Anti-lock braking control based on interval type-2 fuzzy logic
-
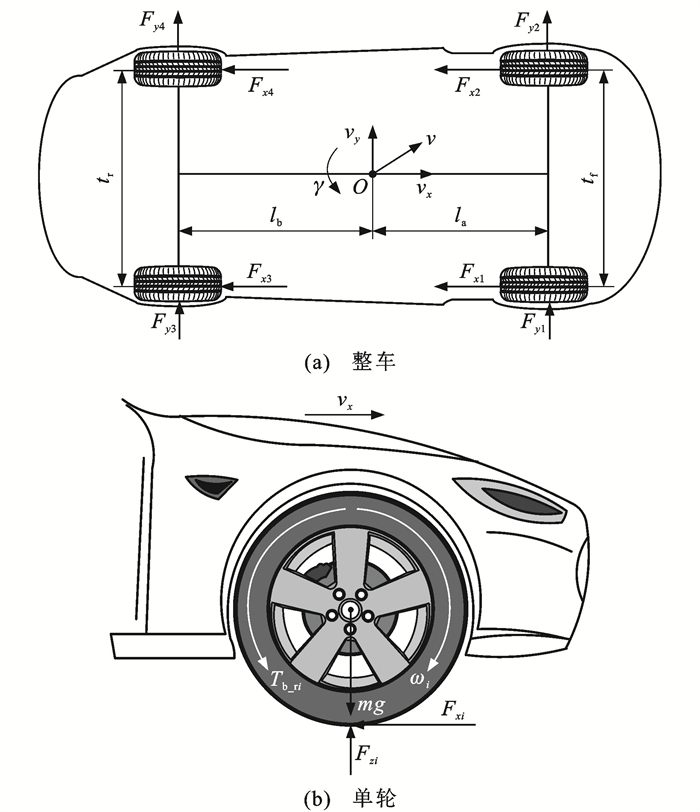
摘要: 针对传统模糊逻辑制动防抱死控制抗干扰能力较弱,在面对不同路面附着系数及理想滑移率时滑移率控制效果较差的问题,提出了一种区间二型模糊逻辑制动防抱死控制系统和方法;控制系统以滑移率误差为输入,利用区间二型模糊集合描述了滑移率误差及其变化率,并经模糊化、模糊推理、模糊降型、解模糊化4个步骤得到理想制动力矩输出;根据上、下隶属度函数确定的模糊变量隶属度计算模糊规则激活度区间,以增强系统的抗干扰能力,并保证滑移率精准跟踪;基于MATLAB/SIMULINK软件,针对搭载了提出的控制器与传统控制器的车辆,模拟了在不同路面附着条件下的防抱死控制性能,并搭建了防抱死硬件在环平台,进行了验证分析。研究结果表明:在区间二型模糊逻辑制动防抱死控制下,车辆在低附着系数路面下前、后轮滑移率误差均方分别下降了52.96%和57.36%,制动距离缩短了0.24 m,制动时间降低了0.04 s;在中附路面下前、后轮滑移率误差均方分别下降了65.15%和73.32%,制动距离缩短了0.36 m,制动时间降低了0.05 s;在高附着系数路面下前、后轮滑移率误差均方分别下降了47.20%和39.57%,制动距离缩短了0.19 m,制动时间降低了0.02 s。由此可见,相比于传统模糊逻辑制动防抱死控制,提出的区间二型模糊逻辑制动防抱死控制在不同制动条件下均能取得更好的滑移率控制效果。Abstract: To cope with the problem of weak anti-interference ability and poor slip ratio control effect when the traditional fuzzy logic anti-lock braking control facing different road surface adhesion coefficients and different ideal slip ratios, an interval type-2 fuzzy logic anti-lock braking control system and method were proposed. The slip ratio error was taken as input of the control system. The interval type-2 fuzzy sets were utilized to describe the slip ratio error and its change rate. Then the ideal braking torque output was obtained after the fuzzification, fuzzy inference, fuzzy type-reduction, and defuzzification. The fuzzy rule activation degree interval was calculated on the premise of fuzzy variables membership degree determined by the upper and lower membership functions. Through this process, the system's anti-interference ability was enhanced, and the accurate slip ratio tracking was ensured. Using the MATLAB/SIMULINK software, the vehicles equipped with the proposed controller and traditional controller were simulated for the anti-lock braking control performance under different road surface adhesion conditions, and the anti-lock hardware-in-the-loop platform was conducted for verification analysis. Research results show that under the interval type-2 fuzzy logic anti-lock braking control, the error mean squares of slip ratios for front and rear wheels of vehicles on the low adhesion coefficient road surface decrease by 52.96% and 57.36%, respectively, the braking distance reduces by 0.24 m, and the braking time declines by 0.04 s. On the middle adhesion coefficient road surface, the error mean squares of slip ratios decrease by 65.15% and 73.32%, respectively, the braking distance reduces by 0.36 m, and the braking time declines by 0.05 s. On the high adhesion coefficient road surface, the error mean squares of slip ratios decrease by 47.20% and 39.57%, respectively, the braking distance reduces by 0.19 m and the braking time declines by 0.02 s. It can be seen that compared with the traditional fuzzy logic anti-lock braking control, the proposed interval type-2 fuzzy logic anti-lock braking control achieves better slip ratio control effects under different braking conditions.
-
表 1 Burckhardt轮胎模型典型路面参数
Table 1. Typical road surface parameters of Burckhardt tire model
路面类型 c1 c2 c3 μp λd 干沥青 1.30 24.00 0.52 1.20 0.16 湿沥青 0.85 33.80 0.35 0.80 0.13 干水泥 1.20 25.17 0.54 1.09 0.15 湿鹅卵石 0.40 33.72 0.10 0.34 0.14 雪 0.20 94.10 0.05 0.20 0.05 冰 0.05 306.40 0.01 0.05 0.03 表 2 区间二型模糊逻辑控制规则
Table 2. Control rules of interval type-2 fuzzy logic
Tb_i $\dot{e}$ NE ZE PO e NE PB PB PM ZE PM PM PS PO PS PS PS 表 3 仿真参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 M/kg 960 hg/m 0.48 A/m2 2.57 Ii/(kg·m2) 2.10 CD 0.30 r/m 0.29 la/m 1.53 lb/m 1.55 表 4 低附着系数路面防抱死效果评价指标
Table 4. Evaluation indexes of anti-lock effect on low adhesion coefficient road surface
评价指标 控制器1 控制器2 制动距离/m 32.96 33.20 制动时间/s 6.22 6.26 平均充分减速度/(m·s-2) 2.00 1.98 前轮滑移率误差均方 1.27×10-2 2.70×10-2 后轮滑移率误差均方 2.84×10-2 6.66×10-2 表 5 中附着系数路面防抱死效果评价指标
Table 5. Evaluation indexes of anti-lock effect on middle adhesion coefficient road surface
评价指标 控制器1 控制器2 制动距离/m 30.69 31.05 制动时间/s 3.58 3.63 平均充分减速度/(m·s-2) 5.05 4.95 前轮滑移率误差均方 9.79×10-3 2.81×10-3 后轮滑移率误差均方 9.39×10-3 3.52×10-2 表 6 高附着系数路面防抱死效果评价指标
Table 6. Evaluation indexes of anti-lock effect on high adhesion coefficient road surface
评价指标 控制器1 控制器2 制动距离/m 28.18 28.37 制动时间/s 2.42 2.44 平均充分减速度/(m·s-2) 10.69 10.57 前轮滑移率误差均方 3.87×10-2 7.33×10-2 后轮滑移率误差均方 2.72×10-2 3.86×10-2 -
[1] 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国汽车工程学术研究综述·2017[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(6): 1-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.06.001Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China's automotive engineering research progress: 2017[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(6): 1-197. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.06.001 [2] CHIANG W P, YIN De-jun, SHIMIZU H. Slip-based regenerative ABS control for in-wheel-motor drive EV[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2015, 38(2): 220-231. doi: 10.1080/02533839.2014.955974 [3] 刘志强, 濮晛. 电动汽车连续再生制动系统防抱死制动试验研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2018, 40(7): 804-811. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC201807009.htmLIU Zhi-qiang, PU Xian. An experimental study on anti-lock braking of continuous regenerative braking system in electric vehicles[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2018, 40(7): 804-811. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC201807009.htm [4] 王骏骋, 何仁. 电动车辆ABS的改进线性二次型最优控制[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2018, 50(9): 108-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX201809017.htmWANG Jun-cheng, HE Ren. Improved linear quadratic optimal control of ABS for an electric vehicle[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018, 50(9): 108-115. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX201809017.htm [5] MEI Peng, KARIMI H R, YANG Shi-chun, et al. An adaptive fuzzy sliding-mode control for regenerative braking system of electric vehicles[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2022, 36(2): 391-410. doi: 10.1002/acs.3347 [6] AMIRKHANI A, MOLAIE M. Fuzzy controllers of antilock braking system: a review[J]. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2023, 25(1): 222-244. doi: 10.1007/s40815-022-01376-y [7] WANG W Y, CHEN Ming-chang, SU Shun-feng. Hierarchical T-S fuzzy-neural control of anti-lock braking system and active suspension in a vehicle[J]. Automatica, 2012, 48(8): 1698-1706. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.05.033 [8] YAZICIOGLU Y, UNLUSOY Y S. A fuzzy logic controlled anti-lock braking system (ABS) for improved braking performance and directional stability[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 2008, 48(3/4): 299-315. doi: 10.1504/IJVD.2008.022581 [9] PI D W, CHEN N, ZHANG B J. Experimental demonstration of a vehicle stability control system in a split-μ manoeuvre[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2011, 225(3): 305-317. doi: 10.1177/09544070JAUTO1541 [10] AKSJONOV A, AUGSBURG K, VODOVOZOV V. Design and simulation of the robust ABS and ESP fuzzy logic controller on the complex braking maneuvers[J]. Applied Sciences, 2016, 6(12): 382. doi: 10.3390/app6120382 [11] CHEN Y C, TU C H, LIN C L. Integrated electromagnetic braking/driving control of electric vehicles using fuzzy inference[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2019, 13(7): 1014-1021. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2018.5817 [12] FERNÁNDEZ J P, VARGAS M A, GARCÍA J M V, et al. Coevolutionary optimization of a fuzzy logic controller for antilock braking systems under changing road conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(20): 1255-1268. [13] SHAHABI A, KAZEMIAN A H, FARAHAT S, et al. Wheel slip ratio regulation for investigating the vehicle's dynamic behavior during braking and steering input[J]. Mechanics and Industry, 2021, 22: 17. doi: 10.1051/meca/2021016 [14] 王国微, 尹安东. 基于神经网络路面识别的电动汽车ABS控制研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(7): 878-883. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2020.07.003WANG Guo-wei, YIN An-dong. Research on ABS control of electric vehicle based on road recognition using neural network[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 43(7): 878-883. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2020.07.003 [15] 熊璐, 崔天宝, 韩伟, 等. 基于模糊逻辑的电子液压制动系统防抱死控制[J]. 机电一体化, 2018, 24(8): 40-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDTH201808007.htmXIONG Lu, CUI Tian-bao, HAN Wei, et al. Anti-lock braking control for electronic hydraulic braking system based on fuzzy logic[J]. Mechatronics, 2018, 24(8): 40-46. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDTH201808007.htm [16] WU Dong-rui. On the fundamental differences between interval type-2 and type-1 fuzzy logic controllers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(5): 832-848. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2012.2186818 [17] 陈阳, 王大志. 基于加权Karnik-Mendel算法的区间二型模糊逻辑系统降型[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2016, 33(10): 1327-1336. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.60098CHEN Yang, WANG Da-zhi. Type-reduction of interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems with weighted Karnik-Mendel algorithms[J]. Control Theory and Applications, 2016, 33(10): 1327-1336. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.60098 [18] 张彪, 周绍生. 区间二型随机模糊系统的稳定性分析和控制设计[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(7): 985-992. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201507018.htmZHANG Biao, ZHOU Shao-sheng. Stability analysis and control design for interval type-2 stochastic fuzzy systems[J]. Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 32(7): 985-992. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201507018.htm [19] 佃松宜, 梁伟博, 赵涛. 基于改进QPSO的两轮移动机器人区间二型模糊逻辑控制[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(2): 261-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201902005.htmDIAN Song-yi, LIANG Wei-bo, ZHAO Tao. Interval type-2 fuzzy logic control for a two-wheeled mobile robot based on improved QPSO[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(2): 261-268. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC201902005.htm [20] 罗刚, 王永富, 柴天佑, 等. 基于区间二型模糊摩擦补偿的鲁棒自适应控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1298-1306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201907007.htmLUO Gang, WANG Yong-fu, CHAI Tian-you, et al. Robust adaptive control based on interval type-2 fuzzy friction compensation[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1298-1306. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201907007.htm [21] BIN PEEIE M H, OGINO H, OSHINOYA Y. Skid control of a small electric vehicle with two in-wheel motors: simulation model of ABS and regenerative brake control[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2016, 21(5): 396-406. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2016.1147731 [22] YU De-liang, WANG Wen-song, ZHANG Hui-bo, et al. Research on anti-lock braking control strategy of distributed-driven electric vehicle[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 162467-162478. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3021193 [23] YANG Yang, TANG Qing-song, LI Bo-lin, et al. Dynamic coordinated control for regenerative braking system and anti-lock braking system for electrified vehicles under emergency braking conditions[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 172664-172677. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3024918 [24] 姚芳, 林祥辉, 吴正斌, 等. 汽车防抱死制动系统的自抗扰控制研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(3): 235-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.03.018YAO Fang, LIN Xiang-hui, WU Zheng-bin, et al. Active disturbance rejection control for automotive anti-lock braking system[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(3): 235-244. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.03.018 [25] WANG Jun-cheng, HE Ren. Hydraulic anti-lock braking control strategy of a vehicle based on a modified optimal sliding mode control method[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2019, 233(12): 3185-3198. doi: 10.1177/0954407018820445 [26] YANG Feng, CHEN Xin, GUO Dong, et al. Electric-hydraulic compound control anti-lock braking system[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2022, 23(6): 1593-1608. doi: 10.1007/s12239-022-0139-2 [27] 苑磊, 何仁. 基于线性自抗扰控制的汽车ABS滑移率控制研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(9): 1367-1374, 1393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC202109014.htmYUAN Lei, HE Ren. Research on ABS slip ratio control of vehicle based on linear active disturbance rejection control[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(9): 1367-1374, 1393. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC202109014.htm [28] ZHAO Xuan-ming, MO Hong, YAN Ke-fu, et al. Type-2 fuzzy control for driving state and behavioral decisions of unmanned vehicle[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(1): 178-186. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911810 [29] KHALIFA T R, EL-NAGAR A M, EL-BRAWANY M A, et al. A novel Hammerstein model for nonlinear networked systems based on an interval type-2 fuzzy Takagi-Sugeno-Kang system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 29(2): 275-285. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3007460 [30] 靳立强, 孙志祥, 郑迎. 电动轮汽车复合再生制动系统防抱协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1344-1351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201705003.htm [31] 张露, 王国业, 张延立, 等. 电动汽车再生摩擦集成制动系统ABS控制性能研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2015, 46(10): 350-356. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.10.047ZHANG Lu, WANG Guo-ye, ZHANG Yan-li, et al. ABS control performance of integrated brake system with regenerative friction brake in electric vehicle regenerative friction brake in electric vehicle[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(10): 350-356. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.10.047 [32] 周淑文, 陈庆明, 孙大明. 基于EMB系统的整车ABS滑模变结构控制[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(7): 994-997. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.07.018ZHOU Shu-wen, CHEN Qing-ming, SUN Da-ming. Variable structure control with sliding mode for ABS of vehicle based on EMB system[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2016, 37(7): 994-997. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.07.018 [33] PRETAGOSTINI F, FERRANTI L, BERARDO G, et al. Survey on wheel slip control design strategies, evaluation and application to antilock braking systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 10951-10970. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2965644 -





 下载:
下载: