Optimization of end line network with door to door operation mode of highway passenger transport
-
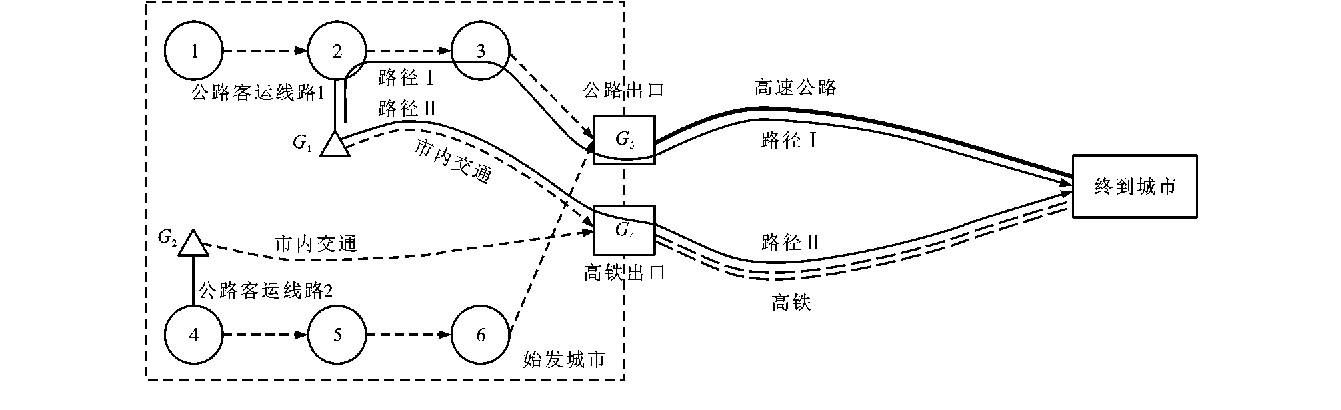
摘要: 为解决高铁时代公路客运难的问题, 提出门到门的公路客运运营模式, 并构建了双层规划模型, 上层模型以公路客运服务商的日运营总利润最大为目标, 优化门到门模式下公路客运的末端线网, 下层模型计算均衡状态下交通网络上的客流量, 最后基于大连至沈阳运输区段的实际数据进行了案例分析。计算结果表明: 公路客运的日运营总利润随末端线路数的增加先升后降, 运营4条末端线路、日发车25班最佳; 高铁开通后原有运营模式下公路客运服务商的日运营总利润为7 270元, 票价为99元, 日均客流量为130人次; 门到门运营模式下公路客运服务商的日运营总利润为37 755元, 票价区间为[88, 105]元, 日均客流量将达到778人次。可见, 公路客运门到门运营模式可以有效提高公路客运的市场份额和运营利润, 在保证公路客运服务商利润的前提下, 大幅度提高整体客运服务水平。Abstract: In order to solve the problem of operation dilemma for highway passenger transport in high-speed railway era, the door to door operation mode of highway passenger transport was proposed, and a bi-level programming model was built.The maximum total daily operating profit of highway passenger transport provider was taken as the object to optimize the end line network of highway passenger transport with the door to door mode in the upper model.The lower model calculated the passenger flow of transport network at equilibrium state.Case analysis was carried out based on real data from Dalian to Shenyang transport section.Calculation result shows that the total daily operating profit of highway passenger transport increases firstly and then decreases with the increase of end line number.Operating 4 lines and dispatching 25 coaches daily are best.The total daily operating profit of highway passenger transport provider with original operation mode after the opening of high-speed railway is 7 270 yuan with 99 yuan for ticket price and 130 person-time for average daily passenger flow.The total daily operating profit of highway passenger transport provider with door to door operation mode is 37 755 yuan with [88, 105]yuan for ticket price region and 778 person-time for average daily passenger flow.The door to door operation mode of highway passenger transport can effectively improve the market share and operating profit of highway passenger transport.With the profit of highway passenger transport provider guaranteed, this mode can significantly improve overall service level of passenger transport.
-
表 1 各小区前往沈阳的日均客流量
Table 1. Daily passenger flow to Shenyang for each area

表 2 公路客运末端线网的优化结果
Table 2. Optimized result of end line network for highway passenger transport

表 3 不同F值下的日发车班数
Table 3. Daily departure numbers with different F values

表 4 大连某公路客运公司三种运营情况下各项指标的变化
Table 4. Index variations of one highway passenger transport company in Dalian under three operation situations

-
[1] LAMPKIN W, SAALMANS P D. The design of routes, service frequencies, and schedules for a municipal bus undertaking: a case study[J]. Operational Research Quarterly, 1967, 18 (4): 375-397. doi: 10.1057/jors.1967.70 [2] HIRSCH W M, DANTZIG G B. The fixed charge problem[J]. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 1968, 15 (3): 413-424. doi: 10.1002/nav.3800150306 [3] SILMAN L A, BARZILY Z, PASSY U. Planning the route system for urban buses[J]. Computers and Operations Research, 1974, 1 (2): 201-211. doi: 10.1016/0305-0548(74)90046-X [4] BAAJ M H, MAHMASSANI H S. An AI-based approach for transit route system planning and design[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 1991, 25 (2): 187-209. doi: 10.1002/atr.5670250205 [5] XIONG Yi-hua, SCHNEIDER J B. Transportation network design using a cumulative genetic algorithm and neural network[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1992 (1364): 37-44. [6] PATTNAIK S B, MOHAN S, TOM V M. Urban bus transit route network design using genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 1998, 124 (4): 368-375. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(1998)124:4(368) [7] BIELLI M, CARAMIA M, CAROTENUTO P. Genetic algorithms in bus network optimization[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2002, 10 (1): 19-34. doi: 10.1016/S0968-090X(00)00048-6 [8] 张启人, 熊桂林. 公共交通大系统建模与优化[J]. 系统工程, 1986, 4 (6): 25-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCXT198606004.htmZHANG Qi-ren, XIONG Gui-lin. Modeling and optimization of large public transport system[J]. Systems Engineering, 1986, 4 (6): 25-39. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCXT198606004.htm [9] 吴稼豪. 城市公共交通车线网络优化模型[J]. 上海机械学院学报, 1987, 9 (2): 7-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDGY198702003.htmWU Jia-hao. A model for the urban transit network optimization and evaluation[J]. Journal of Shanghai Institute of Mechanical Engineering, 1987, 9 (2): 7-13. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDGY198702003.htm [10] 林柏梁, 杨富社, 李鹏. 基于出行费用最小化的公交网络优化模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 1999, 12 (1): 79-83. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.1999.01.012LIN Bo-liang, YANG Fu-she, LI Peng. Designing optimal bus network for minimizing trip times of passenger flows[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 1999, 12 (1): 79-83. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.1999.01.012 [11] 韩印, 李维斌, 李晓峰. 城市公交线网调整优化PSO算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 1999, 12 (3): 100-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL199903014.htmHAN Yin, LI Wei-bin, LI Xiao-feng. The algorithm PSO of adjustment and optimization for public traffic network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 1999, 12 (3): 100-104. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL199903014.htm [12] 单连龙, 高自友. 城市公交系统连续平衡网络设计的双层规划模型及求解算法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2000, 20 (7): 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL200007017.htmSHAN Lian-long, GAO Zi-you. A bilevel programming model for continuous equilibrium network design and its solution algorithm for urban transit system[J]. Systems Engineering Theory and Practice, 2000, 20 (7): 85-93. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTLL200007017.htm [13] 冯树民, 陈洪仁. 公共交通线网优化研究[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2005, 37 (5): 691-693. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.05.033FENG Shu-min, CHEN Hong-ren. Study of public transit network optimization method[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2005, 37 (5): 691-693. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.2005.05.033 [14] 汤可夫, 吴大为. 基于改进遗传算法的公交线网整体优化方法[J]. 重庆交通学院学报, 2004, 23 (6): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT200406024.htmTANG Ke-fu, WU Da-wei. Study on the optimization methods of bus network based on adapted genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2004, 23 (6): 97-101. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT200406024.htm [15] 常玉林, 胡启洲. 城市公交线网优化的线性模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2005, 18 (1): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200501021.htmCHANG Yu-lin, HU Qi-zhou. Optimal line model on urban public traffic line network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2005, 18 (1): 95-98. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200501021.htm [16] 于滨, 杨永志, 杨忠振, 等. 基于直达客流密度最大的公交线网优化[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2009, 41 (2): 205-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200902050.htmYU Bin, YANG Yong-zhi, YANG Zhong-zhen, et al. Transit network optimization based on direct passenger flow density maximization[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009, 41 (2): 205-207. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200902050.htm [17] 于滨, 刘鸿婷, 闫博, 等. 公交线路网优化的双层模型及其解法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2010, 40 (2): 402-405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201002020.htmYU Bin, LIU Hong-ting, YAN Bo, et al. Bi-level model for bus route network optimization and its solution[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Engineering and Technology Edition, 2010, 40 (2): 402-405. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201002020.htm [18] 刘伟铭, 姜山, 付凌峰. 多车型高速公路离散平衡网络设计的双层规划模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2008, 21 (1): 94-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200801018.htmLIU Wei-ming, JIANG Shan, FU Ling-feng. Bi-level program model for multi-type freeway discrete equilibrium network design[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2008, 21 (1): 94-99. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL200801018.htm [19] 马嘉琪, 白雁, 韩宝明. 城市轨道交通线网基本单元与复杂网络性能分析[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2010, 10 (4): 65-70, 102. http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201004011MA Jia-qi, BAI Yan, HAN Bao-ming. Characteristic analysis of basic unit and complex network for urban rail transit[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2010, 10 (4): 65-70, 102. (in Chinese). http://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201004011 [20] 蒋阳升, 罗孝羚. 考虑首末站约束和站间客流强度的公交线网优化[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 37 (1): 106-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201701014.htmJIANG Yang-sheng, LUO Xiao-ling. Optimization of public transit network considering initial and terminal stations location requirements and passenger flow intensity[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 37 (1): 106-111. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL201701014.htm [21] YAO Jia, SHI Feng, AN Shi, et al. Evaluation of exclusive bus lanes in a bi-modal degradable road network[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 60: 36-51. [22] PANASYUK M V, PUDOVIK E M, SABIROVA M E. Optimization of regional passenger bus traffic network[J]. Procedia Economics and Finance, 2013, 5: 589-596. [23] AMIRIPOUR S M M, CEDER A A, MOHAYMANY A S. Designing large-scale bus network with seasonal variations of demand[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2014, 48: 322-338. [24] YU Bin, KONG Lu, SUN Yao, et al. A bi-level programming for bus lane network design[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 55: 310-327. [25] LI Qiang, WANG Yun-jing, ZHOU Yang. Readjustment effect analysis of public bus network in Beijing[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2008, 8 (2): 27-33. [26] ROCA-RIU M, ESTRADA M, TRAPOTE C. The design of interurban bus network in city centers[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2012, 46 (8): 1153-1165. -





 下载:
下载: