Rationality analysis and optimization of guard rail interval and wing rail interval limits at turnouts
-
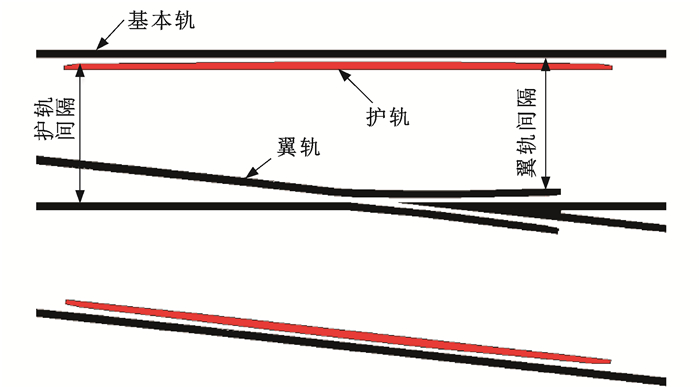
摘要: 针对近年来多次出现的普速铁路道岔护轨位置脱轨问题,研究了脱轨过程与机理,分析了目前护轨间隔、翼轨间隔限值与计算方法的合理性;在全国范围内选取19个车站、124组道岔开展了系统的现场试验研究,探讨了护轨间隔、翼轨间隔限值的优化方法。研究结果表明:道岔护轨位置脱轨的主要原因为车轮冲击护轨开口段导致护轨螺栓松动、护轨低头、顶部磨耗,最终造成车轮爬上护轨脱轨;现场养护维修中,护轨、翼轨间隔分布较离散,合格率较低,为68.97%~73.83%;目前的翼轨间隔限值安全裕量较大,可适当放松,为现场维修提供方便;与同号码复式交分道岔相比,单开道岔护轨开口段轮轨冲击概率略小;随着道岔号码的增大,护轨开口段冲击概率呈减小趋势;目前的护轨间隔限值设置可将车轮冲击直向护轨以及侧向护轨跟端开口段的概率控制在12%以内,但并不能有效防止侧向护轨趾端开口段的轮轨冲击,概率仍高达53.85%~75.00%;实际养护维修过程中,建议将护轨间隔限值修改为1 365 mm,可满足大部分主型道岔的需求,有效减少和避免护轨趾端开口段的轮轨冲击。Abstract: Aiming at the derailment problem of the guard rail positions of conventional speed railway turnouts which has occurred several times in recent years, the derailment process and mechanism were studied. The rationalities of current guard rail interval and wing rail interval limits and their calculation methods were analyzed. Systematic field experimental research was conducted at 19 stations and 124 turnouts nationwide, and the optimization method of guard rail interval and wing rail interval limits was discussed. Research results show that the main reason for derailment at the guard rail position of turnout is wheel's impact on the opening section of guard rail, which leads to the loosening of guard rail bolts and the tipping and wear of guard rail, finally causing wheel to climb guard rail and derails. The distributions of guard rail interval and wing rail interval are relatively discrete during the field maintenance, with a low pass rate ranging from 68.97% to 73.83%. The existing wing rail interval limit includes a substantial safety margin, which can be appropriately relaxed to facilitate field maintenance. Compared with the double slip turnout with the same number, the probability of wheel-rail impact at the opening section of guard rail of simple turnout is slightly smaller. As the number of turnouts increases, the probability of impact at the opening section of guard rail decreases. The current guard rail interval limit setting can control the probabilities of wheel impacting the open section of straight guard rail and heel end of lateral guard rail within 12%. However, it cannot effectively prevent the wheel-rail impact at the opening section of the toe end of lateral guard rail with the probability still as high as 53.85%-75.00%. To facilitate maintenance and repair, the guard rail interval limit should be 1 365 mm, which meets the requirements of most turnouts and effectively reduces and avoids the wheel-rail impact at the opening section of the toe end of guard rail.
-
表 1 道岔护轨间隔、翼轨间隔分布统计
Table 1. Distribution statistics of guard rail interval and wing rail interval of turnouts
道岔类型 间隔类型 分布范围/mm 平均值/mm 标准差/mm 合格率/% 单开/对称道岔 护轨间隔 1 363~1 377 1 369.3 2.625 73.83 翼轨间隔 1 362~1 374 1 369.4 2.627 68.97 复式交分道岔 护轨间隔 1 360~1 375 1 368.5 2.981 71.13 翼轨间隔 1 365~1 376 1 370.1 2.391 69.05 表 2 复式交分道岔护轨磨耗起点间隔分布统计
Table 2. Interval distributions of starting position of wear for guard rail of double slip turnouts
道岔类型 9号复式交分道岔 12号复式交分道岔 趾端磨耗起点间隔/mm 1 355~1 382 1 364~1 378 冲击趾端开口段概率/% 75.00 64.71 跟端磨耗起点间隔/mm 1 367~1 386 1 369~1 382 冲击跟端开口段概率/% 7.32 5.26 表 3 道岔护轨磨耗起点间隔分布统计
Table 3. Distributions statistics of interval corresponding to the starting position of wear for guard rail of turnouts
道岔类型 6号对称 9号单开 12号单开 趾端磨耗起点间隔/mm 1 364~1 374 1 364~1 374 1 366~1 376 冲击趾端开口段概率/% 72.22 75.00 53.85 跟端磨耗起点间隔/mm 1 370~1 387 1 372~1 381 1 376~1 386 冲击跟端开口段概率/% 11.11 0 0 -
[1] 龚凯, 向俊, 余翠英, 等. 曲线上货物列车超速引起的脱轨过程分析[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(1): 172-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNDX201501031.htmGONG Kai, XIANG Jun, YU Cui-ying, et al. Analysis on freight train derailment course induced by overspeed in curve[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 45(1): 172-177. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNDX201501031.htm [2] 龚凯, 刘林芽, 向俊, 等. 客运列车曲线超速引起的脱轨全过程计算[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(9): 2673-2680. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202009033.htmGONG Kai, LIU Lin-ya, XIANG Jun, et al. Calculation of passenger train derailment course induced by overspeeds in curve[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2020, 51(9): 2673-2680. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202009033.htm [3] 司道林, 王树国, 王猛, 等. 6号对称道岔脱轨机理及影响因素[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(2): 300-305. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT202102011.htmSI Dao-lin, WANG Shu-guo, WANG Meng, et al. Derailment mechanism and influence factors on number 6 symmetric switches[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(2): 300-305. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT202102011.htm [4] LAI Jun, XU Jing-mang, WANG Ping, et al. Numerical investigation of dynamic derailment behavior of railway vehicle when passing through a turnout[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 121: 105132. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.105132 [5] 乔雨, 许玉德, 孙小辉, 等. 编组方式对驼峰下道岔区脱轨系数的影响[J]. 华东交通大学学报, 2018, 35(5): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDJT201805002.htmQIAO Yu, XU Yu-de, SUN Xiao-hui, et al. Influence of marshalling mode on derailment coefficient at the turnout of hump yard[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2018, 35(5): 9-16. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDJT201805002.htm [6] 朱耀斌, 孙晓楠, 陈富宾. 驼峰平纵断面条件对脱轨安全性影响及整治方案研究[J]. 中国铁路, 2015(8): 29-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLZG201508007.htmZHU Yao-bin, SUN Xiao-nan, CHEN Fu-bin. Study on the influences of hump horizontal and vertical section conditions on derailment safety and its corresponding treatment scheme[J]. China Railway, 2015(8): 29-33. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLZG201508007.htm [7] WANG Ping, WANG Jian, MA Xiao-chuan, et al. Theoretical 3D model for quasi-static critical derailment coefficient of railway vehicles and a simplified formula[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018, 2018: 7910753. [8] 王健. 基于轮轨关系的小号码道岔转辙器区脱轨机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018.WANG Jian. Study on derailment theory of switch aera in small number turnouts based on wheel-rail relationship[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018. (in Chinese) [9] 王平, 陈嵘, 徐井芒, 等. 高速铁路道岔系统理论与工程实践研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(2): 357-372. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201602016.htmWANG Ping, CHEN Rong, XU Jing-mang, et al. Theories and engineering practices of high-speed railway turnout system: survey and review[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 357-372. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201602016.htm [10] 杨桐, 董昱. 基于多传感器数据融合的道岔区脱轨系数预测算法[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020, 17(8): 1883-1892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202008001.htmYANG Tong, DONG Yu. Prediction algorithm of derailment coefficient in turnout area based on multi-sensor data fusion[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(8): 1883-1892. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202008001.htm [11] LI Chao, ZHAO Lin-hai. A railway turnout closeness state monitoring method based on the switch gap images[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2022, 14(4): 214-229. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2021.3053036 [12] 龚凯, 向俊, 毛建红, 等. 地震引起的货物列车脱轨全过程计算[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(3): 664-670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNDX201603036.htmGONG Kai, XIANG Jun, MAO Jian-hong, et al. Calculation of freight train derailment course induced by earthquake[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 46(3): 664-670. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNDX201603036.htm [13] 王开云, 王少林, 杨久川, 等. 地震环境下铁路轮轨动态安全性能及脱轨研究进展[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2012, 32(6): 82-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGGC201206011.htmWANG Kai-yun, WANG Shao-lin, YANG Jiu-chuan, et al. Progress in study on wheel/rail dynamic safety and derailment of railway during an earthquake[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2012, 32(6): 82-94. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGGC201206011.htm [14] 周智辉, 曾庆元. 列车脱轨分析理论与控制脱轨的桥梁横向刚度限值研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2009, 30(1): 136-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200901026.htmZHOU Zhi-hui, ZENG Qing-yuan. Study on the analysis theory of train derailment and the limit value of bridge lateral rigidity for derailment control[J]. China Railway Science, 2009, 30(1): 136-138. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200901026.htm [15] 肖新标, 金学松, 温泽峰. 钢轨扣件失效对列车动态脱轨的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2006, 6(1): 10-15. https://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200601002XIAO Xin-biao, JIN Xue-song, WEN Ze-feng. Influence of rail fastener failure on vehicle dynamic derailment[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2006, 6(1): 10-15. (in Chinese) https://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/200601002 [16] ZHOU Li, SHEN Zhi-yun. Dynamic analysis of a high-speed train operating on a curved track with failed fasteners[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University—Science A, 2013, 14(6): 447-458. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1200321 [17] 张鹏飞, 杨奥闯, 张庆欢. 新型高速道岔结构研发及列车过岔安全性分析[J]. 铁道建筑, 2024, 64(1): 34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ202401006.htmZHANG Peng-fei, YANG Ao-chuang, ZHANG Qing-huan. Research and development of new high speed turnout structure and safety analysis while train passing through turnout[J]. Railway Engineering, 2024, 64(1): 34-39. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ202401006.htm [18] 马晓川, 王平, 徐金辉, 等. 钢轨轧制不平顺对车岔耦合系统垂向动力特性的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(7): 1942-1950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201707035.htmMA Xiao-chuan, WANG Ping, XU Jin-hui. et al. Effect of rail straightening irregularity on vertical dynamic characteristics of vehicle-turnout coupling system[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(7): 1942-1950. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201707035.htm [19] 司道林, 杨东升, 王树国, 等. 高速道岔辙叉结构不平顺动力学特性分析[J]. 铁道建筑, 2018, 58(1): 67-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ201801016.htmSI Dao-lin, YANG Dong-sheng, WANG Shu-guo, et al. Analysis on dynamic characteristics of high speed turnout frog structure in irregularity state[J]. Railway Engineering, 2018, 58(1): 67-69. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ201801016.htm [20] 周鹏喜, 黄运华, 丁军君, 等. 地震作用下护轨对齿轨车辆运行安全性影响研究[J]. 机械, 2023, 50(9): 31-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MECH202309005.htmZHOU Peng-xi, HUANG Yun-hua, DING Jun-jun, et al. Research on the influence of guard rail on the operation safety of rack railway vehicles under earthquake[J]. Machinery, 2023, 50(9): 31-38. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MECH202309005.htm [21] 郭威. 列车线路碰撞试验平台防护轨结构设计与优化[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2022.GUO Wei. Structural design and optimization of the guardrail for train-to-train collision test bench[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2022. (in Chinese) [22] 刘沛, 陈卫国, 张耀. 基于BIM的铁路车辆-无砟轨道护轨性能分析[J]. 铁道建筑, 2021, 61(9): 138-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ202109029.htmLIU Pei, CHEN Wei-guo, ZHANG Yao. Performance analysis of railway vehicle-ballastless track guard track based on BIM[J]. Railway Engineering, 2021, 61(9): 138-143. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ202109029.htm [23] 刘腾, 周雄飞, 王成全, 等. 列车碰撞事故下轮轨动态作用机理与脱轨抑制技术[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(增1): 67-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BIGO2023S1007.htmLIU Teng, ZHOU Xiong-fei, WANG Cheng-quan, et al. Wheel-rail interaction mechanism and derailment suppression technology for train collision accidents[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S1): 67-78. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BIGO2023S1007.htm [24] 孙丽霞, 姚建伟, 成棣, 等. 高速车辆动态脱轨临界状态评判方法[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2020, 41(2): 113-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202002014.htmSUN Li-xia, YAO Jian-wei, CHENG Di, et al. Critical state evaluation method for dynamic derailment of high speed vehicle[J]. China Railway Science, 2020, 41(2): 113-122. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202002014.htm [25] 鈴木貢. 带防脱轨装置的转向架[J]. 国外铁道机车与动车, 2023(4): 37-39, 48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWMJ202304008.htmSUZUKI H. Bogie with anti-derailment device[J]. Foreign Railway Locomotive and Motor Car, 2023(4): 37-39, 48. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWMJ202304008.htm [26] 翁涛涛. 高速道岔磨耗分析及打磨廓形优化设计[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2023.WENG Tao-tao. Wear analysis and grinding profile optimization design of high-speed turnout[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University, 2023. (in Chinese) [27] 钱鑫. 高速道岔转辙器区优化廓形设计及其适应性分析[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2023.QIAN Xin. Optimal profile design and adaptability analysis of high-speed turnout switch area[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University, 2023. (in Chinese) [28] 林凤涛, 翁涛涛, 杨洋, 等. 道岔辙叉区磨耗车轮动力学分析及摩擦因数影响[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2023, 20(4): 1316-1325. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202304018.htmLIN Feng-tao, WENG Tao-tao, YANG Yang, et al. Dynamic analysis of wear wheel in turnout frog area and influence of friction coefficient[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(4): 1316-1325. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202304018.htm [29] 王树国, 王璞, 葛晶, 等. 高速道岔尖轨磨耗特征及管理限值研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2022, 43(1): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202201002.htmWANG Shu-guo, WANG Pu, GE Jing, et al. Study on wear characteristics and management limit of switch rail in high-speed turnout[J]. China Railway Science, 2022, 43(1): 9-16. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK202201002.htm [30] WANG Pu, WANG Shu-guo, ZHAO Zhen-hua. Mechanism of derailment at the guardrail position of turnout and a reasonable guardrail interval limit[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(17): 8496. doi: 10.3390/app12178496 -





 下载:
下载: