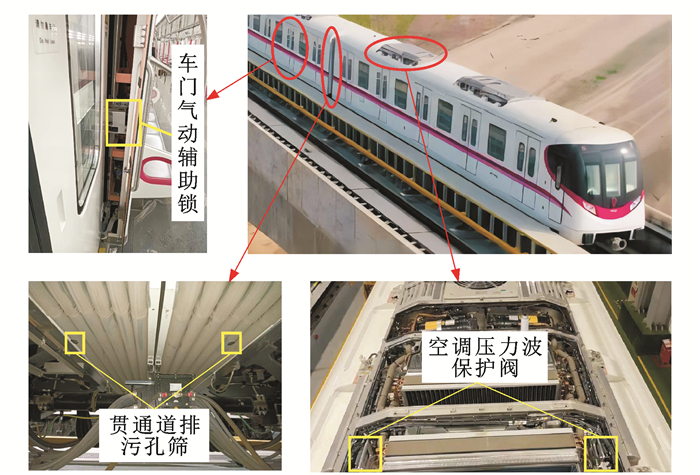
Impact of key airtight components on pressure comfort in metro train
-
摘要: 为全面分析地铁列车运营时车外压力对车内乘客耳压舒适性的影响,采用实车线路试验方法,实测了地铁列车匀速通过隧道时,关键气密部件(空调压力波保护阀、车门气动辅助锁与贯通道排污孔筛)在不同密封条件下的车内、外压力,分析了车外压力波动特性、沿列车长度方向的压力分布规律以及车内关键气密部件对车内压力变化幅值的影响。研究结果表明:头车和中间车的车外压力受车头进入隧道产生的压缩波影响较大,列车车身表面压力峰值从头车向尾车逐渐降低;在空调开启时,相较于启用压力波保护阀,未启用时车内3 s内压力变化幅值增加了48%~61%,1 s内增加了75%~90%,说明空调压力波保护阀对车内压力舒适性影响显著;在空调关闭时,与启用车门气动辅助锁相比,未启用时3 s内车内压力变化幅值增加了39%~46%,1 s内增加了69%~78%,表明车门气动辅助锁对车内压力舒适性的影响仅次于空调压力波保护阀;在空调关闭的情况下,与启用贯通道排污孔筛相比,未启用时3 s内车内压力变化幅值增加了3%~11%,1 s内增加了1%~13%,说明贯通道排污孔筛对车内压力的影响较小。Abstract: To comprehensively analyze the impact of external pressure on passenger ear comfort during metro train operation, a real vehicle line test method was employed to measure the internal and external pressures of key airtight components (pressure wave protection valve for air conditioning, door pneumatic auxiliary lock, and gangway drainage hole screen) under different sealing conditions when the metro train passed through the tunnel at a constant speed. The fluctuating characteristics of external pressure, the pressure distribution law of the train in the longitudinal direction, as well as the influences of key airtight components on the pressure change amplitude inside the train were analyzed. Research results show that external pressures on the head vehicle and the middle vehicle are greatly affected by the compression wave generated while the train head enters the tunnel. The peak pressure on the train body surface gradually decreases from the head vehicle to the tail vehicle. When the air conditioning is on, compared with the situation when the pressure wave protection valve is enabled, the pressure change amplitude inside the train increases by 48%-61% within 3 s and 75%-90% within 1 s when the pressure wave protection valve is not enabled. This indicates that the pressure wave protection valve for air conditioning has a significant effect on the pressure comfort inside the train. When the air conditioning is off, compared with the situation when the door pneumatic auxiliary lock is enabled, the pressure change amplitude inside the train increases by 39%-46% within 3 s and by 69%-78% within 1 s when the door pneumatic auxiliary lock is not enabled. This indicates that the importance of the door pneumatic auxiliary lock's effect on the pressure comfort inside the train is second to the pressure wave protection valve for air conditioning. When the air conditioning is off, compared with the situation when the gangway drainage hole screen is enabled, the pressure change amplitude inside the train increases by 3%-11% within 3 s and 1%-13% within 1 s when the gangway drainage hole screen is not enabled. This indicates that the gangway drainage hole screen has a relatively small effect on the pressure inside the train.
-
Key words:
- vehicle engineering /
- metro train /
- real vehicle test /
- pressure wave /
- airtightness /
- comfort
-
表 1 试验工况
Table 1. Test conditions
工况 空调状态 压力波保护阀状态 气动辅助锁状态 贯通道排污孔筛状态 1 关机 未启用 启用 启用 2 开机 启用 启用 启用 3 开机 未启用 启用 启用 4 关机 未启用 未启用 启用 5 关机 未启用 启用 未启用 表 2 列车内、外测点压力变化幅值
Table 2. Pressure change amplitudes of measurement points inside and outside train
测点 幅值类型 测试1/ Pa 测试2/ Pa 测试3/ Pa 平均偏差/ Pa 相对平均偏差/% W5 峰峰值 626 645 658 11 1.8 3 s内变化幅值 558 585 587 12 2.2 N6 峰峰值 272 284 293 7 2.6 3 s内变化幅值 212 225 234 8 3.5 表 3 工况1条件下列车内测点压力变化幅值
Table 3. Pressure change amplitudes of measurement points inside train under condition 1
测点 峰峰值/Pa 3 s内压力变化幅值/Pa 1 s内压力变化幅值/Pa N1 286 228 158 N2 282 225 151 N3 278 221 151 N4 278 224 152 N5 284 223 156 N6 282 224 158 N7 271 223 165 N8 270 229 159 表 4 工况1~3条件下车内测点压力变化幅值
Table 4. Pressure change amplitudes of measurement points inside train under conditions 1-3
工况 时间尺度/s 测点压力变化幅值/Pa N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 N6 N7 N8 1 3 228 225 221 224 223 224 223 229 1 158 151 151 152 156 158 165 159 2 3 258 251 249 247 234 241 254 246 1 159 151 157 153 159 162 174 169 3 3 389 382 385 377 376 374 377 375 1 290 287 285 291 300 302 305 301 表 5 空调压力波保护阀对车内压力变化幅值的影响
Table 5. Impact of pressure wave protection valve for air conditioning on pressure change amplitude inside train
对比情况 时间尺度/s 测点工况对比增量/% N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 N6 N7 N8 工况2对比工况1 3 13 12 13 10 5 7 14 7 1 0 0 4 1 1 2 6 6 工况3对比工况1 3 71 70 75 69 69 67 69 64 1 83 90 88 91 92 91 85 89 工况3对比工况2 3 51 52 55 53 61 55 48 52 1 82 90 82 90 89 86 75 78 表 6 工况1和4条件下车内测点压力变化幅值
Table 6. Pressure change amplitudes of measurement points inside train under conditions 1 and 4
工况 时间尺度/s 测点压力变化幅值/Pa N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 N6 N7 N8 1 3 228 225 221 224 223 224 223 229 1 158 151 151 152 156 158 165 159 4 3 322 323 322 319 322 321 321 319 1 268 266 266 271 274 279 278 279 表 7 车门气动辅助锁对车内压力变化幅值的影响
Table 7. Impact of door pneumatic auxiliary lock on pressure change amplitude inside train
对比情况 时间尺度/s 测点工况对比增量/% N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 N6 N7 N8 工况4对比工况1 3 41 43 46 42 45 43 44 39 1 69 76 75 78 75 77 69 75 表 8 工况1和5条件下车内测点压力变化幅值
Table 8. Pressure change amplitudes of measurement points inside train under conditions 1 and 5
工况 时间尺度/s 测点压力变化幅值/Pa N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 N6 N7 N8 1 3 228 225 221 224 223 224 223 229 1 158 151 151 152 156 158 165 159 5 3 246 247 245 250 238 239 245 237 1 160 158 160 172 164 162 174 167 表 9 贯通道排污孔筛对车内压力变化幅值的影响
Table 9. Impact of gangway drainage hole screen on pressure change amplitude inside train
对比情况 时间尺度/s 测点工况对比增量/% N1 N2 N3 N4 N5 N6 N7 N8 工况5对比工况1 3 8 10 11 11 7 7 10 3 1 1 4 6 13 5 2 6 5 -
[1] 刘友梅. 论电力牵引轨道交通的技术发展[J]. 中国工程科学, 2000, 2(10): 51-55, 62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2000.10.014LIU You-mei. Technology development of electric traction rail traffic[J]. Engineering Science, 2000, 2(10): 51-55, 62. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2000.10.014 [2] 刘友梅. 城市轨道交通装备技术的多样性发展[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2009, 12(11): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-869X.2009.11.002LIU You-mei. Diversification of urban rail transit equipment technology[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2009, 12(11): 1-4. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-869X.2009.11.002 [3] 李杨, 刘友梅. 时速120 km地铁列车气密性设计与试验[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2023, 44(2): 139-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202302015.htmLI Yang, LIU You-mei. Air-tightness design and test of metro train with speed of 120 km·h-1[J]. China Railway Science, 2023, 44(2): 139-150. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202302015.htm [4] 李杨, 刘友梅, 陈勇, 等. 一种提升轨道车辆安全性与舒适度的格栅控制方案研究[J]. 机车电传动, 2022(2): 21-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCDC202202004.htmLI Yang, LIU You-mei, CHEN Yong, et al. Research on a grille control scheme to enhance safety and comfort of rail vehicles[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2022(2): 21-25. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCDC202202004.htm [5] 李杨, 刘友梅, 柳晓峰, 等. 80 km/h B型地铁列车隧道内运行空气动力学试验研究[J]. 都市快轨交通, 2023, 36(5): 51-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2023.05.008LI Yang, LIU You-mei, LIU Xiao-feng, et al. Experimental study on aerodynamics of 80 km/h B-type metro train running in a tunnel[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2023, 36(5): 51-58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2023.05.008 [6] LI Yang, LIU You-mei. Development of a forward design method for train airtightness: a case study of a metro express line[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology Incorporating Trenchless Technology Research, 2024, 144: 105479. [7] LI Yang, LIU You-mei. Analysis of pressure fluctuations and passenger comfort in metro express: an experimental study on a Wuhan bridge-tunnel line[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2024, 246: 105638. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2024.105638 [8] LI Yang, LIU You-mei. Impact of coupled effects of airtight components at variable cross-section location on vehicle airtightness in Wuhan metro[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2024, DOI: 10.1177/09544097241229120. [9] 杨波, 施柱, 那艳玲, 等. 地铁中间风井前变速运行对乘客舒适性影响[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2021, 18(6): 1555-1562. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202106022.htmYANG Bo, SHI Zhu, NA Yan-ling, et al. Influence of running with varying velocity in front of the middle ventilating shaft of the subway on passenger comfort[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(6): 1555-1562. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202106022.htm [10] 宋剑伟. 关于隧道空气动力学效应造成地铁列车客室压力变化的探讨与建议[J]. 铁道机车车辆, 2021, 41(3): 119-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2021.03.23SONG Jian-wei. Discussion and suggestion on the pressure change of subway train passenger compartment caused by tunnel aerodynamics effect[J]. Railway Locomotive and Car, 2021, 41(3): 119-124. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7842.2021.03.23 [11] XIONG Xiao-hui, ZHU Liang, ZHANG Jie, et al. Field measurements of the interior and exterior aerodynamic pressure induced by a metro train passing through a tunnel[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2020, 53: 101928. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101928 [12] NIU Ji-qiang, ZHOU Dan, LIANG Xi-feng, et al. Numerical study on the aerodynamic pressure of a metro train running between two adjacent platforms[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2017, 65: 187-199. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.03.006 [13] 骆建军. 高速地铁隧道内扩大段和通风竖井对压力波的影响研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2016, 53(4): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSD201604004.htmLUO Jian-jun. The influences of enlarged sections and ventilation shafts on pressure waves in high-speed metro tunnels[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2016, 53(4): 22-28. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSD201604004.htm [14] NIU Ji-qiang, SUI Yang, YU Qiu-jun, et al. Aerodynamics of railway train/tunnel system: a review of recent research[J]. Energy and Built Environment, 2020, 1(4): 351-375. doi: 10.1016/j.enbenv.2020.03.003 [15] GAWTHORPE R. Pressure effects in railway tunnels[J]. Rail International, 2000, 31(4): 10-17. [16] XIE Peng-peng, PENG Yong, WANG Tian-tian, et al. Risks of ear complaints of passengers and drivers while trains are passing through tunnels at high speed: a numerical simulation and experimental study[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(7): 1283. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071283 [17] BAKER C J. A review of train aerodynamics, Part 1— fundamentals[J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2014, 118(1201): 201-228. doi: 10.1017/S000192400000909X [18] SUZUKI H. Research trends on riding comfort evaluation in Japan[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 1998, 212(1): 61-72. doi: 10.1243/0954409981530689 [19] KOBAYASHI M, SUZUKI Y, AKUTSU K, et al. Alleviating aural discomfort of passengers on Shinkansen by controlling air flow rate in ventilation system[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers: Series B, 1998, 41(4): 936-944. [20] LI Wen-hui, LIU Tang-hong, MARTINEZ-VAZQUEZ P, et al. Aerodynamic effects of a high-speed train travelling through adjoining and separated tunnels[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 113: 103973. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.103973 [21] LIANG Xi-feng, GUANG Chen, LI Xiao-bai, et al. Numerical simulation of pressure transients caused by high-speed train passage through a railway station[J]. Building and Environment, 2020, 184: 107228. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.107228 [22] RICCO P, BARON A, MOLTENI P. Nature of pressure waves induced by a high-speed train travelling through a tunnel[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2007, 95(8): 781-808. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2007.01.008 [23] CHEN Xiao, LIU Tang-hong, XIA Yong-hong, et al. The evolution of airtight performance for a high-speed train during its long-term service[J]. Measurement, 2021, 177: 109319. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109319 [24] XIA Yu-tao, CHEN Xiao-dong, LIU Tang-hong, et al. A study on the airtightness of a high-speed train using a reduced-scale method[J]. Measurement, 2022, 188: 110610. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110610 [25] 郭蕾, 宋元全, 王天宇. 城轨车辆车门气密性研究及设计[J]. 轨道交通装备与技术, 2020(5): 39-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGR202005014.htmGUO Lei, SONG Yuan-quan, WANG Tian-yu. Research and design of air tightness of urban rail vehicles[J]. Rail Transportation Equipment and Technology, 2020(5): 39-41. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGR202005014.htm [26] 邓长海. 市域快轨车辆主要部件密封性措施的研究[J]. 铁道车辆, 2021, 59(1): 47-48, 96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2021.01.012DENG Chang-hai. Research on sealing measures for main parts on inner-city rapid rail transit vehicle[J]. Rolling Stock, 2021, 59(1): 47-48, 96. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2021.01.012 [27] 陈勇, 李杨, 左建勇, 等. 时速120 km地铁快线空气动力学试验研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2024, 21(3): 1156-1167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202403024.htmCHEN Yong, LI Yang, ZUO Jian-yong, et al. Experimental study on aerodynamics of 120 km/h metro express line[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(3): 1156-1167. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202403024.htm [28] LIU Tang-hong, CHEN Xiao-dong, LI Wen-hui, et al. Field study on the interior pressure variations in high-speed trains passing through tunnels of different lengths[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 169: 54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2017.07.004 [29] 王虎高, 李杨, 武涛. 时速80 km地铁B型车耳压舒适度测试分析[J]. 电力机车与城轨车辆, 2023, 46(2): 45-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DJJI202302009.htmWANG Hu-gao, LI Yang, WU Tao. Test and analysis of ear pressure comfort for 80 km/h B-type metro train[J]. Electric Locomotives and Mass Transit Vehicles, 2023, 46(2): 45-48. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DJJI202302009.htm [30] 唐明赞, 熊小慧, 杨波, 等. 高速地铁隧道区间风井扩大段压力突变机理试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2023, 44(5): 137-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202305014.htmTANG Ming-zan, XIONG Xiao-hui, YANG Bo, et al. Experimental study on the mechanism of pressure abrupt change at the enlarged section of the interval air shaft in high- speed subway tunnel[J]. China Railway Science, 2023, 44(5): 137-146. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202305014.htm -





 下载:
下载: