Recognition method of road speed limit information based on data mining of traffic trajectory
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
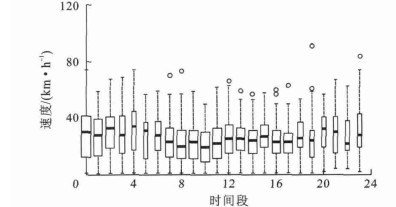
摘要: 分析了道路限速信息的时空变化性, 提出一种基于轨迹数据挖掘技术的道路限速信息自动识别方法。为了实现海量交通轨迹数据的快速处理, 研究了快速地图匹配与数据清洗等预处理算法, 分析了交通轨迹数据的速度分布特性与最高车速限制指标。基于路段行车速度的统计特性, 构建了道路特征向量模型, 以快速提取海量轨迹数据的潜在特征信息。提出了多投票K近邻分类算法对数据特性进行训练与学习, 以实现对道路限速信息的快速识别。以福州市交通路网及其浮动车轨迹数据构建试验样本集进行训练、学习与交叉验证试验。试验结果表明: 在训练过程中, 当样本数量达到1 200时, 方法的识别准确率最高达到93%, 在仅有150个小训练样本下, 方法的识别准确率也达到75%;方法具有近线性的处理性能, 处理1.0×106条道路的限速信息仅用时46ms。Abstract: The spatiotemporal variability of speed limit information was analyzed, and an automatic recognition method of road speed limit information was proposed based on the mining technique of trajectory data.To fast process the massive traffic trajectory data, the pretreatment algorithms such as rapid map matching and data cleaning were researched.The speed distribution features of traffic trajectory data and the maximum speed limit index were analyzed.Based on the speed features at road section, a road feature vector model was constructed to rapid extract the latent characteristics information from the massive trajectory data was achieved.In order to implement a rapid recognition of speed limit information, a classification algorithm based on multi-voting K-nearest neighbor(MV-KNN)algorithm was proposed for the training and learning process of data feature.The training, learning and cross-validation experiments were completed by using the sample sets constructed by actual floating car trajectory data and traffic network in Fuzhou City.Experimental result indicates that the highest system recognitionaccuracy of proposed method is up to 93% by using 1 200 samples in the training process, and the system recognition accuracy is 75% by using only 150 samples.The near-linear processing performance of proposed method is revealed, and the system operating time is only 46 ms in processing 1 000 000 samples of road speed limit information.
-
表 1 测试路段特征向量
Table 1. Feature vectors of test road sections

-
[1] 姜康, 张梦雅, 陈一锴. 山区圆曲线路段半挂汽车列车行驶安全性分析[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2015, 15(3): 109-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2015.03.015JIANG Kang, ZHANG Meng-ya, CHEN Yi-kai. Driving safety analysis of semi-trailer train at circular curve section in mountain area[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2015, 15(3): 109-117. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2015.03.015 [2] AARTS L, SCHAGEN I V. Driving speed and the risk of road crashes: a review[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2006, 38(2): 215-224. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2005.07.004 [3] QUDDUS M. Exploring the relationship between average speed, speed variation, and accident rates using spatial statistical models and GIS[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety and Security, 2013, 5(1): 27-45. doi: 10.1080/19439962.2012.705232 [4] BELLA F. Driving simulator for speed research on two-lane rural roads[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2008, 40(3): 1078-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2007.10.015 [5] HOSSEINLOU M H, KHEYRABADI S A, ZOLFAGHARI A. Determining optimal speed limits in traffic networks[J]. IATSS Research, 2015, 39(1): 36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.iatssr.2014.08.003 [6] SUN Rui, HU Jian-ming, XIE Xu-dong, et al. Variable speed limit design to relieve traffic congestion based on cooperative vehicle infrastructure system[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2014, 138: 427-438. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.07.221 [7] HEYDECKER B G, ADDISON J D. Analysis and modelling of traffic flow under variable speed limits[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2011, 19(2): 206-217. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2010.05.008 [8] LI Zhi-bin, LI Ye, LIU Pan, et al. Development of a variable speed limit strategy to reduce secondary collision risks during inclement weathers[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2014, 72: 134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2014.06.018 [9] GRUMERT E, MA Xiao-liang, TAPANI A. Analysis of a cooperative variable speed limit system using microscopic traffic simulation[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 52: 173-186. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2014.11.004 [10] SOUANI C, FAIEDH H, BESBES K. Efficient algorithm for automatic road sign recognition and its hardware implementation[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2014, 9(1): 79-93. doi: 10.1007/s11554-013-0348-z [11] 王进, 孙开伟, 李钟浩. 超网络道路限速标志识别[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2012, 33(12): 2709-2714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2012.12.027WANG Jin, SUN Kai-wei, LEE C H. Hypernetworks for road speed limit sign recognition[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2012, 33(12): 2709-2714. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2012.12.027 [12] STALLKAMP J, SCHLIPSING M, SALMEN J, et al. Man vs. computer: benchmarking machine learning algorithms for traffic sign recognition[J]. Neural Networks, 2012, 32(2): 323-332. [13] GREENHALGH J, MIRMEHDI M. Real-time detection and recognition of road traffic signs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(4): 1498-1506. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2208909 [14] LILLO-CASTELLANO J M, MORA-JIMéNEZ I, FIGUERA-POZUELO C, et al. Traffic sign segmentation and classification using statistical learning methods[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 153: 286-299. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.11.026 [15] ZAKLOUTA F, STANCIULESCU B. Real-time traffic sign recognition in three stages[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2014, 62(1): 16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2012.07.019 [16] LIU Hua-ping, LIU Yu-long, SUN Fu-chun. Traffic sign recognition using group sparse coding[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 266(10): 75-89. [17] PASCALE A, DEFLORIO F, NICOLI M, et al. Motorway speed pattern identification from floating vehicle data for freight applications[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 51: 104-119. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2014.09.018 [18] 吴佩莉, 刘奎恩, 郝身刚, 等. 基于浮动车数据的快速交通拥堵监控[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 51(1): 189-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201401021.htmWU Pei-li, LIU Kui-en, HAO Shen-gang, et al. Rapid traffic congestion monitoring based on floating car data[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 51(1): 189-198. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFYZ201401021.htm [19] WALKER G, CALVERT M. Driver behaviour at roadworks[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2015, 51: 18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2015.03.019 [20] RAHMANI M, JENELIUS E, KOUTSOPOULOS H N. Non-parametric estimation of route travel time distributions from low-frequency floating car data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 58: 343-362. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.01.015 [21] RAHMANI M, KOUTSOPOULOS H N. Path inference from sparse floating car data for urban networks[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2013, 30(5): 41-54. [22] JIMéNEZ-MEZA A, ARáMBURO-LIZáRRAGA J, FUENTE E. Framework for estimating travel time, distance, speed, and street segment level of service(LOS), based on GPS data[J]. Procedia Technology, 2013, 7(4): 61-70. [23] ALJANAHI A A M, RHODES A H, METCALFE A V. Speed, speed limits and road traffic accidents under free flow conditions[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 1999, 31(1): 161-168. [24] CHEN Bi-yu, YUAN Hui, LI Qing-quan, et al. Map-matching algorithm for large-scale low-frequency floating car data[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2014, 28(1): 22-38. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2013.816427 [25] 王美玲, 程林. 浮动车地图匹配算法研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2012, 41(1): 133-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201201026.htmWANG Mei-ling, CHENG Lin. Study on map-matching algorithm for floating car[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2012, 41(1): 133-138. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201201026.htm [26] BRIN S, PAGE L. Reprint of: the anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual web search engine[J]. Computer Networks, 2012, 56(18): 3825-3833. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2012.10.007 [27] BIJALWAN V, KUMAR V, KUMARI P, et al. KNN based machine learning approach for text and document mining[J]. International Journal of Database Theory and Application, 2014, 7(1): 61-70. doi: 10.14257/ijdta.2014.7.1.06 [28] JIANG Sheng-yi, PANG Guan-song, WU Mei-ling, et al. An improved k-nearest-neighbor algorithm for text categorization[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(1): 1503-1509. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.08.040 [29] LIU Hua-wen, ZHANG Shi-chao. Noisy data elimination using mutual k-nearest neighbor for classification mining[J]. The Journal of Systems and Software, 2012, 85(5): 1067-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2011.12.019 -





 下载:
下载: