Automatic identification algorithm of train track occupancy
-
摘要: 为解决列车在道岔及平行股道区段的轨道占用自动识别问题, 基于LTS-Hausdorff距离, 结合D-S证据理论, 提出了一种新的列车轨道占用自动识别算法, 建立了可用于列车轨道占用自动识别的轨道LTS-Hausdorff距离参考模板, 分析了LTS-Hausdorff距离的计算过程及轨道占用自动识别决策方法, 研究了列车速度与搜索阈值对自动识别算法的影响。验证结果表明: 在轨迹点数量为10时, 该识别算法和基于最大似然准则的轨道识别决策的识别结果相同; 列车速度越高, 轨迹点越少, 算法仍可进行有效识别; 搜索阈值越小, 算法实现时间越短。可见, 识别算法有效。
-
关键词:
- 交通控制 /
- 轨道占用识别 /
- LTS-Hausdorff距离 /
- D-S证据理论 /
- 列车定位
Abstract: In order to resolve the automatic identification problems of train track occupancy at turnouts and on parallel sections, a new automatic identification algorithm was proposed based on LTS-Hausdorff distance and D-S evidence theory. The reference template of track LTS-Hausdorff distance was established, the calculation process of LTS-Hausdorff distance and the decision method of automatic identification were analyzed, and the effects of train speed and search threshold on the algorithm were studied. Test result shows that when there are 10 track points, the results of the new algorithm and the maximum likelihood track identification decision are same. The higher train speed is, the less track points are, and the algorithm is still effective. The smaller search threshold is, the shorter the algorithm realizing time is. So the algorithm is valid. -
0. 引言
列车轨道占用自动识别是指列车在运行过程中能够实时、自主地确定当前占用的轨道, 列车在车站等存在大量平行股道及道岔区段的场地运行时, 占用轨道的精确识别是列车运行控制的重要前提。已有的列车轨道占用识别方法必须依赖检测道岔状态、应用应答器信息, 通过轨旁无线通信设备发送到车载设备, 该方法在一些无联锁区段就失去了应用条件, 因此, 需要对列车轨道占用的自动识别技术进行研究。国内外一些学者提出了一些适用于轨道占用自动识别的算法, 具有代表性的主要有测量列车航向角、地图匹配与基于HMM的轨道占用识别算法等[1-3], 上述算法在实际测试中都能实现轨道占用自动识别的目的, 但也存在成本高, 易受传感器精度及列车速度影响等问题。
本文利用点集匹配领域中广泛应用的Hausdorff距离结合D-S证据理论实现列车轨道占用识别[4-5]。Hausdorff距离是由Huttenlocher等在研究目标检测时首先提出来的, 是描述两组点集之间相似程度的一种量度, 又称为最大最小距离, 其特点是在计算时不需要建立两个待匹配点集中点与点之间的对应关系, 目前应用较为广泛的Hausdorff距离包括部分Hausdorff距离、平均Hausdorff距离及LTS-Hausdorff距离[6-9]。如果将列车运行特征作为一个点集, 不同轨道的形状也用不同的点集来进行描述, 那么轨道占用识别问题就可描述成为点集之间的匹配问题, 用LTS-Hausdorff距离可以表征列车当前运行的轨迹点集与轨道信息点集之间的距离, 也就是相似度, 从而解决轨道占用识别问题。
本文结合列车运行轨迹特点, 提出了一种新的基于LTS-Hausdorff距离和D-S证据理论的列车轨道占用自动识别算法, 该算法充分利用了列车的定位信息及轨道的拓扑结构特点, 实现了低成本条件下的列车轨道占用自动识别。
1. 基于LTS-Hausdorff距离和D-S证据理论的轨道识别算法设计
采用LTS-Hausdorff距离进行轨道占用识别的基本过程见图 1, 包括以下几点: 建立轨道参考模板; 计算列车运行轨迹点集与轨道参考模板点集之间的LTS-Hausdorff距离; 进行轨道占用识别决策。
1.1 轨道LTS-Hausdorff距离参考模板建立
本文选取轨道的平面地理坐标和轨道线路与给定方向的夹角作为轨道LTS-Hausdorff距离特征参考模板的参数。用B表示参考模板, B中包含n个元素, 轨道LTS-Hausdorff距离特征参考模板为
{B={b1,b2,⋯,bn}bt={xt,yt,αt} t=1,2,⋯,n (1)
式中: bt为参考模板元素; xt与yt分别为轨道平面的横纵坐标; αt为轨道线路与给定方向的夹角; t为参数模板中各元素编号。xt、yt与αt均可以用GPS-RTK测量得到。
1.2 LTS-Hausdorff距离计算
本文选用LTS-Hausdorff距离来表征点集之间的距离[9], 用点集A表示列车运行轨迹数据, 则有
{A={a1,a2,⋯,aq}aj={xj,yj,αj} j=1,2,⋯,q (2)
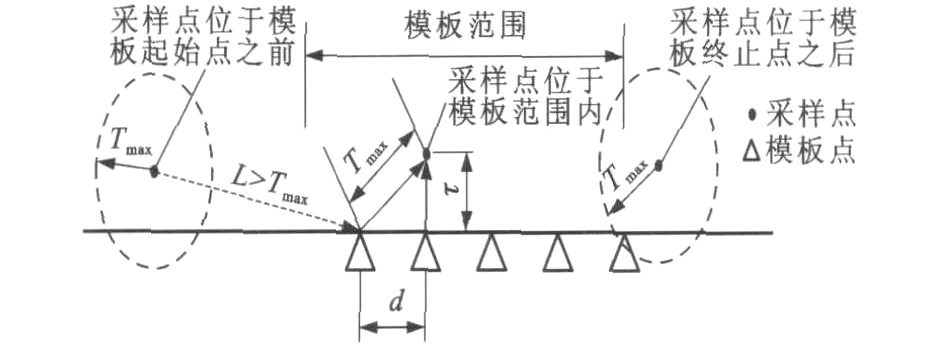
式中: aj为测量得到的列车在不同时刻的位置点; xj与yj分别为轨迹样本点的横纵坐标; αj为轨迹样本点的航向角; j为样本点元素在运行轨迹集中的编号; q为某一运行轨迹集中点个数。列车轨迹采样点见图 2, 计算A中的一个采样点aj到B中各个点之间的距离时, 以aj为中心, 在以阈值Tmax为半径的一个圆域内搜索B中的点, 如果存在满足条件的点, 选择其中距离最小的点bt对应的距离作为aj到B的距离, 如果该领域内没有B中的点存在, 将aj到B之间的距离设为Tmax, 采样点与模板点之间的距离为L。
采用2-范数定义计算轨迹采样点与给定模板的LTS-Hausdorff距离时, Tmax的计算式为[10]
Τmax=√d2+τ2 (3)
式中: d为2个模板点间的距离, 由列车运行时允许的最大速度决定; τ为采样点与实际点之间的最大偏差值, 由列车定位数据误差决定。
1.3 轨道占用自动识别决策
计算得到列车当前占用的轨道数据点集与实际轨道特征数据点集之间的LTS-Hausdorff距离后, 可以采用基于最大似然准则的轨道占用识别决策[11], 但这种决策方法受列车运行速度的影响较大, 本文运用文献[12]中的D-S证据理论方法将列车运行轨迹点集与轨道参考模板点集间的LTS-Hausdorff距离与列车运行轨迹的方向信息分别作为位置信息证据与方向信息证据进行轨道识别决策。
首先根据D-S证据理论建立一个非空集合识别框U为
U={A1‚
式中: Ai表示当前时刻列车运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 上。U中各个元素之间是互相排斥的, 根据D-S证据理论中证据的相关定义, 设Di为运行轨迹到编号为i的股道(或正线) 参数模板上的LTS-Hausdorff距离, 令
c1, i=
式中: c1, i为编号为i的股道(或正线) 的轨道模板的位置信息证据的中间计算量; 均值μ1与方差σ1为列车运行轨迹点集到所有轨道参考模板之间的LTS-Hausdorff距离的统计结果; u[m1 (Ai) ]为编号为i的股道(或正线) 的轨道模板的位置信息局部决策值; m1 (Ai) 为未经权值修正得到的列车位置信息基本概率分配函数。得出局部决策值u[m1 (Ai) ]后可以计算得到权值ωi, 进一步得到修正后的基本概率分配函数为
式中: m1* (E) 为修正后的位置信息基本概率; E为列车运行信息全集, 表示当前时刻不能判定列车运行在哪条轨道上; ω1为位置概率信息证据的可靠性参数, 即权值。
设βi为列车当前运行轨迹与编号为i的股道(或正线) 之间的航向角偏差, 令
c2, i=
βi=αi-α (9)
m2* (Ai) =c2, i
m2* (E) = (1-ω2)
式中: c2, i为编号为i的股道(或正线) 的轨道模板的航向角信息证据的中间计算量; α为列车运行轨迹点进行拟合后得到的航向角(这里只取与正北方向的夹角); αi为编号i的股道(或正线) 航向角(与正北方向夹角), 若计算过程中βi为0时, 则令其等于一个很小的非0数值; 均值μ2与方差σ2为列车航向信息与所有轨道参数模板方向角之差统计结果; u[m2 (Ai) ]为编号为i的股道(或正线) 的轨道模板的航向信息局部决策值; m2 (Ai) 为未经权值修正得到的列车航向信息基本概率分配函数; m2* (Ai) 为利用权值修正后对列车当前运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 的轨道上的航向信息的基本概率分配函数; m2* (E) 为修正后的航向信息基本概率, 表示当前时刻不能判定列车运行在哪条轨道上的概率度量; ω2为航向概率信息证据的可靠性参数, 即权值。将m1* (Ai) 和m2* (Ai) 融合成为一个基本概率赋值函数为
式中: m* (Ai) 为综合列车位置信息及航向信息后对列车当前运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 的轨道上的基本概率分配函数; K为概率融合时的计算参数。在最终进行决策时, 采用基于Pignistic概率的决策规则[13], 用P (Ai) 表示列车运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 上的Pignistic概率密度函数, 则有
式中: G (Ai) 为列车运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 的信任函数, 即对列车运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 上的信任程度; R (Ai) 为列车运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 上的似然函数, 即不否认列车当前运行在编号为i的股道(或正线) 上的概率度量。本文选择max{P (Ai) }对应的轨道作为列车当前占用的轨道识别结果。
2. 实例分析
本文采用在北京铁路局三家店站测量获得的实际线路数据和列车的实际运行数据, 根据1.1介绍的过程构建了LTS-Hausdorff距离算法模板, 用MATLAB分别仿真了基于最大似然准则的轨道识别决策和基于D-S证据理论的轨道识别决策。
表 1给出了列车在道岔区段运行5次获得的样本轨迹与该道岔的样本轨道参考模板点集进行匹配后输出的累加对数似然概率值及D-S证据理论做出的识别判决结果(10个样本点), 其中参考模板Ⅰ、Ⅱ分别表示正线与侧线模板, 并由线路的地理位置信息组成。表 2给出了列车在第7、8、9三条平行股道上获得的运行样本轨迹进行匹配后输出的累加对数似然概率及D-S证据理论做出的识别结果(10个样本点), 其中模板Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ分别表示车站内第7、8、9股道的地理位置模板信息, 包括各股道的二维地理坐标及方向角。
表 1 道岔区段轨道识别Table 1. Track identification on switch sections样本类型 参考模板Ⅰ 参考模板Ⅱ D-S识别结果 正线 -16.831 -100.410 正线 -17.952 -98.451 -16.735 -75.105 侧线 -89.364 -19.352 侧线 -96.350 -20.382 表 2 平行股道区段轨道识别Table 2. Track identification on parallel track sections样本类型 模板Ⅰ 模板Ⅱ 模板Ⅲ D-S识别结果 第7股道样本 -20.63 -150.40 -512.80 第7股道 第8股道样本 -153.00 -15.36 -149.60 第8股道 第9股道样本 -510.90 -151.10 -16.64 第9股道 表 1中正线表示连结车站并贯穿或直股伸入车站的线路, 侧线表示连接车站但不以直股伸入车站的线路。表 1、2中的样本与各模板匹配后的输出为基于最大似然准则的轨道识别决策中得到的各模板累加对数似然概率, 识别结果是基于D-S证据理论的轨道识别决策得到的。从表 1、2可以看出, 在轨迹点数量为10的条件下, 基于D-S证据理论的轨道识别决策和基于最大似然准则的轨道识别决策都能给出正确的识别结果, 在不同的轨迹点数量条件下, 得到的累加概率结果会有不同。
3. 列车速度对轨道自动识别算法的影响
列车的运行速度对轨道自动识别算法的影响与列车定位数据输出频率密切相关, 一般情况下, 对特定型号的道岔, 其长度是固定的[14], 列车轨迹点个数N与列车速度v及列车定位数据输出频率f的关系为
式中: C为模板距离即轨道模板起始点与终止点的距离。在C与f一定的条件下, 列车速度与所能得到的运行轨迹点个数成反比关系, 对基于最大似然准则的轨道识别决策而言, 运行轨迹点个数的多少直接影响了列车运行轨迹与参考模板之间的累加对数似然概率和, 过少的运行轨迹点将导致累加对数似然概率和减小, 无法有效识别轨道, 这种情况下要提高列车通过道岔的速度, 就必须提高列车定位数据输出频率以保证提供足够的轨迹信息来进行轨道占用自动识别, 列车定位数据输出频率越高, 其成本也相应的增加。表 3给出了列车以5、10、25 m·s-1的速度经过道岔区段时基于最大似然准则的轨道识别决策得到的累加对数似然概率和结果。
表 3 不同列车速度对轨道识别的影响Table 3. Influences of different train speeds on track identification车速/ (m·s-1) 5 (正线样本) 10 (侧线样本) 25 (正线样本) 正线模板 -159.665 -143.770 -7.537 侧线模板 -500.870 -127.230 -11.548 从表 3可以看到, 列车通过道岔区段的速度越高, 得到的轨迹点越少, 模板之间的累加对数似然概率和结果差别也越小, 无法进行有效识别; 通过加入轨迹方向信息, 并利用D-S证据理论进行融合决策后, 输出结果可以使正线与侧线之间的区别得到有效放大, 具体见表 4。
从表 4可以看出, 利用D-S证据理论引入轨迹的方向信息后, 即使在轨迹点比较少的情况下也能进行有效识别, 降低了对列车定位数据输出频率的要求, 也可以降低轨道占用识别系统的成本。
表 4 不同列车速度下的融合结果Table 4. Fusion results at different train speeds车速/ (m·s-1) 5 (正线样本) 10 (侧线样本) 25 (正线样本) 正线模板 0.651 0.235 0.673 侧线模板 0.183 0.712 0.351 4. 搜索阈值对轨道自动识别算法的影响
计算列车当前运行轨迹点集中的点到轨道参考模板点集的距离时, 为提高距离计算效率, 本文引入了阈值Tmax。Tmax的取值影响到轨道识别算法的计算复杂度和实时性, 图 3为不同的Tmax下完成轨道识别算法需要的时间比较。
从图 3可以看出, 阈值Tmax越小, 需要的搜索时间越少, 但Tmax并不是越小越好, 当Tmax过小时, 可能会导致列车运行轨迹点集中的点在搜索领域内都找不到满足条件的参考模板中的点, Tmax对LTS-Hausdorff距离计算的影响见图 4。
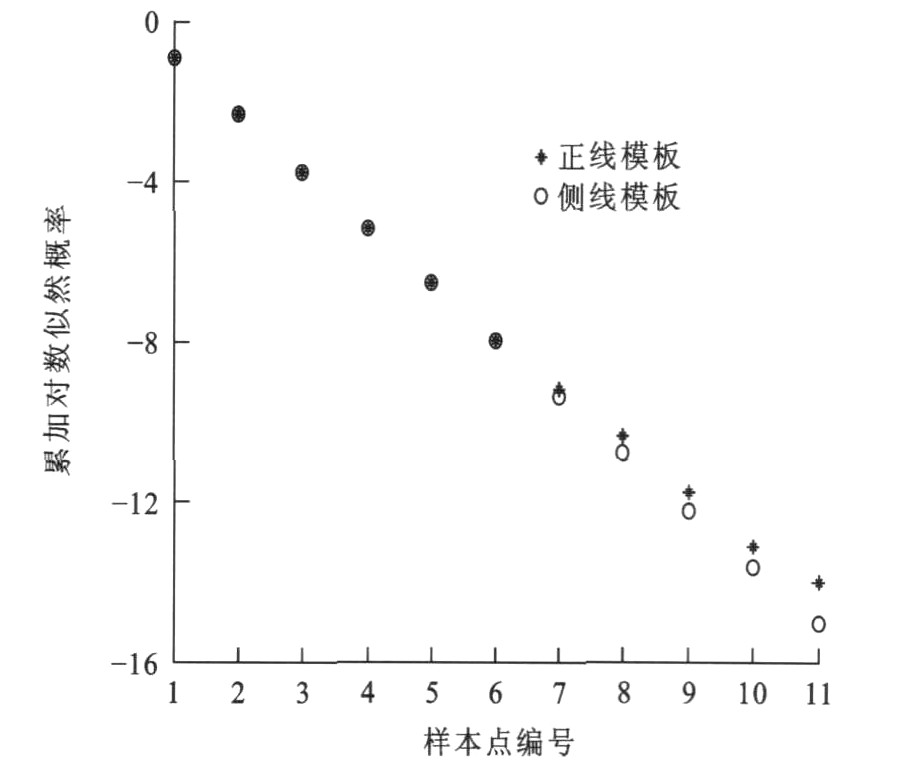
图 4中, a1~a4分别为列车在不同时刻的4个位置点, b1~b5分别为某一特定轨道的5个模板点元素。由图 4可以看到, 在Tmax取值过小的情况下, 一些远离轨道实际坐标的点也成为合法的点, 输出的累加对数似然概率几乎完全重合, Tmax为0.5 m时的正线样本累加对数似然概率, 见图 5。在Tmax过小的情况下, 正线样本与正线模板及侧线模板之间经识别计算后得到的对数似然概率差别极小, 很难有效区分。此外, 在Tmax过小时得到的LTS-Hausdorff距离可能出现偏差, 导致D-S证据理论融合结果的可信度降低。Tmax也不能设的过大, 否则会带来额外的时间成本, 降低算法的效率。
5. 结语
本文在充分利用列车定位信息及轨道拓扑结构特点的基础上, 提出了一种新的轨道占用自动识别算法, 并对算法中引入的搜索阈值进行了分析。实际列车的运行数据测试表明, 该算法能够在列车运行轨迹点数量相对较少的情况下对列车当前占用的轨道进行有效识别, 降低了对GPS数据输出频率的要求, 有利于降低列车运行控制系统成本。
-
表 1 道岔区段轨道识别
Table 1. Track identification on switch sections
样本类型 参考模板Ⅰ 参考模板Ⅱ D-S识别结果 正线 -16.831 -100.410 正线 -17.952 -98.451 -16.735 -75.105 侧线 -89.364 -19.352 侧线 -96.350 -20.382 表 2 平行股道区段轨道识别
Table 2. Track identification on parallel track sections
样本类型 模板Ⅰ 模板Ⅱ 模板Ⅲ D-S识别结果 第7股道样本 -20.63 -150.40 -512.80 第7股道 第8股道样本 -153.00 -15.36 -149.60 第8股道 第9股道样本 -510.90 -151.10 -16.64 第9股道 表 3 不同列车速度对轨道识别的影响
Table 3. Influences of different train speeds on track identification
车速/ (m·s-1) 5 (正线样本) 10 (侧线样本) 25 (正线样本) 正线模板 -159.665 -143.770 -7.537 侧线模板 -500.870 -127.230 -11.548 表 4 不同列车速度下的融合结果
Table 4. Fusion results at different train speeds
车速/ (m·s-1) 5 (正线样本) 10 (侧线样本) 25 (正线样本) 正线模板 0.651 0.235 0.673 侧线模板 0.183 0.712 0.351 -
[1] 王剑, 张辉, 蔡伯根, 等. 基于GNSS的轨道占用识别技术综述[J]. 铁道学报, 2010, 32 (2): 93-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201002018.htmWANG Jian, ZHANG Hui, CAI Bai-gen, et al. ASurvey oftrack occupancy recognition technology based on GNSS[J]. Journal of the China Rail way Society, 2010, 32 (2): 93-97. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201002018.htm [2] SAAB S S. A map matching approach for train positioningpart I: development and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2000, 49 (2): 467-475. doi: 10.1109/25.832978 [3] 王剑, 张辉, 蔡伯根, 等. 基于HMM的列车轨道占用识别中算法研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2009, 31 (3): 54-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB200903011.htmWANG Jian, ZHANG Hui, CAI Bai-gen, et al. The algo-rithm of automatic track occupying identification based onHMM[J]. Journal of the China Rail way Society, 2009, 31 (3): 54-58. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB200903011.htm [4] 谭青, 向阳辉. 加权证据理论信息融合方法在故障诊断中的应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2008, 27 (4): 112-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ200804030.htmTAN Qing, XIANG Yang-hui. Application of weighted evidential theory and its information fusion method in fault diagnosis [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2008, 27(4): 112-116. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ200804030.htm [5] BUSTOS J P, DONOSO F, GUESALAGA A, et al. Matchingradar and satellite i mages for ship trajectory esti mation usingthe Hausdorff distance[J]. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2007, 1 (1): 50-58. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20060025 [6] AHN Y J. Hausdorff distance between the offset curve ofquadratic bezier curve and its quadratic approxi mation[J]. Communications of the Korean Mathematical Society, 2007, 22 (4): 641-648. [7] LU Yue, TAN C L, HUANG Wei-hua, et al. An approach to word image matching based on weighted Hausdorff distance[C]//IEEE. Sixth International Conference on Document Analysisand Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2001: 921-925. [8] KANGJian-xin, QI Nai-ming, HOUJian. A hybrid method combining hausdorff distance, genetic algorithm and simulated annealing algorithm for image matching[C]//IEEE. ICCMS 10 Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Computer Modeling and Si mulation. Sanya: IEEE, 2010: 435-439. [9] SHANG Fu-hua, WANG Hui, MA Nan. A method of depth correction of logging curves based on LTS Hausdorff distance[C]// IEEE. 2010International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling. Taiyuan: IEEE, 2010: 108-112. [10] SHEN Shu-han, SHI Wen-huan, LI U Yun-cai. Monocular3-D tracking of inextensible deformable surfaces under L2-Norm[J]. IEEE Transactions on I mage Processing, 2010, 19 (2): 512-521. [11] SCHMITT L, MEYK H. Asystematic framework for iterativemaxi mumlikelihood receiver design[J]. IEEE Transactionson Communications, 2010, 58 (7): 2035-2045. [12] 谷正气, 胡林, 黄晶, 等. 基于改进D-S证据理论的车辆导航地图匹配[J]. 汽车工程, 2008, 30 (2): 141-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC200802010.htmGU Zheng-qi, HULin, HUANGJing, et al. Vehicle naviga-tion map matching based on modified D-S evidence rule[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2008, 30 (2): 141-145. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC200802010.htm [13] SUDANO J J. Inverse pignistic probability transforms[C]∥IEEE. Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Information Fusion. Indianapolis: IEEE, 2002: 763-768. [14] 王剑. 基于GNSS的列车定位方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2007.WANG Jian. Research of the train positioning technologies based on GNSS technology[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2007. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载: