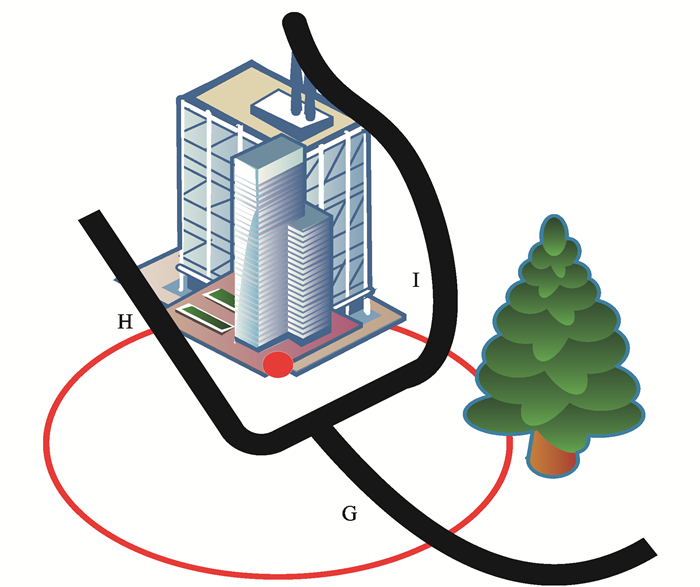
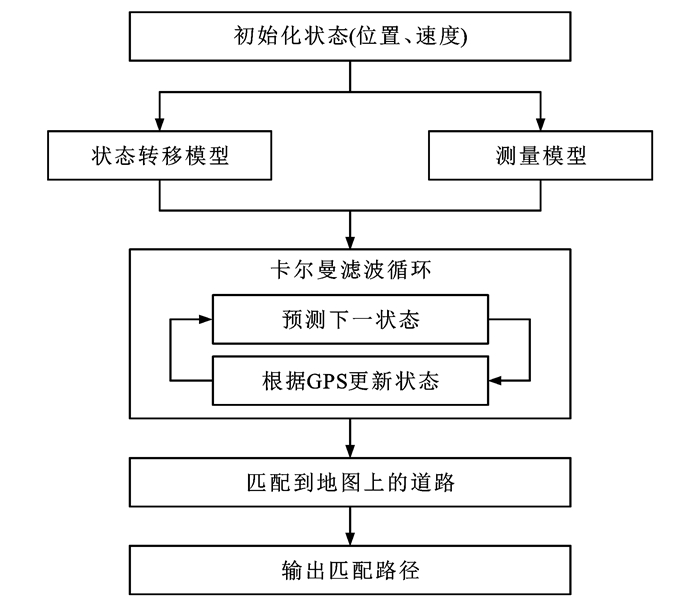
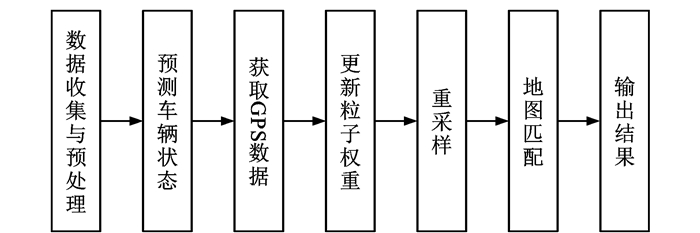
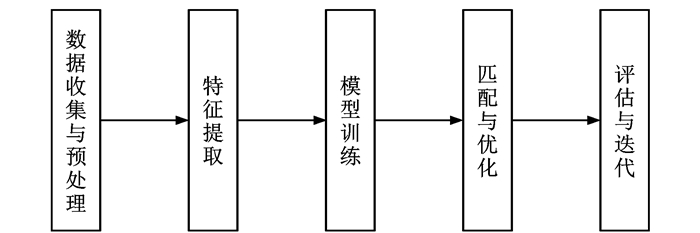
Review on map matching technologies in intelligent transportation scenarios
-
摘要: 为推动地图匹配技术的发展,从匹配方法角度深入研究地图匹配算法并分类阐述原理、特点及应用场景,全面介绍了现有地图匹配数据集,总结了地图匹配在智能交通领域的应用场景,提出了地图匹配技术未来的研究方向。研究结果表明:GPS数据的准确性和完整性可能会因多种因素而受到影响,导致轨迹数据变得稀疏,稀疏的GPS轨迹会导致车辆的实际行驶路径无法被准确还原,增加地图匹配的不确定性;车道级匹配需求因智能交通系统的发展、自动驾驶技术的兴起和城市交通网络的日益复杂等因素而日益迫切;未来地图匹配技术的研究方向主要集中在2个方面;对于稀疏轨迹的地图匹配技术,需聚焦数据插值技术,提高轨迹的连续性,运用多传感器数据融合技术,增强定位的准确性和可靠性,应用深度学习技术,提高匹配算法的智能水平;对于车道级的地图匹配技术,重点在于整合高精度地图数据和实时交通信息,提供更准确的道路特征和交通状况信息,优化深度学习模型,识别复杂的交通模式和道路特征,开发适应动态交通环境的算法,提高算法的稳定性和适应性;这些研究方向将有助于提高地图匹配技术的准确性、可靠性和实时性,为智能交通系统和自动驾驶技术提供更有力的支持。Abstract: To promote the development of map matching technology, an in-depth study of map-matching algorithms was conducted from the perspective of matching methods. The principles, characteristics, and application scenarios were classified and described. The existing map matching datasets were comprehensively introduced. The application scenarios of map matching in the field of intelligent transportation were summarized, and future research directions for map matching technology were proposed. Research results indicate that the accuracy and completeness of global position system (GPS) data can be affected by various factors, which results in sparse trajectory data. Sparse GPS trajectories can result in the inability to accurately reconstruct the actual driving paths of vehicles, increasing the uncertainty in map matching. The demand for lane-level matching has become increasingly urgent due to the development of intelligent transportation systems, the rise of autonomous driving technology, and the growing complexity of urban transportation networks. The future research directions of map matching technology primarily focus on two aspects. For map matching technology with sparse trajectories, attention needs to be paid to data interpolation techniques to improve trajectory continuity, multi-sensor data fusion technology should be employed to enhance the accuracy and reliability of positioning, and deep learning techniques should be applied to improve the intelligence level of matching algorithms. For lane-level map matching technology, the focus lies in integrating high-precision map data with real-time traffic information to provide more accurate information on road characteristics and traffic conditions, optimizing deep learning models to recognize complex traffic patterns and road characteristics, and developing algorithms that adapt to dynamic traffic environments to obtain algorithms with improved stability and adaptability. These research directions will help enhance the accuracy, reliability, and real-time performance of map matching technology and provide stronger support for intelligent transportation system and autonomous driving technology.
-
Key words:
- intelligent transportation system /
- map matching /
- hidden Markov model /
- deep learning /
- GPS trajectory
-
0. 引言
现代道路交通系统中,以电动车辆为代表的载运装备动力清洁化的技术革新一直是国内外研究的热点。而电动车辆行驶时的动态无线电能传输技术可有效缓解里程焦虑,提升续航里程,这一技术引发了交通工程领域的深刻变革,相关的技术水平快速提高[1-4]。然而如何对动态无线充电车辆进行准确的特征识别,实现车辆分型是这一技术在智能交通系统中应用所面临的一个关键问题。
在传统车辆的分类方法中,车辆地磁信息检测技术得到了较多的研究和应用[5-7]。Wahlström等[8]对静止车辆的磁场分布情况进行了研究,同时研究了2个传感器节点偏离车辆中心轴时传感器的输出;Li等[9]通过分析采集的地磁扰动波形,提取了相对车长、波形总能量、波形平均能量等特征,采用分层决策树算法进行车型分类;He等[10]将传感器采集的三轴信息中2个方向的信息映射到二维空间中,通过闭合曲线变化趋势来判断车辆有无和车辆行驶方向;Balid等[11]研究了一种新型的交通监测智能车辆计数和分类传感器,用于车辆检测、速度和长度估计,并实时对车辆进行分类。国内学者中,马芳兰等[12]主要研究车型分类算法,通过动态基准值算法将车辆信号从原始信号中分离;张增超等[13]提出了一种改进的基于有向无环图的支持向量机车型分类算法;林渊博等[14]提出通过地磁传感器采集停车位磁场变化,结合状态机与自适应匹配算法来实现分类检测;叶青等[15]研究了一种基于环形线圈车辆电磁感应波形的新实时车型判别法, 结合了自适应共振神经网络进行聚类建模来动态分类车型。以上文献的车型分类方法中选择的特征有峰值、谷值、峰值谷值比、峰值时间、谷值时间、峰值谷值时间比、波形总能量、波形平均能量等。这些特征具有独立性、可区分性、数量少的优点,但是稳定性不高,需要通过算法提高分类精度,并且这些现有的分型方法不能识别无线充电车辆的特征。
故对于新能源无线充电车辆的分型而言,有必要研究更好的车辆特征信息捕捉技术。良好的车辆特征信息应具有可区分性强、稳定性高、特征之间具有独立性和特征数量少等特点。张献等[16]主要研究了动态无线供电系统的电能耦合机构与切换控制方法;Nagendra等[17-18]报告了一种电动车辆检测方法,该方法利用特设的路面发射器线圈产生的自由谐振电流识别无线充电车辆,这类发射器线圈必须足够靠近车辆才能感应谐振电流,并且发射器线圈的启动也需进行额外的时序控制;Wang等[19]研究了电动汽车充电中的动态无线电力传输系统接收器的位置传感,利用谐振器阵列输入阻抗识别接收器线圈位置,提出了简单有效的定位算法;Patil等[20]提出了一种新型正交线圈排列的电动汽车高速行驶检测系统,用于依次启动路侧的电能传输装置;Sonapreetha等[21]研究了非重叠线圈设置作为异物和车辆位置的无线固定电动汽车充电器检测;Deng等[22-23]通过捕获感应电压和电流的相角差等方法来检测电动汽车的边缘和位置;Hasan等[24]对时变的功率传输和效率分布进行解析描述,提出了不依赖线圈位置检测的电能传输控制算法;Lu等[25]对一种基于电容电感(CL)补偿的混合无线电能传输系统进行研究;Feng等[26]通过磁传感器进行道路交通监控,采用多个磁偶极子来模拟行驶中的车辆,通过对移动车辆造成的局部磁场扰动进行建模,用于车辆识别和速度估算;徐诗卉等[27]研究了一种新型方形线圈,提出了优化的近距离精确定位方法,解决了磁偶极子模型的传统定位方法误差较大的问题;Chen等[28]对动态无线电能传输技术的发展进行了综述性质的研究;白叶红等[29-30]利用交通仿真和非线性优化方法研究了充电车道的长度,最小化系统成本。
通过以上文献分析可以看出,与无线充电车辆特征相关的技术研究主要围绕在电动汽车动态无线充电的快速响应方法领域,实现相关车型分类的研究却较少涉及。
本文基于车-路协同搭建了一种基于混合电磁感应单元和地磁场感应单元的复合感应装置,完成无线充电车辆的磁电数据捕获,以实现其动态分型。其中,所提出的混合电磁感应单元由车载端的电感线圈和车载辅助电容极板,配合路面端敷设的电容极板和感应线圈组成,以谐振电流的有效值检测为特征实现无线充电车辆的识别。这一单元电路拓扑具有高阶的双边CL补偿结构,与传统的单一磁场感应或电场感应技术相比,这一混合耦合感应装置不仅可以节约电容极板元件的尺寸,还可以改善半开域耦合的缺陷,扩大检测范围,有效识别动态无线充电车辆。在地磁场感应单元中,提出了一种基于集合经验模态分解(Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition,EEMD)的地磁波形特征向量提取法,进一步实现具体的小型三厢轿车、中型两厢轿车、中型厢式货车和大型客车等4种形状类型的判断。这样,在地磁场感应单元与混合电磁感应单元相互“与”的逻辑配合下,这一车-路协同磁电特征捕获装置可实现车辆的无线充电信息和明显车辆型式等2个典型特征的动态抗偏移识别,有助于公路交通系统的智能调度和管理。
1. 系统组成
无线充电车辆动态分型系统由路面感应、中继节点和后台数据分析等3个子系统构成,而本文主要研究的路面感应子系统包括混合电磁场感应单元和地磁场感应单元2部分。
混合电磁场感应单元由车载侧和路侧2个部分配合组成。车载侧利用车载无线充电的感应线圈并添加辅助电容极板去传输电能,而路侧部分则由路面敷设的电容极板、电能接收和信号传输电路组成。地磁场感应单元由若干个三轴地磁传感器组成。系统的中继节点可采用WiFi路由器安装在灯杆或路面立杆,通过上位机软件实现传感数据的接收、处理和车辆信息解算,得出无线充电车辆的类型。复合感应系统的场景如图 1所示。
2. 混合电磁感应单元
2.1 电路拓扑
本文的混合电磁感应电路拓扑结构如图 2所示,图中:L1为混合电磁感应单元电路的电感线圈的电感量;L2为这一感应单元电路在路侧端感应线圈的电感量;M12为线圈之间的互感;Vin为这一感应单元在车载侧设定的独立直流电压;Lf1和Lf2分别为原、副边谐振网络的补偿电感;C1和C2分别为原、副边补偿电容;Cf1和Cf2分别为原、副边谐振网络并联补偿电容;C0为路侧感应电路的滤波电容;CS1和CS2均为感应系统中耦合极板的等效电容;P1、P3均为一次侧极板;P2、P4均为二次侧极板,且由红色虚线分隔开,P1和P2耦合极板放在车载底盘,而P3和P4敷设在路侧表面,由路侧端接收感应电能并通过信号传输模块发送给中继节点;S1~S4均为金属氧化物半导体场效应管;D1~D4均为整流二极管;V1为原边谐振网络等效的高频交流电压;V2为路侧端谐振网络等效的输出用交流电压;i1为流过车载侧并联补偿电容的电流;i2为流过路侧并联补偿电容的电流。
图 2中,L1可以选择利用车载侧无线电能接收端的充电耦合线圈得到,即感应单元与充电机构两者共用主电感。而两者的电路结构和谐振参数都不同,实际上各自独立,互不影响。
值得指出的是,这一混合电磁感应单元的电路拓扑本身含有2种耦合形式,即极板之间形成的电场耦合和线圈之间形成的磁场耦合,其中电场耦合为电容电能传输(Capacitive Power Transfer,CPT),磁场耦合为感应电能传输(Inductive Power Transfer, IPT),且该拓扑具有高阶的双边CL补偿结构。与传统的单一磁场感应或电场感应技术相比,这一混合耦合感应装置不仅可以节约电容极板元件的尺寸,而且有助于改善半开域耦合缺陷,扩大动态无线充电车辆的有效识别范围。
2.2 混合电磁耦合器设计
混合电磁感应电路的简化拓扑如图 3所示,系统输入在经过车载端的高频逆变器后会产生方波电压,C1和C2两端电压分别为Vc1和Vc2。
这一电路得到的输出功率Pout包含电场耦合输出功率PCPT和磁场耦合输出功率PIPT两部分,即
Pout=PCPT+PIPT (1) {PCPT=CSCf1Cf2ω|V1||V2|C1CS+C1C2+C2CSPIPT=M12|V1||V2|ωLf1Lf2 (2) M12=k√L1L2 (3) 式中:CS为等效电容;ω为系统工作角频率;k为耦合系数。
由于C1和C2都远大于CS,则电路的输入功率Pin=Pout,因此,可将式(1)化简为
Pin =Pout ≈ωCSCf1Cf2|V1||V2|C1C2+k√L1L2|V1||V2|ωLf1Lf2 (4) 将IPT子系统和CPT子系统传输的功率比用rI-C表示,则可得
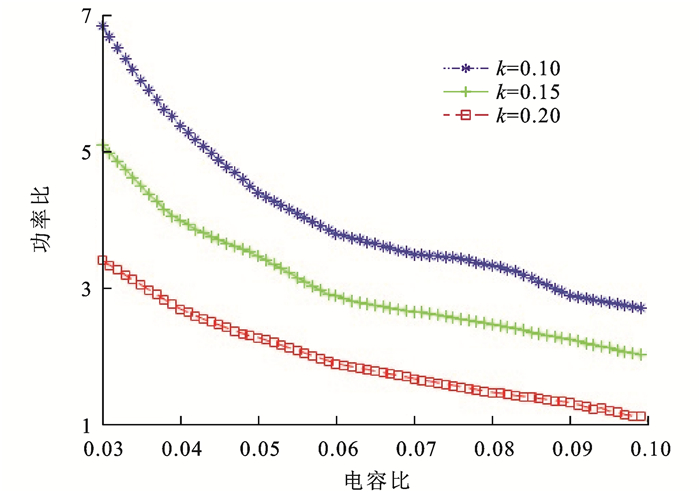
rI−C=PIPTPCPT=(CSC2+C2C1+CSC1)M12CSCf2Cf1Lf2Lf1ω2 (5) 将CS和C1之间的电容比kc定义为kc=CS/C1,通过对式(5)进一步化简和分析,在车载端和路侧端线圈的耦合系数k分别取0.10、0.15和0.20时,可得出线圈与极板传输的功率比rI-C与电容比kc关系曲线,如图 4所示。若k=0.15,则rI-C的变化范围是2.00~5.10。
2.3 开域耦合状态
在感应线圈出现位置偏移时,线圈完全错开属于开域耦合,其场强远小于闭域耦合,从而难以检测。可以用有限元方法对磁场强度φ用场强梯度泛函数F(·)表征
F(φ)=m∑e=1F(φe) (6) 式中:φe为第e个分格单元的磁场强度;m为分格的单元总数。
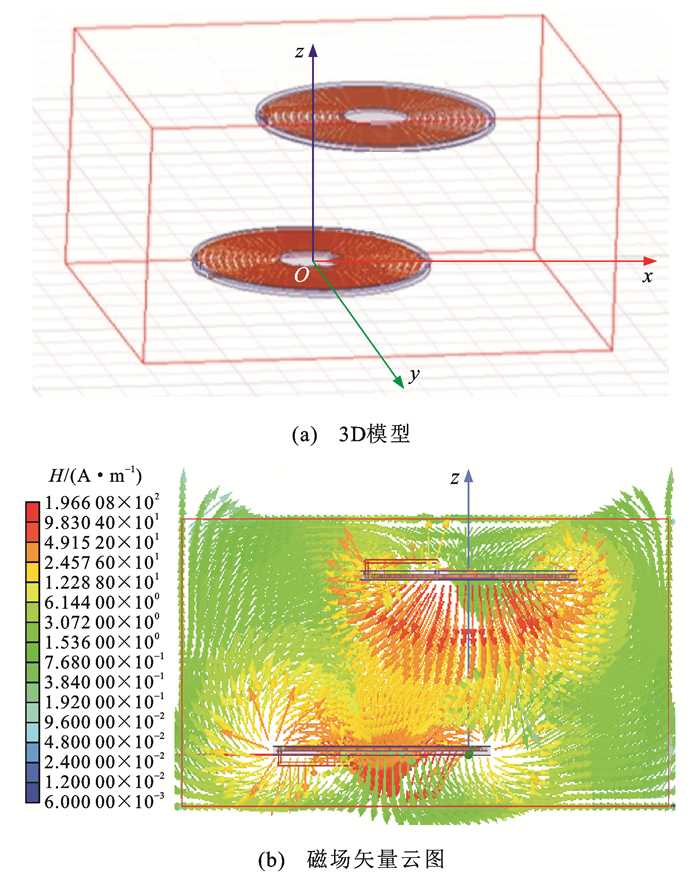
介于开域和闭域之间,称之为半开域耦合。建立一个以车载端线圈中心为原点O的Oxyz坐标系,其中,沿线圈水平向右为x轴正方向,垂直于线圈平面向上为z轴正方向,垂直于xOz平面向外为y轴正方向。图 5是在本文的试验条件下,当对称线圈的一侧沿x轴正方向偏移11 cm时,感应线圈系统的半开域磁耦合的3D模型及其磁场强度H的云图。
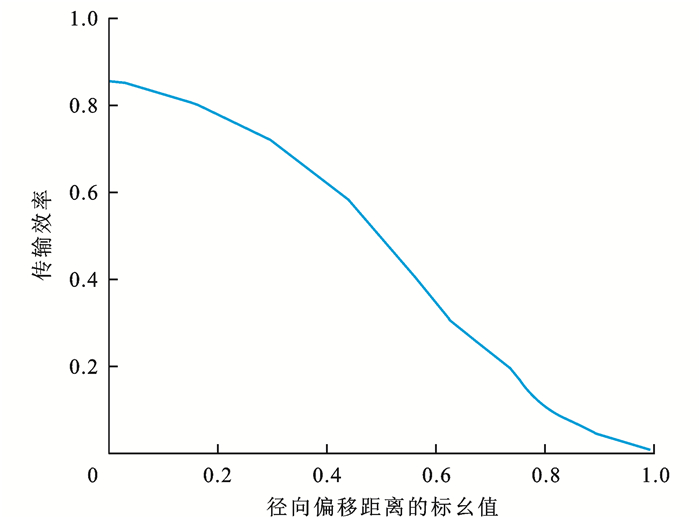
经过数值分析,可得出电感线圈径向偏移后,感应信号的无线传输效率随径向偏移距离变化的曲线,如图 6所示,图中采用了单位化的表征方法,横坐标是径向偏移距离的标幺值σ。
以r为耦合电感线圈的外圈半径,x1为电感线圈的径向偏移距离,则σ为
σ=x12r (7) 可见,与完全闭域耦合相比,在半开域耦合情况下的系统场分布变化复杂,出现更多的边缘通量和磁漏,均匀性变差,平均磁场强度降低约26%。而在径向偏移使线圈完全错开的全开域情况下,系统感应电能的传输效率接近为0,不能实现有效感应。
可以加入电容极板所形成的电场耦合,以对磁耦合偏移的缺失进行补充。在磁场全开域的耦合状态下,混合电磁感应的电场耦合机构结构3D视图如图 7所示,图中:车载侧作为发射端由2块电场极板P1、P2和线圈L1组成,路侧端由极板P3、P4和线圈L2进行感应接收,上下结构完全对称;d为相邻电容极板的水平距离;h为电容极板的z向间隙距离。图 7中,假定作为车载端的上极板向右侧偏移一个x1的距离,则橘色线框是此时平板电容的有效极板范围,其x轴向的有效极板边长是一个变化量c。
在不同的半开域和全闭域2种耦合状态下,线圈与极板传输的功率比不同。在本文系统测试的参数条件下,rI-C与其输出电压基波有效值U2的关系曲线如图 8所示,水平移动车载端电容极板的位置,使耦合机构处于rI-C= 0.5的半开域耦合条件下,检测到输出直流电压为6.0 V,在rI-C≥2.0后,系统进入全闭域状态,系统等效负载的输出直流电压为9.6 V。
3. 地磁场感应单元
3.1 基于EEMD的地磁扰动信号预处理
通过地磁传感器可捕获车辆通过时的地磁场扰动信号,从而得出车辆的分型信息。然而这一地磁扰动信号内通常含有叠加的杂波,不利于被测信号的特征提取。
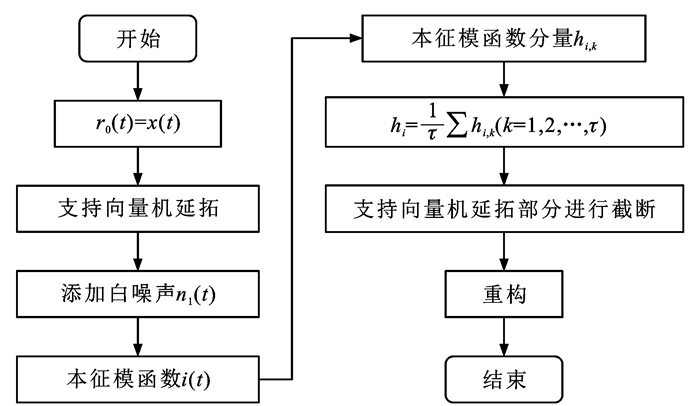
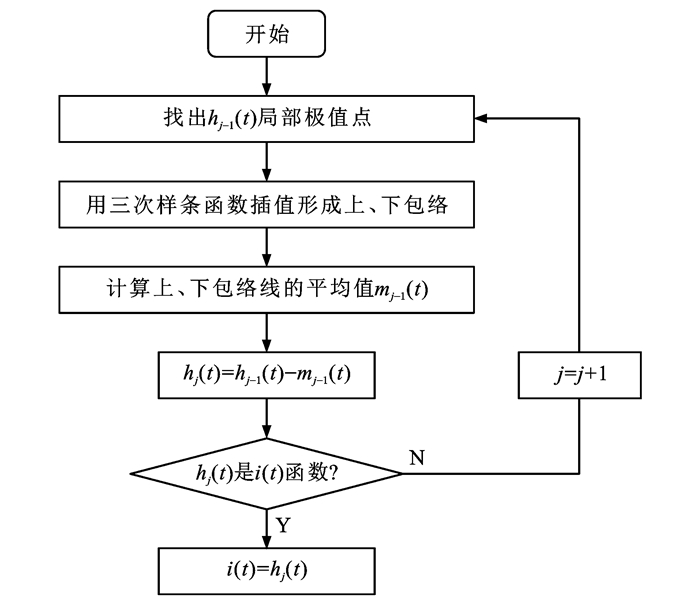
EEMD法在分析非线性非平稳信号方面具有较高信噪比的优势,本文据此使用一种新的基于EEMD的地磁场扰动信号数据滤波方法,该方法主要有8个步骤,主要流程如图 9所示:x(t)为t时刻的原始信号;r0(t)为t时刻的初始剩余信号;n1(t)为t时刻的白噪声;i(t)为对t时刻原始复杂信号分解的i个本征模函数(i =1, 2,…,n)。为了抑制端点效应,对每个本征模函数都进行了k次的平行延拓极值,hi为其分量的集合平均值。
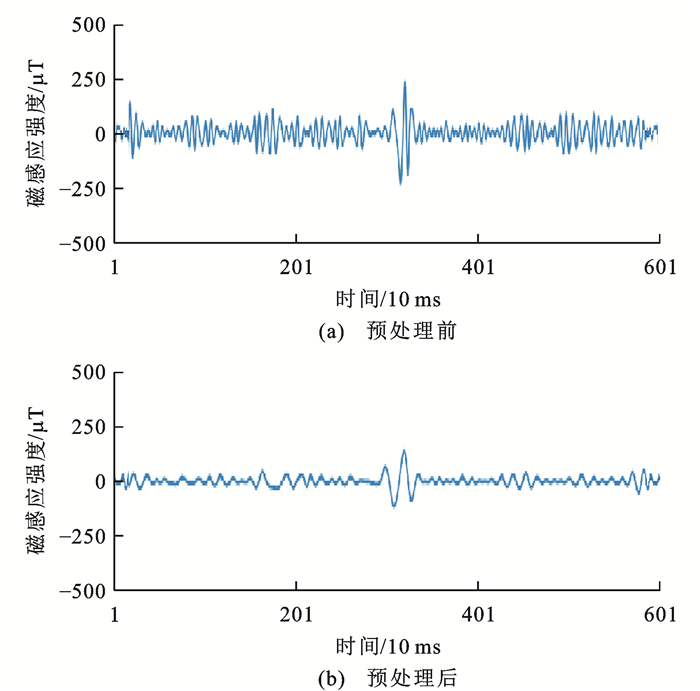
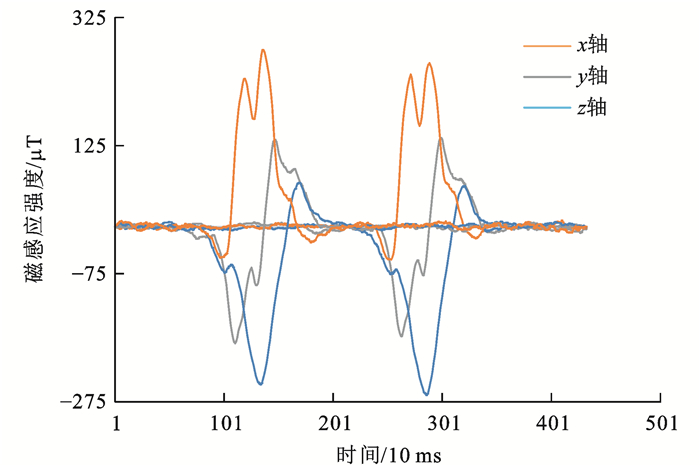
其中,得到i(t)的过程如图 10所示,图中:hj(t)为t时刻循环累加j次的集合平均值。地磁传感器的输出信号在滤波预处理前后进行的对比如图 11所示。
通过集合经验模态分解EEMD法的数据处理,被测地磁场扰动信号能较好地抑制杂波。
图 11中,纵坐标以微特斯拉(μT)为度量单位,用于显示乘用车的地磁扰动信号,这一度量单位约为地磁场平均磁感应强度的1/50。横坐标是传感器节点的采样周期,设为10 ms。城市通行中的车辆,速度一般介于10~60 km·h-1,同时根据车辆分类的国家标准,城市内常见车辆的长度在3.7~12.0 m,则车辆对传感器节点的扰动时间范围在0.22~4.30 s不等,曲线的数据长度在22~430。通过扰动曲线所反映的信号宽度,亦可在测速的前提下判断被测车辆的长度。
3.2 典型车辆的地磁扰动信号捕获
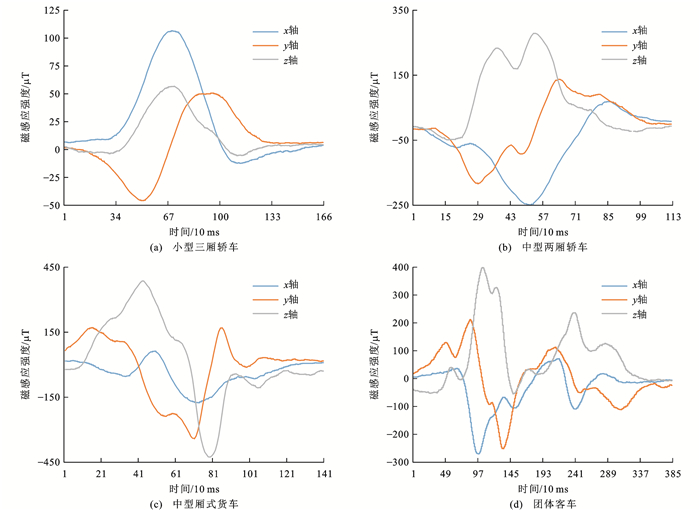
《汽车、挂车及汽车列车的术语和定义》(GB/T 3730—2022)和交通运输行业标准《营运客车类型划分及等级评定》(JT/T 325—2018)是中国车辆分类的2个专业标准。本文考虑城市内常见车辆类型和所获取的样本量,按照以上2个标准,选取某小型三厢轿车、中型两厢轿车、中型厢式货车和大型客车等4种车型作为典型试验样本,其外形尺寸如表 1所示。对这4种车辆类型进行分类亦可以实时了解城市道路的交通状态,具有较好的实用性。
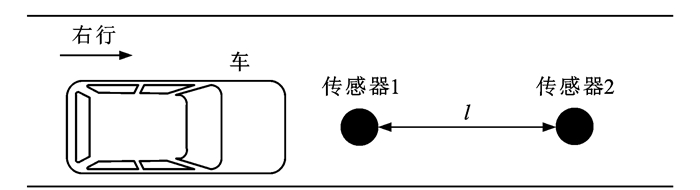
表 1 典型测试车辆的外形尺寸Table 1. Dimensions of typical test vehiclesmm 序号 车身型式 外形尺寸:长×宽×高 1 小型三厢轿车 4 300×1 705×1 460 2 中型两厢轿车 4 733×1 839×1 673 3 中型厢式货车 6 995×2 420×3 650 4 团体客车 10 490×2 500×3 600 本文采用2个地磁三轴传感器检测,传感器埋设在需要检测的道路中央。双传感器的位置布置如图 12所示,2个传感器的间距l小于一辆车的车长,以保证2个地磁车辆检测器在检测时间上的连续性。
使用双地磁传感器捕获的一种中型两厢轿车的地磁扰动信息如图 13所示。
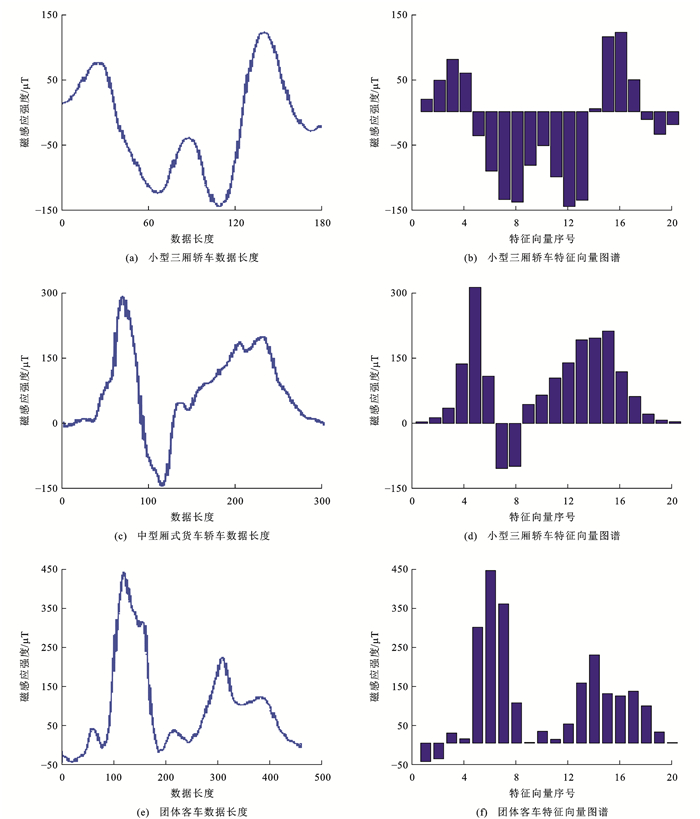
从背景磁场中分离出来的小型三厢轿车、中型两厢轿车、中型厢式货车和大型客车等4种典型测试车辆的三轴地磁扰动曲线如图 14所示,可以看出不同的车辆类型其扰动波形显著不同,从而反映车辆的长度特征信息。
3.3 车辆尺寸特征信息提取
车辆通过传感器节点时,由于车辆长度和速度不同,对传感器节点的扰动时间也不相同,因此,曲线的长度也不相同。本文采用曲线的特征向量直接提取法,即将车辆地磁曲线转化为特征向量。
已知a(·)为融合后的车辆地磁扰动数据组,总长度为I。fb为第b个特征向量,b=1, 2, …, N。将a(·)依次平均分成N份,每份的长度为Δn,即
Δn=I/N (8) 对平分后的b组数据取平均得到第b个特征向量的值,计算式为
f1=[a(1)+⋯+a(⌊bΔn⌋)+a(⌈bΔn⌉)(bΔn−⌊bΔn⌋)]/Δnb=1 (9) fb={a[⌈(b−1)Δn⌉][⌈(b−1)Δn⌉−(b−1)Δn]+a[⌈(b−1)Δn⌉+1]+⋯+a[⌈bΔn⌉][⌈bΔn⌉−bΔn]}/Δnb=2,⋯,N−1 (10) fN={a[⌈(b−1)Δn⌉][⌈(b−1)Δn⌉−(b−1)Δn)]+⋯a(b)}/Δnb=N (11) 设定N =15,以小型三厢轿车的x轴地磁扰动曲线为分析对象,行使速度为40 km·h-1,对被测车辆进行特征向量的提取,获得的图谱如图 15所示。
4. 系统测试
系统测试分别对混合电磁感应单元、地磁场感应单元进行独立测试,分别实现无线充电特征和车型尺寸特征的识别,其中车型尺寸特征识别在学校的汽车试验场完成。
4.1 混合电磁感应单元测试
通过一个设计案例可对本文的混合电磁感应单元进行测试。设定该单元的工作频率为600 kHz,车载端提供12V的Vin车内电源条件。全闭域条件下的耦合系数k设定为0.15,各元件的主要参数值参见表 2,表中:N1和N2分别为2个感应线圈的匝数。
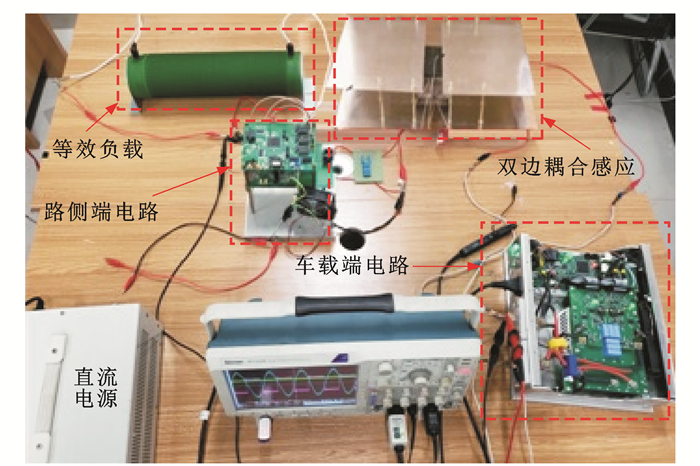
表 2 混合电磁感应电路各元件的参数值Table 2. Parameters of hybrid electromagnetic circuit结构参数 数值 结构参数 数值 Cf1/nF 4.26 C2/pF 394.7 Cf2/nF 5.18 CS/pF 4.5 Lf1/μH 16.53 M12/μH 58.18 Lf2/μH 13.6 N1 56 L1/μH 843.27 N2 12 L2/μH 178.42 d/mm 150 C1/pF 83.51 h/mm 180 搭建的试验电路如图 16所示,车载端的功率单元选用C2M0080120D碳化硅器件,路侧端的功率单元选用MUR1520G快恢复型二极管。
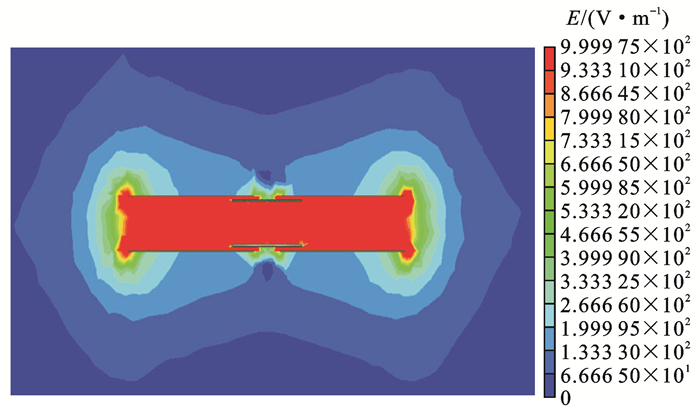
混合电磁感应单元在闭域耦合下的电容极板间的电场强度E和磁感应强度B分布分别如图 17、18所示,可实现电磁感应能量的传递。
图 19是图 2中车载端的输入电压V1和路侧端感应电流i2的波形。其中,图 19(b)前半部分是半开域耦合范围时检测到i2的波形。在进入全闭域范围时,i2的波形见图 19(b)后半部分,其有效值为0.85A。结合图 7的半开域和全闭域的耦合分析,以路侧端这一感应谐振电流的有效值为特征,通过电流霍尔对其进行数值检测,并设定识别阈值,可在偏移后的半开域耦合条件下实现无线充电车辆的特征识别。
在电感线圈径向偏移导致的全开域条件下,则以电容极板的电场耦合感应为主,此时的电容极板耦合面积为识别范围的初始条件。
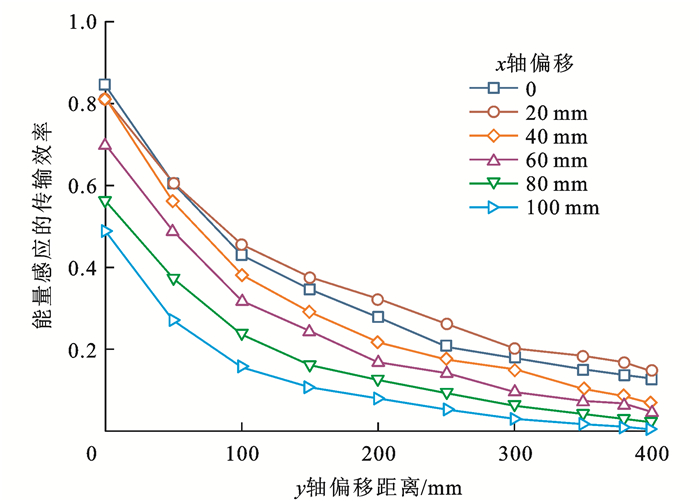
若车载侧动极板进一步x轴向偏移,则可通过研究电容极板的偏移距离与感应能量传输效率的变化关系得出偏移范围,即识别范围。相应的偏移距离与能量感应传输效率的变化变化曲线如图 20所示。
从图 20中可以看出,全开域条件下,车载侧的电容动极板在x轴方向偏移100 mm后,感应信号的传输效率为49.2%。由于极板间还存在交叉耦合问题,经测试x轴方向的有效识别范围约为220 mm。若x轴不偏移,仅y轴方向上偏移,则不存在极板的交叉耦合,这种情况下,以感应信号传输效率的30.0%为有效感应,则其可识别的偏移范围约为170 mm。与单一的磁场耦合识别相比,增加电容极板后的感应单元的识别范围将扩大约62.8%,因此,这一混合电磁感应单元,有助于扩大车辆在行驶偏移条件下的识别范围。而不同的电容极板设计,其识别的偏移范围不同,系统应根据功率比参数权衡确定。
4.2 地磁场感应单元测试
在学校的汽车试验场进行地磁场感应单元测试,场景如图 21所示。
地磁传感器采用双MMC3416模块,并设定被测车辆的长度在3.7~12.0 m,速度在2.78~16.67 m·s-1。传感器节点的采样周期为10 ms,则曲线的数据长度在22~430,N=20时,捕获的小、中、大3种车型的磁扰动曲线特征向量提取图谱如图 22所示。
5. 结语
(1) 设计了一种基于混合电磁感应单元和地磁场感应单元的复合感应装置,在无线充电车辆行驶偏移条件下,完成相关典型车型的磁电特征数据捕获。其中,混合电磁感应单元用于实现车辆无线充电特征的识别,地磁场感应单元用于实现车辆型式尺寸特征的识别。
(2) 混合电磁感应单元以实现路侧的谐振电流有效值检测为特征目标,其电路拓扑含有线圈之间形成的磁场耦合和极板之间形成电场耦合等2种耦合形式,拓扑具有高阶的双边CL补偿结构。与传统的单一磁场感应或电场感应技术相比,这一混合耦合感应装置不仅可以节约电容极板元件的尺寸,又有助于改善半开域耦合问题,有助于扩大车辆偏移条件下的识别范围。
(3) 对于地磁场感应单元,提出了一种地磁信号的集合经验模态分解法,以改善非线性非平稳信号的提取效果,并引入曲线的特征向量提取法,以小型三厢轿车、中型两厢轿车、中型厢式货车和大型客车等4种车型的尺寸作为典型试验样本,将不同车辆的地磁曲线信号转化为特征向量图谱,以实现车辆形状类型的准确判断。
(4) 若在路面分布敷设多组混合电磁感应单元,这一检测装置可提高对无线充电车辆特征的动态捕捉能力。然而,这一装置在实际应用中较容易受到外界因素的干扰,如异物干扰、电容耦合器的边缘效应及频率漂移等问题,这需要对装置的耦合机构参数进行多目标优化设计以改善系统鲁棒性。
-
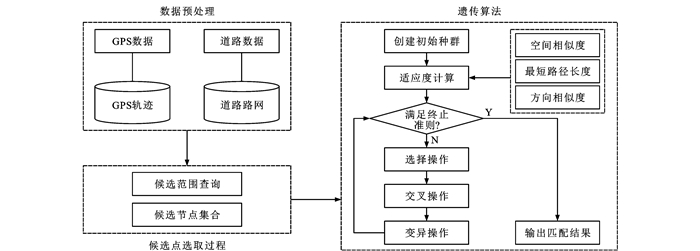
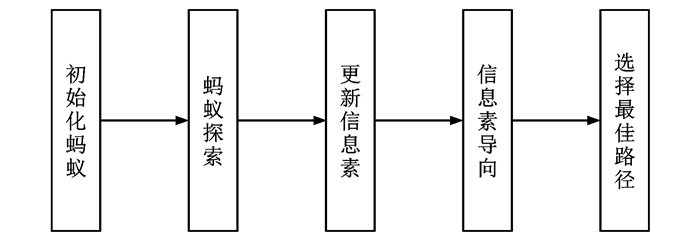
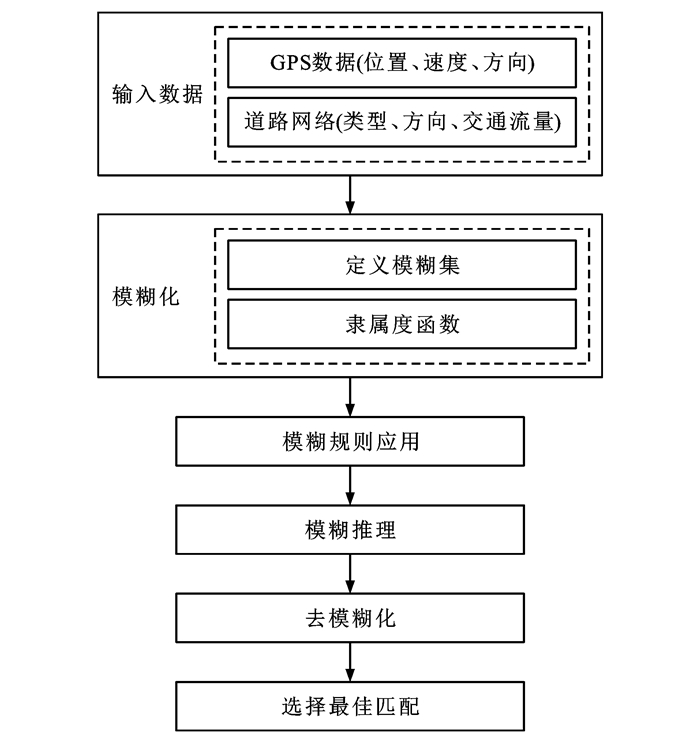
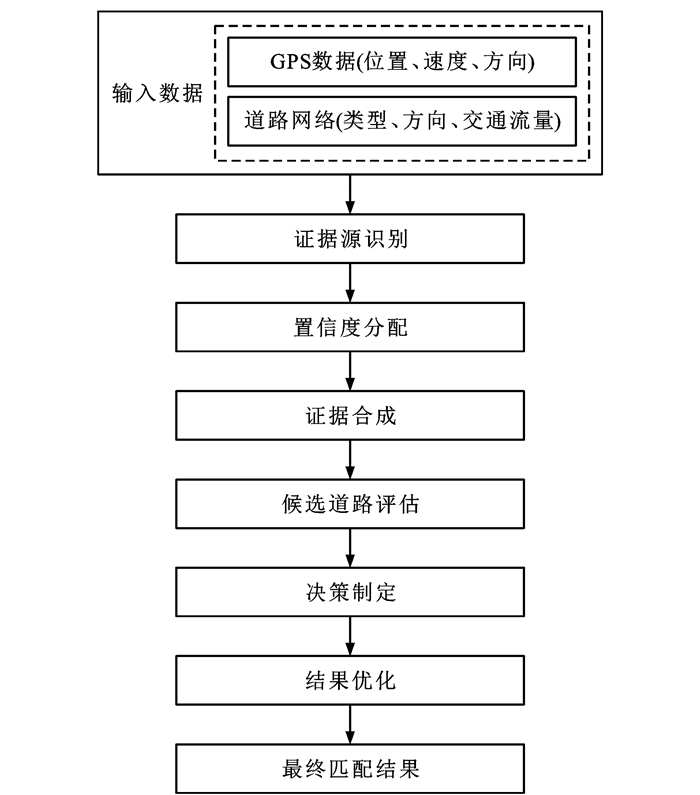
表 1 各类地图匹配算法简介
Table 1. Introduction of various map matching algorithms
算法 匹配方法 文献 特点 适用场景 传统地图匹配算法 几何 [13] 简单高效,易于实现,对噪声敏感 适用于道路网络较为简单或者对实时性要求较高的情况 拓扑 [14] 快速确定候选路段,实时性好,受初始匹配结果影响较大,容错性差 适用于道路网络结构复杂,例如在城市环境中,平行道路和频繁的路段变更 基于优化算法的地图匹配算法 遗传算法 [15] 全局最优搜索能力,处理复杂问题,容错性,适应性强 适合于需要在多个匹配结果中寻找最优解的复杂道路网络,以及需要快速响应的实时地图匹配应用 蚁群算法 [16] 全局最优解,自适应和局部搜索策略 适用于解决空间数据集中和融合中的关键技术问题,如同名实体匹配,复杂的道路网匹配问题,实时匹配 基于逻辑和推理的地图匹配算法 模糊逻辑 [17] 处理不确定性和模糊性,基于规则的推理,集成多种数据源 适用于复杂的交通网络环境,尤其是在城市密集道路网络中,以及存在不确定性的匹配问题 D-S证据理论 [18] 处理不确定性和证据冲突,鲁棒性 适用于城市复杂路网,车辆监控和管理系统 基于概率统计的地图匹配算法 概率决策 [19] 考虑车辆定位的不确定性,有效减少待匹配的路段数量,对置信区域设置敏感 适用于简单路网环境,定位误差较小的情况,通常需要与其他地图匹配技术结合 滤波器 [20] 考虑传感器误差和地图误差,较高的可信度,效率较低 适用于对定位精度要求较高的场景,如城市复杂道路环境中的车辆导航系统、自动驾驶汽车、无人机导航等 HMM [21] 考虑测量噪声和道路布局,处理时间序列数据,动态规划优化 适合于处理不准确和稀疏的GPS数据 扩展HMM [22] 考虑实时移动方向,综合空间、时间和方向特征,减少计算成本 适用于道路网络复杂,低采样率GPS轨迹,需要更精细匹配结果的场景 基于深度学习的地图匹配算法 [23] 能够处理低质量(噪声、低频率、非均匀采样)的GPS轨迹数据,利用深度学习模型提高匹配质量 适合于需要处理大量复杂轨迹数据的情况,尤其是在数据质量较差时 表 2 基于HMM的地图匹配算法比较
Table 2. Comparison of map matching algorithms based on HMM
算法 具体方法 输入信息 改进 HMM[21] HMM+Viterbi 时间戳的纬度、经度对,道路网络图 通过手动匹配或已知的行驶路线来验证和校正算法 理想HMM[82] 简化的HMM框架+Viterbi 时间戳的纬度、经度对,道路网络图 简化了状态转移概率,使其适应理想HMM框架,以避免在寻找最可能路径时的缺陷 OHMM[83] HMM+VSW+SVW+概率评分机制+Viterbi 车辆的经度、纬度、速度和时间戳,道路网络;其他传感器数据和拓扑信息 利用支持向量机(Support Vector Machine, SVM)来学习转移概率函数,而不是事先选择模型并估计其参数 基于IRL的HMM[84] HMM+IRL+Viterbi+Dijkstra+最大熵IRL GPS数据点,真实路线,道路网络 考虑了转弯次数作为评估路线可能性的指标 混合贝叶斯框架匹配算法[85] 卡尔曼滤波器+HMM+链式状态空间表示 传感器数据,差分全球定位系统(DifferentialGlobal Position System, DGPS)接收器提供的GPS位置数据,道路网络 引入了链式状态空间表示,允许使用精确的线性方程进行多传感器数据融合,提出了一个段选择策略,用于假设跟踪 快速HMM[86] HMM+Dijkstra+懒惰评估 GPS数据点,道路网络,搜索半径 经过优化以减少计算复杂性,特别是在处理稀疏和嘈杂的GPS轨迹数据时 SnapNet[87] 一系列过滤器+插值+增量式HMM+Viterbi 由纬度、经度和误差估计值组成的位置信息,数字地图 运用道路转换启发式规则,处理虚假转换,减少不必要的道路切换 基于HMM的增强模型[88] HMM+Viterbi GPS数据和手机定位数据,道路网络,几何数据,精炼的四叉树数据 对于状态空间的定义,使用四叉树网格结构化道路网络,以减少计算复杂性 FMM[89] 预计算+HMM+Viterbi+空间索引技术+线性引用算法 位置、时间戳、速度、方向和加速度的GPS观测数据,道路网络 通过预计算和使用哈希表搜索来替换重复的路由查询 基于路口决策域和HMM[90] HMM+路口决策域模型+Viterbi 车辆的实时位置信息,道路网络 定义路口决策域,综合道路宽、路口角、GPS及路网精度,划定区域,指导车辆GPS位置匹配,减少误差 基于拓扑关系的快速匹配算法[91] HMM+A*算法+Viterbi 车辆的纬度、经度、时间、速度、方向角度,道路网络数据 预计算每个区域包含的道路段,提高了查找候选道路段的效率,改进了A*算法的启发式搜索效率,减少了计算量 加速HMM[92] HMM+道路网络分割+空间感知启发式方法+Viterbi 原始GPS点,道路网络 通过道路网络分割和空间感知启发式方法显著加速转移概率计算 IHMM[93] 误差置信椭圆+IHMM+Viterbi 原始GPS点,道路网络 基于方向和距离权重的发射概率计算,以及考虑道路段曲率的状态转移概率计算 表 3 基于深度学习的地图匹配算法比较
Table 3. Comparison of map matching algorithms based on deep learning
模型 数据集信息 采样间隔/s 神经网络的输入 神经网络的输出 FNN[98] 郑州城市区域测试车辆GPS轨迹 4 投影距离以及方位角之间的差异 地图匹配度 ANN[99] 芝加哥5条道路区域内的GPS轨迹,包含13 204个GPS点 速度、水平精度因子和常数 GPS点的水平偏移量,包括长度和方向 基于Seq2Seq学习框架,结合注意力机制[100] 北京地区车辆GPS轨迹包含12 436名用户的1 336 567条 11 原始轨迹数据和道路网络信息 匹配后的轨迹和校准后的轨迹 DMM框架[101] 伦敦198条车辆GPS轨迹,总长度为1 701 km,涉及2 848个不同的蜂窝基站 5个等级 蜂窝基站序列,包含了基站的标识符(ID)和时间戳以及道路网络地图 道路轨迹和匹配精度 Transformer[102] 韩国首尔江南区运营的出租车上安装的DTG GPS轨迹 点级或线级路线 RoutesFormer[103] 上海8 407辆出租车的GPS轨迹 60、180、300、420 不连续的路径(道路链接)、已行驶的路径 最有可能的下一个链接、完整推断路径 ImIn-GAIL框架[104] 杭州和洛杉矶地区GPS车辆轨迹 0.1 稀疏驾驶轨迹、驾驶状态、驾驶行为 密集驾驶轨迹、模仿性能、插值性能 L2MM[23] 波尔图市200 000条GPS轨迹、重庆市100 000条GPS轨迹 15 低质量GPS轨迹、高质量GPS轨迹、道路网络数据 映射后的轨迹、轨迹表示、识别的模式 表 4 地图匹配数据集
Table 4. Map matching datasets
数据集类型 数据集名称 是否公开 公开数据集 优点 缺点 GPS数据集 GPS[105-107] 部分公开 GeoLife GPS Trajectories、T-Drive Taxi Trajectories、SynMob等 全球范围覆盖,精度较高 室内效果差,信号易受遮挡,能耗高 传感器数据集 AVI[77-78, 95] 私有 精度高 数据稀疏 INS[108] 部分公开 多IMU车载GNSS/INS数据集、KITTI等 抗干扰能力强,高频采样,短时间内精度较高 长时间使用会产生误差累积,成本较高 PDR[109] 私有 无需外部信号,可与手机传感器结合 误差会随步数增加而累积 SLAM[110-113] 部分公开 UZH-FPV Drone Racing、OpenLORIS-Scene、OxfordRobotCar、Newer College等 实时性好,精度较高 容易受动态障碍物和视线遮挡影响 无线网络数据集 WiFi[114] 部分公开 SODIndoorLoc、RSSI、UJIIndoorLoc等 成本低,覆盖范围广 精度较低,受环境因素干扰大 蓝牙 部分公开 成本低,功耗低 受环境因素干扰大 RFID 私有 精度较高,功耗低 成本高 UWB[116] 部分公开 精度高,抗干扰能力强,实时定位效果好 成本高 地图数据集 OSM[117] 公开 OpenStreetMap 开源,全球覆盖,数据多样 数据精度不均,信息不完整,格式复杂 街景图像[118-120] 部分公开 Google地图、百度地图、高德地图等 提供360°全景视角 隐私问题,存储成本高 -
[1] 于娟, 杨琼, 鲁剑锋, 等. 高级地图匹配算法: 研究现状和趋势[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(9): 1818-1829.YU Juan, YANG Qiong, LU Jian-feng, et al. Advanced map matching algorithms: a survey and trends[J]. Acta Electonica Sinica, 2021, 49(9): 1818-1829. (in Chinese) [2] KUBICKA M, CELA A, MOUNIER H, et al. Comparative study and application-oriented classification of vehicular map-matching methods[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2018, 10(2): 150-166. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2018.2806630 [3] 孙健, 张颖, 张纯. 基于驾驶人路径选择偏好的OD行程时间预测方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(2): 143-149. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2016.02.017SUN Jian, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Chun. Prediction method of OD travel time based on driver's route choice preference[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(2): 143-149. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2016.02.017 [4] HUANG Zhen-feng, QIAO Shao-jie, HAN Nan, et al. Survey on vehicle map matching techniques[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2021, 6(1): 55-71. doi: 10.1049/cit2.12030 [5] NIKOLIC M, JOVIC J. Implementation of generic algorithm in map-matching model[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 72: 283-292. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.10.061 [6] 廖律超, 蒋新华, 林铭榛, 等. 基于交通轨迹数据挖掘的道路限速信息识别方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2015, 15(5): 118-126. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2015.05.015LIAO Lyu-chao, JIANG Xin-hua, LIN Ming-zhen, et al. Recognition method of road speed limit information based on data mining of traffic trajectory[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2015, 15(5): 118-126. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2015.05.015 [7] SIRI E, SIRI S, SACONE S. A topology-based bounded rationality day-to-day traffic assignment model[J]. Communications in Transportation Research, 2022, 2: 1-16. [8] ZHANG Wen-wei, ZHAO Hui, XU Min. Optimal operating strategy of short turning lines for the battery electric bus system[J]. Communications in Transportation Research, 2021, 1: 1-12. [9] 张平, 陈一凡, 江书真, 等. 高速公路上自动超车过程的轨迹规划与跟踪控制[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2022, 13(3): 463-472.ZHANG Ping, CHEN Yi-fan, JIANG Shu-zhen, et al. Trajectory planning and tracking control of automatic overtaking process on highway[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2022, 13(3): 463-472. (in Chinese) [10] 孙智威, 裴晓飞, 刘一平, 等. 无人驾驶清扫车的路径跟踪及远程控制[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2022, 13(4): 729-737.SUN Zhi-wei, PEI Xiao-fei, LIU Yi-ping, et al. Path tracking and remote control of driverless sweeper[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2022, 13(4): 729-737. (in Chinese) [11] LIU Zhi-yuan, LIU Yang, LYU Cheng, et al. Building personalized transportation model for online taxi-hailing demand prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 51(9): 4602-4610. [12] CHAO Ping-fu, XU Ye-hong, HUA Wen, et al. A survey on map-matching algorithms[C]//BOROVICA-GAJIC R. Databases Theory and Applications: 31st Australasian Database Conference. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 121-133. [13] BERNSTEIN D, KORNHAUSER A. An introduction to map matching for personal navigation assistants[J]. New Jersey Institute of Technology, 1998, DOI: 10.1001/archopht.122.7.1082-b. [14] MAHPOUR A, FORSI H, VAFAEENEJAD A, et al. An improvement on the topological map matching algorithm at junctions: a heuristic approach[J]. International Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2022, 9(4): 749-761. [15] 谷远利, 陆文琦, 邵壮壮. 基于多目标遗传算法的浮动车地图匹配方法[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2019, 45(6): 585-592.GU Yuan-li, LU Wen-qi, SHAO Zhuang-zhuang. Multi-criteria genetic algorithm-based map-matching method for floating car data[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2019, 45(6): 585-592. (in Chinese) [16] 王跃钢, 文超斌, 左朝阳, 等. 自适应混沌蚁群径向分析算法求解重力辅助导航匹配问题[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 8(63): 454-459.WANG Yue-gang, WEN Chao-bin, ZUO Chao-yang, et al. Adaptive chaotic ant colony radial analysis algorithm for solving gravity-assist navigation matching problem[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 8(63): 454-459. (in Chinese) [17] QUDDUS M A, NOLAND R B, OCHIENG W Y. A high accuracy fuzzy logic based map matching algorithm for road transport[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2006, 10(3): 103-115. doi: 10.1080/15472450600793560 [18] 谷正气, 胡林, 黄晶, 等. 基于改进D-S证据理论的车辆导航地图匹配[J]. 汽车工程, 2008, 30(2): 141-145.GU Zheng-qi, HU Lin, HUANG Jing, et al. Vehicle navigation map matching based on modified D-S evidence rule[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2008, 30(2): 141-145. (in Chinese) [19] QUDDUS M A, NOLAND R B, OCHIENG W Y. Validation of map matching algorithms using high precision positioning with GPS[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2005, 58(2): 257-271. doi: 10.1017/S0373463305003231 [20] YU Biao, DONG Lin, XUE De-yi, et al. A hybrid dead reckoning error correction scheme based on extended Kalman filter and map matching for vehicle self-localization[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 23(1): 84-98. [21] NEWSON P, KRUMM J. Hidden Markov map matching through noise and sparseness[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 17th ACM Sigspatial International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems. New York: ACM, 2009: 336-343. [22] HSUEH Y L, CHEN He-qian. Map matching for low-sampling- rate GPS trajectories by exploring real-time moving directions[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 433: 55-69. [23] JIANG Lin-li, CHEN Chao-xiong, CHEN Chao. L2MM: learning to map matching with deep models for low-quality GPS trajectory data[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2023, 17(3): 1-25. [24] 刘峰, 郭阳, 郑辛, 等. 基于道路几何特征的地图匹配方法研究[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2020, 7(1): 67-72.LIU Feng, GUO Yang, ZHENG Xin, et al. Study on map matching method based on geometric features of road[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2020, 7(1): 67-72. (in Chinese) [25] MICHAU G, NANTES A, BHASKAR A, et al. Bluetooth data in an urban context: retrieving vehicle trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(9): 2377-2386. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2642304 [26] WHITE C E, BERNSTEIN D, KORNHAUSER A L. Some map matching algorithms for personal navigation assistants[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2000, 8(1-6): 91-108. doi: 10.1016/S0968-090X(00)00026-7 [27] 汪小寒, 何增宇, 胡王悟, 等. 复杂路段的角度差和后续点地图匹配方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(2): 379-384.WANG Xiao-han, HE Zeng-yu, HU Wang-wu, et al. Map matching method for complex road sections via difference and subsequent points[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(2): 379-384. (in Chinese) [28] TAYLOR G, BLEWITT G, STEUP D, et al. Road reduction filtering for GPS-GIS navigation[J]. Transactions in GIS, 2001, 5(3): 193-207. doi: 10.1111/1467-9671.00077 [29] CHEN D, DRIEMEL A, GUIBAS L J, et al. Approximate map matching with respect to the Fréchet distance[C]// WHITFORD A B. 2011 Proceedings of the Thirteenth Workshop on Algorithm Engineering and Experiments. Naples: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2011: 75-83. [30] 上官伟, 袁重阳, 蔡伯根, 等. 北斗二代在西部低密度铁路中的应用[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(5): 132-141. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2016.05.015SHANGGUAN Wei, YUAN Chong-yang, CAI Bai-gen, et al. Application of BDS in western low-density railway lines[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(5): 132-141. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2016.05.015 [31] XU Qian, WANG Mei-ling, DU Zhi-fang, et al. A positioning algorithm of autonomous car based on map-matching and environmental perception[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control Conference. New York: IEEE, 2014: 707-712. [32] HAN Yong-qian, ZHAO Dun-hui, ZHANG Xin-gang, et al. Map matching algorithm based on trajectory feature identification[C]//IEEE. 2021 40th Chinese Control Conference. New York: IEEE, 2021: 3657-3661. [33] BLAZQUEZ C A, VONDEROHE A P. Simple map-matching algorithm applied to intelligent winter maintenance vehicle data[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2005(1935): 68-76. [34] PEREIRA F C, COSTA H, PEREIRA N M. An off-line map-matching algorithm for incomplete mapdatabases[J]. European Transport Research Review, 2009, 1(3): 107-124. doi: 10.1007/s12544-009-0013-6 [35] LIU You-wen. Forecast map matching model for vehicle- borne navigation based on roadway character-istic[C]//IEEE. 2010 International Conference on Optoelectronics and Image Processing. New York: IEEE, 2010: 569-571. [36] VELAGA N R, QUDDUS M A, BRISTOW A L. Improving the performance of a topological map-matching algorithm through error detection and correction[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 16(3): 147-158. doi: 10.1080/15472450.2012.691852 [37] 李殿茜, 王翌, 刘垒, 等. 一种地图匹配算法的设计与实现[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2017, 4(2): 31-34.LI Dian-xi, WANG Yi, LIU Lei, et al. The design and implementation of a map matching algorithm[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2017, 4(2): 31-34. (in Chinese) [38] QUDDUS M A, OCHIENG W Y, ZHAO Lin, et al. A general map matching algorithm for transport telematics applications[J]. GPS Solutions, 2003, 7(3): 157-167. doi: 10.1007/s10291-003-0069-z [39] VELAGA N R, QUDDUS M A, BRISTOW A L. Developing an enhanced weight-based topological map-matching algorithm for intelligent transport systems[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2009, 17(6): 672-683. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2009.05.008 [40] YUAN Jing, ZHENG Yu, ZHANG Cheng-yang, et al. An interactive-voting based map matching algorithm[C]//IEEE. 2010 Eleventh International Conference on Mobile Data Management. New York: IEEE, 2010: 43-52. [41] QUDDUS M, WASHINGTON S. Shortest path and vehicle trajectory aided map-matching for low frequency GPS data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 55: 328-339. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.02.017 [42] DU Zi-xue, LIU Bin-yan, XIA Qin. Map matching algorithm based on V2I technology[C]//IEEE. 2018 International Conference on Robots and Intelligent System. New York: IEEE, 2018: 137-140. [43] 张贺, 孙婉莹, 宋国平. 基于特征权重的地图匹配算法研究[J]. 中国新技术新产品, 2022, DOI: 10.13612/j.cnkicntp.2022.23.027.ZHANG He, SUN Wan-ying, SONG Guo-ping. Research on feature weight-based map matching algorithm[J]. China New Technology and New Products, 2022, DOI: 10.13612/j.cnkicntp.2022.23.027.(inChinese) [44] ZHANG Lun, ZHANG Meng, YANG Wen-chen, et al. Golden ratio genetic algorithm based approach for modelling and analysis of the capacity expansion of urban road traffic network[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2015, 2015(1): 1-9. [45] CHEN Peng, TONG Rui, LU Guang-quan, et al. The α-reliable path problem in stochastic road networks with link correlations: a moment-matching-based path finding algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 110: 20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.05.022 [46] 吴刚, 邱煜晶, 王国仁. 基于隐马尔可夫模型和遗传算法的地图匹配算法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 38(4): 472-475.WU Gang, QIU Yu-jing, WANG Guo-ren. Map matching algorithm based on hidden markov model and genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2017, 38(4): 472-475. (in Chinese) [47] CHEHREGHAN A, ALI ABBASPOUR R. A geometric-based approach for road matching on multi-scale datasets using a genetic algorithm[J]. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 2018, 45(3): 255-269. doi: 10.1080/15230406.2017.1324823 [48] SINGH S, SINGH J, SEHRA S S. Genetic-inspired map matching algorithm for real-time GPS trajectories[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2020, 45(4): 2587-2603. doi: 10.1007/s13369-019-04247-1 [49] YIN Dan-dong, DU Shi-hong, WANG Shao-wen, et al. A direction-guided ant colony optimization method for extraction of urban road information from very-high-resolution images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(10): 4785-4794. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2477097 [50] 巩现勇, 武芳, 姬存伟, 等. 道路网匹配的蚁群算法求解模型[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2014, 39(2): 191-195.GONG Xian-yong, WU Fang, JI Cun-wei, et al. Ant colony algorithm solution model for road network matching[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(2): 191-195. (in Chinese) [51] GONG Yue-jiao, CHEN En, ZHANG Xing-lin, et al. AntMapper: an ant colony-based map matching approach for trajectory-based applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 19(2): 390-401. [52] LIU Ji-ping, XU Sheng-hua, ZHANG Fu-hao, et al. A hybrid genetic-ant colony optimization algorithm for the optimal path selection[J]. Intelligent Automation and Soft Computing, 2017, 23(2): 235-242. doi: 10.1080/10798587.2016.1196926 [53] FU Meng-yin, LI Jie, WANG Mei-ling. A hybrid map matching algorithm based on fuzzy comprehensive judgment[C]// IEEE. The 7th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. New York: IEEE, 2004: 613-617. [54] SYED S, CANNON M E. Fuzzy logic based-map matching algorithm for vehicle navigation system in urban canyons[C]// WELLS J K. Proceedings of the 2004 National Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation. Washington DC: Institute of Navigation, 2004: 982-993. [55] ZHANG Yong-qiang, GAO Yan-yan. A fuzzy logic map matching algorithm[C]//IEEE. 2008 Fifth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery. New York: IEEE, 2008: 132-136. [56] 张涛, 杨殿阁, 李克强, 等. 车辆导航中带匹配度反馈的模糊地图匹配算法[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 49(2): 277-280.ZHANG Tao, YANG Dian-ge, LI Ke-qiang, et al. Fuzzy map-matching algorithm with confidence feedback for vehicle navigation[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University: Science and Technology, 2009, 49(2): 277-280. (in Chinese) [57] YANG Yan-lan, YE Hua, FEI Shu-min. Integrated map-matching algorithm based on fuzzy logic and dead reckoning[C]//IEEE. 2010 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems. New York: IEEE, 2010: 1139-1142. [58] NASSREDDINE G, ABDALLAH F, DENലUX T. Map matching algorithm using belief function theory[C]//IEEE. 2008 11th International Conference on Information Fusion. New York: IEEE, 2008: 1-8. [59] 胡林, 谷正气, 杨易, 等. 基于权值D-S证据理论的车辆导航地图匹配[J]. 中国公路学报, 2008, 21(2): 116-120.HU Lin, GU Zheng-qi, YANG Yi, et al. Map matching in vehicle navigation based on weighted DS evidence theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2008, 21(2): 116-120. (in Chinese) [60] 曹闻, 朱述龙, 彭煊, 等. 基于短时预测的地图匹配算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2010, 30(11): 2910-2913.CAO Wen, ZHU Shu-long, PENG Xuan, et al. Map matching algorithm based on short-term prediction[J]. Computer Applications, 2010, 30(11): 2910-2913. (in Chinese) [61] ZHAO Xiang-mo, CHENG Xin, ZHOU Jing-mei, et al. Advanced topological map matching algorithm based on D-S theory[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2018, 43: 3863-3874. doi: 10.1007/s13369-017-2569-0 [62] YANG Feng-bao, WEI Hong, FENG Pei-pei. A hierarchical dempster-shafer evidence combination framework for urban area land cover classification[J]. Measurement, 2020, 151: 105916. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.09.058 [63] NIE Qing-hui, XIA Jing-xin, QIAN Zhen-dong, et al. Use of multisensor data in reliable short-term travel time forecasting for urban roads: Dempster-Shafer approach[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2015(2526): 61-69. [64] CAI Jian-nan, JEON J H, CAI Hu-bo, et al. Fusing heterogeneous information for underground utility map generation based on Dempster-Shafer theory[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2020, 34(3): 1-14. [65] 杨易, 谷正气, 胡林, 等. 基于概率决策的车辆导航系统地图匹配算法[J]. 汽车工程, 2006, 28(10): 897-901.YANG Yi, GU Zheng-qi, HU Lin, et al. Map matching algorithm for vehicle navigation system based on probability decision rule[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2006, 28(10): 897-901. (in Chinese) [66] ZHAO Shuai-dong, ZHANG Kui-lin. A distributionally robust optimization approach to reconstructing missing locations and paths using high-frequency trajectory data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 102: 316-335. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2019.03.012 [67] JABBOUR M, BONNIFAIT P, CHERFAOUI V. Map-matching integrity using multihypothesis road-tracking[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2008, 12(4): 189-201. doi: 10.1080/15472450802448179 [68] CHEN Bi-yu, YUAN Hui, LI Qing-quan, et al. Map-matching algorithm for large-scale low-frequency floating car data[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2014, 28(1): 22-38. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2013.816427 [69] ZHANG Qing-xiang, WANG Mei-ling, YUE Yu-feng. Robust semantic map matching algorithm based on probabilistic registration model[C]//IEEE. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. New York: IEEE, 2021: 5289-5295. [70] OBRADOVIC D, LENZ H, SCHUPFNER M. Fusion of map and sensor data in a modern car navigation system[J]. The Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image, and Video Technology, 2006, 45(1/2): 111-122. [71] CHU H J, TSAI G J, CHIANG K W, et al. GPS/MEMS INS data fusion and map matching in urban areas[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(9): 11280-11288. doi: 10.3390/s130911280 [72] WANG Hong-yu, LI Jin, HOU Zhen-shan, et al. Research on parallelized real-time map matching algorithm for massive GPS data[J]. Cluster Computing, 2017, 20: 1123-1134. doi: 10.1007/s10586-017-0869-5 [73] ASGHAR R, GARZÓN M, LUSSEREAU J, et al. Vehicle localization based on visual lane marking and topological map matching[C]//IEEE. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. New York: IEEE, 2020: 258-264. [74] 王东京, 刘继涛, 俞东进. 电动自行车轨迹简化与自适应地图匹配算法[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(8): 3793-3820.WANG Dong-jing, LIU Ji-tao, YU Dong-jin. Trajectory simplification and adaptive map matching algorithm for electric bicycle[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(8): 3793-3820. (in Chinese) [75] XU Hao, LIU Hong-chao, TAN C W, et al. Development and application of an enhanced Kalman filter and global positioning system error-correction approach for improved map-matching[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2010, 14(1): 27-36. doi: 10.1080/15472450903386013 [76] YUAN Yu-shan, LYU Jin-yang. Research on train positioning system based on map matching and multi-information fusion[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications. New York: IEEE, 2020: 2271-2275. [77] YU Bao-guo, JIA Hao-nan, WANG Xin-jian, et al. An indoor map matching algorithm based on improved particle filter[C]//IEEE. 2022 IEEE 10th International Conference on Information, Communication and Networks. New York: IEEE, 2022: 158-163. [78] 赖国良, 胡钊政, 周哲, 等. 基于语义似然与高精度地图匹配的智能车辆同时定位与检测[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023. DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.086.LAI Guo-liang, HU Zhao-zheng, ZHOU Zhe, et al. Simultaneous detection and localization for intelligent vehicles from HD map matchingwith semantic likelihood model[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, DOI: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.086.(inChinese) [79] RAO Wen-ming, WU Yao-jan, XIA Jing-xin, et al. Origin-destination pattern estimation based on trajectory reconstruction using automatic license plate recognition data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 95: 29-46. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.07.002 [80] YANG Jian-hao, SUN Jian. Vehicle path reconstruction using automatic vehicle identification data: an integrated particle filter and path flow estimator[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 58: 107-126. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.07.003 [81] FENG Yu, SUN Jian, CHEN Peng. Vehicle trajectory reconstruction using automatic vehicle identification and traffic count data[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2015, 49(2): 174-194. doi: 10.1002/atr.1260 [82] RAYMOND R, MORIMURA T, OSOGAMI T, et al. Map matching with hidden Markov model on sampled road network[C]//IEEE. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2012: 2242-2245. [83] GOH C Y, DAUWELS J, MITROVIC N, et al. Online map-matching based on hidden markov model for real-time traffic sensing applications[C]//IEEE. 2012 15th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. New York: IEEE, 2012: 776-781. [84] OSOGAMI T, RAYMOND R. Map matching with inverse reinforcement learning[C]//ROSSI F. Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Beijing: International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, 2013: 2547-2553. [85] SMAILI C, NAJJAR M E B E, CHARPILLET F. A hybrid Bayesian framework for map matching: formulation using switching kalman filter[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 2014, 74(3/4): 725-743. [86] KOLLER H, WIDHALM P, DRAGASCHNIG M, et al. Fast hidden Markov model map-matching for sparse and noisy trajectories[C]//IEEE. 2015 IEEE 18th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. New York: IEEE, 2015: 2557-2561. [87] MOHAMED R, ALY H, YOUSSEF M. Accurate real-time map matching for challenging environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 18(4): 847-857. [88] LUO An, CHEN Sheng-hua, XU Bin. Enhanced map-matching algorithm with a hidden Markov model for mobile phone positioning[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2017, 6(11): 327. doi: 10.3390/ijgi6110327 [89] YANG Can, GIDOFALVI G. Fast map matching, an algorithm integrating hidden Markov model with precomputation[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2018, 32(3): 547-570. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2017.1400548 [90] QI Hui, DI Xiao-qiang, LI Jin-qing. Map-matching algorithm based on the junction decision domain and the hidden Markov model[J]. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14(5): 1-20. [91] LI Hai-jun, CHEN Zhan-fang, CUI Guang-cai, et al. A fast map matching algorithm based on topological relation of road network[C]//IEEE. 2019 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data and Business Intelligence. New York: IEEE, 2019: 14-18. [92] DOGRAMADZI M, KHAN A. Accelerated map matching for GPS trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(5): 4593-4602. [93] 袁祎, 陈光武. 基于改进HMM的车辆轨迹匹配方法研究(英文)[J]. 计量科学与仪器, 2024, 15(2): 235-243.YUAN Yi, CHEN Guang-wu. Research on vehicle trajectory matching method based on improved HMM[J]. Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation, 2024, 15(2): 235-243. (in Chinese) [94] LOU Yin, ZHANG Cheng-yang, ZHENG Yu, et al. Map-matching for low-sampling-rate GPS trajectories[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 17th ACM Sigspatial International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems. New York: ACM, 2009: 352-361. [95] CAO Qi, DENG Yue, REN Gang, et al. Jointly estimating the most likely driving paths and destination locations with incomplete vehicular trajectory data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2023, 155: 1-27. [96] CAO Qi, REN Gang, LI Da-wei, et al. Map matching for sparse automatic vehicle identification data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(7): 6495-6508. [97] JIANG Lin-li, CHEN Chao-xiong, CHEN Chao, et al. From driving trajectories to driving paths: a survey on map-matching algorithms[J]. CCF Transactions on Pervasive Computing and Interaction, 2022, 4(3): 252-267. doi: 10.1007/s42486-022-00101-w [98] 苏海滨, 王光政, 王继东. 基于模糊神经网络的地图匹配算法[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2012, 34(1): 43-47.SU Hai-bin, WANG Guang-zheng, WANG Ji-dong. Map matching algorithm based on fuzzy neural networks[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2012, 34(1): 43-47. (in Chinese) [99] HASHEMI M, KARIMI H A. A machine learning approach to improve the accuracy of GPS-based map-matching algorithms[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE 17th International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration. New York: IEEE, 2016: 77-86. [100] ZHAO Kai, FENG Jie, XU Zhao, et al. Deep MM: deep learning based map matching with data augmentation[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 27th ACM Sigspatial International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems. New York: ACM, 2019: 452-455. [101] SHEN Zhi-hao, DU Wan, ZHAO Xi, et al. DMM: fast map matching for cellular data[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking. New York: ACM, 2020: 1-14. [102] JIN Zhi-xiong, KIM J, YEO H, et al. Transformer-based map-matching model with limited labeled data using transfer-learning approach[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2022, 140: 1-25. [103] QIU Shu-han, QIN Guo-yang, WONG M, et al. Routes former: a sequence-based route choice transformer for efficient path inference from sparse trajectories[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2024, 162: 1-38. [104] WEI Hua, CHEN Cha-cha, LIU Chang, et al. Learning to simulate on sparse trajectory data[C]//DONG Yu-xiao. 2021 European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: Applied Data Science Track. Berlin: Springer, 2021: 530-545. [105] ZHENG Yu, XIE Xing, MA Wei-ying. GeoLife: a collaborative social networking service among user, location and trajectory[J]. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, 2010, 33(2): 32-39. [106] YUAN Jing, ZHENG Yu, ZHANG Cheng-yang, et al. T-drive: driving directions based on taxi trajectories[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems. New York: ACM, 2010: 99-108. [107] ETEMAD M, SOARES JÚNIOR A, MATWIN S. Predicting transportation modes of gps trajectories using feature engineering and noise removal[C]//Canadian Society for Intelligent Research. 2018 Canadian Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 259-264. [108] ABDELAZIZ N, EL-RABBANY A. Deep learning-aided inertial/visual/lidar integration for GNSS-challenging environments[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(13): 1-20. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3287172 [109] ASRAF O, SHAMA F, KLEIN I. PDRNet: a deep-learning pedestrian dead reckoning framework[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 22(6): 4932-4939. [110] DELMERICO J, CIESLEWSKI T, REBECQ H, et al. Are we ready for autonomous drone racing? The UZH-FPV drone racing dataset[C]//IEEE. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. New York: IEEE, 2019: 6713-6719. [111] SHI Xue-song, LI Dong-jiang, ZHAO Peng-peng, et al. Are we ready for service robots? The openloris-scene datasets for lifelong slam[C]//IEEE. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. New York: IEEE, 2020: 3139-3145. [112] MADDERN W, PASCOE G, LINEGAR C, et al. 1 year, 1000 km: the Oxford robotcar dataset[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2017, 36(1): 3-15. doi: 10.1177/0278364916679498 [113] RAMEZANI M, WANG Y, CAMURRI M, et al. The newer college dataset: handheld lidar, inertial and vision with ground truth[C]//IEEE. 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. New York: IEEE, 2020: 4353-4360. [114] BI Jing-xue, WANG Yun-jia, YU Bao-guo, et al. Supplementary open dataset for WiFi indoor localization based on received signal strength[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2022, 3(1): 1-15. [115] 吴欢欢, 周建平, 许燕, 等. RFID发展及其应用综述[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2013, 30(12): 203-206.WU Huan-huan, ZHOU Jian-ping, XU Yan, et al. A comprehensive review on RFID development and ITS application[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2013, 30(12): 203-206. (in Chinese) [116] NGUYEN T M, YUAN Sheng-hai, CAO Mu-qing, et al. NTU VIRAL: a visual-inertial-ranging-lidar dataset, from an aerial vehicle viewpoint[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2022, 41(3): 270-280. [117] MOONEY P, MINGHINI M. A review of OpenStreetMap data[J]. Mapping and the Citizen Sensor, 2017, DOI: 10.5334/bbf.c. [118] ZAMIR A R, SHAH M. Accurate image localization based on google maps street view[C]//BARROW H G. 11th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2010: 255-268. [119] 王昭雨, 庄惟敏. 基于图像深度学习的街区更新后评估方法研究——以北京什刹海街区为例[J]. 新建筑, 2022(3): 5-8.WANG Zhao-yu, ZHUANG Wei-min. Research on block renewal post occupancy evaluation methods based on image deep learning: a case study of Shichahai in Beijing[J]. New Architecture, 2022(3): 5-8. (in Chinese) [120] 李力, 张婧, 瓦希德·穆萨维, 等. 大数据驱动的城市更新设计方法初探[J]. 新建筑, 2021(2): 37-41.LI Li, ZHANG Jing, MOOSAVI V, et al. A preliminary study of big data driven urban renewal design[J]. New Architecture, 2021(2): 37-41. (in Chinese) [121] 陈滨, 王平, 施文灶, 等. GPS轨迹数据的综合地图匹配算法研究[J]. 电子科技, 2014, 27(12): 20-23.CHEN Bin, WANG Ping, SHI Wen-zao, et al. An integrated map-matching algorithm based on GPS[J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2014, 27(12): 20-23. (in Chinese) [122] HASHEMI M, KARIMI H A. A critical review of real-time map-matching algorithms: current issues and future directions[J]. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 2014, 48: 153-165. [123] GAN Nian-fei, ZHANG Miao-miao, ZHOU Bing, et al. Spatio-temporal heuristic method: a trajectory planning for automatic parking considering obstacle behavior[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles, 2022, 5(3): 177-187. [124] ZHAO Jian-sen, MA Xin, YANG Bing, et al. Global path planning of unmanned vehicle based on fusion of A* algorithm and Voronoi field[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles, 2022, 5(3): 250-259. [125] 彭涛, 许庆, 陈强, 等. 异构载货车辆队列高速换道分布式反馈线性化控制[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2022, 13(3): 473-481.PENG Tao, XU Qing, CHEN Qiang, et al. Distributed feedback linear control for heterogeneous freight vehicle platoon on highway[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2022, 13(3): 473-481. (in Chinese) [126] DABIRI A, KULCSÁR B. Incident indicators for freeway traffic flow models[J]. Communications in Transportation Research, 2022, 2: 1-9. [127] 陈华伟, 邵毅明, 敖谷昌, 等. 面向在线地图的GCN-LSTM神经网络速度预测[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(4): 183-196. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.04.014CHEN Hua-wei, SHAO Yi-ming, AO Gu-chang, et al. Speed prediction by online map-based GCN-LSTM neural network[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(4): 183-196. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.04.014 [128] TSCHARAKTSCHIEW S, REIMANN F. Less workplace parking with fully autonomous vehicles?[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles, 2022, 5(3): 283-301. [129] ZHANG Dong-qing, DONG Yu-cheng, GUO Zhao-xia. A turning point-based offline map matching algorithm for urban road networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 565: 32-45. [130] LYU Cheng, WU Xin-hua, LIU Yang, et al. A partial-Fréchet- distance-based framework for bus route identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(7): 9275-9280. [131] 李军, 唐爽, 黄志祥, 等. 融合稳定性的高速无人驾驶车辆纵横向协调控制方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(2): 205-218. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.017LI Jun, TANG Shuang, HUANG Zhi-xiang, et al. Longitudinal and lateral coordination control method of high- speed unmanned vehicles with integrated stability[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(2): 205-218. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.017 -






 下载:
下载:






















 下载:
下载: