Variation laws of self-magnetic flux leakage signals of high-strength steel wires in bridge cables under coupling effect of corrosion-fatigue loads
-
摘要:
为增强桥梁拉索高强钢丝漏磁检测的实用性,开展了腐蚀、应力单一因素作用试验与预腐蚀-疲劳-腐蚀、预疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳三阶段交互作用试验,阐述了腐蚀-疲劳耦合作用对自漏磁信号的影响机制。研究结果表明:腐蚀区域的自漏磁信号极值随腐蚀时间的增加而增加,且变化特征越发明显,腐蚀缺陷引起的异常自漏磁信号最大变化可达50 000 nT;随着疲劳加载循环次数的增加,无锈蚀高强钢丝自漏磁信号整体呈现先增加后稳定的趋势,当疲劳加载循环次数大于10 000时,磁场强度的增加速率降低且趋于平缓;预腐蚀后施加的交变应力场会削弱腐蚀缺陷引起的自漏磁信号,再次腐蚀后的磁场信号变化与预腐蚀程度有关,预腐蚀9 h后施加疲劳荷载,之后再腐蚀3 h,与单一腐蚀12 h相比,自漏磁信号强度削弱了32%;施加预疲劳交变应力场可强化磁场,导致腐蚀后自漏磁信号极值增加,当预疲劳加载循环次数从1 000增加至100 000时,自漏磁信号强度增大了30%。由此可见,早期腐蚀引起的高强钢丝异常自漏磁信号可被疲劳作用掩盖,考虑单一腐蚀与应力变化难以反映高强钢丝自漏磁检测效果,需综合考虑腐蚀-疲劳的耦合效应,以获得桥梁拉索高强钢丝自漏磁信号变化规律,从而为桥梁拉索无损检测提供分析依据。
Abstract:To enhance the practicality of magnetic flux leakage detection for high-strength steel wires in bridge cables, the corrosion and stress single factor tests, as well as three-stage interaction tests of pre-corrosion-fatigue-corrosion and pre-fatigue-corrosion-fatigue were conducted, and the mechanism for the influence of corrosion-fatigue coupling effect on the self-magnetic flux leakage signal was explained. Research results show that the extreme self-magnetic flux leakage signals in the corrosion area increase with the corrosion time, and the variation characteristics are becoming more and more obvious. The maximum variation in the abnormal self-magnetic flux leakage signals caused by the corrosion defect can reach up to 50 000 nT. As the fatigue loading cycle number increases, the self-magnetic flux leakage signal of non-corroded high-strength steels wire is on an overall increasing trend before getting stabilized. When the fatigue loading cycle number exceeds 10 000, the increasing rate of magnetic field intensity decreases and tends to be stable. The alternating stress field applied after the pre-corrosion weakens the self-magnetic flux leakage signal caused by the corrosion defect, and the variation in the magnetic field signal after the second corrosion is related to the degree of pre-corrosion. Under the fatigue load after the pre-corrosion for 9 h, and then in the second corrosion for 3 h, the strength of the self-magnetic flux leakage signal reduces by 32% compared with that in the single corrosion for 12 h. Applying a pre-fatigue alternating stress field can strengthen the magnetic field, leading to an increase in the extreme self-magnetic flux leakage signal after the corrosion. When the pre-fatigue loading cycle number increases from 1 000 to 100 000, the strength of the self-magnetic flux leakage signal increases by 30%. It follows that the abnormal self-magnetic flux leakage signals of high-strength steel wires caused by the initial corrosion can be masked by the fatigue effect, making it difficult to reflect the detection effect of self-magnetic flux leakage of high-strength steel wires by just considering a single factor of variation in the corrosion or stress. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the corrosion-fatigue coupling effect, so as to obtain the variation laws of self-magnetic flux leakage signals of high-strength steel wires in bridge cables, thereby providing an analytical basis for the non-destructive test of bridge cables.
-
0. 引言
拉(吊)索作为索承体系桥梁中承受荷载的重要构件,其性能直接影响桥梁的安全运营[1]。大量检测数据表明[2-3],随着桥梁拉(吊)索服役时间的增长,索体护套表面出现诸多裂纹,当外界水蒸气与腐蚀性水通过开裂护套进入索体内部并长期不能排出时,内部钢丝或钢绞线会出现不同程度的腐蚀[4],并引起索体力学性能的下降。此外,在风与车辆荷载的反复作用下[5-6],当腐蚀达到一定程度时,索体会发生脆性断裂[7-8]。
近几十年,平行钢丝索广泛应用于中国大跨度索承体系桥梁中,参考国外已有经验,国内桥梁索体的性能退化问题将陆续出现。索内高强钢丝在长期疲劳荷载和腐蚀环境的作用下,索体的耐久性降低,内力分布也会发生不规则变化[9-10],因此,实时获取索体内部锈蚀与缺陷程度至关重要。目前,针对桥梁拉(吊)索内部缺陷的无损检测研究,诸多学者提出的检测方法主要有磁声发射(Magnetomechanical Acoustic Emission, MAE)检测法[11-12]、磁致伸缩导波[13]、射线检测(Radiographic Testing, RT)法[14]和漏磁(Magnetic Flux Leakage, MFL)检测法[15-17]等。与常规无损检测方法相比,漏磁检测法具有更快、更方便、更准确和可操作性好等优点。Roskosz[18]通过比较基于金属磁记忆原理[19]的自漏磁(Self-Magnetic Flux Leakage, SMFL)检测与放射学测试的检测结果,发现漏磁检测技术在钢焊缝缺陷检测中更有优越性。
能够揭示铁磁材料自漏磁信号产生机理的经典理论模型主要为基于能量守恒定律的磁偶极子理论模型[20-21]和力-磁耦合模型[22-23]。以此为基础,众多学者为推动自漏磁检测技术的广泛应用做了大量试验研究,获得了腐蚀或带有缺陷的无应力金属材料的磁性特征。周建庭等[24]验证了自漏磁检测技术在钢绞线腐蚀检测中的可行性;赵亚宇等[25]分析了锈蚀钢绞线SMFL信号的分布特征,为判断腐蚀程度和信号的对应关系提供了试验数据支撑;Xia等[26]提出了一种桥梁索体腐蚀程度评估方法,通过大量腐蚀钢丝的漏磁检测试验,获得了SMFL信号的概率分布;Wu等[27]通过建立磁导函数的理论模型,提出了一种用于评估桥梁缆索横截面损失的新型检测方法。除锈蚀以外,应力会改变金属材料内部的磁畴分布形式,一些学者针对静态荷载作用下的金属材料磁性特征进行了研究。邱俊澧等[28]利用漏磁检测技术探究了钢筋混凝土内部锈蚀钢筋所承受的弯曲荷载与SMFL信号的变化关系;Shi等[29]通过测量弹性荷载和塑性变形耦合作用下低碳钢的SMFL信号分布,发现随着弹性荷载的增加,塑性变形能够显著影响SMFL信号;Wang等[30]采用理论模型分析了钢材受拉时局部应力集中区域的SMFL信号分布,定量描述了信号随缺陷深度和位置的变化规律;Yao等[31]通过测量铁磁材料在非铁磁和铁磁压头静压作用下的SMFL信号,发现铁磁压头与非铁磁压头的信号峰值变化幅度有巨大差异,并建立了受压试件早期损伤的信号评价依据。除静态荷载以外,疲劳应力作用也会显著改变金属材料的磁性特征。钱正春等[32]研究了铁磁材料在疲劳荷载作用下的SMFL信号变化规律,并进行了统计分析,发现信号随加载次数的增加趋于稳定;朱达荣等[33]获得了金属材料在疲劳加载过程中SMFL信号随加载循环次数和荷载量值的变化规律,准确量化了疲劳损伤评估机制;龙飞飞等[34]针对球墨铸铁试件开展了拉伸疲劳试验,发现漏磁检测技术能够有效识别球墨铸铁的损伤;Li等[35]监测了铁磁材料的疲劳裂纹扩展行为,随着疲劳裂纹的不断扩展,异常磁信号也愈加明显。
以上研究证明,漏磁检测技术能很好地应用于金属材料(比如桥梁索体)锈蚀缺陷的检测,并获得了碳钢在不同腐蚀条件与静力加载条件下的SMFL信号变化规律,初步阐述了加-卸载条件下碳钢SMFL信号的分布形式,同时统计分析了铁磁材料在疲劳荷载下的SMFL信号变化规律,得到了磁信号随疲劳加载次数增加的变化规律,通过相关试验发现漏磁检测技术在识别损伤方面有很大的优势。索体高强钢丝在服役过程中受到腐蚀、疲劳、疲劳-腐蚀的耦合作用,Meng等[36]初步探究了疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳三阶段自漏磁信号的变化规律。目前相关研究中,腐蚀缺陷与疲劳应力耦合作用下SMFL信号的变化规律与影响机理尚不清晰,国内外学者对腐蚀-疲劳耦合作用下高强钢丝SMFL信号的研究仍有不足,仍需进一步明确不同应力状态下的腐蚀/未腐蚀高强钢丝SMFL信号的变化规律,这些都限制了漏磁检测技术在桥梁索体检测领域中的应用。
在试验室研究过程中确实存在着一定的局限性,桥梁拉索在实际运营过程中影响因素更为复杂,不仅有腐蚀和疲劳的影响,还有许多其他的影响因素,如荷载、风雨、环境温度变化、索体初始几何曲线、日照等综合因素的影响。此外桥梁拉索是高强钢丝的束集,探究单根高强钢丝的腐蚀疲劳特性也不能满足实际工程需要。诸多文献指出,腐蚀与疲劳是导致索体损伤的两大主要因素,研究单根钢丝在腐蚀-疲劳耦合作用下SMFL信号的影响机制和变化规律,是漏磁检测技术能实际运用到桥梁检测领域的前提之一,但目前能够阐述清楚腐蚀-疲劳耦合作用下高强钢丝SMFL信号的影响机制和变化规律的相关研究并不多见。为进一步解决这些问题,本文基于高强钢丝SMFL信号试验平台,提出高强钢丝腐蚀、疲劳单一因素作用试验与预腐蚀-疲劳-腐蚀、预疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳三阶段交互作用试验方案,进一步明确了疲劳-腐蚀耦合作用下SMFL信号的变化规律,探究其影响机理,以期针对以往众多学者在腐蚀-疲劳耦合作用下高强钢丝SMFL信号变化规律方面的研究做出有益补充。
1. 试验方案
1.1 试件制备
采用桥梁拉索热镀锌钢丝试件,钢丝为高碳钢材料,钢丝直径为7 mm,单位面积镀层质量不小于300 g·m-2,在同一根索体钢丝上截取长度均为400 mm的标准试件并依次编号,主要微量元素质量占比与宏观性能分别见表 1、2。
表 1 镀锌钢丝微量元素占比Table 1. Proportions of micro-elements in galvanized steel wire% 元素 C Mn Si Cr Cu 占比 0.90~0.95 0.30~0.90 0.12~1.20 ≤0.35 ≤0.20 表 2 镀锌钢丝宏观性能Table 2. Macroscopic properties of galvanized steel wire参数 断后伸长率/% 密度/(g·cm-3) 强度/MPa 弹性模量/MPa 取值 ≥4.0 7.85 1 860 2.0×105 1.2 试验流程
依据规范《桥梁缆索用热镀锌或锌铝合金钢丝》(GB/T 17101—2019),开展钢丝试件疲劳加载试验,试件左右两端50 mm长度范围为夹持端。为探究钢丝SMFL信号变化规律,首先开展腐蚀、单向静拉应力与疲劳应力等单因素作用试验,然后再开展腐蚀-疲劳三阶段交互作用试验,试验工况见表 3。
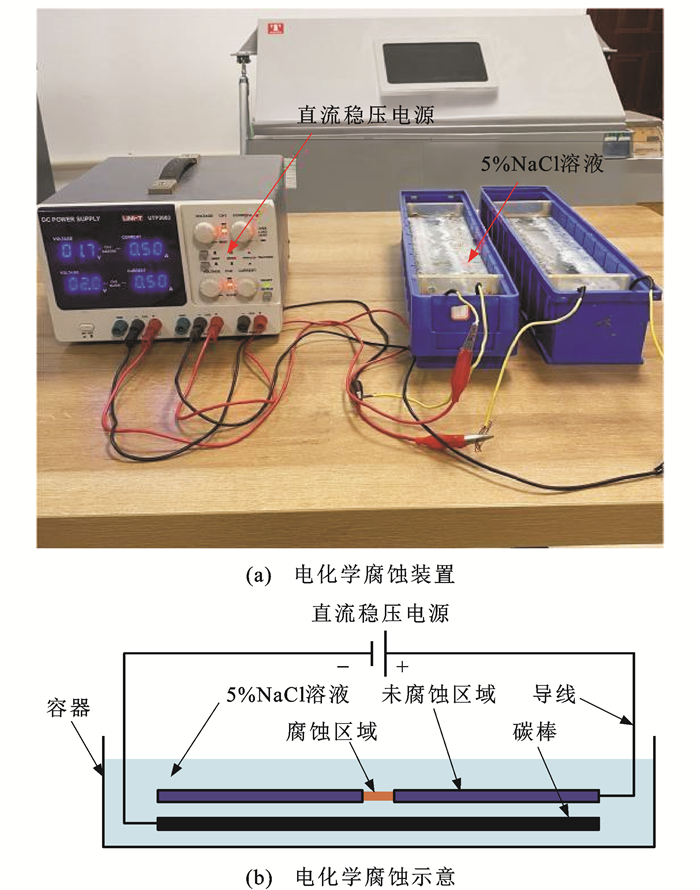
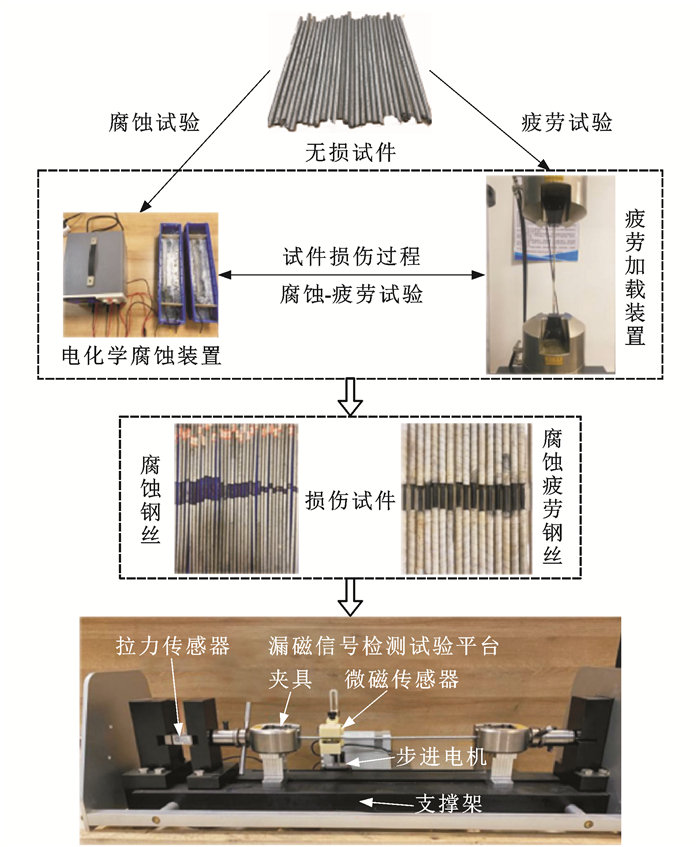
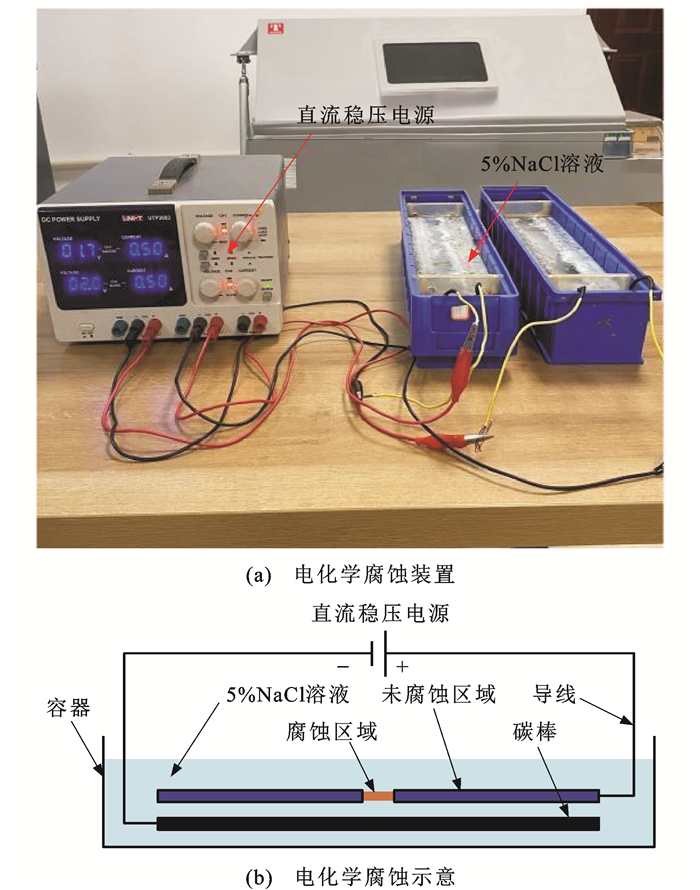
表 3 试验工况Table 3. Test conditions工况 编号 腐蚀宽度/mm 腐蚀时间/h 加载应力幅/MPa 疲劳加载次数 腐蚀 C-1 1 1、2、3、4 0 0 C-2 3 3、6、9、12 0 0 C-3 5 5、10、15、20 0 0 静拉应力 Y-1 0 0 0、260、520、780、1 040、1 300 0 疲劳 F-1 0 0 0、260、520、780,1 040、1 300 10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000 预腐蚀-疲劳-腐蚀 C-F-C-1 3 预腐蚀3 h,再腐蚀6 h 260 10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000 C-F-C-2 3 预腐蚀6 h,再腐蚀9 h 260 10、100、1 000、10 000 C-F-C-3 3 预腐蚀9 h,再腐蚀12 h 260 10、100、1 000 预疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳 F-C-F-1 3 3 260 预疲劳加载1 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000次 F-C-F-2 3 6 260 预疲劳加载1 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000次 F-C-F-3 3 9 260 预疲劳加载1 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000次 F-C-F-4 3 3 260 预疲劳加载10 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000次 F-C-F-5 3 6 260 预疲劳加载10 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000次 F-C-F-6 3 9 260 预疲劳加载10 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000次 F-C-F-7 3 3 260 预疲劳加载100 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000次 F-C-F-8 3 6 260 预疲劳加载100 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000次 F-C-F-9 3 9 260 预疲劳加载100 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000次 利用电化学腐蚀装置获得腐蚀镀锌钢丝,稳定电流控制在0.5 A,通过腐蚀时间控制腐蚀深度。试验开展前对未腐蚀未施加荷载的高强钢丝试件进行了SMFL信号采集,获得了初始状态下的SMFL信号分布并作为后续试验的标定依据。试验过程中当试件承受静态与疲劳荷载时,相对于初始状态下的试件SMFL信号改变即为荷载引起的信号变化。针对疲劳荷载,本文重点研究了预疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳,预腐蚀-疲劳-腐蚀三阶段交互作用下高强钢丝SMFL信号变化规律,阐明了疲劳应力对SMFL信号的影响机制。疲劳试验中循环加载方式为恒幅正弦波形,应力比R为0.57,加载频率f为10 Hz。自制镀锌钢丝电化学加速腐蚀装置如图 1所示,镀锌钢丝通过导线连接直流稳压电源正极,直流稳压电源负极通过导线与碳棒连接,钢丝与溶液底部保持一定距离,可减少Fe2O3等残渣残留试件表面。电解质溶液采用质量浓度为5%的NaCl溶液,利用不透水胶带包裹覆盖不参与腐蚀的钢丝部位,隔绝其与电解质溶液的接触,通过调节直流稳压电源的电流和腐蚀时间控制镀锌钢丝腐蚀过程。
相关文献[37-38]研究结果表明,对于铁磁材料的SMFL信号而言,疲劳荷载卸载后一段时间内与疲劳荷载在线测量的结果基本一致。基于自主设计的钢丝SMFL信号检测试验平台测量卸载后钢丝周围的磁场信号,通过2个上下对称分布的磁传感器同时采集钢丝周围磁场数据,从而判定镀锌钢丝的损伤位置和损伤程度,试验流程如图 2所示。
试件制备过程中,将高强钢丝试件两端非腐蚀区用防水胶带缠绕,则腐蚀区域长度为暴露区域,通过改变胶带缠绕区域的长度来控制腐蚀区域长度。
2. 单一影响因素作用试验
2.1 提离距离因素
试验中高强钢丝的SMFL信号由地球磁场产生,受周围环境影响较大。在采集磁信号之前,先采集微磁传感器移动路径周围的环境磁场数据,验证环境磁场的稳定性。上下2个微磁传感器探头以0.5 m·min-1的移动速度收集数据,磁场强度分布如图 3(a)所示,其中:x为沿高强钢丝轴线方向的移动距离;Bx为沿高强钢丝轴线方向的磁场强度。从图 3(a)中可以看出:上、下微磁传感器探头测量的环境磁场强度为-1 000~1 500 nT,在钢丝中部100~200 mm范围内分布较为均匀,表明钢丝试验区间的环境磁场较为理想,从而便于展开后续试验;由于两端夹具的退火消磁不完全,钢丝两端夹具处的环境磁感应强度明显增强。
改变上部微磁传感器的提离距离,绘制钢丝周围磁场强度分布曲线,如图 3(b)所示,可以看出:随着传感器与钢丝之间的提离距离增加,会使磁偶极子理论模型中正、负磁荷到缺陷处任意一点P的距离矢量r1和r2增大,SMFL信号强度呈明显下降趋势,且下降趋势逐渐减弱,随着提离距离持续增加,所测磁场将接近地磁场,结合磁偶极子理论模型可知,提离距离增加的同时P点距正、负磁荷面的距离增加,导致周围磁场减弱并趋近环境磁场强度,与磁偶极子理论模型完全吻合。
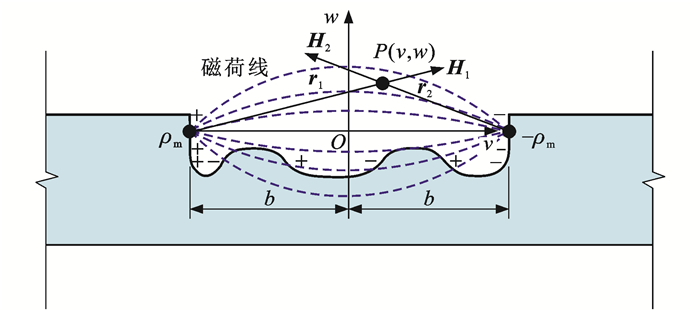
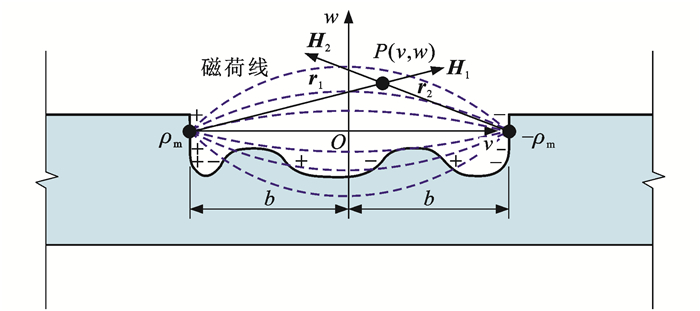
磁偶极子理论认为缺陷处的漏磁场由极性相反的偶极子产生,腐蚀高强钢丝表面缺陷如图 4所示,其中:坐标系vOw的原点O位于缺陷中点,v轴向右为正方向,w轴向上为正方向;ρm和-ρm分别为正、负磁荷面磁荷密度;H1为正磁荷面在P点产生的磁场强度;H2为负磁荷面在P点产生的磁场强度;b为坐标原点O到磁荷面的距离。
桥梁缆索的实际检测环境处于非真空的地球磁场中,磁偶极子存在于铁磁材料空间中,称其为磁介质,铁磁材料受地磁场的影响产生附加磁场。假设各向同性的铁磁材料缺陷内部存在符号相反、磁荷密度ρm相等、真空磁导率为μ0的磁荷线,正、负磁荷在与它们相距 r1和r2的P点产生的磁场强度分别为H1和H2,则磁偶极子在平面坐标系内P点的磁场强度 H为H1和H2矢量和[39-40],即
{H1=ρm2πμ0r21r1H2=ρm2πμ0r22r2H=H1+H2r1=√(v+b)2+w2r2=√(b−v)2+w2 (1) 由式(1)可知,当铁磁材料的腐蚀缺陷长度或传感器提离距离增加时,随着r1和r2的增加,磁场强度 H减小,检测精度也会随之降低。
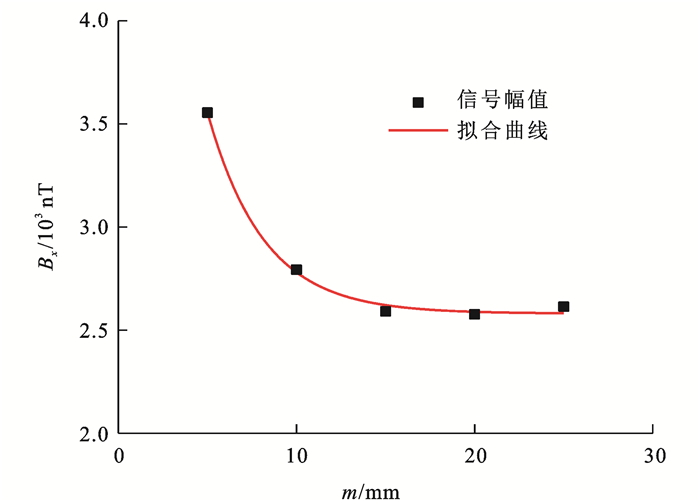
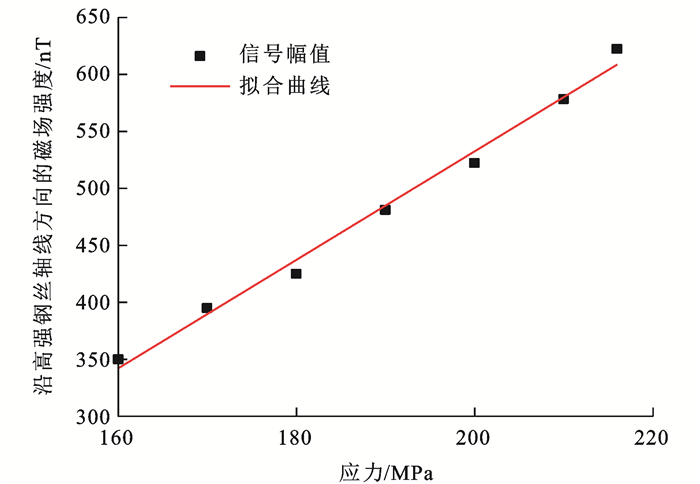
随着r1和r2的增加,磁场强度先降低后趋于地磁场强度。为更加直观展现磁场强度与提离距离的关系,选取指数模型Bx=Bx0+AeR0m进行拟合,其中:m为提离距离;Bx0=2.58×103 nT,为提离距离趋于无穷大时的磁场强度;A=4.76,R0=-0.32,均为拟合参数。绘制x=150 mm位置处磁场强度随提离距离的变化曲线,如图 5所示,可知:随着提离距离的增加,磁场强度减小且趋于稳定,当提离距离达到10 mm时磁场强度减小的幅度开始变缓,曲线的线性拟合优度达到0.99以上,其变化规律符合指数模型,但随着提离距离的增加,采集到的磁场强度越小,检测精度越低,越难以反映材料的损伤特征,不利于检测试验的开展;当提离距离为25 mm时,磁场强度为2.50×103 nT,提离距离为5 mm时的磁场强度为3.60×103 nT,是前者的1.44倍,为保证磁场强度的稳定性,后续试验中提离距离选为5 mm。
2.2 腐蚀因素
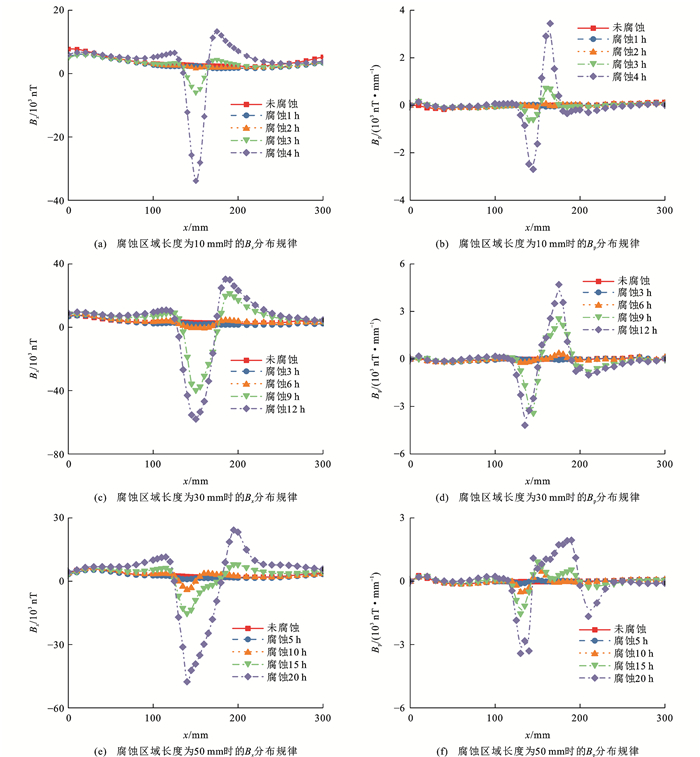
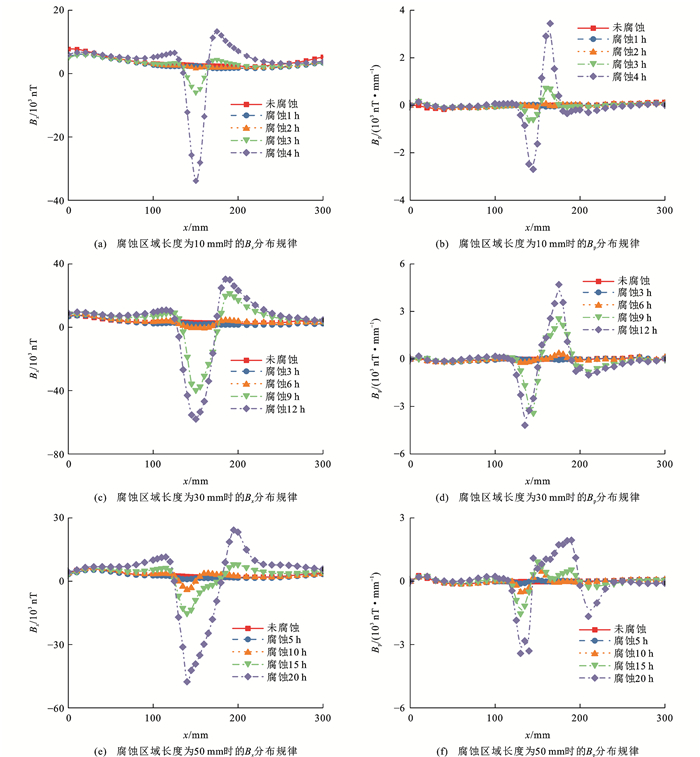
考虑腐蚀单一影响因素,通过改变钢丝腐蚀区域长度和腐蚀时间来探究锈蚀钢丝SMFL信号的分布规律,如图 6所示,其中:Bp为沿钢丝轴线方向磁信号的一阶微分,以表征磁信号的变化梯度。由图 6(a)、(c)和(e)可知:钢丝未腐蚀区域SMFL信号无明显波动,腐蚀区域内的磁信号出现显著突变;随着腐蚀区域长度的变化,腐蚀区域长度越大,信号波动区间的长度也越大;当腐蚀区域长度恒定时,随着腐蚀时间的增加,腐蚀区域的SMFL信号极值增加且变化特征越发明显,当腐蚀区域长度为50 mm时,腐蚀10 h后的磁场强度为8.0×103 nT,腐蚀20 h后的磁场强度为5.0×104 nT,是前者磁场强度的6.25倍,漏磁区域的磁场强度最大变化可达5.0×104 nT;随着腐蚀区域长度的增加,异常SMFL信号的范围扩大,信号极值出现先增后减的变化趋势,且因腐蚀的不均匀性出现极值偏移现象,但其极值都处于腐蚀区域中。从图 6(b)、(d)、(f)中可看出:SMFL信号切向分量变化梯度在腐蚀区域形成了一个波谷和一个波峰,随着腐蚀时间的增加,谷峰值不断增大,并在波谷和波峰相交处切向分量为0,此处SMFL信号达到极值。
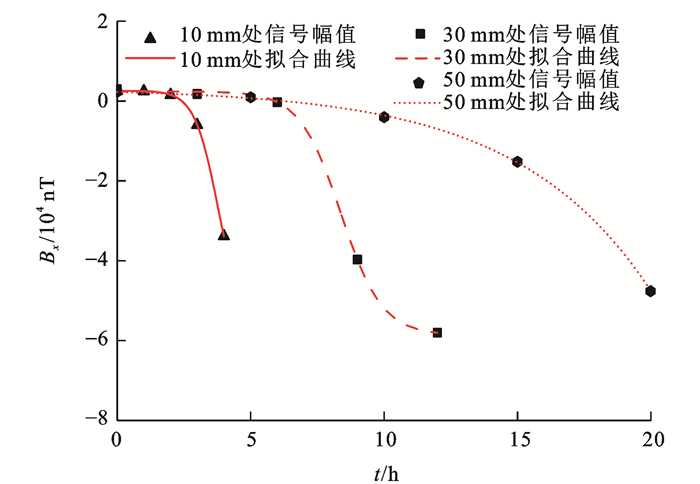
随腐蚀时间的增加,磁场强度增加且极值变化率随之增加,故选取Boltzmann模型Bx=A1−A21+e(t−t0)/dt+A2对曲线进行拟合,其中:t为腐蚀时间;A1、A2和t0均为拟合参数。绘制SMFL信号极值随腐蚀时间的变化曲线,如图 7所示,可知:不同腐蚀区域长度下信号极值随腐蚀时间的变化趋势基本相同,随着腐蚀时间的增加,信号极值的增加呈先缓后急趋势;拟合腐蚀区域长度分别为10、30和50 mm处磁场强度随时间的变化曲线,线性拟合优度达到0.99以上,故磁场强度极值随时间变化曲线与Boltzmann模型高度吻合;由磁偶极子理论可知,试件腐蚀和未腐蚀区域交界处的侧壁形成2个磁荷面,磁荷面大小受腐蚀深度(均匀腐蚀深度)和腐蚀区域长度的综合影响,当腐蚀区域长度不变时,腐蚀时间越长,质量损失率越大,缺陷越深,两侧磁荷面聚集的磁荷也越多,直接导致SMFL信号极值的增加,而腐蚀区域局部的蚀坑深度也会随着腐蚀时间的增长而增加,从而增加信号极值;腐蚀区域长度影响2个磁荷面的距离,腐蚀区域长度越大,SMFL信号变化范围扩大,蚀坑分布的随机性导致SMFL信号极值分布的不均匀性越明显,呈偏移趋势;此外,腐蚀区域长度的增加会增加磁荷面之间距离,从而减弱信漏磁信号极值,故试验中腐蚀区域长度为50 mm,腐蚀20 h情况下的SMFL信号极值为4.9×104 nT,小于腐蚀区域长度为30 mm且腐蚀12 h情况下的SMFL信号极值5.8×104 nT。在桥梁拉索损伤检测过程中,如果仅获取SMFL信号强度,尚不能确定缆索内部高强钢丝的腐蚀区域长度,应结合由外观检测图像数据推得的腐蚀时间,进而评判内部高强钢丝的损伤程度,从而及时养护索体构件。
2.3 应力因素
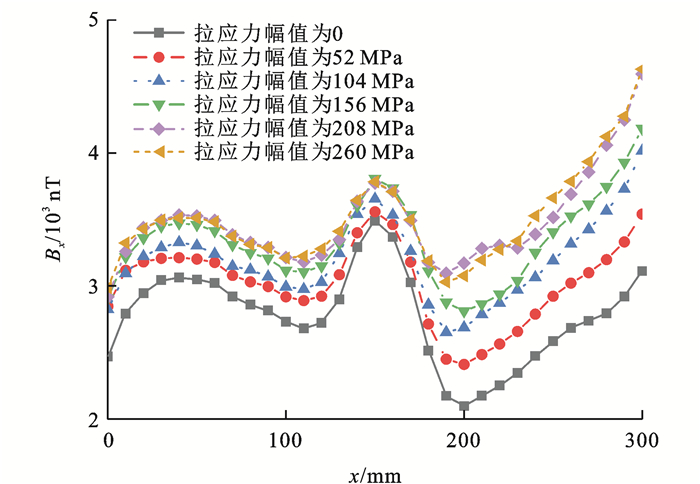
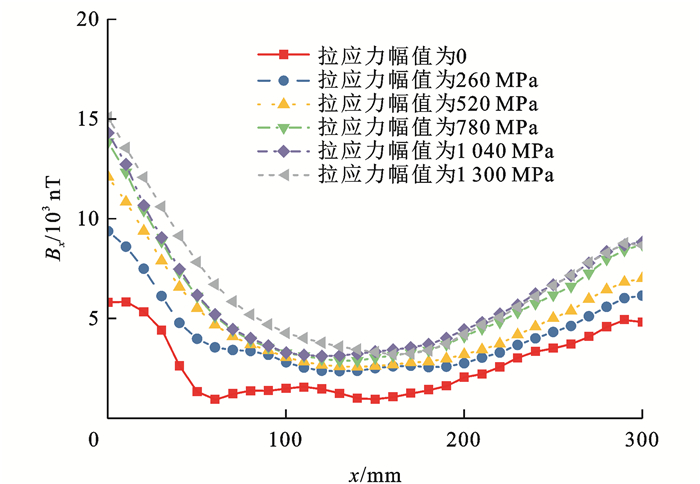
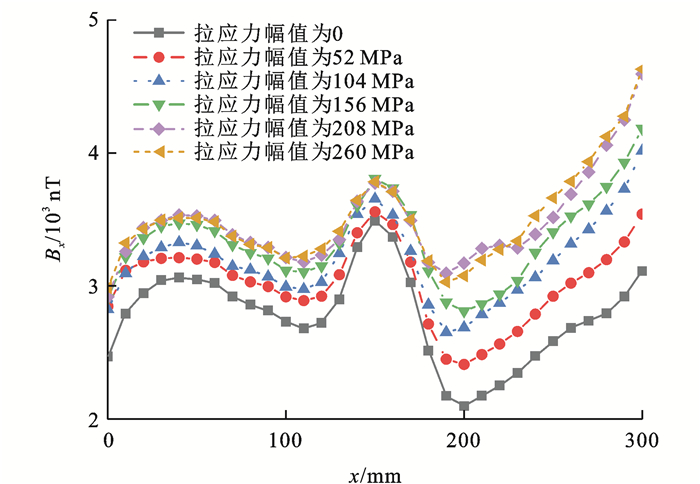
桥梁拉索主要承受静态荷载和疲劳荷载,试验过程中施加静态荷载和疲劳荷载产生的最大应力未超过高强钢丝的屈服强度,应力和变形基本符合线弹性变化,故本文只研究应力作用影响因素下的SMFL信号变化规律和影响机制。在弹性状态下高强钢丝信号随应力的增大而整体增强,疲劳荷载对应的最大应力为600 MPa,最小应力为340 MPa。考虑单向拉应力的单一影响因素,绘制不同拉应力下无损钢丝试件的SMFL信号强度变化曲线,如图 8所示,可知:施加260 MPa拉应力后,磁场强度最多可增加1 640 nT。
为进一步探究应力与钢丝磁场强度的关系,对钢丝进行加-卸载试验,施加不同拉应力幅值,采集卸载后的SMFL信号,如图 9所示可知:卸载后试件SMFL信号变化明显,表现出整体增强的趋势;随着拉力幅值的增大,磁场强度随着增强,最多可增加9 275 nT。
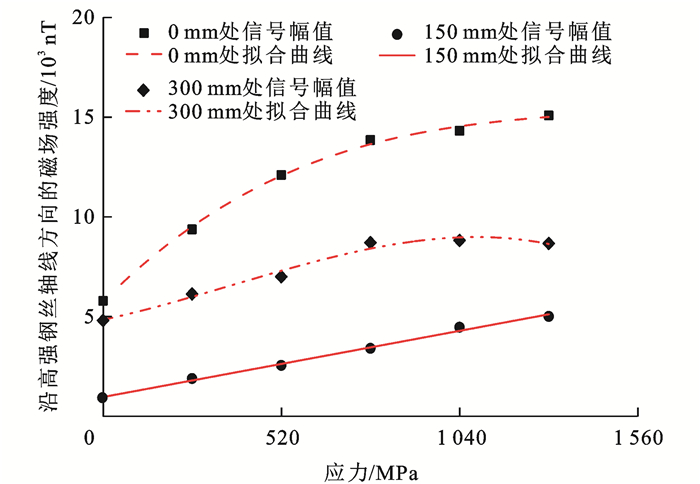
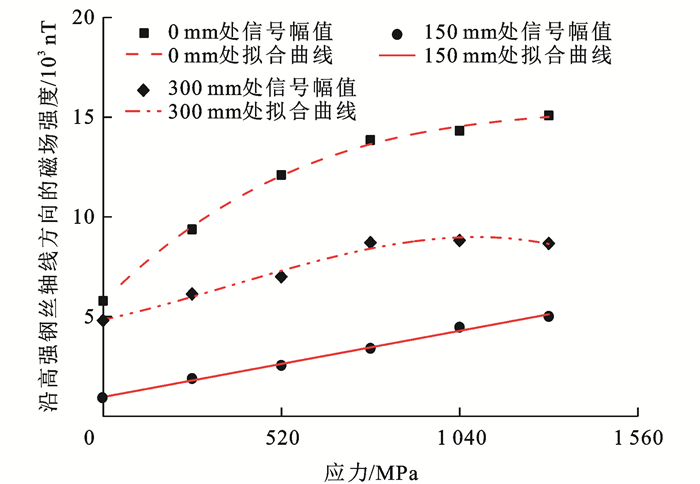
选取试件两端与中间部位绘制卸载后磁场强度随加载应力幅的变化曲线,根据力-磁耦合模型的特点,对磁场稳定区域(x=150 mm)选取一次函数进行线性拟合,试件两端磁信号极值变化率呈先增强后变弱的特点,故根据其变化规律选取三次函数进行非线性拟合,如图 10所示,可知:随着加载应力的增加,试件两端信号幅值增加幅度大于中间位置,且相比于固定端,受拉端应力磁化增强效应更为明显,x=150 mm处拟合斜率为3.3,在磁场稳定区域磁场强度与应力呈线性关系;当处于地磁场环境中的钢丝试件承受静态拉压应力时,内部磁畴发生定向转动,宏观上材料磁性显示强化效应,故卸载后立即开展试验,此时磁畴形态可近似认为与瞬时加-卸载时的形态相同。
根据铁磁学理论,当铁磁材料受到弹性应力σ作用时,会产生应力能Fσ,则总自由能F为
F=Fex+Fk+Fms+Fσ (2) 式中:Fex为电子自旋间的交换相互作用产生的能量(交换能);Fk为电子自旋之间及自旋与轨道之间的耦合作用所产生的能量(磁晶各向异性能);Fms为铁磁体内磁性与弹性相互作用而引起的磁弹性能量(磁弹性能)。
铁磁材料产生磁化效应的根本原因为外应力作用下材料内部应力能增加,破坏了无应力作用下的能量平衡状态,部分应力能向磁弹性能等能量形式转化,内部磁能重新分配且趋于最小,因此,材料内部能量达到新的平衡状态并在宏观上表现出材料磁性改变。
假设铁磁材料为磁各向同性材料,在恒定的磁场和等温环境下,铁磁材料的无磁滞理想磁场强度Man为[41-42]
Man =Ms[coth(Hea)−aHe] (3) 式中:Ms为饱和磁场强度;ɑ为材料规划参数;He为有效磁场强度。
材料的磁滞伸缩系数λ与材料磁场强度M的拟合关系为
λ=∞∑i=0γi(σ)M2i (4) 式中:γi(σ)为弹性应力σ状态下第i阶的拟合函数。
γi(σ)可用泰勒级数展开为
γi(σ)=γi(0)+∞∑i=0σnn!γni(0) (5) 式中:n为泰勒级数展开次数。
令式(5)中的i=2,考虑应力变化对材料磁场强度的影响,微弱磁场下的应力磁化模型为[43]
dM dσ={σ(Man−M)/(Eξ)+cMs[csch2(He/a)− a/H2e]3/μ0[(γ1(0)+γ(1)1(0)σ)M+2(γ(1)2(0)+ γ2(0)σ)M3]}/{1−cM[csch2(He/a)− a/H2e][3σ/μ0(γ1(0)+6γ2(0)M2)+α]} (6) 式中:E为高强钢丝的弹性模量;ξ为单位体积能量度量因子;c为反映磁畴壁的柔性系数;μ0为真空磁导率;α为磁畴耦合参数。
相关参数选取如下:Ms=1.59×106 A·m-1,E=2.00×105 MPa,σ=160 MPa,α=8.44×10-6,μ0=4π×10-7 N·A-2,c=0.25,a=600 A·m-1,ξ=2.45×104 Pa,γ1(0)=7.00×10-18 A-2·m2,γ1(1)(0)=-1.0×10-25 A-2·m2·Pa-1,γ2(0)= -3.30×10-30 A-4·m4,γ2(1)(0)=2.10×10-38 A-4·m4·Pa-1。在弱磁场下磁场强度随应力的变化关系如图 11所示,磁信号随应力的增大而增强。
式(6)和图 11可以反映铁磁材料在地球磁场(50 μT)这种微弱环境磁场下的力-磁耦合关系,确定应力变化对材料磁场强度的影响。式(6)对弹性变形状态下高强钢丝在不同应力状态下的力-磁耦合关系都适用,可用于解释SMFL信号变化情况。图 10中位置为150 mm处线性拟合优度达到0.99以上,其拟合曲线斜率为3.30,图 11中理论模型曲线斜率为3.41,两者相差3.2%,可认为高度吻合。
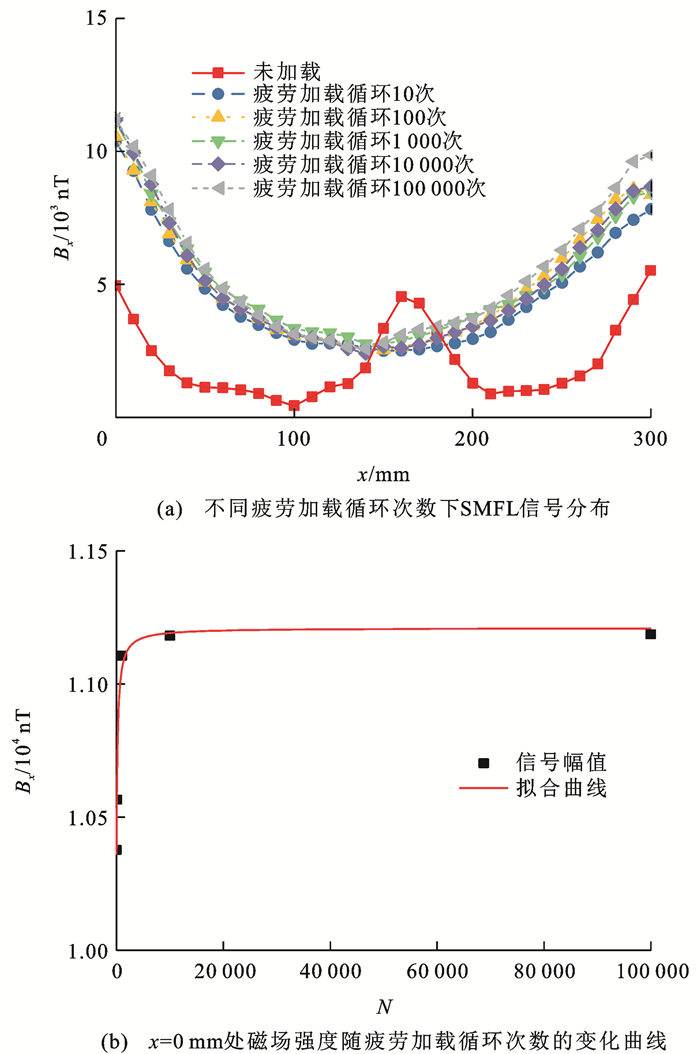
进一步开展疲劳试验,可发现随着疲劳加载循环次数的增加,试件SMFL信号整体增强且趋于稳定,如图 12(a)所示,在试件两端表现出明显的信号增强,试件中间(100~200 mm)磁场幅值曲线则较为平缓。绘制钢丝x=0 mm位置处的磁场强度随疲劳加载循环次数变化曲线,根据试件SMFL信号随疲劳加载循环次数增加呈先增加后趋于平缓的变化特征,选取单参数指数函数模型Bx=-ln(B)BN进行数据拟合,如图 12(b)所示,其中:B为单参数指数模型系数;N为疲劳加载循环次数。在疲劳加载循环次数少于1 000时,随着疲劳加载循环次数的增加,磁场强度增强趋势较为明显,当疲劳加载循环次数继续增加时,磁场强度的增加速率降低,变化趋于平缓。对x=0 mm处磁场强度随疲劳加载循环次数变化进行曲线拟合,线性拟合优度达到0.98以上,故此处磁场强度随疲劳加载循环次数变化曲线与单参数指数函数模型高度吻合。对于各向同性铁磁材料,随着疲劳加载循环次数的增加,内部磁弹性效应导致磁弹性能密度变化趋于稳定,由力-磁耦合理论模型可知,磁弹性能转化为其他能量形式,引起漏磁场的改变,磁弹性能密度变化越稳定,卸载后铁磁材料饱和磁致伸缩应变的恢复时间也越长。
3. 腐蚀-疲劳耦合作用试验
3.1 预腐蚀-疲劳-腐蚀三阶段交互作用试验
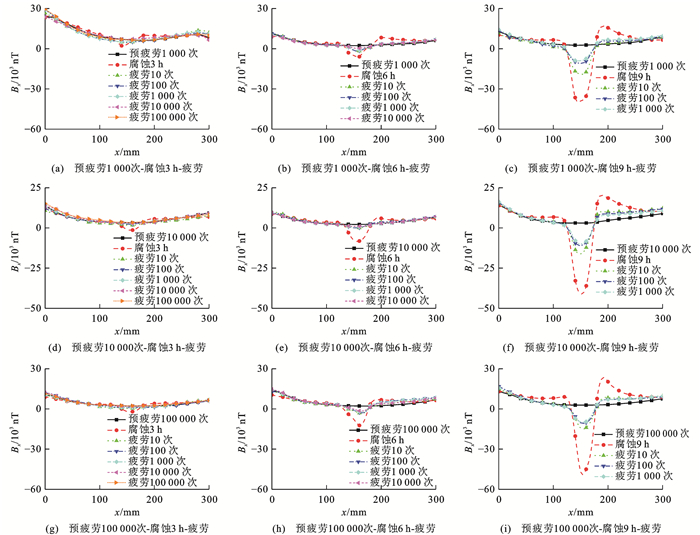
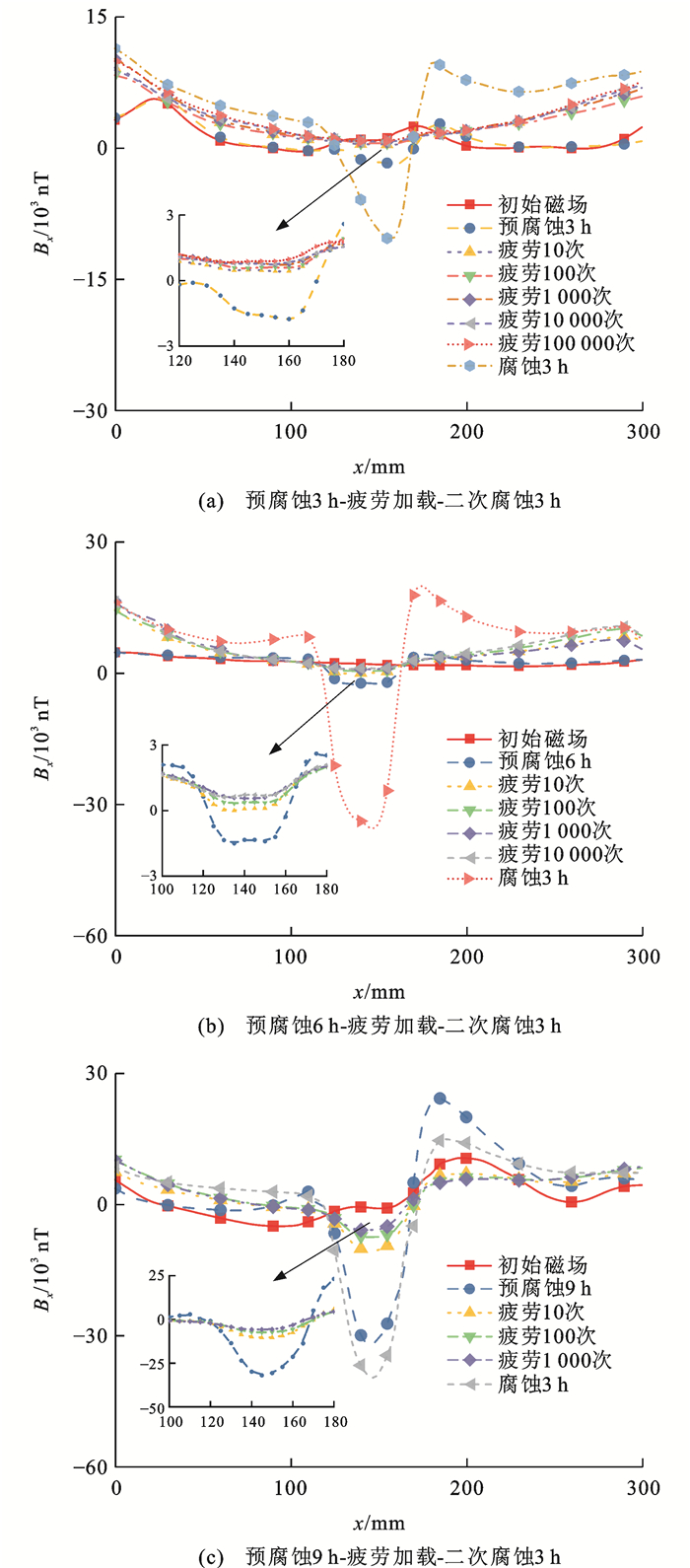
由第2节中的腐蚀试验结果可知,相比于10和50 mm的腐蚀区域长度,当腐蚀区域长度为30 mm时,腐蚀对SMFL信号分布的影响较为显著,故后续试验的腐蚀区域长度取为30 mm;当应力幅为260 MPa时疲劳对SMFL信号分布的影响较为显著,以此开展预腐蚀-疲劳-腐蚀三阶段交互作用试验,预腐蚀时间分别取3、6和9 h,为保证腐蚀高强钢丝不发生疲劳脆性断裂,随着预腐蚀时间的增加,疲劳加载循环次数相应减少。试验过程中高强钢丝在经历不同疲劳加载循环次数和腐蚀时间情况下的SMFL信号分布曲线如图 13所示,可以看出:在经历预腐蚀后的SMFL信号出现谷形峰值,随着疲劳加载循环次数的增加,谷形峰值逐渐削弱并趋于稳定;预腐蚀时间越长削弱效果越显著,腐蚀量不大时(如腐蚀时间为3 h),疲劳加载可以完全削弱腐蚀引起的信号峰值,疲劳后随着二次腐蚀时间的增加,试件腐蚀区域出现的谷形峰值逐渐增加。
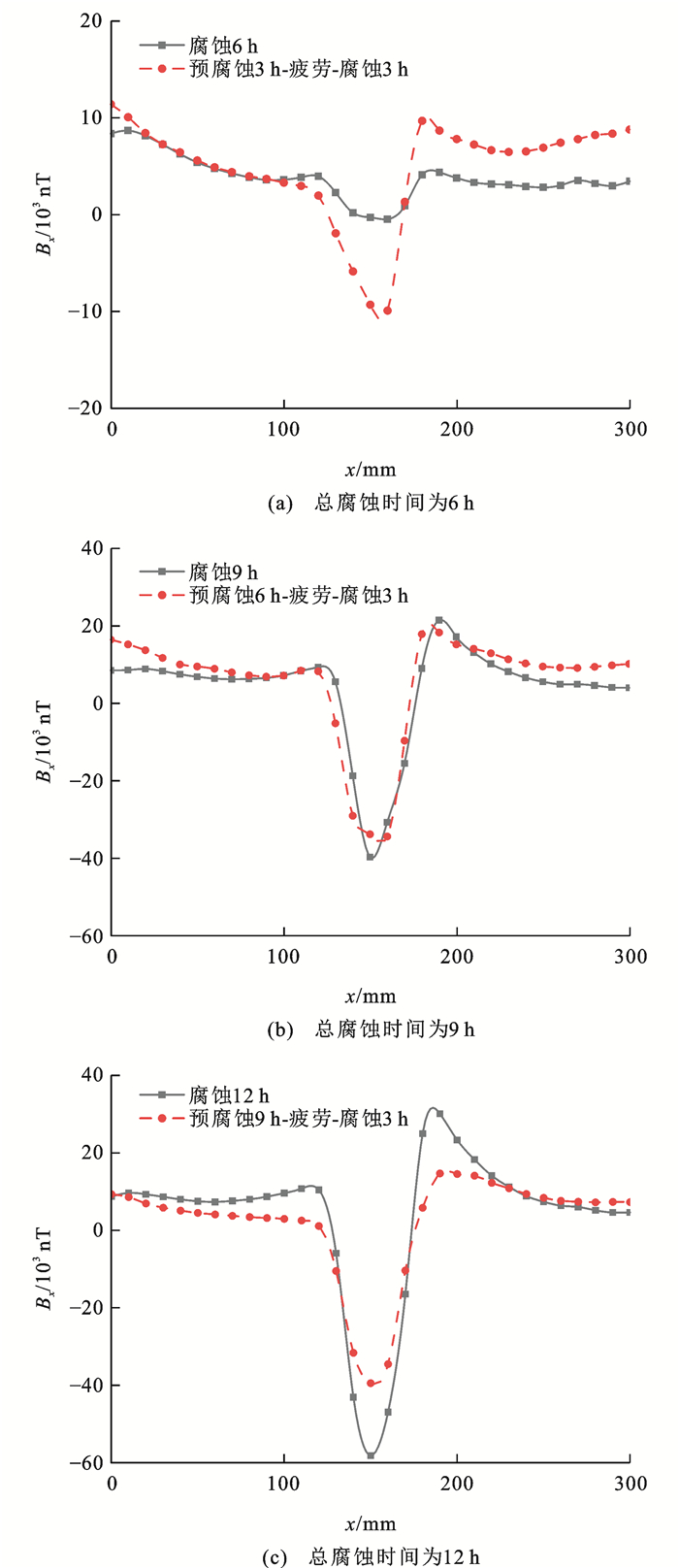
为进一步探究腐蚀过程中疲劳加载对SMFL信号的影响,绘制不同工况下高强钢丝的SMFL信号分布,如图 14所示,可知:腐蚀过程中考虑疲劳加载可显著影响信号分布,单一腐蚀因素下,腐蚀时间为6、9和12 h时,磁场强度极值分别为300、40 000和58 000 nT;考虑疲劳加载时,总腐蚀时间为6、9和12 h情况下的磁场强度极值分别为11 000、38 000和39 000 nT;总腐蚀时间较短时(6 h),疲劳荷载会增加试件的磁场强度,故再次腐蚀会增加信号极值;总腐蚀时间较长时(12 h),磁场强度随腐蚀时间的增加而增大,当预腐蚀时间达到一定程度(9 h)时,高强钢丝腐蚀程度加深,再施加疲劳荷载会使得SMFL信号发生倒转现象[44],对比仅考虑单一腐蚀因素的情况,其所引起的SMFL信号极值会减小。
3.2 预疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳三阶段交互作用试验
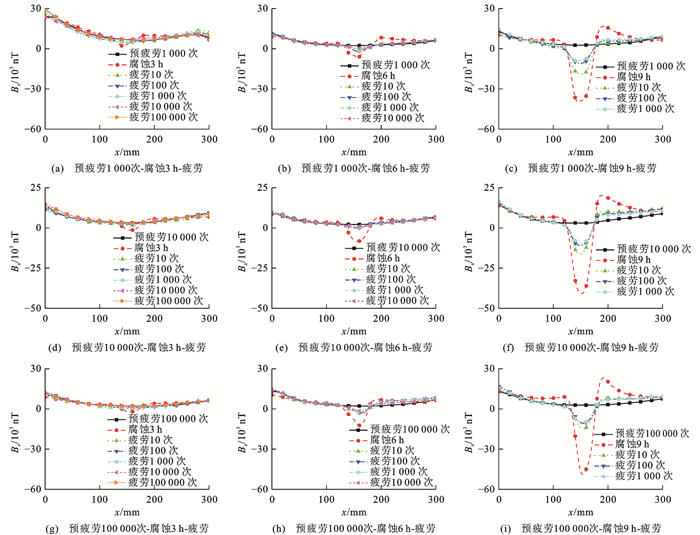
开展预疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳交互作用试验,对高强钢丝分别进行1 000、10 000和100 000次预疲劳加载并将其作为初始状态,之后进行不同程度的腐蚀,再施加不同循环次数的疲劳荷载,不同工况下的SMFL信号分布如图 15所示,可以看出:预疲劳加载后高强钢丝信号幅值总体增强,腐蚀后再经过疲劳加载,在一定程度上削弱了腐蚀区域的异常信号,以预疲劳加载循环1 000次腐蚀时间为9 h为例,再施加疲劳荷载循环1 000次,SMFL信号约减小77.16%。
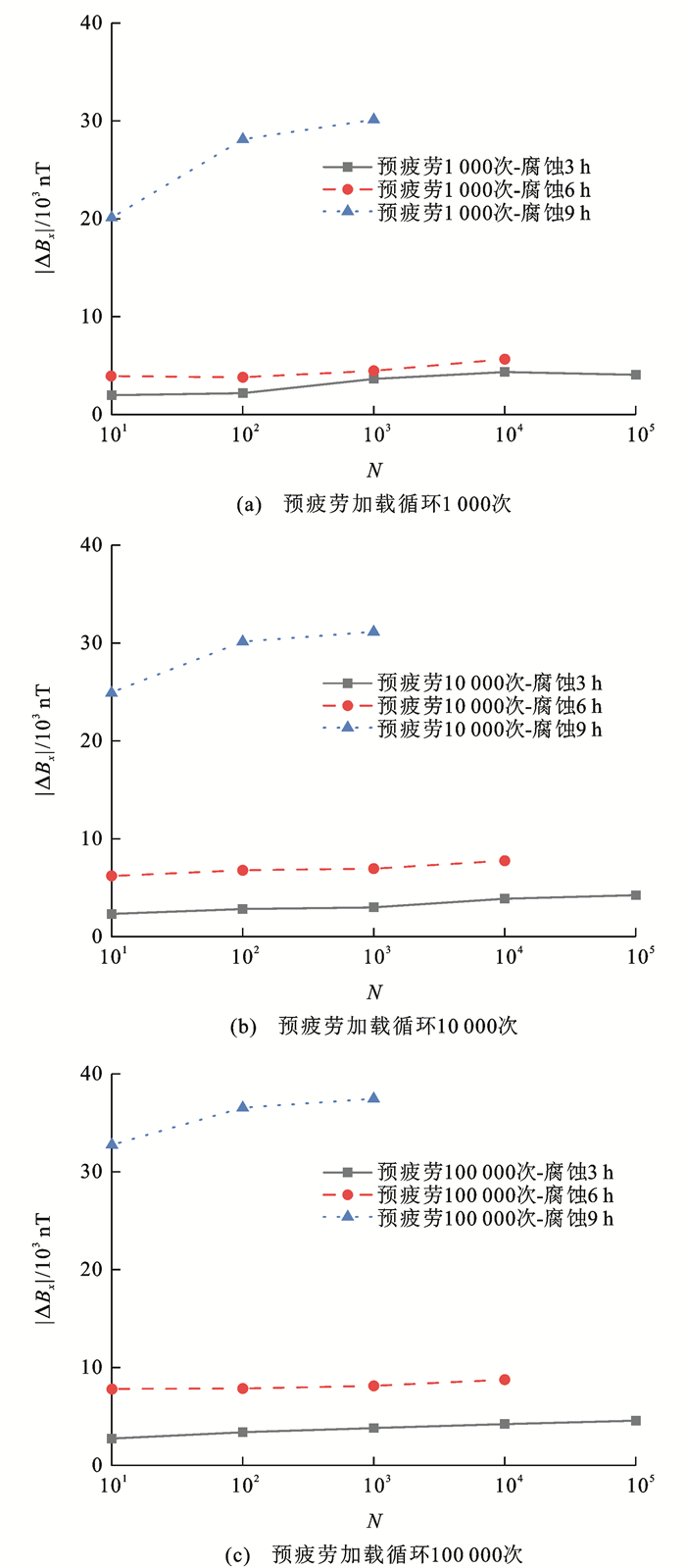
为进一步探究预疲劳作用对高强钢丝SMFL信号的影响,绘制考虑不同预疲劳加载循环次数下磁场强度变化量ΔBx的变化曲线,如图 16所示,可以看出:在腐蚀3 h情况下,SMFL信号异常峰值幅值被削弱甚至基本消失,而在腐蚀6与9 h情况下,随着疲劳加载循环次数的增加,信号异常峰值幅值依然被削弱,但信号并未被完全消除;随着预疲劳加载循环次数的增加,SMFL信号变化记忆性特征愈发显著,磁场强度变化增大,说明预疲劳与腐蚀均对SMFL信号异常峰值变化具有积极作用,与预疲劳加载循环次数为1 000,腐蚀9 h情况相比,循环次数为100 000,腐蚀9 h情况下SMFL信号峰值变化增加了24.27%;结合力-磁耦合模型可知,施加预疲劳荷载后,未腐蚀高强钢丝磁场强度增强,磁通量增加,导致后期腐蚀的磁场强度变化增加。
4. 讨论
桥梁缆索平行高强钢丝在服役期间承受腐蚀-疲劳耦合作用,结合试验结果,可推出其对钢丝SMFL信号的影响机制主要体现在以下几个方面。
(1) 腐蚀高强钢丝承受的疲劳荷载:相比于未腐蚀钢丝,腐蚀钢丝的表面粗糙度增加,由磁偶极子理论模型可知,腐蚀缺陷处的不连续性会产生漏磁场。当腐蚀钢丝承受疲劳荷载时,腐蚀缺陷处存在应力集中,磁畴壁在应力的作用下进行旋转与定向运动,磁导率会随之增加,试件内部的磁通量增加,因此,施加疲劳荷载后,腐蚀缺陷处的漏磁场强度降低。
(2) 高强钢丝承受疲劳荷载后的腐蚀作用:施加疲劳荷载后,在应力的作用下,宏观表现为磁通量的增加,因此,相比于单一腐蚀,高强钢丝承受疲劳荷载后,腐蚀作用会导致腐蚀缺陷处泄漏更多的磁通量,腐蚀缺陷处的漏磁场强度增加。
(3) 高强钢丝承受疲劳荷载后进行腐蚀,之后施加二次疲劳载荷:施加第1次疲劳荷载后,腐蚀缺陷处的漏磁场强度增加,当再次施加疲劳载荷时,腐蚀缺陷处的漏磁场强度的削弱量会有所增加。
(4) 腐蚀高强钢丝承受疲劳荷载后,再进行腐蚀:施加疲劳荷载后,钢丝磁导率增加,当预腐蚀时间达到一定程度(9 h)时,钢丝的腐蚀程度加深,再施加疲劳荷载会产生磁信号倒转现象,腐蚀缺陷处的漏磁场强度被大幅削弱,其在预腐蚀9 h-疲劳-腐蚀3 h情况下的SMFL信号极值3.9×104 nT低于单一腐蚀12 h的SMFL信号极值5.8×104 nT。
5. 结语
(1) 腐蚀作用引起高强钢丝表面几何形状变化,在SMFL信号切向分量梯度变化曲线的波谷和波峰相交处信号达到极值,随着腐蚀时间的增加,信号极值先缓慢增长后急剧增加,整体规律符合非线性Boltzmann方程,SMFL信号的最大变化可达5.0×104 nT。随着腐蚀区域长度的增加,信号极值不再持续增加,且其位置呈偏移趋势,当腐蚀区域长度为30 mm时,信号极值达到5.9×104 nT后其变化趋于平稳,偏移与蚀坑分布的随机性特征有关。
(2) 疲劳加载应力变化会引起试件内部磁畴的位错运动,进而在地磁场与应力场的综合作用下影响磁信号分布。整体看来,随着疲劳加载循环次数的增加,SMFL信号整体增强且趋于稳定,磁场强度时程曲线随疲劳加载循环次数的增加服从单参数指数函数模型,信号强度达到极值11 186 nT后趋于稳定。静态应力变化下高强钢丝SMFL信号时变规律与理论推导结果高度重合。
(3) 腐蚀与疲劳荷载的作用顺序不同,高强钢丝SMFL信号会产生较大差异,预腐蚀后进行疲劳加载,施加的交变应力场会削弱腐蚀缺陷引起的SMFL信号,疲劳荷载作用后再进行二次腐蚀,磁场信号的变化与预腐蚀程度有关。预腐蚀9 h后施加疲劳荷载,之后再腐蚀3 h,与单一腐蚀12 h相比,SMFL信号强度削弱32%。
(4) 疲劳荷载作用过程中如考虑腐蚀作用,预疲劳应力会诱导磁场,导致磁荷线性积累,强化后的磁场促进腐蚀缺陷导致的SMFL信号峰值增加;在此基础上腐蚀后施加疲劳荷载时,随着预疲劳加载循环次数的增加,腐蚀缺陷处的SMFL信号峰值削弱量增加。与预疲劳荷载循环1 000次之后腐蚀9 h再施加疲劳加载情况相比,当预疲劳加载循环增加至100 000次时,SMFL信号强度增强30%。
(5) SMFL检测技术能够定点定量精细化描述金属的缺陷特征,检测精度较高,SMFL检测方法需在全索范围内开展爬索检测,有彩灯等干扰时不可检,而且锚头区域为检测盲区。目前已经将相关成果应用到团队自主研发的爬索机器人中,机器人携带SMFL检测传感器阵列,能进行拉索内部损伤识别与定位。
(6) 使用SMFL检测法检测桥梁缆索损伤时,仅关注内部钢丝/钢绞线的腐蚀程度与索力变化均值,不能准确获得索体的损伤状态,因此,需考虑腐蚀-疲劳耦合效应的影响,进一步研究高强钢丝内磁信号出现的倒转现象。
-
表 1 镀锌钢丝微量元素占比
Table 1. Proportions of micro-elements in galvanized steel wire
% 元素 C Mn Si Cr Cu 占比 0.90~0.95 0.30~0.90 0.12~1.20 ≤0.35 ≤0.20 表 2 镀锌钢丝宏观性能
Table 2. Macroscopic properties of galvanized steel wire
参数 断后伸长率/% 密度/(g·cm-3) 强度/MPa 弹性模量/MPa 取值 ≥4.0 7.85 1 860 2.0×105 表 3 试验工况
Table 3. Test conditions
工况 编号 腐蚀宽度/mm 腐蚀时间/h 加载应力幅/MPa 疲劳加载次数 腐蚀 C-1 1 1、2、3、4 0 0 C-2 3 3、6、9、12 0 0 C-3 5 5、10、15、20 0 0 静拉应力 Y-1 0 0 0、260、520、780、1 040、1 300 0 疲劳 F-1 0 0 0、260、520、780,1 040、1 300 10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000 预腐蚀-疲劳-腐蚀 C-F-C-1 3 预腐蚀3 h,再腐蚀6 h 260 10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000 C-F-C-2 3 预腐蚀6 h,再腐蚀9 h 260 10、100、1 000、10 000 C-F-C-3 3 预腐蚀9 h,再腐蚀12 h 260 10、100、1 000 预疲劳-腐蚀-疲劳 F-C-F-1 3 3 260 预疲劳加载1 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000次 F-C-F-2 3 6 260 预疲劳加载1 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000次 F-C-F-3 3 9 260 预疲劳加载1 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000次 F-C-F-4 3 3 260 预疲劳加载10 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000次 F-C-F-5 3 6 260 预疲劳加载10 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000次 F-C-F-6 3 9 260 预疲劳加载10 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000次 F-C-F-7 3 3 260 预疲劳加载100 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000、100 000次 F-C-F-8 3 6 260 预疲劳加载100 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000、10 000次 F-C-F-9 3 9 260 预疲劳加载100 000次,再疲劳加载10、100、1 000次 -
[1] MAYRBAURL R M, CAMO S. Cracking and fracture of suspension bridge wire[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2001, 6(6): 645-650. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2001)6:6(645) [2] 缪长青, 尉廷华, 王义春, 等. 大跨桥梁缆索钢丝腐蚀速率的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(3): 513-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201403022.htmMIAO Chang-qing, WEI Ting-hua, WANG Yi-chun, et al. Corrosion rate test of cable wires of large span bridge[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(3): 513-518. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201403022.htm [3] RAE P J, DICKSON P M. A review of the mechanism by which exploding bridge-wire detonators function[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2019, 475(2227): 20190120. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2019.0120 [4] 杨世聪, 张劲泉, 姚国文. 在役桥梁拉吊索腐蚀-疲劳损伤与破断机理分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(3): 80-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201903012.htmYANG Shi-cong, ZHANG Jin-quan, YAO Guo-wen. Analysis on corrosion-fatigue damage and fracture mechanism of cables/hangers in service bridges[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(3): 80-86. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201903012.htm [5] 许福友, 陈艾荣, 张建仁. 缆索承重桥梁的颤振可靠性[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(5): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200605011.htmXU Fu-you, CHEN Ai-rong, ZHANG Jian-ren. Flutter reliability of cable supported bridge[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2006, 19(5): 59-64. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200605011.htm [6] 孙晓燕, 徐冲, 王海龙, 等. 用于疲劳可靠性分析的公路桥梁荷载效应研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2011, 28(5): 80-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201105016.htmSUN Xiao-yan, XU Chong, WANG Hai-long, et al. Investigation of highway bridge load effect for fatigue reliability analysis[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2011, 28(5): 80-85. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201105016.htm [7] MAHMOUD K M. Fracture strength for a high strength steel bridge cable wire with a surface crack[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2007, 48(2): 152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2007.05.006 [8] DENG Yang, LIU Yang, CHEN Su-ren. Long-term in-service monitoring and performance assessment of the main cables of long-span suspension bridges[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(6): 1414. doi: 10.3390/s17061414 [9] LIU Zhong-xiang, GUO Tong, HUANG Ling-yu, et al. Fatigue life evaluation on short suspenders of long-span suspension bridge with central clamps[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2017, 22(10): 04017074. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001097 [10] LIU Zhong-xiang, GUO Tong, HEBDON M H, et al. Corrosion fatigue analysis and reliability assessment of short suspenders in suspension and arch bridges[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2018, 32(5): 04018060. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001203 [11] 唐力伟, 张晓涛, 王平. 管状金属构件裂纹电磁声发射激发特性试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(19): 48-51, 58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201419010.htmTANG Li-wei, ZHANG Xiao-tao, WANG Ping. Tests for exciting features of electromagnetic acoustic emission of tubular metal parts'crack[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(19): 48-51, 58. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201419010.htm [12] 张闯, 刘素贞, 杨庆新, 等. 基于电磁声发射的金属板裂纹检测实验研究[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2011, 30(1): 84-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGDN201101019.htmZHANG Chuang, LIU Su-zhen, YANG Qing-xin, et al. Experiment of crack detection of metal plate based on electromagnetically induced acoustic emission[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2011, 30(1): 84-88. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGDN201101019.htm [13] 高伟. 基于磁致伸缩导波长钢管及钢带非接触缺陷检测技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.GAO Wei. Research on noncontact defect detection technology of magnetostrictive guided wave for long steel pipe and steel strip[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese) [14] RAMANDI H L, CHEN Hong-hao, CROSKY A, et al. Interactions of stress corrosion cracks in cold drawn pearlitic steel wires: an X-ray micro-computed tomography study[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 145: 170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2018.09.009 [15] 汪友生, 徐小平, 沈兰荪. 铁磁材料的漏磁检测[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2000, 14(3): 45-48, 59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZIY200003010.htmWANG You-sheng, XU Xiao-ping, SHEN Lan-sun. Testing of MFL for ferromagnetic materials[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2000, 14(3): 45-48, 59. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZIY200003010.htm [16] KARTHIK M M, TERZIOGLU T, HURLEBAUS S, et al. Magnetic flux leakage technique to detect loss in metallic area in external post-tensioning systems[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 201: 109-765. [17] 苏三庆, 刘馨为, 王威, 等. 金属磁记忆检测技术研究新进展与关键问题[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(12): 1557-1572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD202012003.htmSU San-qing, LIU Xin-wei, WANG Wei, et al. Progress and key problems in the research on metal magnetic memory testing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2020, 42(12): 1557-1572. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD202012003.htm [18] ROSKOSZ M. Metal magnetic memory testing of welded joints of ferritic and austenitic steels[J]. NDT and E International, 2011, 44(3): 305-310. doi: 10.1016/j.ndteint.2011.01.008 [19] DUBOV A A. A study of metal properties using the method of magnetic memory[J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1997, 39(9): 401-405. doi: 10.1007/BF02469065 [20] HWANG J H, LORD W. Finite element modeling of magnetic field/defect interactions[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 1975, 3(1): 21-25. doi: 10.1520/JTE10129J [21] CHENG Yu-hua, WANG Yong-gang, YU Hai-chao, et al. Solenoid model for visualizing magnetic flux leakage testing of complex defects[J]. NDT and E International, 2018, 100: 166-174. doi: 10.1016/j.ndteint.2018.09.011 [22] JILES D C, ATHERTON D L. Theory of the magnetisation process in ferromagnets and its application to the magnetomechanical effect[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1984, 17(6): 1265-1281. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/17/6/023 [23] JILES D C. Theory of the magnetomechanical effect[J]. Journal of physics D: Applied Physics, 1995, 28(8): 1537-1546. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/28/8/001 [24] 周建庭, 赵亚宇, 何沁, 等. 基于磁记忆的镀锌钢绞线腐蚀检测试验[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 39(1): 81-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201901011.htmZHOU Jian-ting, ZHAO Ya-yu, HE Qin, et al. Experimental of corrosion detection of galvanized steel strands based on magnetic memory[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 39(1): 81-89. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201901011.htm [25] 赵亚宇, 周建庭, 夏润川, 等. 基于磁记忆弱漏磁效应的钢绞线腐蚀检测[J]. 深圳大学学报(理工版), 2019, 36(3): 260-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZDL201903006.htmZHAO Ya-yu, ZHOU Jian-ting, XIA Run-chuan, et al. The detection of corrosion of steel strands based on weak magnetic flux leakage effect of metal magnetic memory[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University (Science and Engineering), 2019, 36(3): 260-267. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZDL201903006.htm [26] XIA Run-chuan, ZHANG Hong, ZHOU Jian-ting, et al. Probability evaluation method of cable corrosion degree based on self-magnetic flux leakage[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2021, 522: 167544. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167544 [27] WU Xin-jun, YUAN Jian-ming, BEN An-ran. A novel magnetic testing method for the loss of metallic cross-sectional area of bridge cables[J]. International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 2012, 39(1/2/3/4): 195-201. [28] 邱俊澧, 周建庭, 廖棱, 等. 锈蚀钢筋混凝土梁受弯承载力与自发漏磁相关性试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2020, 41(9): 127-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJB202009013.htmQIU Jun-li, ZHOU Jian-ting, LIAO Leng, et al. Experimental study on correlation between bending capacity and self-magnetic flux leakage of corroded RC beams[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2020, 41(9): 127-136. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJB202009013.htm [29] SHI Peng-peng, BAI Pei-gen, CHEN Hong-en, et al. The magneto-elastoplastic coupling effect on the magnetic flux leakage signal[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2020, 504: 166669. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166669 [30] WANG Z D, YAO K, DENG B, et al. Quantitative study of metal magnetic memory signal versus local stress concentration[J]. NDT and E International, 2010, 43(6): 513-518. doi: 10.1016/j.ndteint.2010.05.007 [31] YAO K, WU L B, WANG Y S, et al. Nondestructive evaluation of contact damage of ferromagnetic materials based on metal magnetic memory method[J]. Experimental Techniques, 2019, 43(3): 273-285. doi: 10.1007/s40799-019-00311-5 [32] 钱正春, 黄海鸿, 姜石林, 等. 铁磁性材料拉/压疲劳磁记忆信号研究[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2016, 30(4): 506-517. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZIY201604002.htmQIAN Zheng-chun, HUANG Hai-hong, JIANG Shi-lin, et al. Research on magnetic memory signal of ferromagnetic material under tensile and compressive fatigue loading[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2016, 30(4): 506-517. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZIY201604002.htm [33] 朱达荣, 潘志远, 刘涛, 等. 金属疲劳过程磁记忆信号多特征量提取研究[J]. 现代制造工程, 2018(10): 123-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXGY201810020.htmZHU Da-rong, PAN Zhi-yuan, LIU Tao, et al. The magnetic memory signal wavelet packet frequency band energy feature extraction[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2018(10): 123-129. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXGY201810020.htm [34] 龙飞飞, 王建锃, 宋阳, 等. 基于磁记忆的球墨铸铁疲劳损伤检测[J]. 无损检测, 2014, 36(8): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSJC201408009.htmLONG Fei-fei, WANG Jian-zeng, SONG Yang, et al. The fatigue damage inspection of compressor crankshaft based on magnetic memory technology[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2014, 36(8): 29-32. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSJC201408009.htm [35] LI Chong-chong, DONG Li-hong, WANG Hai-dou, et al. Metal magnetic memory technique used to predict the fatigue crack propagation behavior of 0.45%C steel[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2016, 405: 150-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.12.035 [36] MENG Qing-ling, PAN Peng-chao, YANG Xin-lei, et al. Self-magnetic flux leakage-based detection and quantification for high-strength steel wires of bridge cables considering corrosion-fatigue coupling effect[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2022, 561: 169641. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169641 [37] 郑思檬. 基于改进J-A模型的磁力学关系研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2020.ZHENG Si-meng. Study on magneto-mechanical relationship based on improved J-A model[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) [38] 时朋朋, 张鹏程, 金科, 等. 铁磁材料力磁耦合本构模型与微磁检测的定量化理论[C]//厦门大学. 2018远东无损检测新技术论坛论文集. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2018: 779-785.SHI Peng-peng, ZHANG Peng-cheng, JIN Ke, et al. Magneto-mechanical coupling constitutive relation and quantitative theory for metal magnetic memory testing methods[C]//Xiamen University. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Far East NDT New Technology and Application Forum. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2018: 779-785. (in Chinese) [39] 时朋朋. 缺陷漏磁场磁偶极子模型的若干解析解[J]. 无损检测, 2015, 37(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSJC201503001.htmSHI Peng-peng. Analytical solutions of magnetic dipole model for defect leakage magnetic fields[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2015, 37(3): 1-7. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSJC201503001.htm [40] 张贺. 基于弱磁法管道应力内检测技术研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2022.ZHANG He. Research on pipeline stress internal detection technology based on weak magnetic method[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese) [41] SULIGA M, BOROWIK L, CHWASTEK K. Estimation of the level of residual stress in wires with a magnetic method[J]. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 2015, 60(1): 409-413. doi: 10.1515/amm-2015-0067 [42] 刘清友, 罗旭, 朱海燕, 等. 基于Jiles-Atherton理论的铁磁材料塑性变形磁化模型修正[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(10): 297-306.LIU Qing-you, LUO Xu, ZHU Hai-yan, et al. Modeling plastic deformation effect on the hysteresis loops of ferromagnetic materials based on modified Jiles-Atherton model[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(10): 297-306. (in Chinese) [43] SHI Peng-peng, JIN Ke, ZHENG Xiao-jing. A general nonlinear magnetomechanical model for ferromagnetic materials under a constant weak magnetic field[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 119(14): 145103. doi: 10.1063/1.4945766 [44] 黄爽. 锈蚀及持荷作用后钢筋混凝土梁疲劳性能及压磁效应研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2022.HANG Shuang. Study on fatigue behavior and piezomagnetic effect of reinforced concrete beams after corrosion and sustained loading[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:
















 下载:
下载: