Intelligent dimensional inspection method for steel box arch prefabricated components based on Harris features and NDT-ICP algorithm
-
摘要:
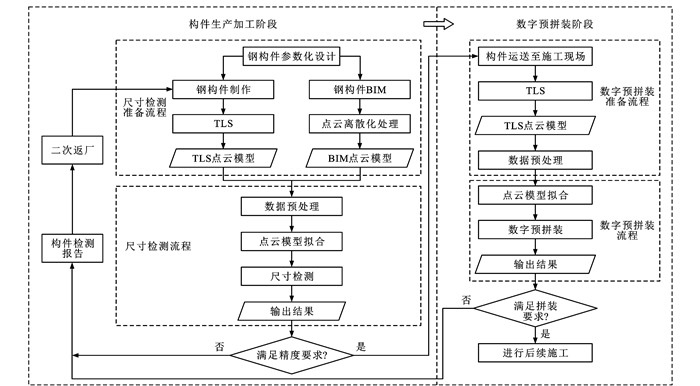
针对桥梁建造时传统人工尺寸检测在面对海量桥梁预制件时效率低、成本高的难题,使采用地面激光扫描(TLS)技术的智能尺寸检测突破现有数据处理算法的精度与效率瓶颈,建立了基于建筑信息模型(BIM)-TLS的桥梁钢预制件尺寸智检框架,包含构件几何尺寸检测与数字预拼装2个环节;二次开发了BIM点云化处理技术,构建了参照点云模型,采用直通滤波、统计去噪(SOR)滤波、体素化网格(VG)处理等算法预处理点云数据,实现了基于k近邻(kNN)算法的尺寸检测指标评价;通过3D-Harris特征点检测、正态分布变换(NDT)粗配准与迭代最近点(ICP)精配准提出了基于Harris特征与NDT-ICP算法的快速配准尺寸智检策略,并结合工程需求应用于某大跨拱梁组合结构钢箱拱预制件尺寸智检中。研究结果表明:采用提出的智检方法对2个相邻节段钢箱拱进行尺寸检测的最大偏差分别为1.689和1.571 mm,均满足制造偏差(小于2 mm)要求;与传统NDT-ICP算法相比,该方法将点云整体配准精度提高了35.3%,效率提高了61.88%,可见该方法表现高效且结果准确,促进了钢预制件几何尺寸检测智能化;基于该方法的拱肋数字预拼装监测点最大检测拼装偏差为1.953 3 mm,符合拼装偏差(小于2 mm)要求,实现了精准偏差检测,为后续桥位顺利架设提供了良好保障,且为相似结构的尺寸检测提供了参考。
Abstract:In response to the challenges of low efficiency and high cost of traditional manual dimensional inspection in face of massive bridge prefabricated components during the bridge construction, and to break through the accuracy and efficiency bottlenecks of existing data processing algorithms in the intelligent dimensional inspection using the terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) technology, an intelligent dimensional inspection framework for bridge steel prefabricated components was established based on the building information modeling (BIM)-TLS, including two links: geometric dimensional inspection and digital pre-assembly of components. The BIM point cloud processing technology was customized, and the reference point cloud model was constructed. The point cloud data were preprocessed by using the straight-through filtering, statistical outlier removal (SOR) filtering, voxel grid (VG), and other algorithms. The dimensional inspection index evaluation based on the k-nearest neighbor (kNN) algorithm was realized. Through the 3D-Harris feature point inspection, normal distributions transform (NDT) coarse registration, and iterative closet point (ICP) fine registration, a fast registration intelligent dimensional inspection strategy based on the Harris feature and NDT-ICP algorithm was proposed and applied to the intelligent dimensional inspection of steel box arch prefabricated components of a large-span arch beam composite structure in combination with the engineering requirements. Research results show that the maximum deviations of the proposed intelligent inspection method for the dimensional inspection of two steel box arches at adjacent segments are 1.689 and 1.571 mm, respectively, and meet the requirement of the manufacturing deviation (less than 2 mm). Compared with the traditional NDT-ICP algorithm, the proposed method improves the overall registration accuracy of the point cloud by 35.3% and the efficiency by 61.88%. It can be seen that the method is efficient, and the results are accurate. It promotes the intelligence of the geometric dimensional inspection of steel prefabricated components. Based on the method, the maximum inspection assembly deviation of the digital pre-assembly monitoring point for the arch rib is 1.953 3 mm, and meets the requirement of the assembly deviation (less than 2 mm). The method realizes the accurate deviation inspection. It provides a good guarantee for the smooth erection of subsequent bridge positions and a reference for dimensional inspections of similar structures.
-
表 1 预拼装拱肋节段监测点偏差
Table 1. Monitoring point deviations of pre-assembled arch rib segments
mm 拱肋节段 监测点 Dx Dy Dz 几何尺寸偏差 总偏差 G1 A01 0.027 78 0.006 51 1.730 28 0.058 23 1.758 2 A02 -0.018 35 0.004 88 1.973 53 0.550 96 1.955 3 A03 0.001 13 0.009 75 0.106 24 0.692 17 0.107 4 A04 -0.006 53 -0.009 84 -0.220 27 0.251 16 0.226 8 G2 B01 0.012 08 -0.007 26 -1.098 52 0.104 28 1.086 5 B02 -0.002 27 0.002 22 0.322 81 0.025 91 0.320 5 B03 0.230 31 -0.309 01 -0.409 44 0.507 37 0.180 5 B04 -0.002 82 0.008 71 0.423 13 0.226 85 0.420 3 表 2 不同算法下的RMSE对比
Table 2. Comparison of RMSEs under different algorithms
算法 RMSE/mm 迭代次数 NDT 1 382.342 65 80 ICP 16.393 82 80 传统NDT-ICP 8.998 36 80 基于Harris特征与NDT-ICP 5.820 55 80 -
[1] RASHIDI M, MOHAMMADI M, KIVI S S, et al. A decade of modern bridge monitoring using terrestrial laser scanning: review and future directions[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(22): 3796. doi: 10.3390/rs12223796 [2] 刘占省, 孙啸涛, 史国梁. 智能建造在土木工程施工中的应用综述[J]. 施工技术(中英文), 2021, 50(13): 40-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS202113006.htmLIU Zhan-sheng, SUN Xiao-tao, SHI Guo-liang. Summary of application of intelligent construction in civil engineering construction[J]. Construction Technology, 2021, 50(13): 40-53. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS202113006.htm [3] CHEN Zhi-ping, ZHANG Wen-dian, HUANG Rong-gang, et al. 3D model-based terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) observation network planning for large-scale building facades[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 144: 104594. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104594 [4] WANG Yin-gang, HE Xiong-jun, HE Jia, et al. Virtual trial assembly of steel structure based on BIM platform[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 141: 104395. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104395 [5] DABOUS S A, FEROZ S. Condition monitoring of bridges with non-contact testing technologies[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 116: 103224. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103224 [6] 卢颖. 基于三维激光扫描的桥梁检测技术应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.LU Ying. Application research on the bridge detection technology based on the three-dimensional laser scanning[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese) [7] 鲍跃全, 李惠. 人工智能时代的土木工程[J]. 土木工程学报, 2019, 52(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201905001.htmBAO Yue-quan, LI Hui. Artificial intelligence for civil engineering[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2019, 52(5): 1-11. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201905001.htm [8] NOGHABAEI M, LIU Ya-jie, HAN K. Automated compatibility checking of prefabricated components using 3D as-built models and BIM[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 143: 104566. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104566 [9] REBOLJ D, PU AČG KO Z, BABI AČG N AČG, et al. Point cloud quality requirements for Scan-vs-BIM based automated construction progress monitoring[J]. Automation in Construction, 2017, 84: 323-334. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2017.09.021 [10] 梁栋, 蒲洁, 赵恺, 等. 钢桥塔的点云虚拟装配及其整体线形控制方法[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2022, 55(8): 828-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX202208007.htmLIANG Dong, PU Jie, ZHAO Kai, et al. Point cloud virtual assembly of steel bridge towers and its overall linear control method[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2022, 55(8): 828-838. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX202208007.htm [11] 杨莎莎, 郝龙, 宋成年, 等. 基于BIM和LST的结构外观尺寸量测方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2023, 56(4): 455-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD202304009.htmYANG Sha-sha, HAO Long, SONG Cheng-nian, et al. Research on the structure appearance dimension inspection method based on BIM and LST[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2023, 56(4): 455-462. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD202304009.htm [12] LIU Jin-dian, ZHANG Qi-lin, WU Jie, et al. Dimensional accuracy and structural performance assessment of spatial structure components using 3D laser scanning[J]. Automation in Construction, 2018, 96: 324-336. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2018.09.026 [13] 刘金典, 张其林, 张金辉. 基于建筑信息模型和激光扫描的装配式建造管理与质量控制[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(1): 33-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ202001005.htmLIU Jin-dian, ZHANG Qi-lin, ZHANG Jin-hui. Construction management and quality control of prefabricated building based on BIM and 3D laser scanning[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2020, 48(1): 33-41. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ202001005.htm [14] KIM M K, THEDJA J P P, WANG Qian. Automated dimensional quality assessment for formwork and rebar of reinforced concrete components using 3D point cloud data[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 112: 103077. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103077 [15] 齐宏拓, 刘界鹏, 程国忠, 等. 基于点云数据的大型复杂钢结构智能化施工方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2024, 57(1): 65-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC202401007.htmQI Hong-tuo, LIU Jie-peng, CHENG Guo-zhong, et al. Intelligent construction of large and complex steel structure based on point cloud data[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2024, 57(1): 1065-1075. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC202401007.htm [16] 陆军, 陈坤, 范哲君. 点邻域尺度差异描述的点云配准算法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2021, 43(3): 128-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GFKJ202103015.htmLU Jun, CHEN Kun, FAN Zhe-jun. Point cloud registration algorithm based on scale difference descriptor of point neighborhood[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2021, 43(3): 128-134. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GFKJ202103015.htm [17] CHATTERJEE S. ISSAC K K. Viewpoint planning and 3D image stitching algorithms for inspection of panels[J]. NDT and E International, 2023, 137: 102837. doi: 10.1016/j.ndteint.2023.102837 [18] 朱明芳, 程效军, 李金涛, 等. 基于底面特征匹配的钢结构桥梁虚拟预拼装[J]. 北京测绘, 2022, 36(2): 168-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJCH202202012.htmZHU Ming-fang, CHENG Xiao-jun, LI Jin-tao, et al. A digital virtual pre-assembly method of steel structure bridge based on features matching of bottom surface[J]. Beijing Surveying and Mapping, 2022, 36(2): 168-172. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJCH202202012.htm [19] 马永强. 改进ICP算法在桥梁三维激光扫描数据配准中的应用研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2020, 43(11): 173-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBCH202011047.htmMA Yong-qiang. Application research of improved ICP algorithm on bridge 3D laser scanning data registration[J]. Geomatics and Spatial Information Technology, 2020, 43(11): 173-176. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBCH202011047.htm [20] 胡绍兰, 黄凤玲, 张国兴, 等. 基于BIM+点云数据的钢结构质量智能检测方法[J]. 土木工程与管理学报, 2022, 39(5): 28-33, 49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCJ202205004.htmHU Shao-lan, HUANG Feng-ling, ZHANG Guo-xing, et al. Steel structure quality intelligent detection method based on BIM+point cloud data[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 2022, 39(5): 28-33, 49. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCJ202205004.htm [21] ZOTKIN S P, IGNATOVA E V, ZOTKINA I A. The organization of Autodesk Revit software interaction with applications for structural analysis[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 153: 915-919. [22] 袁华, 庞建铿, 莫建文. 基于体素化网格下采样的点云简化算法研究[J]. 电视技术, 2015, 39(17): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSSS201517012.htmYUAN Hua, PANG Jian-keng, MO Jian-wen. Research on simplification algorithm of point cloud based on voxel grid[J]. Video Engineering, 2015, 39(17): 43-47. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSSS201517012.htm [23] 石雪飞, 徐梓齐, 朱荣, 等. 基于三维模型重构技术的公路预制构件尺寸检验评价方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(2): 66-81. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.02.006SHI Xue-fei, XU Zi-qi, ZHU Rong, et al. Dimensional inspection and evaluation method of highway prefabricated components based on 3D model reconstruction technology[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(2): 66-81. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.02.006 [24] SHAO Yu-yuan, TONG Guo-feng, PENG Hao. Mining local geometric structure for large-scale 3D point clouds semantic segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 500: 191-202. [25] ZHU Tian-yu, MA Xiao-dan, GUAN Hai-ou, et al. A calculation method of phenotypic traits based on three-dimensional reconstruction of tomato canopy[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 204: 107515. [26] SHI Xiu-ying, PENG Jian-jun, LI Ji-ping, et al. The iterative closest point registration algorithm based on the normal distribution transformation[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2019, 147: 181-190. [27] 贾薇, 舒勤, 黄燕琴. 基于FPFH的点云特征点提取算法[J]. 机算机应用与软件, 2020, 37(7): 165-169, 245. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10147-1024319775.htmJIA Wei, SHU Qin, HUANG Yan-qin. Feature point extraction algorithm of point cloud based on FPFH[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2020, 37(7): 165-169, 245. (in Chinese) https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10147-1024319775.htm [28] 仲宇, 白钒, 刘勇, 等. 基于改进3D-Harris角点检测算法的电厂地下管廊点云拼接方法研究[J]. 热力发电, 2023, 52(1): 89-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLFD202301009.htmZHONG Yu, BAI Fan, LIU Yong, et al. Study on point cloud splicing method of underground pipe gallery in power plants based on improved 3D-Harris operator[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2023, 52(1): 89-97. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RLFD202301009.htm [29] 张晓, 张爱武, 王致华. 基于改进正态分布变换算法的点云配准[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2014, 51(4): 041002. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ201404016.htmZHANG Xiao, ZHANG Ai-wu, WANG Zhi-hua. Point cloud registration based on improved normal distribution transform algorithm[J]. Laser and Optoelectronics Progress, 2014, 51(4): 041002. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ201404016.htm [30] GAO Hui-ping, XU Gui-li, ZHANG Zi-li, et al. A novel probability iterative closest point with normal vector algorithm for robust rail profile registration[J]. Optik—International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2021, 243: 166936. -





 下载:
下载: