Modeling and prediction method of ship maneuvering motion facing environmental uncertainty
-
摘要: 为解决复杂环境因素影响下的船舶操纵运动预报精度问题,提出了一种面向环境不确定性的船舶操纵运动灰箱辨识建模与预报方法;参考分离型船舶操纵运动模型结构,考虑船舶操纵运动机理,建立了简化的灰箱模型;选取合适的试验对象,运用最小二乘支持向量机算法对建立的船舶操纵运动灰箱模型进行参数辨识,并通过旋回试验和Z形操纵试验测试了模型的泛化性;通过环境不确定性因素分析,构建了波浪作用力干扰模型、数据传输延时模型和感知设备误差模型,并以此为基础,生成了具有多种环境不确定性因素影响的船舶运动响应训练数据;通过仿真试验,验证了预报方法在环境不确定性因素干扰下的预报精度。研究结果表明:在引入环境不确定性因素影响的船舶操纵运动预报试验中,当感知设备误差由0逐渐提升至5%和10%时,除受较小的初始数量级因素影响的横摇速度外,其余船舶运动响应预报结果的均方根误差增幅均小于10%,预测模型的精度可以得到有效保证;而在感知设备误差达到20%的极端条件下,纵荡速度、横荡速度、艏摇速度预报误差相较于0时分别提升4.65%、15.97%、18.17%,误差增幅仍能有效控制在20%以下。可见,船舶操纵运动建模与预报方法可在一定程度上实现环境不确定性因素干扰下的高精度船舶操纵运动预报。Abstract: In response to the issue of prediction accuracy of ship maneuvering motion under complicated environmental factors, a grey box identification modeling and prediction method for ship maneuvering motion under environmental uncertainty was proposed. The separated ship maneuvering motion model structure was referenced, the ship maneuvering motion mechanism was considered, and a simplified grey box model was developed. Suitable test subjects were selected, and parameter identification was conducted on the established ship maneuvering motion grey box model using the least squares support vector machine algorithm. The generalization ability was examined by means of the turning cycle tests and zigzag maneuvering tests. By analyzing the environmental uncertainty factors, the wave force interference model, data transmission delay model, and sensing device error model were constructed. Based on these models, the ship motion response training data affected by multiple environmental uncertainties were generated. Through the simulated tests, the prediction accuracy of the proposed method under environmental uncertainties was validated. Research results reveal that in ship maneuvering motion prediction tests with environmental uncertainty factors, when the sensing device error gradually increases from 0 to 5% and 10%, except for the rolling speed affected by a small initial magnitude, the root mean square errors (RMSEs) of other ship motion response prediction results increase by less than 10%, so the accuracy of the prediction model can be effectively guaranteed. Under the extreme condition with a 20% sensing device error, the prediction errors of surge speed, sway speed, and yawing speed increase by 4.65%, 15.97%, and 18.17%, respectively compared to the 0 error level, so the error increase is effectively controlled below 20%. Thus, the ship maneuvering motion modeling and prediction method can achieve a high-precision prediction of ship maneuvering motion under the interference of environmental uncertainty factors to a certain extent.
-
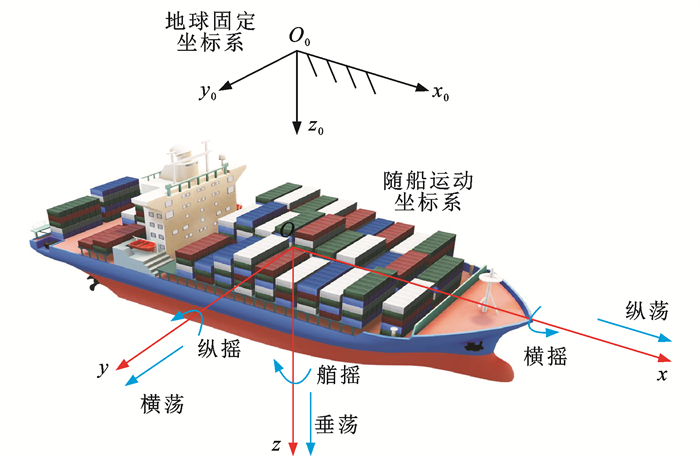
表 1 船舶操纵运动各参数和符号
Table 1. Parameters and symbols of ship maneuvering motion
物理量 x轴方向 y轴方向 z轴方向 速度 纵荡速度u 横荡速度v 垂荡速度ω 角速度 横摇角速度p 纵摇角速度q 艏摇角速度r 力 纵向力X 横向力Y 垂向力Z 力矩 横摇力矩K 纵摇力矩M 艏摇力矩N 转动角 横摇角φ 纵摇角θ 艏摇角ψ 表 2 船舶主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters of ship
船舶部分 参数 数值 船体 船长/m 175 船宽/m 25.4 平均吃水/m 8.5 排水体积/m3 21 222 方形系数 0.559 菱形系数 0.58 浮心纵坐标/m 0.8 螺旋桨 螺距比 1.009 螺旋桨直径/m 6.533 船舵 舵面积/m2 33.037 6 舵叶高/m 7.758 3 舵展弦比 1.821 9 表 3 辨识参数a1~a7结果对比
Table 3. Results comparison of identification parameters a1-a7
参数 实际值 SVM LS-SVM(多项式核) LS-SVM(线性核) 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% a1 -0.000 000 29 -0.000 000 29 0.00 -0.000 000 29 0.00 -0.000 000 29 0.00 a2 -0.000 073 09 -0.000 071 10 2.72 -0.000 072 39 0.96 -0.000 072 18 1.25 a3 -0.001 457 04 -0.001 434 13 1.57 -0.001 399 43 3.95 -0.001 438 53 1.27 a4 0.907 771 59 0.903 933 34 0.42 0.910 438 28 0.29 0.911 635 92 0.43 a5 8.884 944 44 8.806 729 29 0.88 8.770 213 97 1.29 8.900 255 72 0.17 a6 0.022 659 59 0.023 012 62 1.56 0.022 345 10 1.39 0.022 665 56 0.03 a7 0.000 000 02 0.000 000 02 0.00 0.000 000 02 0.00 0.000 000 02 0.00 表 4 辨识参数b1~b7结果对比
Table 4. Results comparison of identification parameters b1-b7
参数 实际值 SVM LS-SVM(多项式核) LS-SVM(线性核) 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% b1 -0.049 617 18 -0.049 163 92 0.91 -0.049 223 49 0.79 -0.050 105 66 0.98 b2 2.351 321 57 2.305 617 39 1.94 2.297 371 16 2.29 2.363 733 14 0.53 b3 -0.719 577 94 -0.721 057 47 0.21 -0.715 657 80 0.54 -0.712 723 42 0.95 b4 -0.016 349 38 -0.016 667 46 1.92 -0.016 434 06 0.52 -0.016 191 90 0.96 b5 0.700 191 47 0.694 044 18 0.88 0.682 917 40 2.47 0.691 264 30 1.27 b6 -16.624 404 30 -16.389 888 80 1.41 -16.480 080 10 0.87 -16.723 567 60 0.60 b7 0.000 000 03 0.000 000 03 0.00 0.000 000 03 0.00 0.000 000 03 0.00 表 5 辨识参数c1~c8结果对比
Table 5. Results comparison of identification parameters c1-c8
参数 实际值 SVM LS-SVM(多项式核) LS-SVM(线性核) 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% c1 -0.000 153 60 -0.000 153 87 0.18 -0.000 148 71 3.18 -0.000 151 47 1.39 c2 -0.154 792 83 -0.157 176 09 1.54 -0.154 363 12 0.28 -0.154 855 89 0.04 c3 0.003 359 45 0.003 400 62 1.23 0.003 472 35 3.36 0.003 338 40 0.63 c4 -0.160 294 87 -0.155 069 42 3.26 -0.156 557 90 2.33 -0.157 363 69 1.83 c5 0.001 070 22 0.001 099 11 2.70 0.001 091 84 2.02 0.001 089 65 1.82 c6 -0.042 358 33 -0.043 156 25 1.88 -0.042 662 44 0.72 -0.042 332 88 0.06 c7 1.890 381 41 1.907 600 78 0.91 1.899 991 69 0.51 1.908 146 97 0.94 c8 -0.000 000 02 -0.000 000 02 0.00 -0.000 000 02 0.00 -0.000 000 02 0.00 表 6 辨识参数d1~d9结果对比
Table 6. Results comparison of identification parameters d1-d9
参数 实际值 SVM LS-SVM(多项式核) LS-SVM(线性核) 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% 辨识值 误差/% d1 -0.001 684 95 -0.001 681 57 0.20 -0.001 738 22 3.16 -0.001 699 62 0.87 d2 -0.139 527 25 -0.137 589 79 1.39 -0.140 386 58 0.62 -0.139 302 33 0.16 d3 -0.114 888 94 -0.117 081 82 1.91 -0.115 708 05 0.71 -0.115 976 92 0.95 d4 -1.950 281 07 -2.007 297 55 2.92 -1.925 972 44 1.25 -1.965 205 09 0.77 d5 -0.933 494 72 -0.919 446 13 1.50 -0.916 512 48 1.82 -0.923 135 09 1.11 d6 -0.001 636 63 -0.001 663 34 1.63 -0.001 646 35 0.59 -0.001 643 57 0.42 d7 -0.002 635 53 -0.002 601 33 1.30 -0.002 626 50 0.34 -0.002 626 79 0.33 d8 0.419 498 29 0.416 518 18 0.71 0.421 785 57 0.55 0.421 283 48 0.43 d9 -0.000 000 01 -0.000 000 01 0.00 -0.000 000 01 0.00 -0.000 000 01 0.00 表 7 辨识时间消耗对比
Table 7. Comparison of identification time
s 辨识算法 SVM LS-SVM(多项式核) LS-SVM(线性核) 辩识时间 0.45 0.56 0.19 表 8 灰箱辨识模型的RMSE
Table 8. RMSEs of grey box identification model
辨识算法 RMSE 纵荡速度/(m·s-1) 纵荡速度/(m·s-1) 横摇角速度/[(°)·s-1] 艏摇角速度/[(°)·s-1] SVM 0.177 0.271 0.451 0.168 LS-SVM(多项式核) 0.156 0.296 0.584 0.189 LS-SVM(线性核) 0.134 0.129 0.153 0.053 表 9 波浪参数设置
Table 9. Setting of wave parameters
参数 波高/m 波浪周期/s 波长/m 波浪方向/(°) 数值 1.5 5.5 50 45 表 10 船舶运动响应RMSE
Table 10. RMSEs of ship motion response
感知设备误差/% RMSE 纵荡速度/(m·s-1) 横荡速度/(m·s-1) 横摇角速度/[(°)·s-1] 艏摇角速度/[(°)·s-1] 0 0.129 0.169 0.020 0.073 5 0.131 0.171 0.020 0.074 10 0.131 0.184 0.036 0.081 20 0.135 0.196 0.103 0.087 -
[1] 严新平, 贺亚鹏, 贺宜, 等. 水路交通技术发展趋势[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2022, 22(4): 1-9. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2022.04.001YAN Xin-ping, HE Ya-peng, HE Yi, et al. Development trends of waterway transportation technology[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2022, 22(4): 1-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2022.04.001 [2] 赵百岗, 张显库, 李争, 等. 船舶运动辨识建模研究现状与展望[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2021, 43(23): 21-24. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2021.12.004ZHAO Bai-gang, ZHANG Xian-ku, LI Zheng, et al. Research on ship motion identification modeling[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2021, 43(23): 21-24. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2021.12.004 [3] ZHANG Yan-yun, WANG Zi-hao, ZOU Zao-jian. Black-box modeling of ship maneuvering motion based on multi-output nu-support vector regression with random excitation signal[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 257: 111279. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111279 [4] 张秀凤, 王晓雪, 孟耀, 等. 船舶运动建模与仿真研究进展及未来发展趋势[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2021, 47(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLHS202101001.htmZHANG Xiu-feng, WANG Xiao-xue, MENG Yao, et al. Research progress and future development trend of ship motion modeling and simulation[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2021, 47(1): 1-8. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLHS202101001.htm [5] 卢冠宇, 姚建喜. 基于SVR的船舶操纵运动黑箱建模[J]. 中国航海, 2021, 44(4): 13-19, 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2021.04.003LU Guan-yu, YAO Jian-xi. Black-box modeling of ship maneuvering by means of SVR[J]. Navigation of China, 2021, 44(4): 13-19, 31. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2021.04.003 [6] 梅斌, 孙立成, 史国友, 等. 基于单参数自调节RM-GO-LSVR的船舶操纵灰箱辨识建模[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(2): 88-99. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.008MEI Bin, SUN Li-cheng, SHI Guo-you, et al. Grey box identification modeling for ship maneuverability based on single parameter self-adjustable RM-GO-LSVR[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(2): 88-99. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.008 [7] LUO Wei-lin, ZOU Zao-jian. Identification of response models of ship maneuvering motion using support vector machines[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2007, 11(6): 832-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2007.06.003 [8] WANG Xue-gang, ZOU Zao-jian, YU Long, et al. System identification modeling of ship manoeuvring motion in 4 degrees of freedom based on support vector machines[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2015, 29(4): 519-534. doi: 10.1007/s13344-015-0036-9 [9] CHEN Li-jia, YANG Pei-yi, LI Sheng-wei, et al. Grey-box identification modeling of ship maneuvering motion based on LS-SVM[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 112957. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112957 [10] 徐锋, 刘志平, 郑海斌, 等. 基于LS-SVM的船舶操纵运动在线建模[J]. 船舶力学, 2021, 25(6): 752-759. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2021.06.007XU Feng, LIU Zhi-ping, ZHENG Hai-bin, et al. On-line modeling of ship maneuvering motion by using LS-SVM[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2021, 25(6): 752-759. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2021.06.007 [11] 谢朔, 初秀民, 柳晨光, 等. 基于改进LSSVM的船舶操纵运动模型在线参数辨识方法[J]. 中国造船, 2018, 59(2): 178-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.02.019XIE Shuo, CHU Xiu-min, LIU Chen-guang, et al. Online parameter identification method for ship maneuvering models based on improved LSSVM[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2018, 59(2): 178-189. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.02.019 [12] 邱文钦, 唐存宝, 唐强荣. 不确定条件下内河航道通航环境风险评价[J]. 中国航海, 2019, 42(1): 52-55, 67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.01.011QIU Wen-qin, TANG Cun-bao, TANG Qiang-rong. Navigation environment risk assessment of uncertain inland waterway[J]. Navigation of China, 2019, 42(1): 52-55, 67. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.01.011 [13] 范存龙, 张笛, 姚厚杰, 等. 海上自主水面船舶航行风险识别[J]. 中国航海, 2019, 42(2): 75-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.02.015FAN Cun-long, ZHANG Di, YAO Hou-jie, et al. Navigational risk identification for maritime autonomous surface ship[J]. Navigation of China, 2019, 42(2): 75-82. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.02.015 [14] 黄柏刚, 邹早建. 基于固定网格小波神经网络的不规则波中船舶横摇运动在线预报[J]. 船舶力学, 2020, 24(6): 693-705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2020.06.001HUANG Bai-gang, ZOU Zao-jian. Online prediction of ship roll motion in irregular waves using a fixed grid wavelet network[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2020, 24(6): 693-705. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2020.06.001 [15] WANG Tong-tong, LI Guo-yuan, WU Bai-hang, et al. Parameter identification of ship manoeuvrling model under disturbance using support vector machine method[J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2021, 16(S1): 13-21. [16] 夏召丹, 马翔, 刘义, 等. 基于虚实结合的波浪环境下船舶操纵运动机器学习建模研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2022, 37(6): 763-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDLJ202206003.htmXIA Zhao-dan, MA Xiang, LIU Yi, et al. Machine learning for ship maneuvering in wave[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2022, 37(6): 763-768. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDLJ202206003.htm [17] JIANG Yan, HOU Xian-rui, WANG Xue-gang, et al. Identification modeling and prediction of ship maneuvering motion based on LSTM deep neural network[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2022, 27(1): 125-137. doi: 10.1007/s00773-021-00819-9 [18] XUE Yi-fan, CHEN Gang, LI Zhi-tong, et al. Online identification of a ship maneuvering model using a fast noisy input Gaussian process[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 250: 110704. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110704 [19] 姜岩, 王雪刚, 侯先瑞, 等. 深度循环神经网络在船舶操纵运动辨识中的对比研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2023, 38(2): 187-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDLJ202302004.htmJIANG Yan, WANG Xue-gang, HOU Xian-rui, et al. Comparative study on identification of ship maneuvering motion based on deep recurrent neural network[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 2023, 38(2): 187-194. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDLJ202302004.htm [20] ZHOU Xiao, ZOU Lu, OUYANG Zi-lu, et al. Nonparametric modeling of ship maneuvering motions in calm water and regular waves based on R-LSTM hybrid method[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 285: 115259. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115259 [21] 曾道辉, 蔡成涛. 基于修正辅助变量法的船舶操纵响应模型辨识[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2023, 44(2): 161-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBG202302001.htmZENG Dao-hui, CAI Cheng-tao. Identification of the ship maneuvering response model based on recursive refined instrumental variable least-squares[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2023, 44(2): 161-171. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBG202302001.htm [22] 曾柯, 顾民, 鲁江, 等. 方形波浪中船舶参数横摇数值模拟方法研究[J]. 中国造船, 2021, 62(4): 65-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2021.04.005ZENG Ke, GU Min, LU Jiang, et al. Numerical prediction of parametric rolling of ships in cross waves[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2021, 62(4): 65-74. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2021.04.005 [23] SON K, NOMOTO K. On the coupled motion of steering and rolling of a high speed container ship[J]. Journal of the Society of Naval Architects of Japan, 1981, 1981(150): 232-244. doi: 10.2534/jjasnaoe1968.1981.150_232 [24] HU Yi, SONG Li-fei, LIU Zu-yuan, et al. Identification of ship hydrodynamic derivatives based on LS-SVM with wavelet threshold denoising[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(12): 1356-1356. doi: 10.3390/jmse9121356 [25] CHEN Li-jia, YANG Pei-yi, LI Shi-gang, et al. Online modeling and prediction of maritime autonomous surface ship maneuvering motion under ocean waves[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 276: 114183. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114183 [26] NIE Zhi-hong, SHEN Feng, XU Ding-jie, et al. An EMD-SVR model for short-term prediction of ship motion using mirror symmetry and SVR algorithms to eliminate EMD boundary effect[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 217: 107927. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107927 [27] 孟耀, 张秀凤, 陈雨农. 基于改进灰狼算法的船舶数学模型参数辨识[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2023, 44(8): 1304-1312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBG202308009.htmMENG Yao, ZHANG Xiu-feng, CHEN Yu-nong. Parameter identification of a ship mathematical model based on the modified grey wolf algorithm[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2023, 44(8): 1304-1312. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBG202308009.htm [28] 侯先瑞. 基于支持向量回归机的波浪中船舶运动辨识建模研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017.HOU Xian-rui. Identification modeling of ship motions in waves based on support vector regression[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2017. (in Chinese) [29] 张心光. 基于支持向量回归机的船舶操纵运动在线辨识建模[J]. 船舶工程, 2019, 41(3): 98-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CANB201903022.htmZHANG Xin-guang. Online identification modeling of ship manoeuvring motion using support vector regression[J]. Ship Engineering, 2019, 41(3): 98-101. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CANB201903022.htm [30] WANG Zi-hao, XU Hai-tong, XIA Li, et al. Kernel-based support vector regression for nonparametric modeling of ship maneuvering motion[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 216: 107994. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107994 [31] SHEN Wen-he, YAO Jiang-xi, HU Xin-jue, et al. Ship dynamics model identification based on semblance least square support vector machine[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 287: 115908. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115908 [32] 董磊, 马翔, 封佳祥, 等. 基于改进LSTM的船舶操纵运动在线预报方法研究[J]. 中国造船, 2023, 64(2): 184-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2023.02.017DONG Lei, MA Xiang, FENG Jia-xiang, et al. Online prediction method of ship maneuvering motion based on improved long-short term memory neural network[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2023, 64(2): 184-198. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2023.02.017 [33] LUO Wei-lin, SOARES C G, ZOU Zao-jian. Parameter identification of ship maneuvering model based on support vector machines and particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 2016, 138(3): 031101. doi: 10.1115/1.4032892 [34] 刘长德, 顾宇翔, 张进丰. 基于小波滤波和LSTM神经网络的船舶运动极短期预报研究[J]. 船舶力学, 2021, 25(3): 299-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2021.03.005LIU Chang-de, GU Yu-xiang, ZHANG Jin-feng. Extreme short-term prediction of ship motions based on wavelet filter and LSTM neural network[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2021, 25(3): 299-310. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2021.03.005 [35] PARAND K, AGHAEI A A, JANI M, et al. Parallel LS-SVM for the numerical simulation of fractional Volterra's population model[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2021, 60(6): 5637-5647. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2021.04.034 [36] 沈文君, 赵志娟, 刘利琴, 等. 波浪周期对小型船舶动力响应的影响研究[J]. 船舶力学, 2022, 26(3): 342-352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2022.03.004SHEN Wen-jun, ZHAO Zhi-juan, LIU Li-qin, et al. Research of wave period effect on the dynamic response characteristics of a small ship[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2022, 26(3): 342-352. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2022.03.004 [37] 张腾, 任俊生, 梅天龙. 基于傅汝德-克雷洛夫力非线性法的规则波浪中船舶运动数学模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(2): 77-87. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.007ZHANG Teng, REN Jun-sheng, MEI Tian-long. Mathematical model of ship motions in regular waves based on Froude-Krylov force nonlinear method[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(2): 77-87. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.007 [38] 钱小斌, 尹勇, 张秀凤, 等. 海上不规则波浪扰动对船舶运动的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(3): 116-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.03.014QIAN Xiao-bin, YIN Yong, ZHANG Xiu-feng, et al. Influence of irregular disturbance of sea wave on ship motion[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(3): 116-124. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.03.014 [39] 江洪, 孙士尉, 魏常进, 等. 智能航运船岸通信系统设计与网络数据传输优化[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2020, 42(20): 178-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCKX202020061.htmJIANG Hong, SUN Shi-wei, WEI Chang-jin, et al. Design of intelligent shipping ship-shore communication system and optimization of network data transmission[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2020, 42(20): 178-180. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCKX202020061.htm [40] SUTULO S, GUEDES SOARES C. An algorithm for offline identification of ship manoeuvring mathematical models from free-running tests[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2014, 79: 10-25. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.01.007 -





 下载:
下载: