Road safety level evaluation based on grey fixed weight clustering model and factors analysis
-
摘要: 为衡量区域内高等级公路的整体交通安全水平, 辨析道路因素对交通安全的影响程度, 综合运用灰类白化权函数聚类理论、模糊一致性理论及层次分析法, 提出了一种系统评价道路安全性的新方法, 通过灰色定权聚类对区域内高等级公路分类, 采用模糊一致性矩阵确定聚类权, 运用AHP分析道路因素重要度。算例分析结果显示公路5属于低安全等级灰类, 层次总排序结果表明平纵线形组合、隔离防护设施、视距和混流程度4项道路因素是导致其安全等级低的主要原因。这说明该方法可客观划分高等级公路安全级别, 并对影响交通安全的各项因素按照重要度进行排序, 实现了道路交通安全性的系统评价。Abstract: In order to determine the holistic traffic safety levels of higher-class highways in a district, and distinguish the influence degrees of road factors on traffic safety, grey clustering theory of whitenization weight function, fuzzy theory and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) were studied, a new synthesized method for evaluating road safety level was put forward.Higher-class highways in a district were categorized into several safety grades by utilizing grey fixed weight clustering.The weight of each clustering criterion was determined by adopting fuzzy consistency matrix.Main road factors that influenced traffic safety were quantificationally analyzed by using AHP.Analysis result of an example shows that highway No.5 belongs to the grey group of low safety grade, its namely alignment combination, safeguard facilities, sight distance and mixed degree are main reasons to result in the low safety grade.Which indicates that the method can objectively compartmentalize the traffic safety levels of higher-class highways, give a reasonable order of the factors that affected traffic safety, and realize the systematic evaluation of road traffic safety.
-
Key words:
- traffic safety /
- higher-class highway /
- grey clustering /
- fuzzy consistency matrix /
- AHP /
- safety evaluation
-
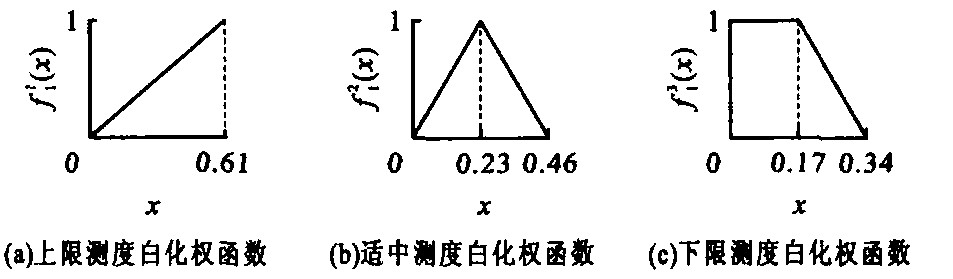
表 1 聚类白化数矩阵
Table 1. Clustering whitenization matrix
路线名称 当量事故率 事故严重程度 当量死亡率 平均交通量/ (104veh·a-1) 公路1 0.229 0 0.042 6 0.412 7 55.635 7 公路2 0.170 0 0.023 5 0.206 7 92.378 8 公路3 0.213 0 0.126 8 0.274 0 160.722 8 公路4 0.292 0 0.020 3 0.134 3 87.362 9 公路5 0.614 0 0.075 3 0.927 7 73.675 4 表 2 MAC判断矩阵
Table 2. Judgment matrix MAC
A C1 C2 C3 C4 W0 一致性检验结果 C1 1 1/7 1/6 1/3 0.053 5 λmax0=4.174 8CI0=0.058 3RI0=0.89CR0=0.07 < 0.10 C2 7 1 3 5 0.542 9 C3 6 1/3 1 4 0.291 3 C4 3 1/5 1/4 1 0.112 3 表 3 MC1P判断矩阵
Table 3. Judgment matrix MC1P
C1 P1 P2 P3 P4 W1 一致性检验结果 P1 1 1 6 3 0.387 5 λmax1=4.100 4CI1=0.033 5RI1=0.89CR1=0.04 < 0.10 P2 1 1 6 3 0.387 5 P3 1/6 1/6 1 1/5 0.054 2 P4 1/3 1/3 5 1 0.170 8 表 4 MC2P判断矩阵
Table 4. Judgment matrix MC2P
C2 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 W2 一致性检验结果 P5 1 1/4 1/7 1/6 1/3 2 0.047 2 λmax2=6.283 6CI2= 0.056 7RI2=1.26CR2= 0.05 < 0.10 P6 4 1 1/6 1/3 1 4 0.112 2 P7 7 6 1 3 6 8 0.467 0 P8 6 3 1/3 1 3 6 0.234 9 P9 3 1 1/6 1/3 1 4 0.104 5 P10 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/6 1/4 1 0.034 2 表 5 MC3P判断矩阵
Table 5. Judgment matrix MC3P
C3 P11 P12 P13 P14 W3 一致性检验结果 P11 1 1 4 1/5 0.154 8 λmax3=4.180 7CI3=0.060 2RI3=0.89CR3=0.07 < 0.10 P12 1 1 6 1/5 0.181 1 P13 1/4 1/6 1 1/8 0.048 2 P14 5 5 8 1 0.616 0 表 6 MC4P判断矩阵
Table 6. Judgment matrix MC4P
C4 P15 P16 P17 P18 P19 W4 一致性检验结果 P15 1 1/3 1 1 1/6 0.080 1 λmax4=5.058 5CI4= 0.014 6RI4=1.12CR4= 0.01 < 0.10 P16 3 1 3 3 1/4 0.211 9 P17 1 1/3 1 1 1/6 0.080 1 P18 1 1/3 1 1 1/6 0.080 1 P19 6 4 6 6 1 0.547 6 表 7 影响因素层次总排序
Table 7. Final orders of road influence factors
P C 各影响因素总排序权重 各影响因素重要度排序 C1 C2 C3 C4 0.053 5 0.542 9 0.291 3 0.112 3 P1 0.387 5 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.020 7 11 P2 0.387 5 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.020 7 11 P3 0.054 2 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.002 9 19 P4 0.170 8 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.009 1 15 P5 0.000 0 0.047 2 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.025 6 9 P6 0.000 0 0.112 2 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.060 9 5 P7 0.000 0 0.467 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.253 5 1 P8 0.000 0 0.234 9 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.127 5 3 P9 0.000 0 0.104 5 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.056 7 6 P10 0.000 0 0.034 2 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.018 6 13 P11 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.154 8 0.000 0 0.045 1 8 P12 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.181 1 0.000 0 0.052 8 7 P13 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.048 2 0.000 0 0.014 0 14 P14 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.616 0 0.000 0 0.179 4 2 P15 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.080 1 0.009 0 16 P16 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.211 9 0.023 8 10 P17 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.080 1 0.009 0 16 P18 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.080 1 0.009 0 16 P19 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.547 6 0.061 5 4 ∑Pi 1 1 1 1 1 -
[1] 杨宏志, 许金良, 李建士. 基于计算机仿真的公路线形设计评价[J]. 中国公路学报, 2005, 18 (1): 14-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200501004.htmYang Hong-zhi, Xu Jin-liang, Li Jian-shi. Evaluation of highway route design based on computer simulation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2005, 18 (1): 14-18. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200501004.htm [2] 丁艺. 应用模糊评判法评价高速公路交通安全[J]. 福建林学院学报, 2001, 21 (2): 128-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJLB200102008.htmDing Yi. Applying the method of fuzzy synthetically judgement toappraising the traffic safety of the expressway[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 2001, 21 (2): 128-131. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJLB200102008.htm [3] 成卫, 丁同强, 李江. 道路交叉口交通冲突灰色评价研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2004, 21 (6): 97-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK200406025.htmCheng Wei, Ding Tong-qiang, Li Jiang. Evaluation of traffic conflict based on gray theory at intersection[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2004, 21 (6): 97-100. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK200406025.htm [4] Barry R, Ralph M, Stair J. Quantitative Analysis for Man-agement[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2001. [5] 谭跃进, 陈英武, 易进先. 系统工程原理[M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 1999. [6] 刘思峰, 郭天榜, 党耀国. 灰色系统理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000. [7] Chen Zhi-xiang. An application of grey clustering method inthe sporting clothing style evaluation[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2001, 12 (2): 19-22. [8] Mikhailov L, Tsvetinov P. Evaluation of services using a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2004, 5 (1): 23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2004.04.001 [9] Kaguei S, Ohsato A. The rank of a fuzzy matrix andits evaluation[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1990, 38 (3): 355-364. doi: 10.1016/0165-0114(90)90208-N [10] 姚敏, 张森. 模糊一致矩阵及其在决策分析中的应用[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 1998, 18 (5): 78-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL805.014.htmYao Min, Zhang Sen. Fuzzy consistent matrix and its application in decision making[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering Theory and Practice, 1998, 18 (5): 78-81. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL805.014.htm [11] 张生瑞, 马壮林. 高速公路隧道交通环境评价指标体系[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 26 (2): 77-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200602018.htmZhang Sheng-rui, Ma Zhuang-lin. Evaluation indices for trafficenvironment of expressway tunnel[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 26 (2): 77-80. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL200602018.htm [12] 余劲, 张玮. 航道网规划多级模糊综合评价[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2005, 5 (4): 96-100. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200504020Yu Jin, Zhang Wei. Multilevel-fuzziness-comprehensiveness evaluation model of waterway net planning[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2005, 5 (4): 96-100. (in Chinese) http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200504020 -





 下载:
下载: