Influencing factors and mechanism analysis for evaluation of fatigue characteristics of emulsified asphalt residues
-
摘要: 基于简化黏弹性连续介质损伤(S-VECD)理论研究了乳化沥青残留物应力应变响应特征、疲劳损伤特性与疲劳寿命预估,通过傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FTIR)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和原子力显微镜(AFM)等微观手段分析了乳化沥青残留物相态结构、共混改性以及疲劳损伤的影响机理。研究结果表明:普通乳化沥青残留物的损伤曲线存在交错现象,添加改性剂使得损伤曲线不再产生交错,提升了乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能,SBR改性剂的改善效果更为显著;改性乳化沥青残留物在EN、ASTM蒸发方式下的损伤曲线较DHM蒸发方式下更平缓,表现出EN、ASTM蒸发方式下的残留物抵抗损伤能力更强;从疲劳寿命提升幅度上看,不同蒸发方式制备的普通乳化沥青残留物的最大疲劳寿命较最小疲劳寿命提升56.9%,而SBS、SBR改性乳化沥青残留物分别提升179.1%和67.8%,表明蒸发方式对改性乳化沥青残留物的巨大影响,且DHM蒸发方式下改性乳化沥青残留物的疲劳寿命均最小;添加改性剂和改变蒸发方式会引起官能团含量、胶体结构和微观粗糙度的变化;DHM蒸发方式更易使得改性乳化沥青残留物发生氧化作用,并且促使更多的沥青质的产生,使得胶团的胶溶性降低,凝胶化增强,导致乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能降低,影响疲劳性能的评估结果;原子力显微镜试验表明通过DHM蒸发方法制备的改性乳化沥青残留物,分子结构中O2-和H+发生了交换缩合反应,可能产生了化学胶结结构,进而影响了乳化沥青残留物疲劳性能的准确表征与评价。Abstract: The stress-strain response characteristics, fatigue damage characteristics, and fatigue life prediction of emulsified asphalt residues were investigated based on the simplified viscoelastic continuum damage (S-VECD) theory. Microscopic approaches such as Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and atomic force microscope (AFM) were adopted to study the influence mechanisms of morphology structure, blending modification, and fatigue damage of emulsified asphalt residues. Research results show that the damage curves of common emulsified asphalt residues are staggered. The addition of modifiers makes the damage curves no longer staggered, and the fatigue performance of emulsified asphalt residues is improved. Furthermore, the improvement effect of the SBR modifier is more obvious. The damage curves of modified emulsified asphalt residues prepared by the EN and ASTM evaporation methods are smoother than those prepared by the DHM evaporation method, which indicates that the residues obtained by the EN and ASTM evaporation methods have stronger resistance to damage. From the perspective of the fatigue life improvement, the maximum fatigue life of common emulsified asphalt residues prepared by different evaporation methods is 56.9% higher than the minimum fatigue life, and the SBS and SBR modified emulsified asphalt residues increase by 179.1% and 67.8%, respectively. This means that the modified emulsified asphalt residues are highly affected by the evaporation methods, and the fatigue life of modified emulsified asphalt residues is the smallest under the DHM evaporation method. Functional group contents, colloid structures, and microscopic roughness will be changed by adding modifiers and adjusting evaporation methods. The DHM evaporation method is more likely to cause oxidation of modified emulsified asphalt residues and promote the production of more asphaltenes. It decreases the solubility of micelles and enhances the gelation. As a result, the fatigue performance of emulsified asphalt residues reduces, and the evaluation result of fatigue performance is affected. AFM test results suggest that the exchange condensation reaction between O2- and H+ occurs in the molecular structure of modified emulsified asphalt residues prepared by the DHM evaporation method. In addition, chemical cementation structures may appear, and thus the accurate characterization and evaluation of fatigue performance of emulsified asphalt residues are affected.
-
1. 材料与试验方法
1.1 原材料
采用国内常用70号沥青作为基质沥青(记为70#),技术指标见表 1,其中,测试方法参照《公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程》(JTG E20—2011) 执行;选用冷再生用阳离子慢裂型乳化剂制备普通乳化沥青(记为普通70#),乳化剂技术指标见表 2;采用SBS、SBR胶乳对乳化沥青进行改性(分别记为70#+SBS、70#+SBR),技术指标见表 3。
表 1 基质沥青技术指标Table 1. Technical indexes of matrix asphalt技术指标 测试值 测试方法 25 ℃针入度/0.1 mm 72 沥青针入度试验
(T 0604—2011)15 ℃延度/cm >150 沥青延度试验
(T 0605—2011)软化点/℃ 48.8 沥青软化点试验(环球法)
(T 0606—2011)135 ℃布氏旋转黏度/(Pa·s) 0.65 沥青旋转黏度试验(布洛克菲尔德黏度计法)(T 0625—2011) RTFO测试
(163 ℃,85 min)
后残留物质量变化/% -0.2 沥青薄膜加热试验
(T 0609—2011)针入度比/% 74 沥青针入度试验
(T 0604—2011)15 ℃延度/cm 25 沥青延度试验
(T 0605—2011)表 2 乳化剂技术指标Table 2. Technical indexes of emulsifier技术指标 测试值 外观 棕色黏稠液体,易溶于水 固含量/% 72.9% 总胺量/(mmol·g-1) 5.7 pH值 9~11 表 3 改性剂技术指标Table 3. Technical indexes of modifiers类型 固含量/% pH值 密度/(g·cm-3) 机械稳定性/% SBS胶乳 45 5~7 0.97 ≤1.0 SBR胶乳 65 5~7 0.99 ≤1.0 1.2 乳化沥青残留物制备
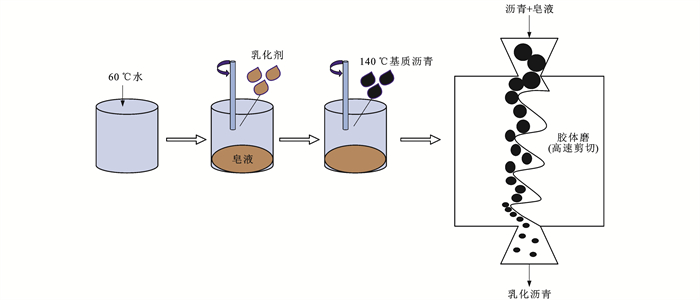
在室内采用胶体磨制备乳化沥青,乳化剂掺量为3%,制备过程见图 1;改性乳化沥青采用先乳化后改性的方式制备,掺量均为乳化沥青的3%。
在制备乳化沥青残留物时,根据水分蒸发时的温度可分为高温蒸发法和低温蒸发法。中国采用的直接加热法(Direct Heating Method, DHM)是一种典型的高温蒸发方式,而欧洲标准(European Standard 13074, EN 13074)和美国材料与试验协会(American Society for Testing and Materials Standard: D7497-09, ASTM D7497-09)采用的蒸发方式则为低温蒸发法(分别记为EN蒸发方式和ASTM蒸发方式)。
(1) DHM蒸发方式:取(300±1) g乳化沥青放置在电炉上缓慢加热,边加热边搅拌(125 ℃为宜,注意防止乳液溅出),直至乳化沥青中的水分完全蒸发,然后在(163±3) ℃下加热1 min后取残留物即可。
(2) EN蒸发方式:取71.89 g乳化沥青倒在直径为214 mm的托盘中, 在室温下放置(24±1) h,然后在(50±2) ℃烘箱中放置(24±1) h,将托盘取出冷却至室温,取其中的残留物进行后续试验。
(3) ASTM蒸发方式:取71.89 g乳化沥青倒在直径为214 mm的硅胶盘中,在25 ℃下放置(24±1) h,然后置于60 ℃烘箱中放置(24±1) h,取出托盘冷却1 h,取其中残留物进行后续试验。
经以上3种方法获取的乳化沥青残留物基本指标如表 4所示。
表 4 乳化沥青残留物测试指标Table 4. Test indexes of emulsified asphalt residues类型 针入度/0.1 mm 软化点/℃ 15 ℃延度/cm 70# 72.0 48.8 >150.0 普通70#(ASTM蒸发方式) 45.3 54.6 29.4 普通70#(EN蒸发方式) 52.9 54.5 44.0 普通70#(DHM蒸发方式) 57.3 51.4 81.9 70#+SBS(ASTM蒸发方式) 41.5 57.3 41.6 70#+SBS(EN蒸发方式) 47.4 56.1 58.4 70#+SBS(DHM蒸发方式) 69.0 54.4 95.5 70#+SBR(ASTM蒸发方式) 44.4 63.3 >150.0 70#+SBR(EN蒸发方式) 45.6 60.8 >150.0 70#+SBR(DHM蒸发方式) 59.7 63.5 >150.0 1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 线性振幅扫描试验
参照AASHTO TP101-14中的试验步骤,采用动态剪切流变仪对每种乳化沥青残留物样品进行3组平行试验,试验温度为25 ℃。首先以0.1~30.0 Hz的频率,控制恒定的0.1%的应变水平进行频率扫描,该步骤用于获得未损坏的材料特性α;之后采用控制应变的方法,以10.0 Hz的恒定频率对样品进行线性振幅扫描,振幅范围为0.1%~30.0%。
1.3.2 红外光谱试验
采用美国PerkinElmer Spectrum Two红外光谱仪,分辨率为0.5 cm-1,扫描速度为40次·s-1,测试范围为400~4 000 cm-1,对普通乳化沥青和SBS、SBR改性乳化沥青在不同蒸发方式下获取的残留物进行红外光谱试验,研究蒸发方式以及添加改性剂前后对乳化沥青残留物官能团等微观特性的影响。
1.3.3 扫描电子显微镜试验
采用Zeiss Supra55型扫描电子显微镜(放大倍率500 K)对普通70#(DHM蒸发方式)、70#+SBS(DHM蒸发方式)和70#+SBR(DHM蒸发方式)3种乳化沥青残留物进行扫描试验,研究乳化沥青残留物微观形貌特征的变化规律。
1.3.4 原子力显微镜试验
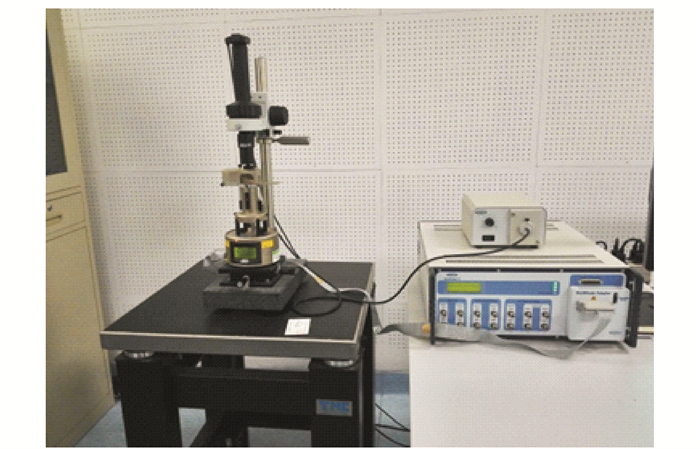
采用英国布鲁克原子力显微镜(图 4)对基质沥青、普通70#和70#+SBR进行测试,以揭示改性剂、蒸发方式等对残留物的作用机制。样品要求表面平整光滑,将残留物加热(基质沥青130 ℃,改性乳化沥青155 ℃)滴在10 mm(长)×10 mm(宽)×1 mm(高)的载玻片上,之后冷却至25 ℃,选取每个样品40 μm×40 μm的区域,采用轻敲模式在样品表面扫描。
1.4 简化黏弹性连续介质损伤理论
近年来,Underwood等[23]为了更好地将黏弹性连续介质损伤(Viscoelastic Continuum Damage, VECD)理论运用于沥青胶结料动态疲劳试验数据分析中,对VECD模型进行合理简化,提出了简化黏弹性连续介质损伤(Simplified Viscoelastic Continuum Damage, S-VECD)理论,引入材料损伤变量和虚模量定义沥青的损伤特性,成功应用于沥青胶结料疲劳性能的分析和预测。
为研究损伤状态下乳化沥青残留物的本构关系,连续介质力学将其在宏观上依然看作一个连续体介质,损伤的影响和量化通过残留物的模量或强度指标的衰减来表征。首先根据线性振幅扫描(Linear Amplitude Sweep, LAS)试验中频率扫描所得复数模量和频率结果计算出未损伤状态下材料特征参数α,即
α=1+1m (1) lg(G∗)=mlg(ω)+b (2) 式中:G*为复数模量;ω为频率;m、b为拟合参数。
材料的损伤变量用S表示,即
S=N∑j=1[D2γ20(Cj−1−Cj)]α/(1+α)(tj−1−tj)1/(1+α) (3) γ0=γG∗0 (4) C=τγ0D (5) 式中:D为动态模量比值(单字母表示变量),一般限制为0.9~1.1;γ0为加载周期内的虚剪切应变峰值;C为材料的虚模量;tj为第j次测试时间;N为输出次数;γ为加载周期内的剪切应变峰值;G0*为材料在25 ℃和10 Hz下的复数模量;τ为加载周期内的应力。
将损伤变量S与虚模量C按式(6)进行拟合,得到材料的S-VECD损伤曲线方程为
C=1−C1SC2 (6) 式中:C1、C2为拟合参数。
基于式(1)~(6),沥青疲劳寿命Nf为
Nf=f2αS1−αC2+α(1−αC2+α)(C1C2)α(γG∗0)2α (7) 式中:f为加载频率。
使用式(7)进行疲劳寿命预测需要知道疲劳失效发生时的损伤变量S的数值,根据Hintz[24]等提出的疲劳失效准则,LAS试验中乳化沥青残留物发生疲劳失效时的虚模量C为0.65,从而基于拟合的疲劳损伤特性曲线可计算出对应的S。
2. 试验结果分析
2.1 LAS试验结果分析
2.1.1 应力应变响应
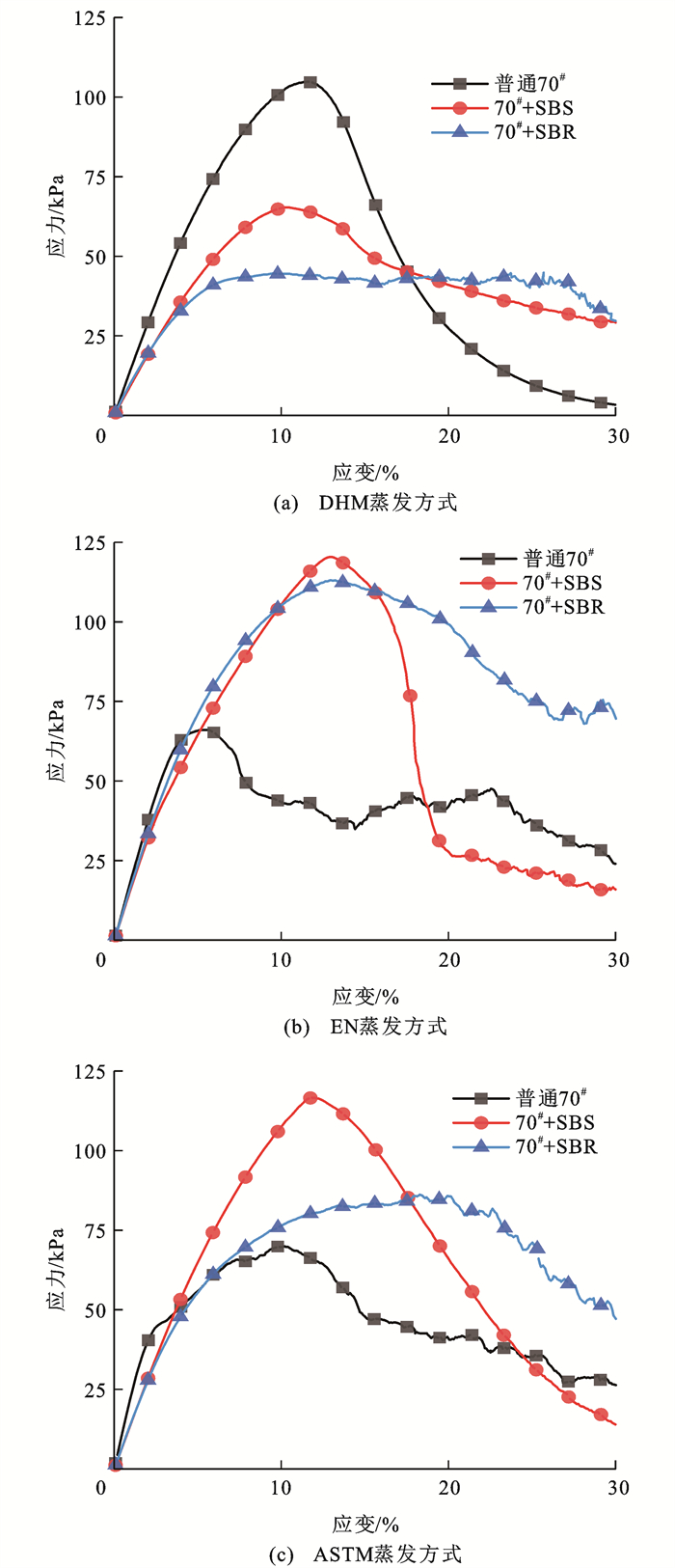
普通70#、70#+SBS和70#+SBR在3种蒸发方式下的应力应变关系如图 5所示。AASHTO TP 101-14将图中的应力峰值点定义为材料的疲劳失效点,该点对应的应力称为屈服应力,应变称为屈服应变。由图 5可知:在ASTM蒸发方式和EN蒸发方式下,SBS改性乳化沥青残留物的屈服应力均最大,而普通乳化沥青残留物的则最小;在DHM蒸发方式下,屈服应力由大到小的排序为普通乳化沥青残留物、SBS改性乳化沥青残留物、SBR改性乳化沥青残留物;SBS改性乳化沥青残留物在不同蒸发方式下的屈服应力均较SBR改性乳化沥青残留物更大。从曲线的走势来看,DHM蒸发方式下获取的乳化沥青残留物应力应变曲线较EN、ASTM条件下所得到的曲线更缓,表明加载过程中应力增长速率相对缓慢,应力应变响应有较大的延迟,且达到应力峰值后出现了一段平缓曲线,产生这一现象的原因是蒸发温度的提高使乳化沥青残留物黏滞性降低,导致其应力应变响应变慢。
在各残留物试样的应力曲线峰值处存在一个较宽范围的峰值区,依据该峰值区的宽度可对残留物的应变敏感性做出推断。当峰值区的范围越宽时,表明材料在荷载作用下可维持一定的应力应变承受能力,其应变敏感性较低[25]。在DHM蒸发方式下,应变敏感性从小到大排序为SBR改性乳化沥青残留物、SBS改性乳化沥青残留物、普通乳化沥青残留物;在ASTM与EN蒸发方式下,应变敏感性从小到大排序为SBR改性乳化沥青残留物、普通乳化沥青残留物、SBS改性乳化沥青残留物。
2.1.2 疲劳损伤特性
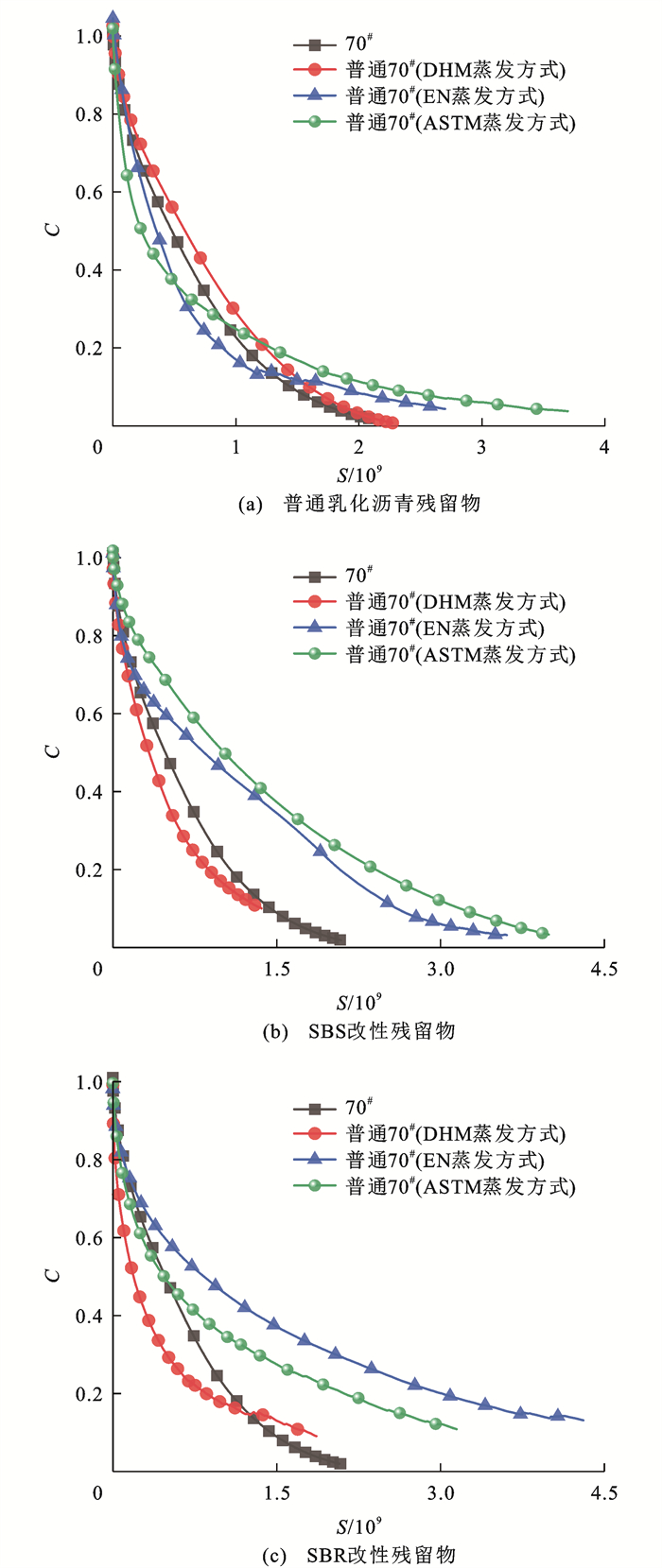
基于式(5)将乳化沥青残留物的虚模量C与损伤变量S进行拟合,拟合参数C1、C2结果见表 5,可得疲劳损伤特性曲线如图 6所示,该曲线在一定程度上表征了材料内部黏弹性损伤的发展和力学响应。
表 5 疲劳参数拟合值Table 5. Fitting value of fatigue parameters拟合值 70# 普通70# 70#+SBS 70#+SBR DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 C1/10-6 22.70 7.94 352.00 2 340.00 44.30 58.30 8.25 1 380.00 211.00 427.40 C2 0.50 0.55 0.37 0.28 0.47 0.44 0.53 0.31 0.38 0.35 绝对系数 0.99 0.99 0.93 0.96 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.97 0.99 0.98 当虚模量C=1时,样本处于未损伤状态,C=0表示沥青样本已被完全破坏,曲线的陡缓程度表征了材料的损伤变化速率,当损伤变量S给定时,C越大,则材料抵抗损伤的能力越强[26]。从图 6(a)可知:ASTM蒸发方式和EN蒸发方式下,普通乳化沥青残留物损伤曲线由陡变缓,材料损伤速率逐渐减小,而DHM蒸发方式下则逐渐增大,直至材料最先达到完全破坏;3种蒸发方式的损伤曲线存在交错现象[27],表明随着材料损伤强度的增大,ASTM蒸发方式下获得的普通乳化沥青残留物抵抗损伤能力逐渐增强,DHM蒸发方式下则逐渐减弱。而在图 6(b)和图 6(c)中,改性乳化沥青残留物曲线表现出了较好的相似性,低温蒸发方式下的损伤曲线较高温蒸发方式下更缓,给定损伤变量S后,低温蒸发方式下的C值均大于高温蒸发方式,表明低温蒸发方式得到的材料抵抗损伤能力更强,这可解释为温度的升高加快了样本的损伤速率,曲线变陡,最终产生了较大的损伤;不同之处是SBS改性乳化沥青在ASTM蒸发方式下的损伤曲线位于EN蒸发方式之上,表明ASTM蒸发方式获取的SBS改性残留物具有更好的抵抗损伤的能力,而SBR改性残留物则在EN蒸发方式下的抵抗损伤能力更强。
总体来看,随着扫描振幅的增大,残留物完整性逐渐降低,对应的损伤则逐渐增加,蒸发方式的改变使得损伤速率发生变化,而改性剂的添加一方面使得损伤曲线不再交错,另一方面也让曲线趋于更缓,这是由于改性剂的加入改变了乳化沥青残留物的微观结构[28],从而提高了残留物抵抗累计损伤的能力。普通乳化沥青残留物各损伤曲线间相隔较近,意味着蒸发方式对其损伤影响较小,3种蒸发方式均可用于制备普通乳化沥青残留物,而改性残留物各损伤曲线间相隔较大,表明蒸发方法对残留物损伤影响显著,应选择合理的蒸发方式以制备改性乳化沥青残留物,确保性能评估的准确性、稳定性。
2.1.3 疲劳寿命预估
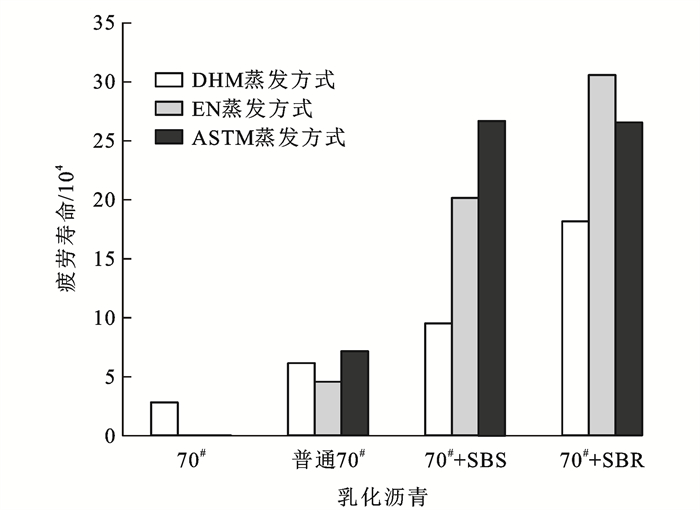
基于简化黏弹性连续介质损伤力学理论得到的加载次数和剪切应变峰值的函数关系(式(7)),计算出对应乳化沥青残留物的预测疲劳寿命,结果如图 7所示。
从图 7中可以看出:乳化沥青和改性乳化沥青残留物的疲劳寿命均较基质沥青有较大提升,其中,70#+SBR的疲劳寿命提升幅度最大,显示出SBR改性剂具有更优良的疲劳性能改善作用。此外,与蒸发方式的变化相比,改性剂对乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能影响更大;普通乳化沥青残留物的疲劳寿命由小到大排序为EN蒸发方式、DHM蒸发方式、ASTM蒸发方式,SBS改性残留物的疲劳寿命由小到大排序为DHM蒸发方式、EN蒸发方式、ASTM蒸发方式,SBR改性残留物疲劳寿命由小到大排序为DHM蒸发方式、ASTM蒸发方式、EN蒸发方式,2种改性乳化沥青残留物均在低温蒸发方式下的疲劳寿命最高,在DHM蒸发方式下的最低;从不同蒸发方式下的疲劳寿命提升幅度上看,普通70#在ASTM蒸发方式下的疲劳寿命较EN提升了56.9%,70#+SBS在ASTM蒸发方式下的疲劳寿命较DHM蒸发方式提升了179.1%,70#+SBR在EN蒸发方式下较DHM蒸发方式提升了67.8%,这表明普通乳化沥青残留物在不同蒸发方法下其疲劳寿命相差不大,即普通乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能受蒸发方法的影响较小;而2种低温蒸发方式制备的改性乳化沥青残留物的疲劳寿命均显著高于高温蒸发方式,其疲劳性能与蒸发方式密切相关,采用不同的蒸发方式所获取的残留物疲劳寿命差异显著。
由此,在制备乳化沥青残留物时应充分考虑蒸发方法对其性能的影响,选择符合实际应用环境的蒸发方式以便更加精准的表征与评价。根据《公路沥青路面再生技术规范》(JTG/T 5521—2019)要求,乳化沥青使用温度不宜高于60 ℃,在冷再生工程中乳化沥青冷再生混合料摊铺一般在常温下进行,其现场施工温度条件与EN或ASTM蒸发方式较为接近。综合疲劳损伤曲线分析和疲劳寿命预估结果,建议制备普通乳化沥青残留物时可采用规范规定的直接加热法,但制备改性乳化沥青残留物时应采用ASTM或EN蒸发方式。
2.2 微观特性
2.2.1 红外光谱试验
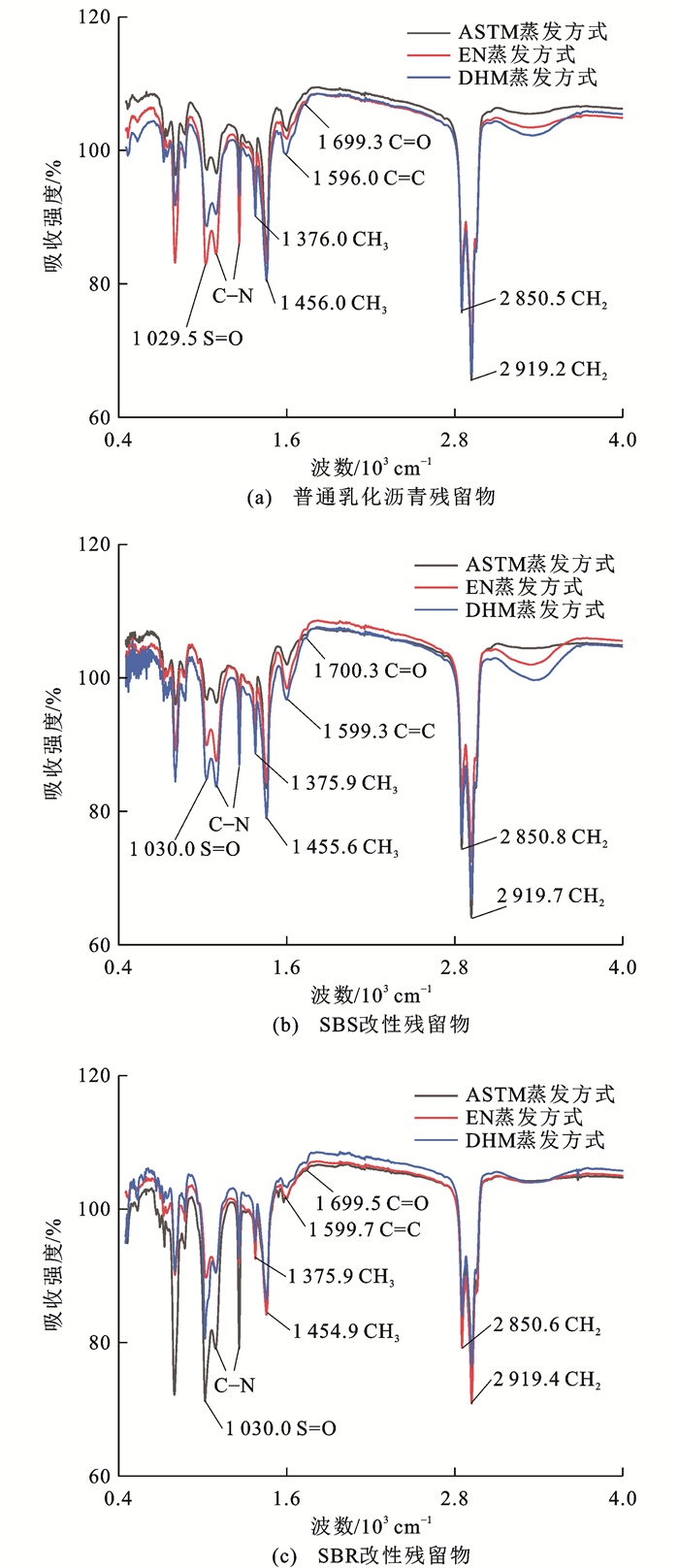
对普通乳化沥青和SBS、SBR改性乳化沥青在不同蒸发方式下制备的残留物进行红外光谱试验,结果如图 8所示,标出了位于中红外区(波数范围1 330~4 000 cm-1)和指纹区(波数范围400~1 330 cm-1)的官能团。基于这些官能团的对比分析,可直观定性地确定蒸发方式以及添加改性剂前后对乳化沥青残留物微观特性的影响。
从图 8可以看出:在中红外区内,由—CH2伸缩振动引起的吸收峰位于2 919和2 850 cm-1处,由羰基C=O伸缩振动引起的吸收峰位于1 700 cm-1处,由苯环C=C共轭双键振动引起的吸收峰位于1 601 cm-1处,由—CH3弯曲振动引起的吸收峰位于1 456和1 376 cm-1处;在指纹区,由C—N伸缩振动引起的吸收峰位于1 262和1 098 cm-1处,由亚砜基S=O伸缩振动引起的吸收峰位于1 030 cm-1处,由—C—H弯曲振动引起的吸收峰则多位于1 000 cm-1以下。
对比各吸收峰出现的位置和个数可以发现:无论是改变蒸发方式或者是添加改性剂,吸收峰的位置和个数都未发生改变,说明在蒸发过程和添加改性剂过程中没有发生化学反应,而从吸收峰的大小可看出官能团的含量有所改变。
为探究官能团含量的变化对乳化沥青残留物微观特性的影响,选取芳香族官能团(Ar)、羰基官能团(C=O)和亚砜基官能团(S=O)作为特征官能团。其中,芳香族官能团可表征沥青中的芳香分含量,羰基官能团则多被当作沥青发生氧化的指标,而亚砜基官能团则与沥青中的沥青质含量密切相关。各官能团指数的计算结果如表 6所示。
表 6 乳化沥青残留物特征官能团指数Table 6. Characteristic functional group indexes of emulsified asphalt residues特征官能团 普通70# 70#+SBS 70#+SBR DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 C=O 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.005 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.003 0.003 Ar 0.137 0.140 0.142 0.129 0.159 0.164 0.134 0.144 0.148 S=O 0.124 0.121 0.115 0.110 0.072 0.068 0.203 0.107 0.058 由表 6可知:普通乳化沥青残留物与SBS、SBR改性乳化沥青残留物均检测出了羰基官能团,说明在制备3种乳化沥青残留物时发生了氧化现象,DHM蒸发方式下制备的70#+SBS和70#+SBR的羰基官能团指数均大于ASTM和EN蒸发方式,反映出DHM蒸发方式由于较高的温度更易造成残留物发生氧化;乳化沥青残留物芳香族官能团指数在不同蒸发方式下呈现一致性的规律,即ASTM蒸发方式下最大,EN蒸发方式下次之,DHM蒸发方式下最小,表明不同的蒸发方式会改变乳化沥青残留物的芳香分含量,并影响其胶体结构,从而对乳化沥青蒸发残留物的疲劳性能产生影响;另一方面,在不同蒸发方式下,普通乳化沥青残留物间的芳香分含量差距不大,而改性残留物在DHM蒸发方式下的芳香分指数与EN、ASTM蒸发方式下有较大差距,证实了改性残留物受蒸发方式影响显著;3种乳化沥青残留物的亚砜基指数在DHM蒸发方式下最大,表明DHM蒸发方式促使了更多沥青质的产生,使得胶团的胶溶性降低,网状结构变发达,沥青区域凝胶化增强,这将对乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能产生负面影响,进而影响实际的乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能评价[29]。
2.2.2 扫描电子显微镜试验
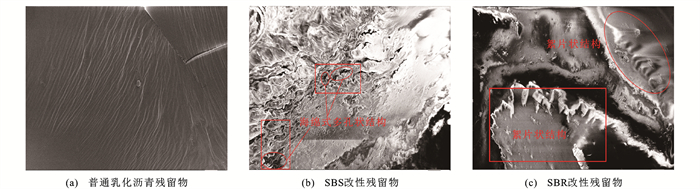
为进一步探究同种蒸发方式下,SBS、SBR改性剂加入后对普通乳化沥青残留物微观形貌特征的影响,选取DHM蒸发方式所制备的普通乳化沥青残留物和SBS、SBR改性乳化沥青残留物进行扫描电镜试验。扫描图像如图 9所示,灰色区域是目标观测对象(乳化沥青蒸发残留物),白色区域是样品高突部分(样品高度差在扫描电镜下会呈现颜色差异),黑色区域是扫描电镜制样所需的导电胶。
从图 9(a)可知:普通乳化沥青表面较为光滑,无明显的结构形式。而从图 9(a)、(b)可以看出:SBS、SBR改性剂的加入改变了普通乳化沥青残留物的微观结构,进而导致沥青的基本性能发生变化[30]。具体表现在SBS改性乳化沥青残留物形成了“海绵式多孔”的网状结构,该类结构具有较好的弹性、塑性,宏观上表现为针入度较大。而SBR改性乳化沥青残留物则形成了具有更好延展性的“絮片状”结构,宏观上表现为延度较大。基于前述FTIR试验结果的分析,这些微观结构的变化可能是由于DHM蒸发方式制备残留物时产生了更多的沥青质,吸附在SBS、SBR改性剂周围,而这种网状或凝胶化的微观结构将影响改性乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能,使得疲劳性能预估的结果与实际应用情况不符。此外,改性乳化沥青残留物呈现出更大疲劳寿命,可能在于改性剂加入后会与沥青产生溶胀效应,破坏了原有的胶体平衡,相应地增加了材料的微观粗糙度,在剪切及温度作用下建立起新的平衡体系[31]。而残留物在疲劳加载过程中的微观应变分布是不均匀的,所以随着材料微观粗糙度的增加,其抵抗由于局部变化导致损伤萌生发展的能力也随之增加,并且构成粗糙度的改性剂也可以分担对应的应力集中,使裂纹扩展时更易发生偏转,从而降低裂纹扩展速率,使得材料的抗损伤能力增强。
2.2.3 原子力显微镜试验
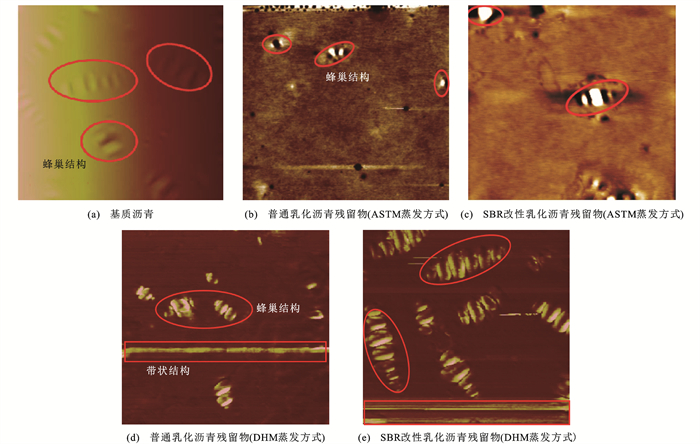
基于前述对乳化沥青残留物疲劳性能的研究结果,考虑到ASTM和EN蒸发方式在疲劳性能的表现上差异不大,且ASTM蒸发方式的温度更高,更易对残留物产生一定影响,因此,文中选取ASTM和DHM蒸发方式制备的基质沥青、普通乳化沥青残留物及SBR改性残留物开展原子力显微镜试验。
AFM图像如图 10所示。从图 10(a)可知:基质沥青表面形态较为光滑,存在少量结构尺寸较小且分布均匀的蜂巢结构。由10(b)、(c)可知:SBR改性残留物的蜂巢结构面积明显增大,这可能是由于SBR改性剂加入后乳化沥青出现了一定的团聚现象,改变了乳化沥青残留物的微观结构进而对疲劳性能产生影响。对比图 10(b)、(c)与图 10(d)、(e)可以看出:DHM蒸发方法制备的普通70#和70#+SBR的AFM图像中除了蜂巢结构的产生,还出现多条带状结构,同时还有片状褶皱的形成,褶皱与带状物连接,意味着材料分子结构中O2-和H+发生了交换缩合反应,并产生了化学胶结结构[32]。这表明ASTM蒸发方式对乳化沥青残留物的影响可能更多地体现在物理变化方面,而DHM蒸发方式却可能使得普通70#和SBR改性乳化沥青残留物发生了一定的化学反应。此外,70#+SBR相较于普通70#,其蜂巢结构的数量更多,面积更大,且带状结构的宽度也更宽,反映出SBR改性剂加入后,化学反应更加剧烈,因此,采用DHM蒸发方法制备乳化沥青残留物时可能会有新物质产生,这种物质同样进一步改变了残留物的材料组成和微观结构,进而影响乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能评价,尤其是SBR改性乳化沥青。而低温蒸发方式更接近于工程实际条件,可作为表征和评价乳化沥青的选择。
3. 结语
(1) DHM蒸发方式下获取的乳化沥青残留物应力-应变曲线较EN、ASTM蒸发方式下所得到的曲线更平缓,表明蒸发温度的提高使乳化沥青残留物的黏滞性降低,应力-应变响应变慢。在不同蒸发方式下,SBR改性乳化沥青残留物的应变敏感性均最小,具有更优异的应力应变承受能力。
(2) ASTM和EN蒸发方式制备的乳化沥青残留物,其损伤发展更慢,可承受更多的累积疲劳损伤;改性剂的加入减慢了损伤发展速率,使得损伤曲线不再交错。3种蒸发方式下,普通70#的损伤曲线间隔较近,疲劳寿命差距不大,而70#+SBS、70#+SBR的间隔较远,有着显著的疲劳寿命差距,体现出蒸发方式对改性乳化沥青残留物的显著影响。
(3) 3种蒸发方式均会造成残留物发生氧化,但DHM蒸发方式所造成的氧化作用更大;DHM蒸发方式更易造成沥青质的产生,使得胶团的胶溶性降低,网状结构变发达,沥青区域凝胶化增强,对残留物的疲劳性能产生不利作用,进而影响疲劳性能的准确评估。改性剂的加入使得残留物的微观粗糙度增大,提升了改性乳化沥青残留物的疲劳性能。
(4) 原子力显微镜试验表明,DHM蒸发方式下出现多条带状物,且有片状褶皱的形成,表明了残留物分子结构中O2-和H+发生了交换缩合反应,并产生了化学胶结结构,进而可能改变残留物的材料组成和微观结构,导致乳化沥青残留物疲劳寿命评估的不准确性。建议在表征与评价乳化沥青疲劳性能时采用EN或ASTM蒸发方式制备其残留物,尤其针对改性乳化沥青,避免高温蒸发方式对疲劳性能评估的影响,确保与工程应用条件的一致性。
(5) 本文主要考虑不同蒸发方式对改性乳化沥青残留物疲劳性能与微观结构的影响,接下来可对不同乳化剂或基质沥青制备的乳化沥青残留物进行研究和分析。
-
表 1 基质沥青技术指标
Table 1. Technical indexes of matrix asphalt
技术指标 测试值 测试方法 25 ℃针入度/0.1 mm 72 沥青针入度试验
(T 0604—2011)15 ℃延度/cm >150 沥青延度试验
(T 0605—2011)软化点/℃ 48.8 沥青软化点试验(环球法)
(T 0606—2011)135 ℃布氏旋转黏度/(Pa·s) 0.65 沥青旋转黏度试验(布洛克菲尔德黏度计法)(T 0625—2011) RTFO测试
(163 ℃,85 min)
后残留物质量变化/% -0.2 沥青薄膜加热试验
(T 0609—2011)针入度比/% 74 沥青针入度试验
(T 0604—2011)15 ℃延度/cm 25 沥青延度试验
(T 0605—2011)表 2 乳化剂技术指标
Table 2. Technical indexes of emulsifier
技术指标 测试值 外观 棕色黏稠液体,易溶于水 固含量/% 72.9% 总胺量/(mmol·g-1) 5.7 pH值 9~11 表 3 改性剂技术指标
Table 3. Technical indexes of modifiers
类型 固含量/% pH值 密度/(g·cm-3) 机械稳定性/% SBS胶乳 45 5~7 0.97 ≤1.0 SBR胶乳 65 5~7 0.99 ≤1.0 表 4 乳化沥青残留物测试指标
Table 4. Test indexes of emulsified asphalt residues
类型 针入度/0.1 mm 软化点/℃ 15 ℃延度/cm 70# 72.0 48.8 >150.0 普通70#(ASTM蒸发方式) 45.3 54.6 29.4 普通70#(EN蒸发方式) 52.9 54.5 44.0 普通70#(DHM蒸发方式) 57.3 51.4 81.9 70#+SBS(ASTM蒸发方式) 41.5 57.3 41.6 70#+SBS(EN蒸发方式) 47.4 56.1 58.4 70#+SBS(DHM蒸发方式) 69.0 54.4 95.5 70#+SBR(ASTM蒸发方式) 44.4 63.3 >150.0 70#+SBR(EN蒸发方式) 45.6 60.8 >150.0 70#+SBR(DHM蒸发方式) 59.7 63.5 >150.0 表 5 疲劳参数拟合值
Table 5. Fitting value of fatigue parameters
拟合值 70# 普通70# 70#+SBS 70#+SBR DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 C1/10-6 22.70 7.94 352.00 2 340.00 44.30 58.30 8.25 1 380.00 211.00 427.40 C2 0.50 0.55 0.37 0.28 0.47 0.44 0.53 0.31 0.38 0.35 绝对系数 0.99 0.99 0.93 0.96 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.97 0.99 0.98 表 6 乳化沥青残留物特征官能团指数
Table 6. Characteristic functional group indexes of emulsified asphalt residues
特征官能团 普通70# 70#+SBS 70#+SBR DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 DHM蒸发方式 EN蒸发方式 ASTM蒸发方式 C=O 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.005 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.003 0.003 Ar 0.137 0.140 0.142 0.129 0.159 0.164 0.134 0.144 0.148 S=O 0.124 0.121 0.115 0.110 0.072 0.068 0.203 0.107 0.058 -
[1] ILIAS M, ADAMS J, CASTORENA C, et al. Performance-related specifications for asphalt emulsions used in microsurfacing treatments[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2017, 2632(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3141/2632-01 [2] SHENG Xiao-hui, WANG Mo, XU Tao, et al. Preparation, properties and modification mechanism of polyurethane modified emulsified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 189: 375-383. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.177 [3] XIAO Jing-jing, JIANG Wei, YE Wan-li, et al. Effect of cement and emulsified asphalt contents on the performance of cement-emulsified asphalt mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 220: 577-586. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.051 [4] 张久鹏, 朱红斌, 裴建中, 等. 基于龚帕斯模型的改性乳化沥青胶浆黏度与沥青破乳评价[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2015, 15(5): 1-7. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2015.05.001ZHANG Jiu-peng, ZHU Hong-bin, PEI Jian-zhong, et al. Evaluation of asphalt demulsification and viscosity of modified asphalt emulsion mortar based on Gompertz model[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2015, 15(5): 1-7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2015.05.001 [5] 李东盛. 乳化沥青流变特性的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.LI Dong-sheng. Rheological properties of asphalt emulsion[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) [6] 邓交龙. 乳化沥青冷再生混合料界面强度机理研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019.DENG Jiao-long. Research on interface strength mechanism of emulsified asphalt cold reclaimed mixture[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019. (in Chinese) [7] ZHANG Qin-qin, FAN Wei-yu, WANG Tie-zhu, et al. Influence of emulsification on the properties of styrene- butadiene-styrene chemically modified bitumens[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 29: 97-101. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.09.005 [8] ABEDINI M, HASSANI A, KAYMANESH M R, et al. The rheological properties of a bitumen emulsion modified with two types of SBR latex[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2016, 34(17/18): 1589-1594. [9] HANZ A J, AREGA Z A, BAHIA H U. Rheological behavior of emulsion residues produced by evaporative recovery method[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2010, 2179(1): 102-108. doi: 10.3141/2179-12 [10] FARRAR M J, SALMANS S T, PLANCHE J P. Recovery and laboratory testing of asphalt emulsion residue: application of the simple aging test (SAT) and 4 mm DSR[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2013, 2370(1): 69-75. doi: 10.3141/2370-09 [11] MOTAMED A, SALOMON D, SAKIB N, et al. Emulsified asphalt residue recovery and characterization: a combined use of moisture analyzer balance and dynamic shear rheometer[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2014, 2444(1): 88-96. doi: 10.3141/2444-10 [12] MARASTEANU M O, CLYNE T R. Rheological characterization of asphalt emulsions residues[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2006, 18(3): 398-407. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2006)18:3(398) [13] MALLADI H, ASNAKE M, LACROIX A, et al. Low- temperature vacuum drying procedure for rapid asphalt emulsion residue recovery[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2018, 2672(28): 256-265. doi: 10.1177/0361198118791913 [14] 汪德才, 郝培文, 乐金朝, 等. 冷再生用乳化沥青残留物的流变特性[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(3): 06081-06087.WANG De-cai, HAO Pei-wen, YUE Jin-chao, et al. Rheological properties of emulsified asphalt residue for cold regeneration[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(3): 06081-06087. (in Chinese) [15] SUN Yang, YUE Jin-chao, WANG Ri-ran, et al. Investigation of the effects of evaporation methods on the high-temperature rheological and fatigue performances of emulsified asphalt residues[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 2020: 1-12. [16] ABEDINI M, HASSANI A I, KAYMANESH M R, et al. Multiple stress creep and recovery behavior of SBR-modified bitumen emulsions[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2020, 48(4): 3116-3124. [17] CHEN Xiao-yang, CHENG Guo-hong, XU Wen. Influence of evaporation temperature on the rheological properties of modified emulsified asphaltic residues[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2020, 22(8): 49-52. [18] 王淋, 郭乃胜, 温彦凯, 等. 改性沥青疲劳破坏判定指标适用性[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(4): 91-106. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.04.007WANG Lin, GUO Nai-sheng, WEN Yan-kai, et al. Applicability of determination indexes for fatigue failure of modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(4): 91-106. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2020.04.007 [19] WANG Chao, ZHANG Han, CASTORENA C, et al. Identifying fatigue failure in asphalt binder time sweep tests[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 121: 535-546. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.06.020 [20] 白琦峰, 钱振东, 赵延庆. 基于流变学的沥青抗疲劳性能评价方法[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2012, 38(10): 1536-1542. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201210017.htmBAI Qi-feng, QIAN Zhen-dong, ZHAO Yan-qing. Asphalt fatigue resistance evaluation method based on the rheology[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2012, 38(10): 1536-1542. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201210017.htm [21] 孙大权, 林添坂, 曹林辉. 基于动态剪切流变试验的沥青疲劳寿命分析方法[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2015, 18(2): 346-350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZCX201502031.htmSUN Da-quan, LIN Tian-ban, CAO Lin-hui. Evaluation method for fatigue life of asphalt based on dynamic shear rheometer test[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2015, 18(2): 346-350. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZCX201502031.htm [22] HASAN M A, HASAN M M, BAIRGI B K, et al. Utilizing simplified viscoelastic continuum damage model to characterize the fatigue behavior of styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) modified binders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 200: 159-169. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.048 [23] UNDERWOOD B S, BAEK C, KIM Y R. Simplified viscoelastic continuum damage model as platform for asphalt concrete fatigue analysis[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2012(2296): 36-45. [24] HINTZ C, VELASQUEZ R, JOHNSON C, et al. Modification and validation of linear amplitude sweep test for binder fatigue specification[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2011(2207): 99-106. [25] 谭忆秋, 郭猛, 曹丽萍. 常用改性剂对沥青粘弹特性的影响[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(4): 7-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201304001.htmTAN Yi-qiu, GUO Meng, CAO Li-ping. Effects of common modifiers on viscoelastic properties of asphalt[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(4): 7-15. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201304001.htm [26] NOTANI M A, NEJAD F M, KHODAⅡ A, et al. Evaluating fatigue resistance of toner- modified asphalt binders using the linear amplitude sweep test[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2019, 20(8): 1927-1940. [27] 张含宇, 徐刚, 陈先华, 等. 不同试验方法的老化沥青疲劳性能研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(1): 168-175.ZHANG Han-yu, XU Gang, CHEN Xian-hua, et al. Fatigue property of aged asphalt binders using different experimental methods[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(1): 168-175. (in Chinese) [28] 张倩, 孙好好, 温志广, 等. 基于宏观性能与微观性状确定SBR胶乳在SBR改性乳化沥青中的最佳添加量[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2018, 36(2): 305-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLKX201802027.htmZHANG Qian, SUN Hao-hao, WEN Zhi-guang, et al. Determination of optimum SBR latex content in SBR modified asphalt emulsion based on macro and micro characters[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 36(2): 305-310. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLKX201802027.htm [29] 梁波, 兰芳, 郑健龙. 沥青的老化机理与疲劳性能关系的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(9): 9083- 9096.LIANG Bo, LAN Fang, ZHENG Jian-long. Research and development of relationship between aging mechanism and fatigue properties of asphalt[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(9): 9083-9096. [30] 罗正斌. 沥青用SBS胶乳的制备及其在微表处中的应用[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019.LUO Zheng-bin. Preparation of SBS latex for asphalt and its application in micro-surfacing[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2019. (in Chinese) [31] 王勇, 侯芸, 张艳红. SBS改性与SBR改性微表处体系差异及机理研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2021, 43(6): 28-33, 60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHGY202106005.htmWANG Yong, HOU Yun, ZHANG Yan-hong. Study on system difference and mechanism of SBS modification and SBR modification micro-surfacing[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2021, 43(6): 28-33, 60. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHGY202106005.htm [32] ZHANG Ji, WANG Jun-long, WU Yi-qian. et al. Preparation and properties of organic palygorskite SBR/organic palygorskite compound and asphalt modified with the compound[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2008, 22(8): 1820-1830. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 宋亮,高冲,范鹏,仰建岗,高杰. 蒸发方式对乳化沥青残留物高温流变性能与疲劳性能影响分析. 市政技术. 2024(11): 23-28+37 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 潘惠雄,陈豫慧,龙兴灵,陈军,向一鸣,赵西杰. 直投式SBS胶乳改性乳化沥青的制备与性能研究. 江西建材. 2024(08): 87-91 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-





 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:









 百度学术
百度学术