Internal welding reinforcement method for fatigue crack at weld root on rib-to-deck of in-service steel bridge deck
-
摘要:
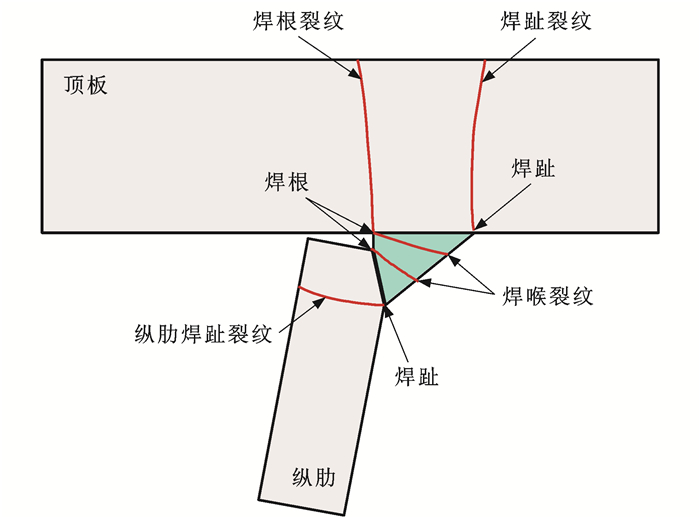
为实现纵肋与顶板焊根疲劳裂纹的有效加固,提出了能够满足在役钢桥面板加固需求的内焊加固方法,研发了自动化焊接机器人和相关关键装备;设计了4个试验模型对方法和装备的有效性和适用性进行研究,验证了纵肋与顶板焊根产生疲劳裂纹的开裂模式;使用所研发的专用焊接设备在纵肋内部进行焊接加固,进行了加固结构的疲劳破坏试验;对比了试验结果与有限元模拟结果,分析了加固后结构的疲劳性能,验证了内焊加固方法的有效性。研究结果表明:内焊加固方法能够将既有的焊根裂纹转化为内部缺陷,研发的装备能够实现原位加固,有效抑制疲劳裂纹的扩展,使已开裂焊接细节的疲劳寿命提高了66%~157%;由于各开裂模式具有不同程度疲劳损伤累积,加固后焊接细节会发生主导开裂模式迁移;对于包含多开裂模式的焊接细节,加固后的剩余疲劳寿命与各开裂模式的实际疲劳损伤累积程度以及加固方法对各开裂模式受力特性的扰动程度两方面的因素密切相关。
Abstract:To achieve effective reinforcement of fatigue crack at weld root on rib-to-deck, an internal welding reinforcement method was proposed to meet the requirements of in-service steel bridge decks, and automated welding robots and associated key equipment were developed. Four test models were designed to study the effectiveness and applicability of the method and equipment. The cracking mode of fatigue crack at weld root on rib-to-deck was validated. The developed specialized welding equipment for internal welding reinforcement was used internally within the rib, and fatigue failure tests on the reinforced structure were conducted. The results of experiment and finite element simulation were compared. The fatigue performance of the structure after reinforcement was analyzed, and the effectiveness of internal welding reinforcement method was confirmed. Research results indicate that the internal welding reinforcement method can transform the existing weld root cracks into internal defects. The developed equipment enables in-site reinforcement, effectively suppressing the expansion of fatigue cracks, and enhancing the fatigue lives of the cracked welded joints by 66%-157%. Due to the different degrees of fatigue damage accumulation in various cracking modes, a transition in the dominant cracking mode of the welded joints occurs after reinforcement. For welded joints containing multiple cracking modes, the remaining fatigue life after reinforcement is closely related to the actual fatigue damage accumulation levels of each cracking mode and the degree of disturbance of reinforcement methods on the stress characteristics of each cracking mode.
-
表 1 加载方案
Table 1. Load schemes
模型编号 焊接类型 荷载幅/kN 应力比 阶段1 阶段2 MRD-Ⅰ 单面焊 50 50 1/11 MRD-Ⅱ 单面焊 45 45 1/10 MRD-Ⅲ 单面焊 45 45 1/10 MRD-Ⅳ 双面焊 50 1/11 表 2 阶段1的疲劳试验结果
Table 2. Fatigue test results of stage 1
模型 开裂模式 作用次数/万次 降幅/% N10 N25 Nf MRD-Ⅰ 焊根裂纹 28.7 44.7 63.5 61.0 MRD-Ⅱ 61.5 86.2 108.5 41.0 MRD-Ⅲ 55.5 74.4 134.0 76.5 MRD-Ⅳ 内侧焊趾 45.4 73.2 90.0 51.0 表 3 阶段2的疲劳试验结果
Table 3. Fatigue test results of stage 2
模型 开裂模式 作用次数/万次 降幅/% N10 N25 Nf MRD-Ⅰ 外侧焊趾 41.5 68.0 123.0 64.9 MRD-Ⅱ 58.5 75.7 124.0 60.0 MRD-Ⅲ 33.5 45.3 50.0 44.0 表 4 阶段1疲劳性能寿命预测
Table 4. Fatigue performance life prediction of stage 1
模型 N10/万次 N25/万次 Nf/万次 试验 预测 试验 预测 试验 预测 MRD-Ⅰ 28.7 33.1 44.7 42.8 63.5 61.7 MRD-Ⅱ 61.5 63.9 86.2 77.1 108.5 100.7 MRD-Ⅲ 55.5 59.5 74.4 71.0 134.0 131.0 表 5 MRD-Ⅲ裂尖应力强度因子
Table 5. MRD-Ⅲ crack tip stress intensity factors
a/mm c/mm 加载阶段 应力强度因子/(MPa·mm1/2) A点 B点 C点 8.7 28.0 阶段1 417.2 260.7 415.7 阶段2 107.8 80.4 106.5 -
[1] WOLCHUK R. Lessons from weld cracks in orthotropic decks on three European bridges[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1990, 116(1): 75-84. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1990)116:1(75) [2] KOLSTEIN M H. Fatigue classification of welded joints in orthotropic steel bridge decks[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2007. [3] 张清华, 卜一之, 李乔. 正交异性钢桥面板疲劳问题的研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(3): 14-30, 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.002ZHANG Qing-hua, BU Yi-zhi, LI Qiao. Review on fatigue problems of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(3): 14-30, 39. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.03.002 [4] 王春生, 翟慕赛, HOUANKPO T N O. 正交异性钢桥面板典型细节疲劳强度研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(8): 102-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX202008012.htmWANG Chun-sheng, ZHAI Mu-sai, HOUANKPO T N O. Fatigue strength of typical details in orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(8): 102-111. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX202008012.htm [5] 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国桥梁工程学术研究综述·2021[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(2): 1-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.02.002Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China's bridge engineering research: 2021[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(2): 1-97. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.02.002 [6] KAINUMA S, YANG M Y, JEONG Y S, et al. Experiment on fatigue behavior of rib-to-deck weld root in orthotropic steel decks[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2016, 119: 113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2015.11.014 [7] DEJONG F. Renovation techniques for fatigue cracked orthotropic steel bridge decks[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2007. [8] MALJAARS J, VAN DOOREN F, KOLSTEIN H. Fatigue assessment for deck plates in orthotropic bridge decks[J]. Steel Construction, 2012, 5(2): 93-100. doi: 10.1002/stco.201210011 [9] 蒋嵘, 吴冲. 顶板与纵肋接头处焊趾与焊根疲劳开裂的对比研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2020, 37(5): 1923-1928, 2314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYLX202005011.htmJIANG Rong, WU Chong. Comparative study onfatigue cracking of weld toe and weld root at joint between deck and longitudinal rib[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2020, 37(5): 1923-1928, 2314. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYLX202005011.htm [10] XIAO Z G, YAMADA K, YA S, et al. Stress analyses and fatigue evaluation of rib-to-deck joints in steel orthotropic decks[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2008, 30(8): 1387-1397. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.10.008 [11] LI M, HASHIMOTO K, SUGIURA K. Influence of asphalt surfacing on fatigue evaluation of rib-to-deck joints in orthotropic steel bridge decks[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2014, 19(10): 04014038. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000610 [12] 王春生, 翟慕赛, HOUANKPO T N O, 等. 正交异性钢桥面板冷维护技术及评价方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(8): 50-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.08.007WANG Chun-sheng, ZHAI Mu-sai, HOUANKPO T N O, et al. Cold maintenance technique and assessment method for orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(8): 50-58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.08.007 [13] CHOI J H, KIM D H. Stress characteristics and fatigue crack behaviour of the longitudinal rib-to-cross beam joints in an orthotropic steel deck[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2008, 11(2): 189-198. doi: 10.1260/136943308784466224 [14] YAMADA K, ISHIKAWA T, KAKⅡCHI T. Rehabilitation and improvement of fatigue life of welded joints by ICR treatment[J]. Advanced Steel Construction, 2015, 11(3): 294-304. [15] ABE T, KAWAI Y, YAMASHITA T, et al. Decreasing effect of stress in orthotropic steel decks by SFRC pavement with ordinary Portland cement and low shrinkage type mixture material[J]. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers, Series E1: Pavement Engineering, 2015, 71(2): 47-62. doi: 10.2208/jscejpe.71.47 [16] LUO Jun, SHAO Xu-dong, CAO Jun-hui, et al. Transverse bending behavior of the steel-UHPC lightweight composite deck: orthogonal test and analysis[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2019, 162: 105708. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2019.105708 [17] 陈辉, 于力, 耍荆荆. 正交异性钢桥面板疲劳病害分析及改造措施研究[J]. 公路工程, 2021, 46(2): 54-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGL202102009.htmCHEN Hui, YU Li, SHUA Jing-jing. Fatigue disease analysis of orthotropic steel bridge deck and research on improvement measures[J]. Highway Engineering, 2021, 46(2): 54-59. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGL202102009.htm [18] 王洋, 邵旭东, 陈杰, 等. 重度疲劳开裂钢桥桥面的UHPC加固技术[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(11): 92-101, 115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC202011010.htmWANG Yang, SHAO Xu-dong, CHEN Jie, et al. UHPC-based strengthening technique for significant fatigue cracking steel bridge decks[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(11): 92-101, 115. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC202011010.htm [19] 张清华, 袁道云, 王宝州, 等. 纵肋与顶板新型双面焊构造细节疲劳性能研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(5): 79-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202005007.htmZHANG Qing-hua, YUAN Dao-yun, WANG Bao-zhou, et al. Fatigue performance of innovative both-side welded rib-to-deck joints[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(5): 79-91. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202005007.htm [20] KAINUMA S, YANG M Y, JEONG Y S, et al. Experimental investigation for structural parameter effects on fatigue behavior of rib-to-deck welded joints in orthotropic steel decks[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2017, 79: 520-537. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.04.028 [21] LI J, ZHANG Q H, BAO Y, et al. An equivalent structural stress-based fatigue evaluation framework for rib-to-deck welded joints in orthotropic steel deck[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 196: 109304. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109304 [22] RODRIGUEZ-SANCHEZ J E, DOVER W D, BRENNAN F P. Application of short repairs for fatigue life extension[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2004, 26(4): 413-420. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2003.07.002 [23] LIU J, GUO T, FENG D M, et al. Fatigue performance of rib-to-deck joints strengthened with FRP angles[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2018, 23(9): 04018060. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001286 [24] FU Z Q, JI B H, KONG X M, et al. Grinding treatment effect on rib-to-roof weld fatigue performance of steel bridge decks[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 129: 163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.09.018 [25] 林上顺. 正交异性钢桥面板典型细节的疲劳损伤分析[J]. 桥梁建设, 2020, 50(4): 54-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLJS202004009.htmLIN Shang-shun. Fatigue damage analysis of typical details of orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. Bridge Construction, 2020, 50(4): 54-60. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLJS202004009.htm [26] KAINUMA S, YANG M Y, JEONG Y S, et al. Fatigue behavior investigation and stress analysis for rib-to-deck welded joints in orthotropic steel decks[J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2018, 18: 512-527. doi: 10.1007/s13296-018-0067-1 [27] 张华, 孙雅洲, 舒先庆, 等. 正交异性钢桥面板U肋内焊技术[J]. 公路, 2018, 63(9): 115-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL201809023.htmZHANG Hua, SUN Ya-zhou, SHU Xian-qing, et al. The orthotropic steel deck rib welding technology[J]. Highway, 2018, 63(9): 115-120. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL201809023.htm [28] WANG D L, XIANG C, MA Y H, et al. Experimental study on the root-deck fatigue crack on orthotropic steel decks[J]. Materials and Design, 2021, 203: 109601. [29] 侯宇博. 焊接初始微裂纹影响下顶板与纵肋构造细节疲劳性能研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021.HOU Yu-bo. Study on fatigue properties of rib-to-deck structural detail under the influence of wedding initial micro-crack[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021. (in Chinese) [30] 张清华, 郭亚文, 李俊, 等. 钢桥面板纵肋双面焊构造疲劳裂纹扩展特性研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(7): 49-56, 110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201907007.htmZHANG Qing-hua, GUO Ya-wen, LI Jun, et al. Fatigue crack propagation characteristics of double-sided welded joints between steel bridge decks and longitudinal ribs[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(7): 49-56, 110. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201907007.htm [31] 段宝山, 冯鹏程, 陈金州, 等. 既有钢桥面板U肋内焊临时孔设计方案研究[J]. 公路, 2022(2): 104-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL202202018.htmDUAN Bao-shan, FENG Peng-cheng, CHEN Jin-zhou, et al. Research on the design scheme of U-rib internal welding temporary aperture in existing steel bridge deck[J]. Highway, 2022(2): 104-110. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGL202202018.htm [32] 肖顺, 童乐为. H形钢梁疲劳裂纹扩展过程数值模拟[J]. 建筑钢结构进展, 2022, 24(6): 101-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJZ202206011.htmXIAO Shun, TONG Le-wei. Numerical simulation of fatigue crack propagation process of H-steel beams[J]. Progress in Steel Building Structures, 2022, 24(6): 101-108. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJZ202206011.htm [33] 童乐为, 顾敏, 朱俊, 等. 基于断裂力学的圆钢管混凝土Y型焊接节点疲劳寿命预测[J]. 工程力学, 2013, 30(4): 331-336, 354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201304047.htmTONG Le-wei, GU Min, ZHU Jun, et al. Prediction of fatigue life for welded t-joints of concrete-filled circular hollow sections based on fracture mechanics[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(4): 331-336, 354. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201304047.htm [34] TALEB W, GARDIN C, SARRAZIN-BAUDOUX C. 3D predictions of the local effective stress intensity factor as the fatigue crack propagation driving force[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2021, 151: 106365. [35] PANG K J, YUAN H. Assessment of three-dimensional multi-crack propagation for fatigue life prediction[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2022, 198: 104660. [36] 祝志文, 黄炎, 李健朋, 等. 正交异性钢桥面板横隔板弧形切口疲劳评价的热点应力法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2018, 18(5): 25-34. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2018.05.003ZHU Zhi-wen, HUANG Yan, LI Jian-peng, et al. Fatigue assessment of floor beam cutout in orthotropic steel bridge deck based on hot-spot stress method[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2018, 18(5): 25-34. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2018.05.003 -





 下载:
下载: