Progress and trends of low-carbon application of waste materials in asphalt pavements
-
摘要: 为了促进固废材料在沥青路面中的低碳化应用, 从固废原材料、固废沥青混合料、固废沥青路面3个维度对固废材料应用进展进行了系统回顾与分析。在固废原材料方面, 归纳了面向减碳的材料分类、变异性、环境风险及其处治方式; 在固废沥青混合料方面, 分别从固废掺量提升及混合料耐久性提升2个方向综述固废材料低碳化路用的现状与趋势; 在固废沥青路面方面, 从结构设计与施工技术2个视角探索固废材料的高层位及全层位应用可行性。研究结果表明: 固废原材料具备路用适配性, 但其变异性与潜在环境影响是限制其大规模利用的关键, 需构建多源固废分类分级体系并配套相应的处治方式; 固废掺量提升将导致混合料路用性能不稳定, 掺量对混合料性能劣化机制以及不同固废相互作用机制仍待明晰, 全量化固废沥青混合料研究尚处于起步阶段, 是未来需要解决的重要问题; 固废沥青混合料耐久性提升技术, 尤其是固废材料与胶结料性能提升领域, 仍有待持续开展机理探索与应用实践; 从面向低碳化的高层位及全层位应用角度来看, 现有沥青路面结构设计与施工方法仍有待提升, 应针对固废特性对结构设计与施工方法进行改进。Abstract: To promote the low-carbon application of waste materials in asphalt pavement, the application progress was systematically reviewed and analyzed from three dimenisons: waste raw materials, waste-modified asphalt mixtures, and waste asphalt pavements. For waste raw materials, material classification oriented toward carbon reduction, variability, environmental risks, and corresponding treatment methods were summarized. For waste-modified asphalt mixtures, the current status and trends of low-carbon pavement application were reviewed from increased waste incorporation ratios and enhanced mixture durability. For waste asphalt pavements, the feasibility of high-level and full-layer applications of waste materials was explored from the aspects of structural design and construction techniques. It is indicated that waste raw materials possess road application adaptability, but their variability and potential environmental impacts are the key factors restricting large-scale utilization. A multi-source waste classification and grading system and corresponding treatment methods are required. Unstable pavement performance of asphalt mixtures is caused by increased waste incorporation ratios. The mechanisms of performance deterioration caused by waste content and the interaction mechanisms among different waste materials have not yet been clarified. Research on fully waste-based mixtures is still at an initial stage and is an important issue to be addressed in the future. Continuous mechanistic exploration and application practice are still required for durability enhancement techniques for waste-modified asphalt mixtures, especially for performance improvement of waste materials and binders. From the perspective of low-carbon-oriented high-level and full-layer applications, existing asphalt pavement structural designs and construction methods are still in need of improvement. Structural design and construction methods should be modified according to the characteristics of waste materials.
-
表 1 固废材料分类、来源及路用优缺点
Table 1. Classification, sources, and advantages and disadvantages of road application of solid waste materials
固废类型 固废名称 来源组成 路用优缺点 天然材料替代类 骨料替代类 钢渣 炼钢过程中排出的高温熔融废渣,经冷却破碎形成,主要成分为CaO、SiO2、Fe2O3、MgO等 优点:力学性能优异、棱角丰富、高碱性
缺点:安定性差、吸油率高、界面性能不稳定;碱性渗滤液污染水体、重金属存在析出风险RAP料 铣刨旧沥青路面所得,含旧骨料和老化沥青 优点:高温性能好、级配与强度适用
缺点:沥青老化、级配与强度不稳定建筑垃圾 拆除、施工产生的混凝土块、砖瓦、砂浆等混合废料 优点:表面粗糙嵌挤性好、有一定胶结活性
缺点:强度低、吸水率高、耐久性差、质量波动大油页岩废渣 油页岩干馏取油后的固体废渣,成分为SiO2、Al2O3、CaO等 优点:密度适中、强度较高
缺点:与沥青相容性差;部分含有机残留,可能有浸出风险填料替代类 粉煤灰 煤燃烧后的烟气中收集的细灰,主要成分为SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、少量CaO 优点:填充性好、火山灰反应
缺点:早期强度低、对水敏感;含微量重金属和可溶盐,粉尘可致呼吸危害煤矸石 煤炭开采与洗选中排出的固体废石,主要为SiO2、Al2O3、少量有机物 优点:不规则填料密实性好、粒径适宜
缺点:强度低、易风化分解、遇水软化;风化粉尘污染,渗水易酸化铁尾矿 选铁矿石过程中排出的细粒尾矿砂,主要为SiO2、Fe2O3等矿物 优点:颗粒坚硬、磨耗性好
缺点:细度高需级配调整;重金属析出风险赤泥 氧化铝生产过程中排出的碱性废渣,主要含Al2O3、Fe2O3、TiO2等 优点:颗粒细、比表面积大、稳定性好
缺点:与沥青相容性差、细粉多易泥化;高碱度渗滤液污染水体,重金属析出风险沥青改性类 废胶粉 废旧轮胎加工成的细橡胶粉,主要为交联橡胶 优点:改善沥青弹性、抗裂性和耐久性
缺点:沥青相容性差、易导致施工难度升高;热加工释放挥发性有机物废塑料 工业生产活动中产生的废弃聚乙烯、聚丙烯、PET等塑料制品 优点:改性沥青可提升抗裂性和耐久性
缺点:与沥青相容性差,热稳定性不足;热加工释放挥发性有机物(VOCs),微塑料颗粒可能长期残留废风电叶片 报废的风电叶片粉碎物,主要为玻璃纤维增强环氧树脂 优点:稳定性极高、纤维增强可提高混合料韧性
缺点:纤维表面残留树脂、界面性能及分散性差;玻璃纤维刺激皮肤并且有吸入风险磷石膏 湿法磷酸生产中生成的副产物,主要成分为CaSO4·2H2O、少量酸 优点:颗粒细、刚性大、表面极性好利于黏附
缺点:含游离酸和可溶磷、吸水率高,易水损;含游离酸、可溶磷、氟化物,污染土壤与水体磷尾矿 选磷矿过程中产生的尾矿砂,主要为CaCO3、SiO2、磷酸盐矿物 优点:硬度高、刚性大、表面粗糙
缺点:盐类杂质不稳定、吸水率高、级配不良;可溶磷污染水体表 2 固废变异性成因及其影响
Table 2. Causes and influence of solid waste variability
变异类型 主要成因 性能影响 典型示例 来源致异 原材料、生产源或回收渠道差异 成分(化学组成、活性组分)和物理性能(粒度、密度)波动大 钢渣(钢厂原料不同)、RAP(旧沥青来源差异)、磷石膏(磷矿石放射性差异)、油页岩废渣(矿床组成不同) 工艺致异 生产工艺参数(温度、破碎方式等)不一致 影响强度、密度、含水率、表面特征等物理性能 钢渣(冷却工艺差异)、建筑垃圾(破碎设备不同)、粉煤灰(除尘工艺影响细度)、RAP(铣刨工艺影响级配和强度) 储运致异 储存方式(露天/密封)、运输污染或混杂 杂质混入(如建筑垃圾混入生活垃圾)、含水率波动(粉煤灰吸湿)、化学反应(煤矸石自燃) 煤矸石(堆放自燃产生SO2)、废塑料(运输中污染)、赤泥(露天堆放碱液渗出)、铁尾矿(渗漏重金属污染) 时空致异 长期堆放导致风化、氧化或降解 化学稳定性下降(钢渣膨胀开裂)、物理性能退化(废胶粉弹性丧失)、有害物质释放(磷石膏放射性析出) 废风电叶片(紫外线降解树脂)、磷尾矿(长期淋溶产酸)、赤泥(干燥后粉尘扩散)、RAP(沥青老化变脆) 表 3 典型路用固废环境风险分类、影响机理与控制
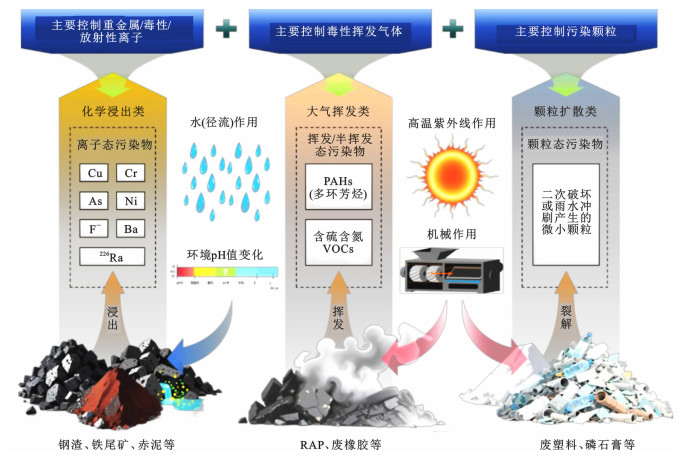
Table 3. Environmental risk classification, impact mechanism and control of typical road solid waste
分类 典型固废 测试方法 影响机制 改善/控制措施 化学浸出 钢渣[19] 浸出试验、常规性能测试、化学组成与元素测定、微观形貌观测、孔隙率及粒径测试等 Cr、Cu、Ba、Ca等在碱性条件下易析出;Cr3+氧化溶解可生成高毒Cr6+ 碳化/硫化;调整级配设计等 煤矸石[20] 饱水煤矸石持续溶出As、Cr、Ni、Cu等,水溶胶体作为载体迁移重金属 微生物封存、复合材料隔层等 磷石膏[21] 含F-、PO43-4、AsI3+、Pb2+、226Ra等,雨淋可导致毒/放射性离子浸出 碱激发沉淀 大气排放 RAP[22-23] 荧光追踪、色谱分析、质谱识别、浸出试验等 旧沥青膜中PAHs(多环芳烃)老化浓缩,在高温、雨淋、破裂、磨损等情况下更易释放 降低再生温度、增强包覆致密性、物理吸附 废橡胶[24] SBS、橡胶沥青在高温条件下裂解生成含硫含氮VOCs 物理吸附,如活性炭、沸石等 颗粒扩散 废塑料[25] 荧光追踪、微观形貌观测、学组成与元素测定等 拌和及使用过程中机械磨耗,紫外热老化、冲刷等原因破坏材料产生微小颗粒 材料预处理增强性能,石粉填充,使用质密结构等 表 4 建设期与营运期碳平衡点变化趋势
Table 4. Trends in carbon balance points during construction and operation phases
技术类别 优缺点 技术特点 物理处治 破碎与筛分 工艺简单、成本低、适配性广,但难以解决化学活性或污染问题 通过破碎和筛分优化骨料的粒径分布,从而提高其适配性与稳定性 磨细与均化 对料进行磨细,确保填料性能稳定,并提高材料的均匀性 浸水处理 调节含水率并消除有害物质,同时稳定材料活性 热处理 改善含水率,稳定/提升活性,增强适用性以及消除有害物质 超声波处理 增强分散性与均匀性,改善微观形貌,促进界面黏附 化学处治 无机化学改性 高效提升材料活性与稳定性,但处理成本高,工艺复杂且可能引发二次污染 通过无机胶凝材料(如硅酸盐水泥、生石灰、粉煤灰)固化有害成分,提高骨料强度和稳定性;或利用强酸/强碱溶解骨料表面杂质,激活潜在活性成分 有机化学改性 利用聚合物(环氧树脂、沥青乳液、聚氨酯)包裹骨料表面,改善抗渗性、柔韧性及界面黏附力;或利用表面活性剂(硅烷偶联剂)改善材料表面形貌,提升黏附性与相容性 物化联合 综合物理、化学处治优点,复合处治性能优越,但操作复杂,能耗高,对技术要求更高 利用磨细、热处理或超声波处理等多种物理处治对固废材料进行一次处理,后再利用有机/无机化学手段对固废进行化学改性二次处理 -
[1] 杜强, 孙强, 杨琦, 等. 中国交通运输业碳排放驱动因素的通径分析方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2017, 17(2): 143-150. https://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201702016DU Qiang, SUN Qiang, YANG Qi, et al. Path analysis method of driving factors of carbon emissions for Chinese transportation industry[J]. Journal of Traffic and Trans-portation Engineering, 2017, 17(2): 143-150. https://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201702016 [2] LIU N, WANG Y Q, BAI Q, et al. Road life-cycle carbon dioxide emissions and emission reduction technologies: A review[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engi-neering: English Edition, 2022, 9(4): 532-555. doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2022.06.001 [3] 郭伊均. 加快推动典型大宗固体废弃物综合利用处置进一步促进"无废城市"高标准建设[J]. 环境保护, 2024, 52(14): 9-11.GUO Yi-jun. Accelerating the comprehensive utilization and disposal of typical bulk solid waste, and further promoting the high-standard construction of "zero-waste city"[J]. Environmental Protection, 2024, 52(14): 9-11. [4] HUANG W, HU J, LUO S. The technological innovation pathway for green, low-carbon, and durable pavement construction and maintenance[J]. Science China Techno-logical Sciences, 2024, 67(12): 3959-3961. doi: 10.1007/s11431-024-2733-6 [5] 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国路面工程学术研究综述·2020[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(10): 1-66.Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China's pavement engineering Research·2020[J]. China Journal of Highway and Trans-port, 2020, 33(10): 1-66. [6] 张军辉, 陈莎莎, 顾凡, 等. 工业废弃料在路基改良中的应用综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(10): 1-16.ZHANG Jun-hui, CHEN Sha-sha, GU Fan, et al. Industrial waste materials utilized in subgrade modification: A review[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2023, 36(10): 1-16. [7] 梁旭. 工业废渣赤泥在公路中的应用技术研究. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2009.LIANG Xu. Research on the application of industrial waste residue red mud in highway engineering. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2009. [8] 司春棣, 崔亚宁, 李松, 等. 铁尾矿在沥青路面中的资源化利用研究进展与展望[J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(22): 35-47.SI Chun-di, CUI Ya-ning, LI Song, et al. Advances and prospects on the resource recovery of iron tailings in asphalt pavement[J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(22): 35-47. [9] 高闻靖. 废风机叶片复合纤维改性沥青制备工艺及技术性能研究. 长沙: 湖南科技大学, 2022.GAO Wen-jing. Preparation process and technical properties of asphalt modified with waste wind turbine blade composite fiber. Changsha: Hunan University of Science and Tech-nology, 2022. [10] MAO R C, DUAN H B, DONG D, et al. Quantification of carbon footprint of urban roads via life cycle assessment: Case study of a megacity-Shenzhen, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 166: 40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.173 [11] GIANI M I, DOTELLI G, BRANDINI N, et al. Compara-tive life cycle assessment of asphalt pavements using reclaimed asphalt, warm mix technology and cold in-place recycling[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2015, 104: 224-238. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.08.006 [12] LUO Y F, ZHAO X C, ZHANG K. Coal gangue in asphalt pavement: A review of applications and performance influence[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2024, 20: e03282. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03282 [13] 徐金枝, 郝培文, 郭晓刚, 等. 厂拌热再生沥青混合料组成设计方法综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(10): 72-88.XU Jin-zhi, HAO Pei-wen, GUO Xiao-gang, et al. Review of mix design method of hot in-plant recycled asphalt mixture[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(10): 72-88. [14] 李超, 陈宗武, 谢君, 等. 钢渣沥青混凝土技术及其应用研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(3): 86-95, 122.LI Chao, CHEN Zong-wu, XIE Jun, et al. A technological and applicational review on steel slag asphalt mixture[J]. Materials Review, 2017, 31(3): 86-95, 122. [15] ZHANG J Z, YAO Z Y, WANG K, et al. Sustainable utili-zation of bauxite residue (Red Mud) as a road material in pavements: A critical review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 270: 121419. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121419 [16] 张强. 钢渣膨胀抑制方法及其沥青混合料路用性能研究. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2023.ZHANG Qiang. Study on expansion suppression methods of steel slag and road performance of asphalt mixtures. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2023. [17] 吴少鹏, 崔培德, 谢君, 等. 钢渣集料膨胀抑制方法及混合料体积稳定性研究现状[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(10): 166-179.WU Shao-peng, CUI Pei-de, XIE Jun, et al. Expansive inhibition method of steel slag aggregate and volume stability of mixture: A review[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(10): 166-179. [18] TAM V W Y, SOOMRO M, EVANGELISTA A C J. A review of recycled aggregate in concrete applications (2000-2017)[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 172: 272-292. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.240 [19] GAN Y W, LI C M, ZOU J F, et al. Evaluation of the impact factors on the leaching risk of steel slag and its asphalt mixture[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 16: e01067. [20] SONG W, XU R P, LI X J, et al. Soil reconstruction and heavy metal pollution risk in reclaimed cultivated land with coal gangue filling in mining areas[J]. Catena, 2023, 228: 107147. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2023.107147 [21] MAINA L, KIEGIEL K, ZAKRZEWSKA-KOŁTUNIEWICZ G. Challenges and strategies for the sustainable environmental management of phosphogypsum[J]. Sustainability, 2025, 17(8): 3473. doi: 10.3390/su17083473 [22] JANDOVÁ V, BUCKOVÁ M, HUZLÍK J, et al. Release of PAHs from reclaimed asphalt mixtures into the water environment after passivation by cold in-place recycling technology[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2025, 32(5): 2455-2466. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-35875-2 [23] LIN A M, TIMSHINA A S, MAGNUSON J K, et al. Emerging polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) and trace metal leachability from reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP)[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 333: 138937. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138937 [24] BORINELLI J B, PORTILLO-ESTRADA M, COSTA J O, et al. Emission reduction agents: A solution to inhibit the emission of harmful volatile organic compounds from crumb rubber modified bitumen[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 411: 134455. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134455 [25] DUAN Y F, WU K, SERRAT C, et al. Assessment of microplastics production from waste plastics-modified asphalt pavement[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2024, 202: 107329. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.107329 [26] ZAUMANIS M, BOESIGER L, KUNZ B, et al. Three indexes to characterise crushing and screening of reclaimed asphalt pavement[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engi-neering, 2022, 23(14): 4977-4990. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2021.1990287 [27] SABERI K F, FAKHRI M, AZAMI A. Evaluation of warm mix asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement and crumb rubber[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 165: 1125-1132. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.079 [28] SUN J, HUANG W, WANG X M, et al. Feasibility of pretreated steel slag for asphalt pavement application and risk assessment of hazardous substance leaching[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 498: 155497. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.155497 [29] AURANGZEB Q, AL-QADI I L, OZER H, et al. Hybrid life cycle assessment for asphalt mixtures with high RAP content[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2014, 83: 77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.12.004 [30] GU J R, LIU X M, ZHANG Z Q. Road base materials prepared by multi-industrial solid wastes in China: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 373: 130860. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130860 [31] Copeland A. Department of transportation. federal highway administration. office of infrastructure research and develop-ment. reclaimed asphalt pavement in asphalt mixtures: State of the practice. McLean: Research, Development, and Technology Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center, 2011. [32] 张志祥, 吴建浩. 再生沥青混合料疲劳性能试验研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(2): 31-35.ZHANG Zhi-xiang, WU Jian-hao. Experimental research on fatigue characteristics of RAP mixtures[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2006, 19(2): 31-35. [33] SHU X, HUANG B S, VUKOSAVLJEVIC D. Laboratory evaluation of fatigue characteristics of recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2008, 22(7): 1323-1330. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.04.019 [34] 赵斌. 沥青混合料热再生机理及技术性能研究. 西安: 长安大学, 2012.ZHAO Bin. Study on recycling mechanism and technical property of the plant hot asphalt mixture. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2012. [35] ZAUMANIS M, MALLICK R B, POULIKAKOS L, et al. Influence of six rejuvenators on the performance properties of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) binder and 100% recycled asphalt mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 71: 538-550. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.08.073 [36] FAN X Z, QIAO Y H, ZHANG J Z, et al. Towards the high RAP dosage obtained by refined processing influence on comprehensive performance of recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 452: 138885. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.138885 [37] NANDA H, SIDDAGANGAIAH A K. Effect of RAP fractionation and dosage on design and mechanical behaviour of cold asphalt mixes[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 422: 135773. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135773 [38] MONTAÑEZ J, CARO S, CARRIZOSA D, et al. Variability of the mechanical properties of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) obtained from different sources[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 230: 116968. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116968 [39] 王晨. 多来源RAP料性能评价及超高比例厂拌热再生利用技术研究. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.WANG Chen. Performance evaluation of multi-source rap materials and technology for ultra-high proportion hot recycling in plant. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021. [40] 钟昆志. 旧沥青路面材料精细化再生利用技术研究. 南京: 东南大学, 2022.ZHONG Kun-zhi. Research on refinement recycling tech-nology of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Nanjing: South-east University, 2022. [41] PEI Z S, YI J Y, XU M, et al. Exploration of the design theory of crack-resistant rejuvenator for warm-mix recycled asphalt mixtures with high RAP contents[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 388: 135855. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.135855 [42] 许勐. 基于分子扩散融合机制的沥青再生剂设计与性能验证. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.XU Meng. Design and performance verification of rejuvenator based on molecular diffusion fusion mechanism. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. [43] 周健. 大旧料掺量再生沥青混合料的高模量化设计理论与性能研究. 南京: 东南大学, 2020.ZHOU Jian. Study on high modulus design theory and performance of recycled asphalt mixture with large amount of RAP. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2020. [44] 周洲. 不同RAP料掺量热再生改性沥青混合料耐久性能研究. 南京: 东南大学, 2015.ZHOU Zhou. Durability Study of Hot Recycled Modified Asphalt Mixtures with Different RAP Contents. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015. [45] CUI P D, WU S P, XIAO Y, et al. Environmental perfor-mance and functional analysis of chip seals with recycled basic oxygen furnace slag as aggregate[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124441. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124441 [46] WU S P, XUE Y J, YE Q S, et al. Utilization of steel slag as aggregates for stone mastic asphalt (SMA) mixtures[J]. Building and Environment, 2007, 42(7): 2580-2585. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2006.06.008 [47] 高振鑫, 申爱琴, 翟超伟, 等. 钢渣沥青混合料体积参数测定与水稳定性影响机理[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2018, 18(2): 1-10. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2018.02.001GAO Zhen-xin, SHEN Ai-qin, ZHAI Chao-wei, et al. Determination of volumetric parameters and impacting mechanism of water stability for steel slag asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2018, 18(2): 1-10. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2018.02.001 [48] LIU J Z, CHEN S H, LIU Q, et al. Influence of steel slag incorporation on internal skeletal contact characteristics within asphalt mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 352: 129073. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129073 [49] XU H Q, ZOU Y X, AIREY G, et al. Interfacial characte-ristics between bitumen and corrosion products on steel slag surface from molecular scale[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 417: 135324. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135324 [50] ZHAO W X, WEN W, LI H R, et al. Research on the performance of asphalt mixture with acid-treated steel slag based on microscopic properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 455: 139134. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.139134 [51] CHEN Z W, GONG Z L, JIAO Y Y, et al. Moisture stability improvement of asphalt mixture considering the surface characteristics of steel slag coarse aggregate[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 251: 118987. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118987 [52] ZHANG Z, ZHENG X G, LI J Y, et al. Mechanism of reinforced interfacial adhesion between steel slag and highly devulcanized waste rubber modified asphalt and its influence on the volume stability in steel slag asphalt mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 447: 138129. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.138129 [53] WANG L, CHEN L, LI Y X, et al. Adhesion characteristics of warm-mix crumb rubber-modified asphalt-steel slag inter-face under water erosion[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2024, 36(9): 04024270. doi: 10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-17981 [54] ZHANG C, YU H N, QIAN G P, et al. Study on the effect of limestone replacement by steel slag on the interface interaction between asphalt and aggregate[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2025, 471: 140709. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.140709 [55] PARANAVITHANA S, MOHAJERANI A. Effects of recycled concrete aggregates on properties of asphalt concrete[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2006, 48(1): 1-12. [56] 张涛. 再生骨料改性及其在沥青混合料中的应用. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2010.ZHANG Tao. Modification of recycled aggregate and its application in asphalt mixtures. Wuhan: Wuhan Univer-sity of Technology, 2010. [57] HOU Y Q, JI X P, SU X L, et al. Laboratory investigations of activated recycled concrete aggregate for asphalt treated base[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 65: 535-542. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.115 [58] WU S H, MUHUNTHAN B, WEN H F. Investigation of effectiveness of prediction of fatigue life for hot mix asphalt blended with recycled concrete aggregate using monotonic fracture testing[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 131: 50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.045 [59] 朱继青. 地震建筑废弃物制备的沥青混合料的性能研究. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2012.ZHU Ji-qing. Investigation on properties of asphalt mixture containing demolition waste obtained from earthquake-damaged buildings. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Tech-nology, 2012. [60] PASANDÍN A R, PÉREZ I. Mechanical properties of hot-mix asphalt made with recycled concrete aggregates coated with bitumen emulsion[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 55: 350-358. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.01.053 [61] ALBAYATI A, WANG Y, WANG Y, et al. A sustainable pavement concrete using warm mix asphalt and hydrated lime treated recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2018, 18: e00081. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2018.e00081 [62] KAREEM A I, NIKRAZ H, ASADI H. Performance of hot-mix asphalt produced with double coated recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 205: 425-433. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.02.023 [63] 侯月琴. 水泥混凝土再生集料在沥青路面中的应用研究. 西安: 长安大学, 2014.HOU Yue-qin. Research on application of recycled cement concrete aggregate in asphalt pavement. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2014. [64] 郭学东, 李颖松, 郭威, 等. 基于中心复合设计法的油页岩废渣改良OGFC抗春融水损性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(1): 73-78.GUO Xue-dong, LI Ying-song, GUO Wei, et al. Spring-thawing stability of OGFC modified by oil shale waste based on central composite design method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 73-78. [65] GUO W, XU H Y, YU Y, et al. Enhancement mechanism of oil shale waste filled asphalt mixtures based on oil adsorption and storage behavior[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2025, 479: 141473. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.141473 [66] 李伟, 程培峰, 李国栋. 煤矸石沥青混合料路用性能的试验[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2009, 37(6): 54-55, 58.LI Wei, CHENG Pei-feng, LI Guo-dong. Experiment on road performance of asphalt mixture of coal gangue[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2009, 37(6): 54-55, 58. [67] LI Z X, FANG C Z, GUO T T, et al. Study on road performance of asphalt mixture based on surface modification of coal gangue[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2024, 21: e03743. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03743 [68] ZHANG F, HU C B. The research for crumb rubber/waste plastic compound modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2016, 124(2): 729-741. doi: 10.1007/s10973-015-5198-4 [69] YAO L Y, LENG Z, LAN J T, et al. Environmental and economic assessment of collective recycling waste plastic and reclaimed asphalt pavement into pavement construction: A case study in Hong Kong[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 336: 130405. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130405 [70] YANG C, WU S P, CUI P D, et al. Performance characte-rization and enhancement mechanism of recycled asphalt mixtures involving high RAP content and steel slag[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 336: 130484. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130484 [71] YAO Y Q, GAO J, YANG J G, et al. Sustainable asphalt concrete containing RAP and coal gangue aggregate: Performance, costs, and environmental impact[J]. Journal of Renewable Materials, 2022, 10(8): 2263-2285. doi: 10.32604/jrm.2022.018911 [72] LIU M J, LUO S, HUANG W, et al. Enabling high-RAP-content recycling in asphalt pavements through epoxy modification: Durability and life cycle assessment[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2025, 45: e01519. [73] SUN J, HUANG W, WANG X M, et al. Epoxy steel slag asphalt mixture: Achieving breakthrough in pavement performance and efficient waste resource utilization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 520: 166262. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2025.166262 [74] SONG Y, XU H Q, WU S P, et al. High-quality utilization of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) in asphalt mixture with the enhancement of steel slag and epoxy asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 445: 137963. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.137963 [75] ZHAO W T, YANG Q. Life-cycle assessment of sustainable pavement based on the coordinated application of recycled asphalt pavement and solid waste: Environment and economy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 434: 140203. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140203 [76] ZHAO W T, QIAN G P, YANG Q. Sustainable pavement design: A comprehensive study on incorporating 100% recycled asphalt pavement and utilizing 100% industrial solid waste[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2025, 462: 139972. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.139972 [77] PEIRIS D, GUNASEKARA C, LAW D W, et al. Impact of treatment methods on recycled concrete aggregate perfor-mance: A comprehensive review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2025, 32(24): 14405-14438. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36497-y [78] WANG F S, HOFF I, YANG F, et al. Comparative assess-ments for environmental impacts from three advanced asphalt pavement construction cases[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 297: 126659. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126659 [79] BHARATH G, REDDY K S, TANDON V, et al. Aggregate gradation effect on the fatigue performance of recycled asphalt mixtures[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2021, 22(1): 165-184. doi: 10.1080/14680629.2019.1620116 [80] SWATHI M, ANDIYAPPAN T, GUDURU G, et al. Design of asphalt mixes with steel slag aggregates using the Bailey method of gradation selection[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 279: 122426. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122426 [81] 吴军, 夏海廷, 郭荣鑫, 等. 基于改进多点支撑骨架状态模型的热再生沥青混合料配合比设计[J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(增1): 178-184.WU Jun, XIA Hai-ting, GUO Rong-xin, et al. Hot recycled asphalt mix proportion design based on improved state model of multi-point support skeleton[J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(S1): 178-184. [82] 李正中, 魏如喜, 宋晓燕, 等. 基于GTM法的温拌胶粉改性沥青混合料设计研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2013, 16(6): 968-974.LI Zheng-zhong, WEI Ru-xi, SONG Xiao-yan, et al. Design and research on the warm-mix rubber-modified asphalt mixture based on the GTM method[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2013, 16(6): 968-974. [83] LIU Z M, SUN L J, ZHAI J H, et al. A review of design methods for cold in-place recycling asphalt mixtures: Design processes, key parameters, and evaluation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 370: 133530. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133530 [84] ZAUMANIS M, POULIKAKOS L, ARRAIGADA M, et al. Hot asphalt recycling in cold climate: Performance-based mixture design and a test section in the Swiss Alps[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2025, 26(8): 1914-1950. doi: 10.1080/14680629.2024.2433166 [85] NING H, CAI J, DENG B, et al. Development of modified balanced mix design method for cold recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2025, 22: e04784. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2025.e04784 [86] SUN Y, ZHANG X, CHEN J J, et al. Mixing design and performance of porous asphalt mixtures containing solid waste[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2024, 21: e03644. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03644 [87] 郭乃胜, 尤占平, 赵颖华, 等. 温拌再生沥青混合料耐久性能[J]. 中国公路学报, 2014, 27(8): 17-22.GUO Nai-sheng, YOU Zhan-ping, ZHAO Ying-hua, et al. Durability of warm mix asphalt containing recycled asphalt mixtures[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014, 27(8): 17-22. [88] 季节, 索智, 许鹰, 等. SMA温拌再生沥青混合料性能试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(5): 28-33.JI Jie, SUO Zhi, XU Ying, et al. Experimental research on performance of warm-recycled mixture asphalt with SMA[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(5): 28-33. [89] KUNA K, AIREY G, THOM N. Mix design considerations of foamed bitumen mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement material[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2017, 18(10): 902-915. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2015.1126271 [90] LIN J T, HUO L, XU F, et al. Development of microstructure and early-stage strength for 100% cold recycled asphalt mixture treated with emulsion and cement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 189: 924-933. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.064 [91] LIU W H, LI H, ZHU H M, et al. The interfacial adhesion performance and mechanism of a modified asphalt-steel slag aggregate[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(5): 1180. doi: 10.3390/ma13051180 [92] ALQARNI A S, ABBAS H, AL-SHWIKH K M, et al. Treatment of recycled concrete aggregate to enhance concrete performance[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 307: 124960. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124960 [93] GAO C, HUANG L, YAN L B, et al. Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete modified by nano-particles[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 241: 118030. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118030 [94] ZHANG J K, SHI C J, LI Y K, et al. Performance enhan-cement of recycled concrete aggregates through carbonation[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2015, 27(11): 04015029. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001296 [95] WANG X F, DU G H, CAI L M, et al. Effect of crystallizer treatment on chloride diffusion and microstructure of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 321: 126273. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.126273 [96] PANGHAL H, KUMAR A. Enhancing concrete performance: Surface modification of recycled coarse aggregates for sustainable construction[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 411: 134432. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134432 [97] OUYANG K, LIU J H, LIU S H, et al. Influence of pre-treatment methods for recycled concrete aggregate on the performance of recycled concrete: A review[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 188: 106717. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106717 [98] KATO K, XIN Y Z, HITOMI T, et al. Surface modification of fly ash by mechano-chemical treatment[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(1): 849-853. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.09.254 [99] YANG Y F, GAI G S, CAI Z F, et al. Surface modification of purified fly ash and application in polymer[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 133(1/2/3): 276-282. [100] XUE X, LIU Y L, DAI J G, et al. Inhibiting efflorescence formation on fly ash-based geopolymer via silane surface modification[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2018, 94: 43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.08.013 [101] HOY M, HORPIBULSUK S, ARULRAJAH A. Strength development of recycled asphalt pavement-fly ash geopolymer as a road construction material[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 117: 209-219. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.04.136 [102] LIU S, JIN J, YU H Y, et al. Performance enhancement of modified asphalt via coal gangue with microstructure control[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 367: 130287. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.130287 [103] LI J R, CAO Y S, SHA A M, et al. Prospective application of coal gangue as filler in fracture-healing behavior of asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 373: 133738. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133738 [104] WEI Z Y, JIA Y S, WANG S Q, et al. Utilization of iron ore tailing as an alternative mineral filler in asphalt mastic: High-temperature performance and environmental aspects[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 335: 130318. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130318 [105] LI J R, SHA A M, WANG Z J, et al. Investigation of the self-healing, road performance and cost-benefit effects of an iron tailing/asphalt mixture in pavement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 422: 135788. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135788 [106] WEI Z Y, JIA Y S, WANG S Q, et al. Influence of iron tailing filler on rheological behavior of asphalt mastic[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 352: 129047. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129047 [107] LI S, ZHANG Z X, SI C D, et al. Evaluation of the rheological properties of asphalt mastic incorporating iron tailings filler as an alternative to limestone filler[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2025, 486: 144444. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144444 [108] WANG H B, LI H, ZHANG H J, et al. Experimental study on the aging behavior of modified asphalt with different types of fine solid wastes under different aging conditions[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 291: 123308. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123308 [109] ZHANG J Z, LI P Z, WANG K, et al. Adhesive behavior and pavement performance of asphalt mixtures incorporating red mud as a filler substitute[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 298: 123855. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123855 [110] CHAVEZ F, MARCOBAL J, GALLEGO J. Laboratory evaluation of the mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures with rubber incorporated by the wet, dry, and semi-wet process[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 205: 164-174. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.01.159 [111] WANG H P, APOSTOLIDIS P, ZHU J Q, et al. The role of thermodynamics and kinetics in rubber-bitumen systems: A theoretical overview[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2021, 22(14): 1785-1800. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2020.1724289 [112] LI H B, ZHOU L C, SUN J M, et al. Analysis of the influence of production method, plastic content on the basic performance of waste plastic modified asphalt[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(20): 4350. doi: 10.3390/polym14204350 [113] IBRAHIM H, MARINI S, DESIDERY L, et al. Recycled plastics and rubber for green roads: The case study of devulcanized tire rubber and waste plastics compounds to enhance bitumen performance[J]. Resources, Conservation & Recycling Advances, 2023, 18: 200157. [114] LIN J, GUO Z X, HONG B, et al. Using recycled waste glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) as filler to improve the performance of asphalt mastics[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 336: 130357. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130357 [115] LAN T H, WANG B Z, ZHANG J C, et al. Utilization of waste wind turbine blades in performance improvement of asphalt mixture[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2023, 10: 1164693. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2023.1164693 [116] YANG Q L, FAN Z P, YANG X, et al. Recycling waste fiber-reinforced polymer composites for low-carbon asphalt concrete: The effects of recycled glass fibers on the durability of bituminous composites[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 423: 138692. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138692 [117] ZHANG T L, HU K, CHEN Y J, et al. Feasibility and environmental assessment of introducing waste polyurethane from wind turbine blades as a modifier for asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 446: 138052. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.138052 [118] 段珍华, 张韦, 朱仄平, 等. 退役风机叶片的回收与资源化应用研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2025, 44(4): 1267-1275.DUAN Zhen-hua, ZHANG Wei, ZHU Ze-ping, et al. Research progress on recycling and resource application of retired wind turbine blades[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2025, 44(4): 1267-1275. [119] TAN Z F, GUO Y Q, HU G W, et al. Upcycling waste wind turbine blades into fiber-reinforced asphalt mortar: A chemical recycling approach and performance assessment[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2025, 489: 142352. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.142352 [120] LUO Y, HUANG J S, WANG Y J, et al. Enhancing the properties and engineering performance of asphalt binders and mixtures with physicochemically treated waste wind turbine blades[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2025, 473: 141023. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.141023 [121] OU L, ZHU H Z, XU Y L, et al. Gray correlation entropy analysis of zero shear viscosity and high-temperature rheological parameters of phosphogypsum-modified asphalt[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 17: e01448. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01448 [122] GUO W, GU K P, XU H Y, et al. Properties enhancement of asphalt mortar incorporating phosphogypsum based on surface activation[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2025, 22: e04251. [123] YIN P, PAN B F, LI Z H, et al. Multi-scale investigation of the adhesion properties of phosphogypsum whisker composite modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 420: 135608. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135608 [124] ZHANG X Q, LI J, OU L, et al. Preparation of calcium sulphate whiskers from phosphogypsum for asphalt modification: Rheological properties and microscopic mecha-nisms[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2024, 25(1): 1-14. [125] YIN P, PAN B F, LI Z H, et al. Effect of surfactant modified phosphogypsum whisker on service performance of asphalt based on multi-scale experiments[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 464: 142774. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142774 [126] CHEN S C, ZOU Y X, LIU Q T, et al. Synthesis of hydrotalcite from phosphate tailings and its effect on the anti-ultraviolet aging properties of asphalt binder[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2022, 34(9): 04022230. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004385 [127] 董泽蛟, 刘美丽, 郑好, 等. 考虑横观各向同性特性的沥青路面动力学分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2012, 25(5): 18-23.DONG Ze-jiao, LIU Mei-li, ZHENG Hao, et al. Dynamic mechanical analysis of asphalt pavement based on cross-isotropic properties[J]. China Journal of Highway and Trans-port, 2012, 25(5): 18-23. [128] YOU L Y, XIAO Z, QUAN W W, et al. Influence of aniso-tropy on structural dynamic response, from the views of mechanism, analysis method, and implications for pavement design[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2025, 26(1): 1-21. [129] 杨涛, 郑健龙, 关宏信, 等. 考虑材料正交各向异性时的沥青路面结构力学性能[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(12): 4283-4291.YANG Tao, ZHENG Jian-long, GUAN Hong-xin, et al. Mechanical properties of asphalt pavement considering orthotropy of each layer materials[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2016, 47(12): 4283-4291. [130] WANG H, AL-QADI I L. Importance of nonlinear anisotropic modeling of granular base for predicting maximum viscoelastic pavement responses under moving vehicular loading[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 139(1): 29-38. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000465 [131] SMITH S, BRAHAM A. Comparing layer types for the use of pavement ME for asphalt emulsion full depth reclamation design[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 158: 481-489. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.10.054 [132] 胡宗文. 冷再生沥青路面材料性能及结构组合研究. 西安: 长安大学, 2012.HU Zong-wen. The study of material properties and structure combination of cold recycled asphalt pavement. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2012. [133] 祝谭雍. 基于再生沥青混合料性能特点的再生路面设计研究. 南京: 东南大学, 2017.ZHU Tan-yong. Structural analysis and design for recycled asphalt pavement based on the performance characteristics of recyled asphalt mixture. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017. [134] 冀欣, 盛燕萍, 路再红, 等. 掺加钢渣的半刚性基层材料性能[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 41(4): 21-31.JI Xin, SHENG Yan-ping, LU Zai-hong, et al. Properties of semi-rigid base material with steel slag[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 41(4): 21-31. [135] 都伟, 张明欣, 王彦敏, 等. 废旧沥青混合料在路面基层中的应用研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(增1): 298-302.DU Wei, ZHANG Ming-xin, WANG Yan-min, et al. Research progress on the application of waste asphalt mixture in pavement base layer[J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(S1): 298-302. [136] 马涛, 栾英成, 何亮, 等. 乳化沥青与泡沫沥青冷再生技术发展综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(2): 1-23. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.02.001MA Tao, LUAN Ying-cheng, HE Liang, et al. Review on cold recycling technology development of emulsified asphalt and foamed asphalt[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(2): 1-23. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.02.001 [137] LI X Q, WU S P, WANG F S, et al. Quantitative assess-ments of GHG and VOCs emissions of asphalt pavement contained steel slag[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 369: 130606. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130606 [138] 梁波, 张海涛, 梁缘, 等. 温拌沥青技术研究综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(2): 24-46. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.02.002LIANG Bo, ZHANG Hai-tao, LIANG Yuan, et al. Review on warm mixing asphalt technology[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(2): 24-46. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.02.002 [139] MARTINHO F C G, PICADO-SANTOS L G, CAPITÃO S D. Influence of recycled concrete and steel slag aggregates on warm-mix asphalt properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 185: 684-696. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.041 [140] PASETTO M, BALIELLO A, GIACOMELLO G, et al. Sustainable solutions for road pavements: A multi-scale characterization of warm mix asphalts containing steel slags[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 166: 835-843. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.212 [141] ZHOU X W, WANG Z J, GUO H Y, et al. Steel slag aggregate property improvement in cold mixed asphalt mixtures through surface modification treatment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 477: 143889. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.143889 [142] 周雄, 武建民, 杨永利, 等. 钢渣沥青混合料碾压温度场[J]. 筑路机械与施工机械化, 2019, 36(3): 79-85.ZHOU Xiong, WU Jian-min, YANG Yong-li, et al. Rolling temperature field of steel slag asphalt mixture[J]. Road Machinery & Construction Mechanization, 2019, 36(3): 79-85. [143] 何亮, 詹程阳, 吕松涛, 等. 钢渣沥青混合料应用现状[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(2): 15-33. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.002HE Liang, ZHAN Cheng-yang, LYU Song-tao, et al. Appli-cation status of steel slag asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(2): 15-33. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.02.002 [144] LIU Z Z, FENG T T, ZHU X Y, et al. Bird's-eye view of recycled solid wastes in road engineering[J]. Journal of Road Engineering, 2024, 4(2): 93-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jreng.2024.05.002 [145] YAN T Y, MENG Y J, LUO X W, et al. Application of aluminum industry solid waste in asphalt mixtures and its impact on performance: Current research and future perspec-tives[J]. Journal of Road Engineering, 2025, 5(4): 554-571. doi: 10.1016/j.jreng.2025.06.002 [146] OLUWASOLA E A, HAININ M R, AZIZ M M A. Compa-rative evaluation of dense-graded and gap-graded asphalt mix incorporating electric arc furnace steel slag and copper mine tailings[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 122: 315-325. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.051 -





 下载:
下载: