENG H T, SHAN H G, ZHUANG W H. Infotainment and road safety service support in vehicular networking: from a communication perspective[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2011, 25(6): 2020-2038. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2010.11.009 [33] 段宗涛, 康军, 唐蕾, 等. 车联网大数据环境下的交通信息服务协同体系[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 34(2): 108-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8879.2014.02.017DUAN Zong-tao, KANG Jun, TANG Lei, et al. Traffic information service cooperation architecture based on vehicular network big data[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Nature Science Edition, 2014, 34(2): 108-114. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8879.2014.02.017 [34] WANG Jian-qiang, NIU Hui-min. Graded-information feedback strategy in two-route systems under ATIS[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering: English Edition, 2014, 1(2): 138-145. doi: 10.1016/S2095-7564(15)30098-2 [35] 陈静, 赵箐, 石建军. 泛在网络在智能交通中的应用初探[J]. 武汉理工大学学报: 交通科学与工程版, 2012, 36(1): 199-202. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1006-2823.2012.01.048CHEN Jing, ZHAO Jing, SHI Jian-jun. An exploration using of ubiquitous network in intelligent transportation system[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology: Transportation Science and Engineering, 2012, 36(1): 199-202. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1006-2823.2012.01.048 [36] SEMEIDA A M. Derivation of travel demand forecasting models for low population areas: the case of Port Said Governorate, North East Egypt[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering: English Edition, 2014, 1(3): 196-208. doi: 10.1016/S2095-7564(15)30103-3 -





 下载:
下载: