Effect of bionic rhombic surface texture on frictional noise of high-speed train
-
摘要: 为了降低高速列车运行时的空气摩擦噪声, 仿生鲨鱼皮的表面织构, 在高速列车车厢气固界面设计了菱形表面织构, 建立了噪声分析模型, 采用非结构化混合网格和k-ε模型求解可压缩N-S方程, 基于宽频噪声源模型求解噪声分布。计算结果表明: 在菱形织构内部产生涡流, 使噪声明显降低, 同时车厢表面的噪声分布也发生变化; 列车产生的空气摩擦噪声随着运行速度的增大而增大, 与光滑表面相比, 优化对角线比的菱形织构的摩擦噪声的最大降幅为24dB, 优化深边比的降幅为20dB。Abstract: In order to reduce the frictional noise of gas-solid interface for running high-speed train, a noise analysis model of gas-solid interface was established by using the rhombic surface texture to mimic the surface texture of jaws shin. The compressible N-S equation was solved by using unstructured hybrid grid and k-ε model, and the noise distribution was obtained based on broadband noise source. Numerical result demonstrates that the noise significantly reduces as result of eddy current in the rhombic structure, and the corresponding noise distribution also changes. The air frictional noise of running train increases with the increase of the speed. Compared with the smooth surface, the maximum reducing value of noise intensity for the surface texture with optimal diagonal ratio is 24 dB and the value with optimal depth to side ratio is 20 dB.
-
Key words:
- vehicle engineering /
- high-speed train /
- frictional noise /
- rhombic texture /
- noise analysis model /
- broadband noise
-
0. 引言
高速铁路的历史始于1964年开通的日本东京至大阪东海道新干线, 2008年, 中国最高速度达370km·h-1的CRH3动车组列车成功在京津城际铁路成功运营, 标志着中国已进入速度达300km·h-1的高速铁路时代。目前, 中国正在研制速度为500km·h-1的高速列车系统。噪声测试结果表明, 列车速度在240km·h-1以下时, 轮轨噪声对沿线环境的影响较大; 列车速度在240km·h-1以上时, 空气动力噪声和集电系统噪声增大, 与轮轨噪声共同成为主要噪声源[1]。由于空气与车体表面的摩擦阻力与列车速度的2次方成正比, 因此, 摩擦阻力产生的摩擦噪声严重污染周围环境。随着列车速度的提高, 摩擦噪声增大, 一般高速铁路只能运营于工作时间, 在夜晚休息时间停止运营, 造成高速铁路资源的极大浪费, 如能降低列车的摩擦噪声, 高速列车能够全天运营, 将产生显著的经济效益和社会效益。摩擦学的研究表明, 一定的表面织构设计可以显著降低摩擦阻力。
表面织构的研究起源于对降低摩擦力的工程要求, Hamilton等在1966年就研究了粗糙表面的端面机械密封性能, 分析了圆形坑和六边形微坑表面织构对流体膜的影响[2]; Rightmire等研究了滑动轴承表面凹陷对流动的扰动, 以减小摩擦力, 分析了凹坑大小、形状、类型和方向对摩擦因数的影响[3]; Etsion等计算了带圆形凹坑表面的机械密封性能[4]; Ronen等计算了活塞环表面上圆形凹坑对发动机摩耗的影响, 得到了最佳的凹坑直径、最佳凹坑面积与名义面积的比[5]; Kligerman等在活塞环上设计了3种圆形凹坑排列, 进行了参数化的润滑计算, 得到了优化设计方案[6]。
由于表面结构明显降低摩擦阻力的效果, 人们开始主动设计表面织构。Etsion综述了激光加工表面织构的发展, 认为表面织构有贮油、微动力润滑和包含磨粒的作用[7]; Wang等分析了5种工程表面的混合润滑, 计算了凹坑大小、深度和面积比对油膜厚度的影响[8]; Tan等针对计算机硬盘, 设计了一种表面微肿块, 认为这种表面织构能减小静摩擦力和动摩擦力[9]; 仿生设计是表面织构设计的方法之一, Yamaguchi仿照蚯蚓表面织构, 设计了6种表面织构, 并测试了磨损量[10]。
本文仿生鲨鱼皮的表面织构, 在高速列车表面设计菱形表面织构, 通过FLUENT软件计算, 研究菱形表面织构对高速列车表面的空气摩擦噪声的影响。
1. 仿生表面织构设计
表面织构有基本表面织构、派生表面织构和复合确定性表面织构3种。基本表面织构是具有不同几何特性平均分布的随机表面, 又是具有相同几何特性但又有分离特性的预定排列的确定性表面; 派生表面织构是具有不同几何特性和重叠特性预定排列的半随机表面; 复合确定性表面织构是由随机和确定性表面织构组合而成[11-12]。
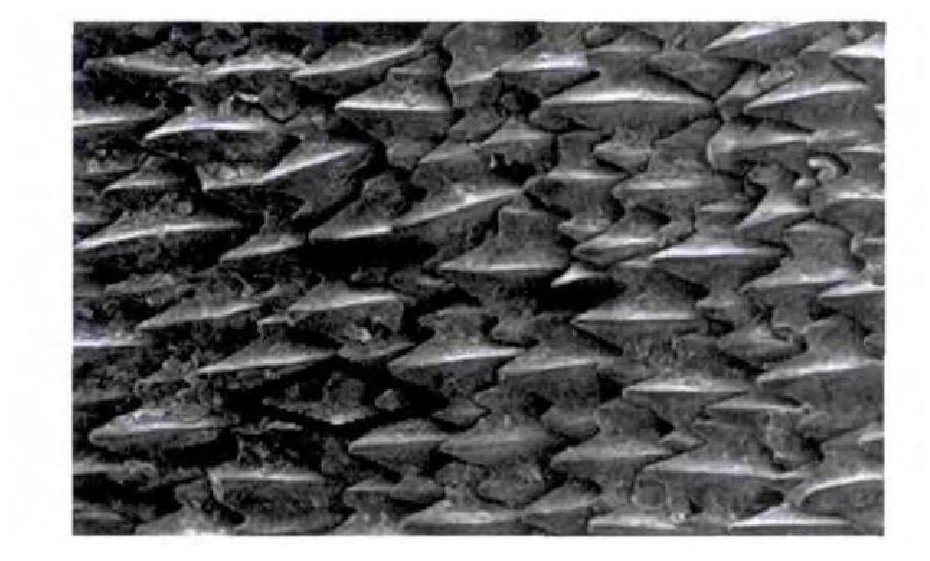
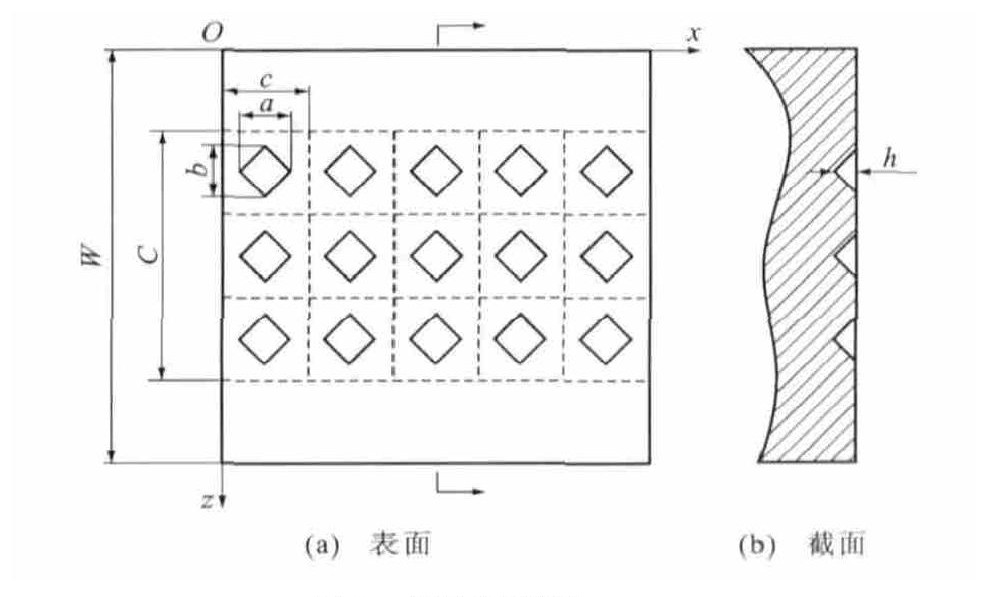
图 1为大白鲨皮的表面织构, 是一种典型的菱形表面。得益于这种表面织构, 大白鲨在水中行进时, 速度快, 阻力小, 并且产生的噪声也很小。本文通过仿生大白鲨皮的表面织构, 在车厢表面设计菱形织构, 分析菱形织构的参数变化对其的影响, 以期提出有效的降噪方案。车厢界面菱形织构见图 2: W为高速列车车厢表面z方向的长度; C为z方向的织构长度; c为织构单元的边长; a、b分别为菱形的2条对角线长度; h为菱形织构的深度。设菱形对角线比为

深边比为

结合上述参数, 设计菱形表面织构, 进行数值模拟计算, 探究菱形织构的降噪效果, 分析不同面积比、深边比与高速列车不同运行速度对表面噪声的影响。
2. 仿生模型建立
以匀速行驶高速列车的车厢为例, 根据相对运动原理, 假定高速列车静止, 而空气流体相对车厢运动, 并作以下假设。
(1) 车厢绝对光滑, 不考虑粗糙度的影响。
(2) 空气流体不受重力影响。
(3) 空气流体为均匀介质。
(4) 在列车运行过程中, 气流稳定, 不考虑外界风的影响。
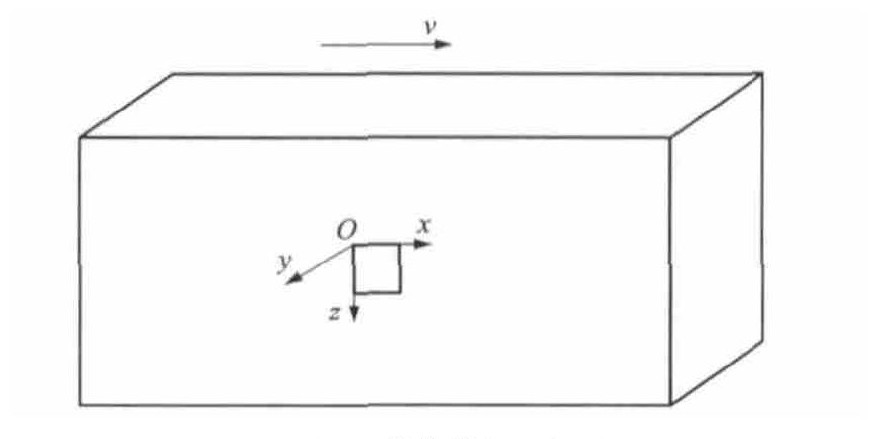
根据动车组实际长度, 如CRH2型动车组的外形尺寸为25.00m×3.50m×3.38m, 常用的宏观空气动力学不足以分析临近车厢表面边界层内各参数对气固界面摩擦噪声的影响, 本文从微观空气动力学的角度出发, 分析临近车厢界面边界层内各参数的变化, 在列车车厢的侧面选取0.50 mm× 0.50mm×0.25mm的几何微元体, 在微元体上设计图 2的表面织构, 分析其内部空气流体的动力学参数和噪声分布。车厢表面的坐标系Oxyz见图 3: O为微元体底面左上角位置; x轴为高速列车运行方向; y轴为车厢侧面垂直方向; z轴为车厢高度方向; v为速度。
基于FLUENT软件的宽频噪声源模型, 通过统计雷诺平均N-S方程所获得的湍流量, 结合半经验修正的Lighthill声学分析理论来模拟宽频噪声, 并利用声压级L来表达声强

式中: pe为待测声压的有效值; p0为基准声压, 是频率在1 000Hz时, 入耳开始能听到的声压, 在空气中, 其值为2.0×10-5Pa。
3. 菱形织构界面模型噪声计算
3.1 菱形织构案例1分析
在车厢表面设计对称的菱形织构, 织构基准参数W为0.5mm, C为0.3mm, c为0.1mm, a、b为0.06mm, h为0.015 mm。从而得到γ为1, λ为0.25, 取列车的行驶速度v为500km·h-1。
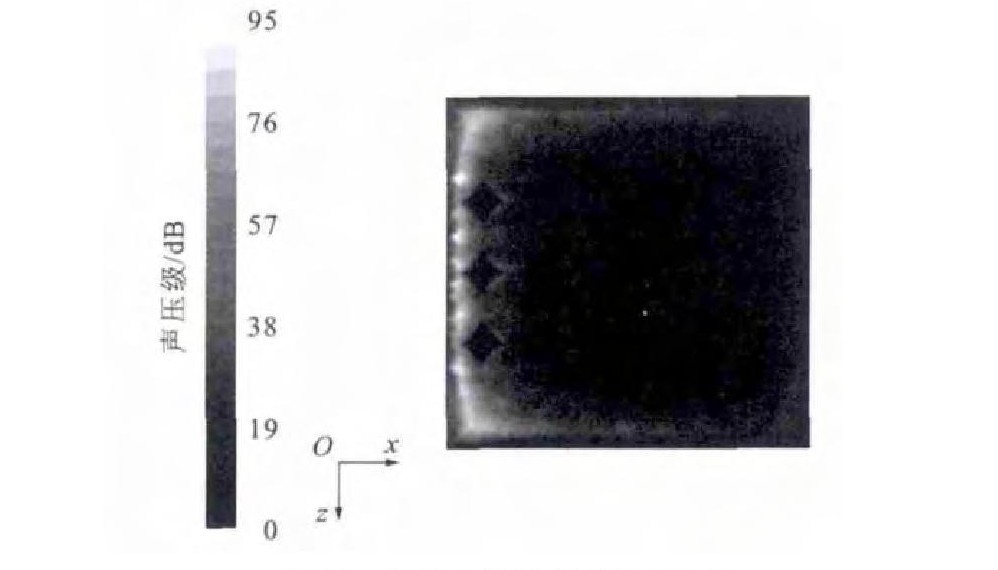
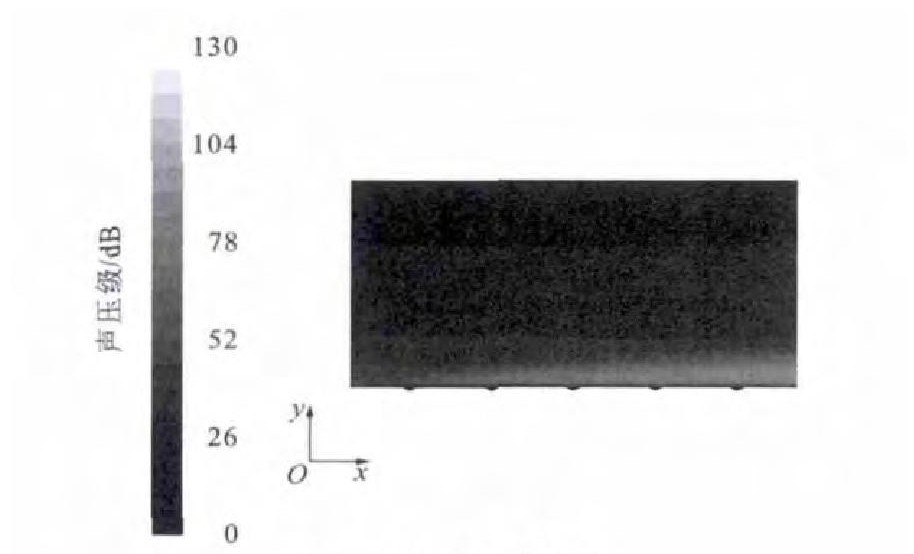
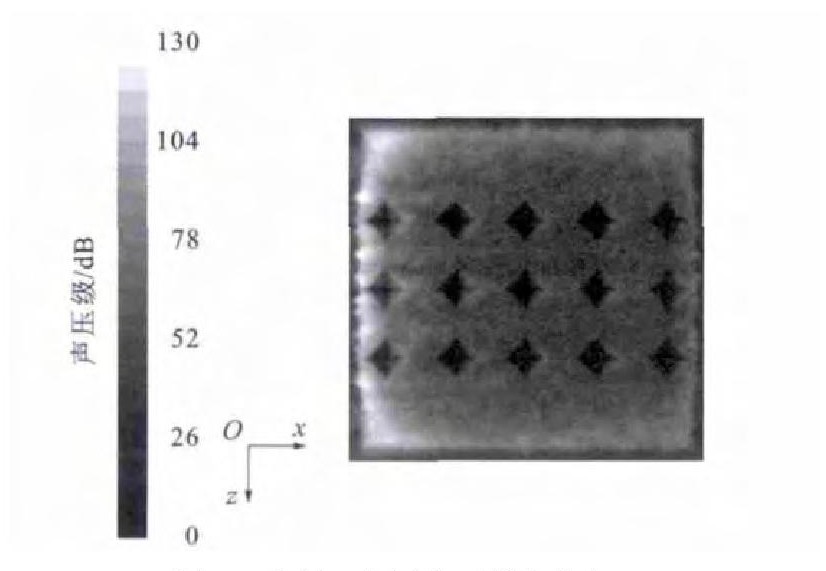
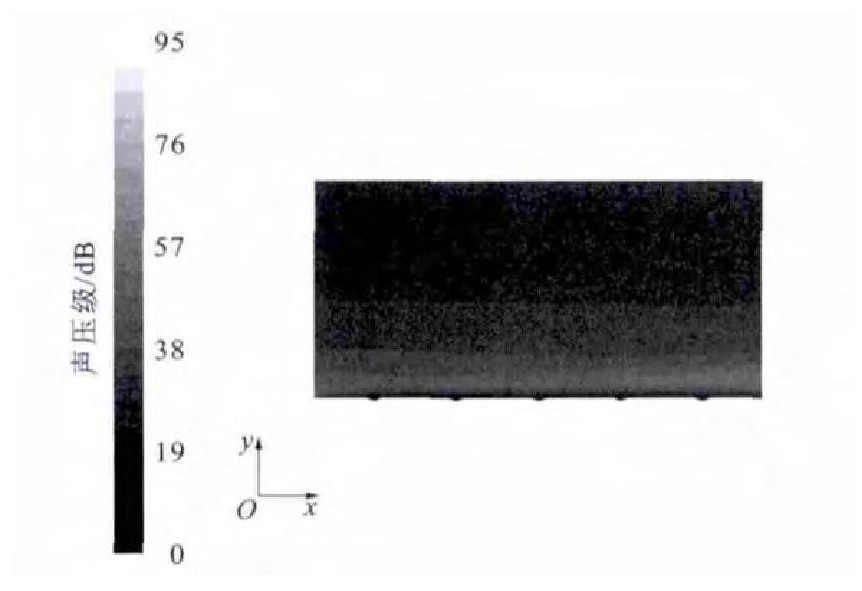
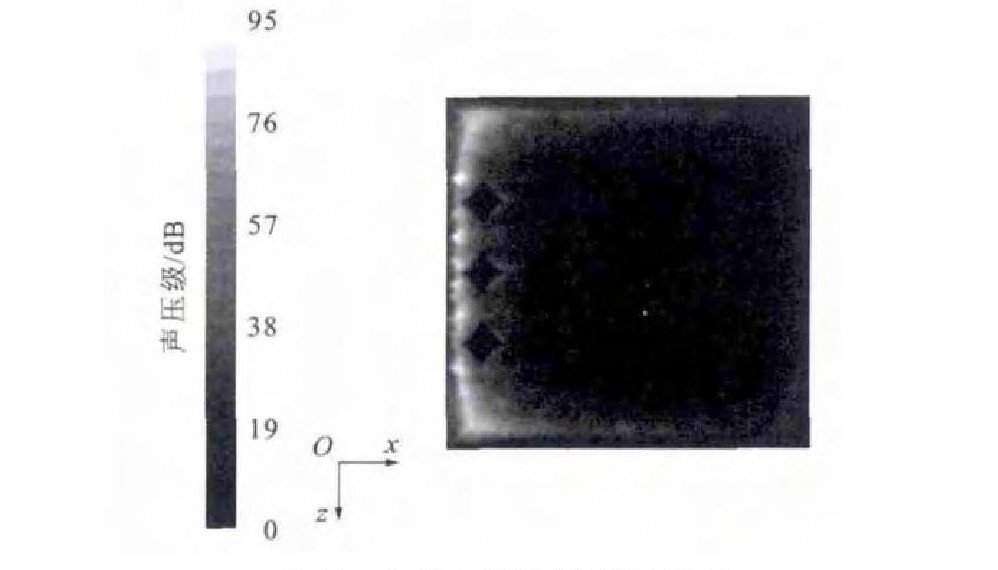
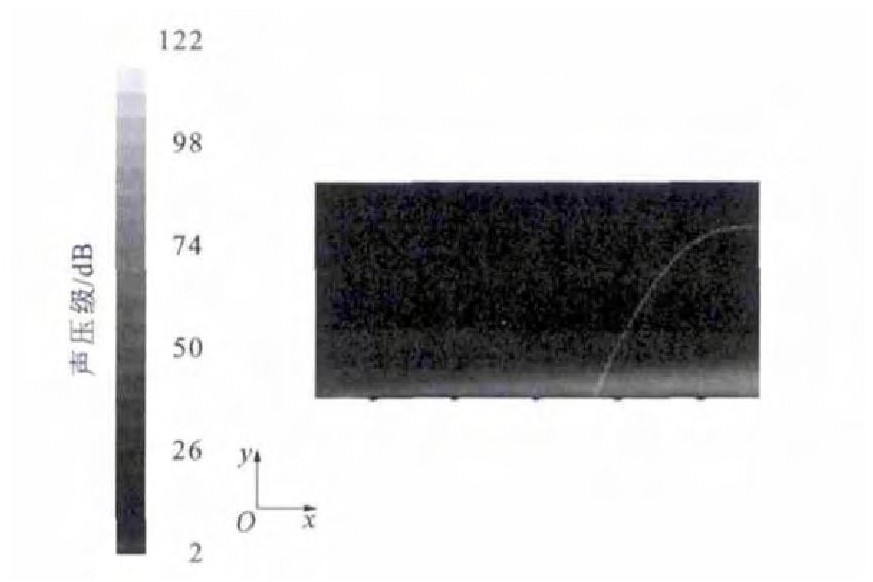
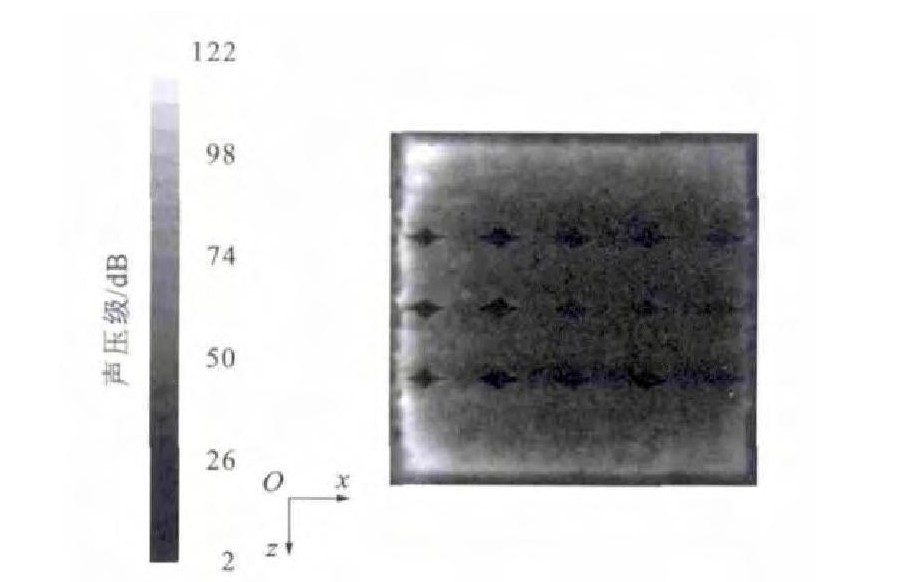
通过数值模拟分析, 得出微元体内部噪声分布见图 4、5。由图 4可以看出: 边界层内的噪声要远大于边界层外部, 噪声主要集中在近壁端, 并且此处变化梯度很大, 最大噪声为129dB, 这比光滑界面的146dB要低17dB, 降噪效果非常明显; 在边界层以外, 随着高度的增加, 噪声逐渐降低, 降低梯度较缓和, 这与光滑表面的情况类似[13]。由图 5可以看出: 菱形织构界面上的噪声分布很不均匀, 噪声主要集中在界面的前端和两侧; 菱形织构内部的噪声比周围的噪声低。
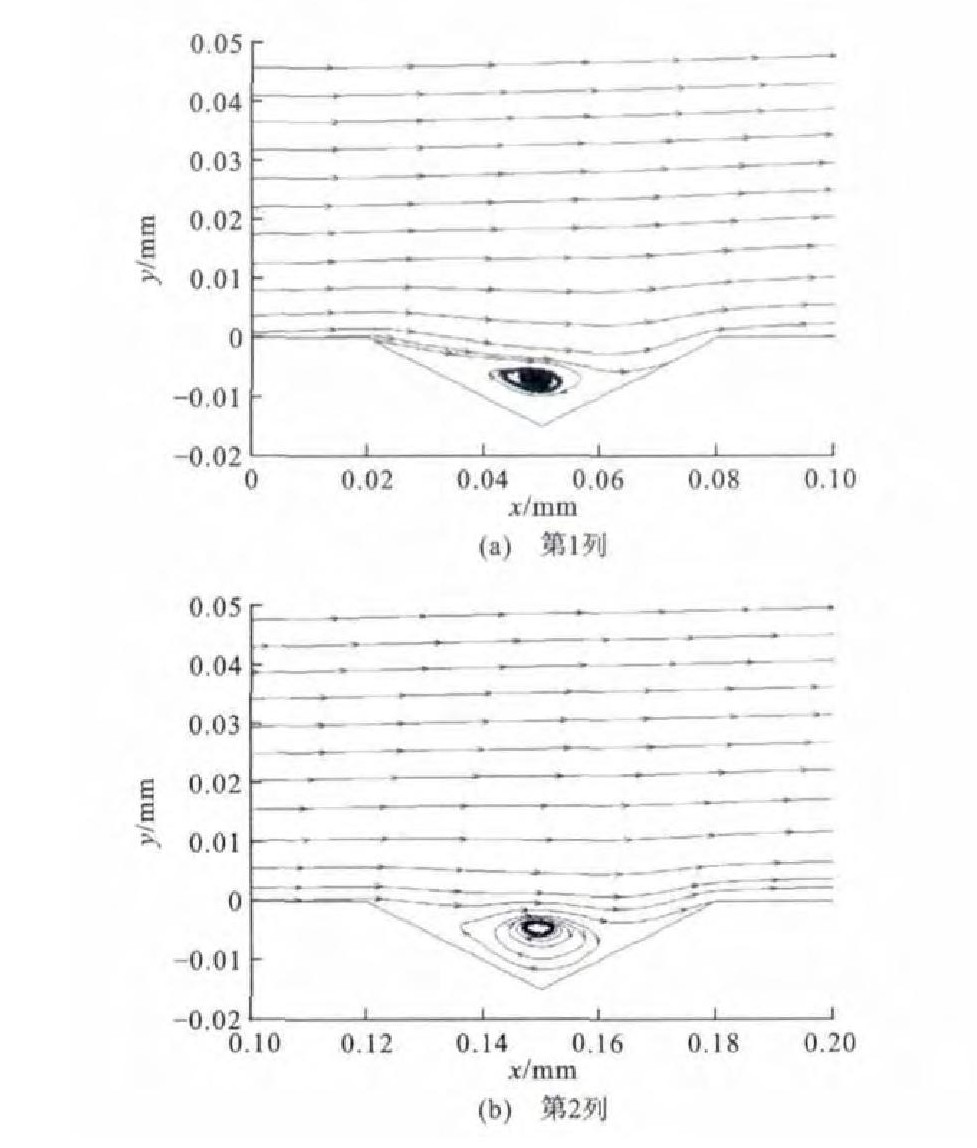
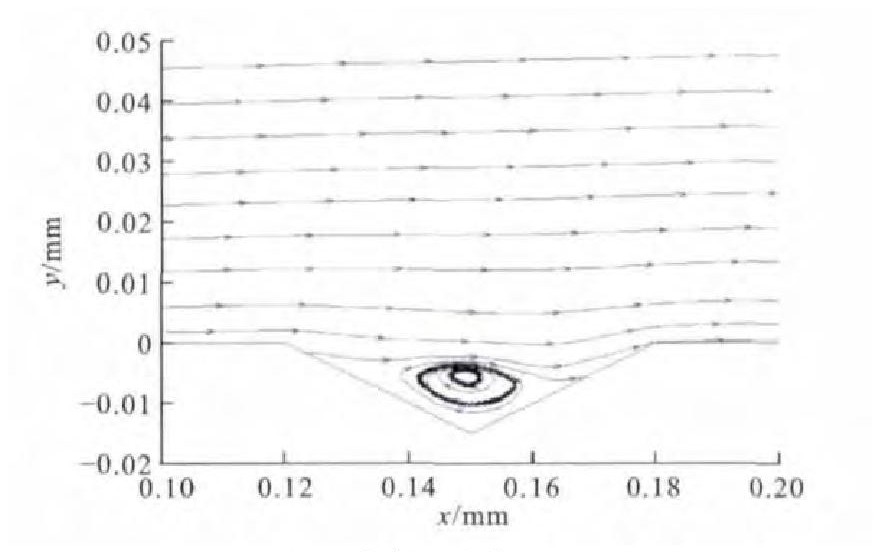
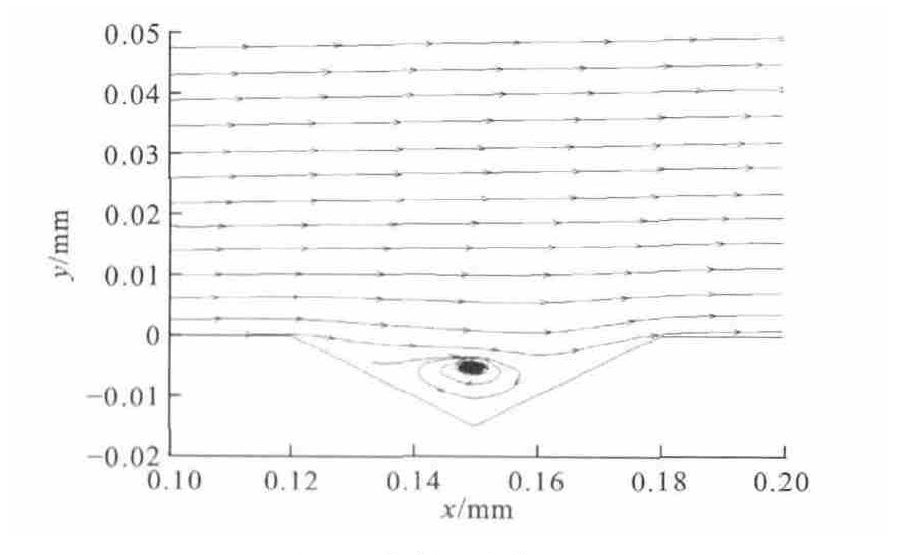
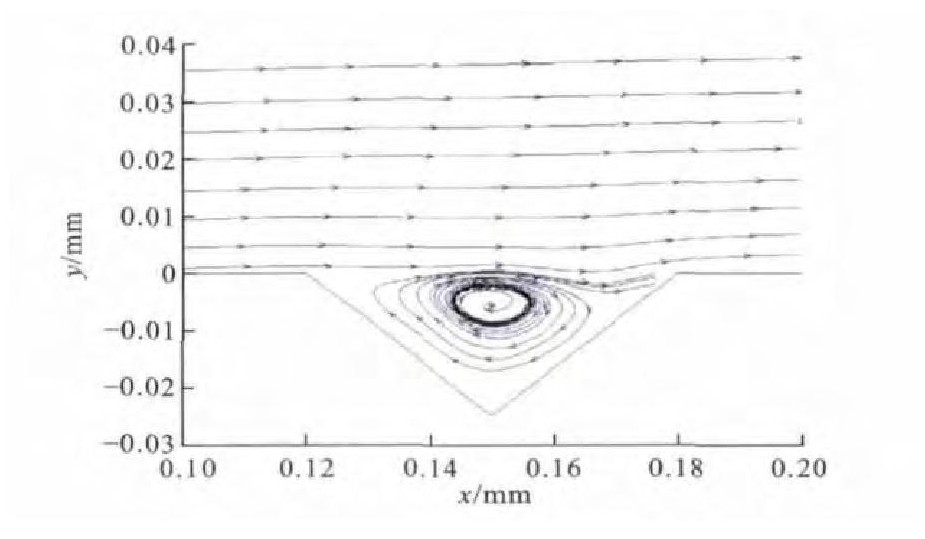
为了进一步研究菱形表面织构的降噪机理, 对菱形织构内部的速度场进行了分析, 图 6为第2排前2个菱形织构内部在xOy平面内的流线图, 箭头为空气流动的方向, 可以看出在菱形织构内部形成涡流, 并且涡的旋向是向着有利于外流场流动的方向。第2个织构内部漩涡中心较高, 距离壁面5μm。在列车运行时, 空气与形成的漩涡产生摩擦, 减少了空气与列车固体表面的直接摩擦, 从而起到降低空气摩擦噪声的作用。
3.2 高速列车运行速度对噪声的影响
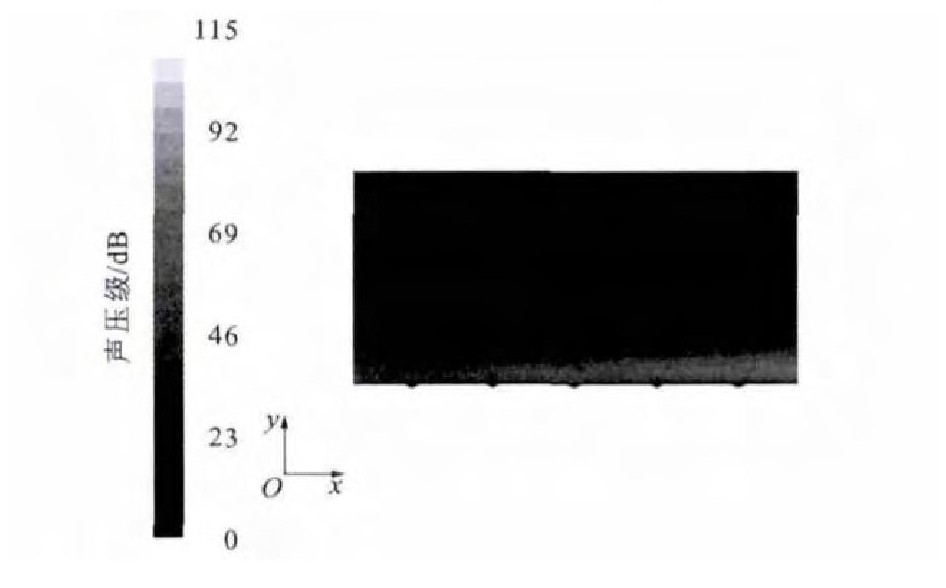
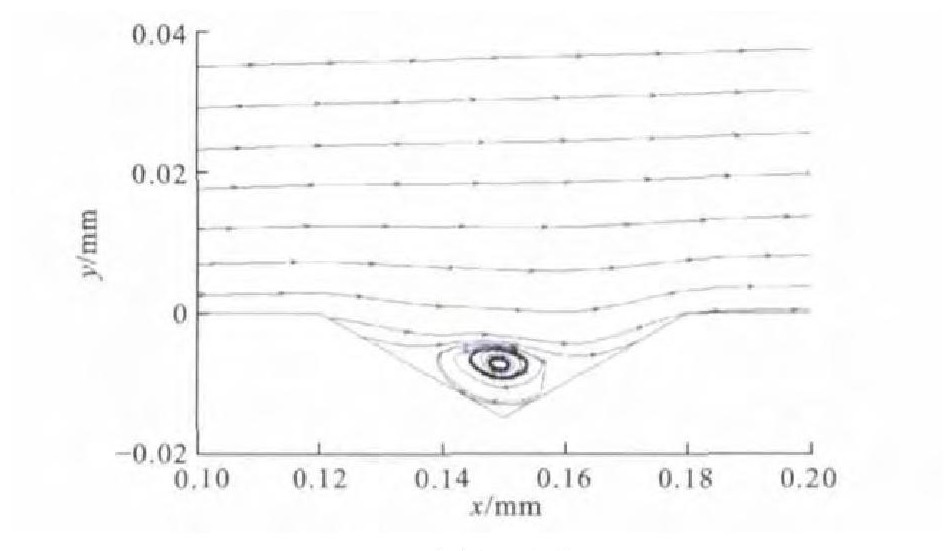
在案例1的基础上, 取列车的行驶速度v为400km·h-1 (案例2), 通过数值模拟分析, 得出微元体内部噪声分布见图 7、8。与案例1相似, 噪声主要集中在界面的前端和两侧; 总体噪声强度降低, 最大噪声为115dB。图 9为第2列第2排菱形织构内部的流线图, 漩涡中心距离壁面6μm。
在案例1的基础上, 取列车的行驶速度v为300km·h-1 (案例3), 通过数值模拟分析得出微元体内部噪声分布见图 10、11。与案例1相似, 噪声主要集中在界面的前端和两侧; 总体噪声强度降低, 最大噪声仅为95dB。图 12为第2列第2排菱形织构内部的流线图, 漩涡中心距离壁面7μm。
综合上述3个案例可以看出: 噪声强度与列车速度成正比, 但噪声的分布情况变化不大; 随着列车行驶速度的增大, 织构内部形成的漩涡的中心距离壁面越近。
3.3 菱形形状对噪声的影响
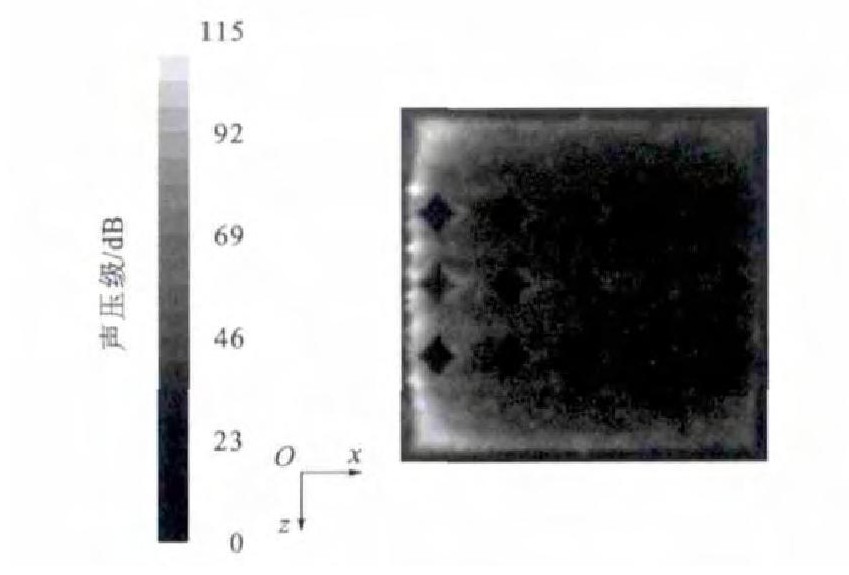
在案例1的基础上, 单独更改菱形织构的对角线比, 取b为0.03mm, 则γ为0.5 (案例4), 通过数值模拟分析, 得出微元体内部噪声分布见图 13、14。与案例1相似, 噪声主要集中在界面的前端和两侧; 总体噪声强度降低, 最大噪声仅为122dB, 相对光滑表面降低了24dB[13]。图 15为第2列第2排菱形织构内部的流线图, 漩涡中心距离壁面5μm。将菱形的对角线比由1.0改为0.5后, 最大噪声相对于γ为1.0时降低了7dB。
3.4 织构深边比对噪声的影响
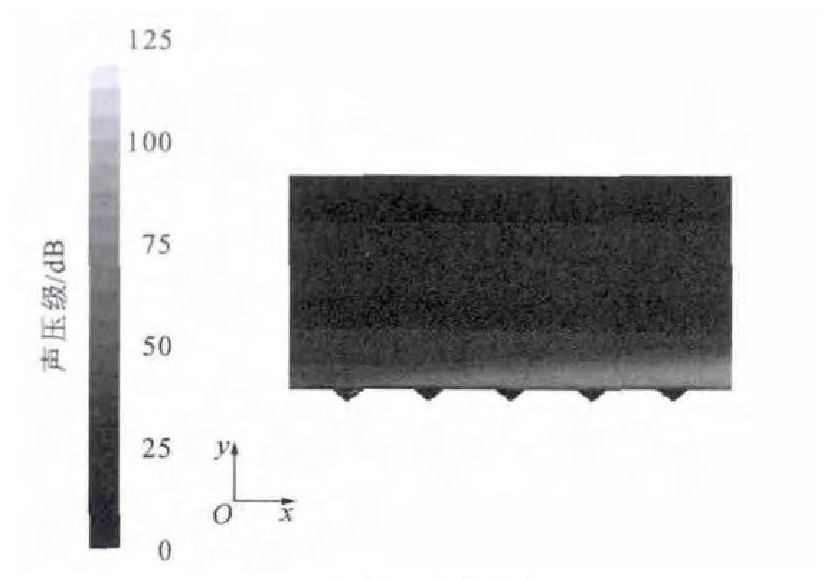
在案例1的基础上, 单独更改菱形织构的深边比, 取h为0.025mm, 则γ为0.42 (案例5), 通过数值模拟分析得出微元体内部噪声分布见图 16、17。与案例1相似, 噪声主要集中在界面的前端和两侧; 总体噪声强度略微降低, 最大噪声为125dB, 相对光滑表面降低了20dB[13]。图 18为第2列第2排菱形织构内部的流线图, 漩涡中心距离车厢壁面6μm。菱形的深边比λ由0.25改为0.42后, 最大噪声相对于λ为0.25时降低了3dB。
4. 结语
(1) 与光滑界面相比, 菱形织构界面的降噪效果非常明显, 噪声的分布也有变化, 空气与织构界面上的摩擦噪声主要集中在界面的两侧和前半部分。
(2) 当列车的运行速度在300~500km·h-1之间时, 菱形织构界面上的噪声分布基本没有变化, 但噪声的最大值随速度的增大而增大。
(3) 菱形织构的形状对噪声的影响很大, 在一定范围内, 速度方向的菱形对角线越长, 降低空气摩擦噪声的效果越好。
(4) 菱形织构的深边比对噪声的影响比较明显, 在一定范围内, 菱形织构的深度越大, 表面织构设计的降噪能力越强。
-
[1] MELLET C, LÉTOURNEAUXA F, POISSON F, et al. High speed train noise emission: latest investigation of the aerodynamic/rolling noise contribution[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 293 (3/4/5): 535-546. [2] HAMILTON D B, WALOWIT J A, ALLEN C M. A theory of lubrication by micro-irregularities[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1966, 88 (1): 177-185. doi: 10.1115/1.3645799 [3] RIGHTMIRE G K, BILL R G, ANDERSON H G. On the flow perturbations and friction reduction introduced by surface dimples[C]∥DOWSON D, TAYLOR C M, GODET M, et al. Proceedings of the 14th Leeds-Lyon Symposium Tribology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1987: 139-143. [4] ETSION I, BURSTEIN L. A model for mechanical seals with regular microsurface structure[J]. Tribology Transactions, 1996, 39 (3): 677-683. doi: 10.1080/10402009608983582 [5] RONEN A, ETSION I, KLIGERMAN Y. Friction-reducing surface-texturing in reciprocating automotive components[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2001, 44 (3): 359-366. doi: 10.1080/10402000108982468 [6] KLIGERMAN Y, ETSION I, SHINKARENKO A. Improving tribological performance of piston rings by partial surface texturing[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2005, 127 (3): 632-638. doi: 10.1115/1.1866171 [7] ETSION I. State of the art in laser surface texturing[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2005, 127 (1): 248-253. doi: 10.1115/1.1828070 [8] WANG Q J, ZHU D. Virtual texturing: modeling the performance of lubricated contacts of engineered surfaces[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2005, 127 (4): 722-728. doi: 10.1115/1.2000273 [9] TAN A H, CHENG S W. A novel textured design for hard disk tribology improvement[J]. Tribology International, 2006, 39 (6): 506-511. [10] YAMAGUCHI K. Surface structure mimicking earthworm[J]. Journal of Japanese Society of Tribologists, 2000, 45 (5): 349-353. [11] WANG Jiu-gen, ZHANG Jian-zhong, XUE Zheng. Bionic design of integrate structures[J]. Journal of Engineering Design, 2007, 14 (1): 78-83. [12] WANG Jiu-gen, XUE Zheng, XIE Yi-jing. Patterns of integrated surface texture[C]∥WU Xian-ming. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference of Frontiers of Design and Manufacturing. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2008: 1-6. [13] 林世才, 汪久根. 圆坑织构高速列车气固界面的摩擦噪声分析[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2012, 12 (3): 53-59. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201203007LIN Shi-cai, WANG Jiu-gen. Frictional noise analysis of gassolid interface with circular dents for high-speed train[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2012, 12 (3): 53-59. (in Chinese). http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201203007 -






 下载:
下载:


















 下载:
下载: